Method for biosynthesizing fatty alcohol by using fatty acyl ACP (acyl carrier protein) reductase
A technology of biosynthesis and reductase, which is applied in the field of modifying the fatty acid metabolism pathway of heterotrophic microorganisms to produce fatty alcohols. It can solve the problems of oil reserve consumption, achieve excellent anti-pollution performance, facilitate genetic manipulation, and reduce pollution.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
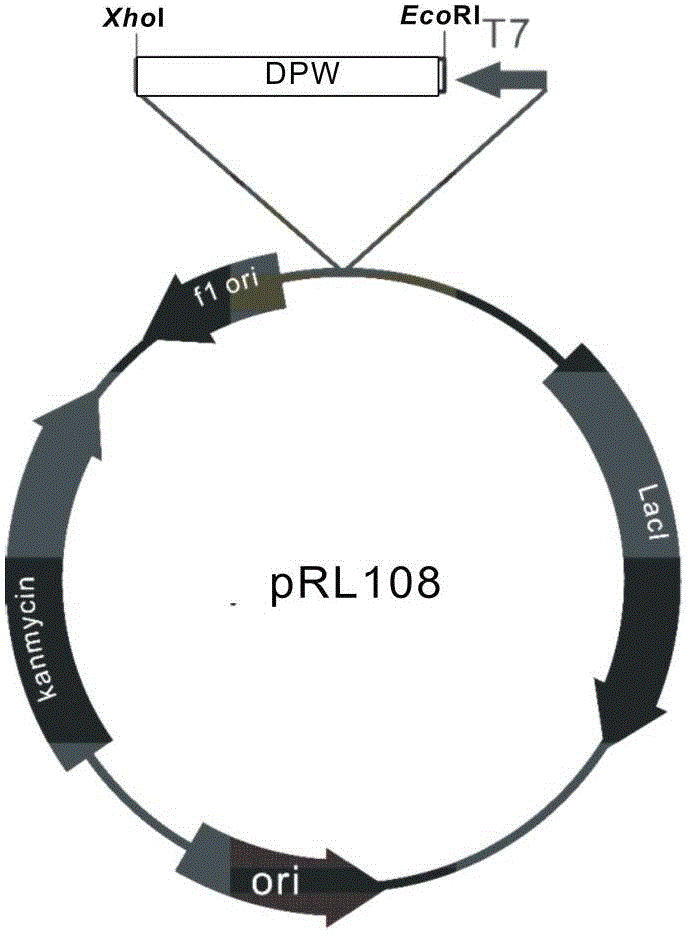
[0037] will be announced DPW Gene sequence (SEQ ID No.1, synthesized by GenScript Biotechnology Co., Ltd.), and passed Eco RI and xho Ⅰ Cloning it into the pET28 vector with two restriction sites, and the constructed plasmid was named pRL108.
[0038] The acyl carrier protein dehydrogenase in BL21(DE3) fad E Gene knockout can reduce the consumption of fatty acyl-CoA, thereby accumulating more fatty acyl carrier proteins and fatty acyl carrier proteins for the production of fatty alcohols. In this instance will knock out fad E The gene of Escherichia coli BL21(DE3) was named TL101. Fatty acyl-CoA synthetase in TL101 fadD Gene knockout can interrupt the formation of fatty acyl-CoA, so that only fatty acyl carrier protein is synthesized in the cell. In this example, according to the principle of homologous recombination, a knockout plasmid was constructed to knock out the fadD Gene. Through two primers pRL1-S(TTAA GCATGC GAAGATTTTA CTGCGGATAT ( Sph Ⅰ)) and pR...
Embodiment 2
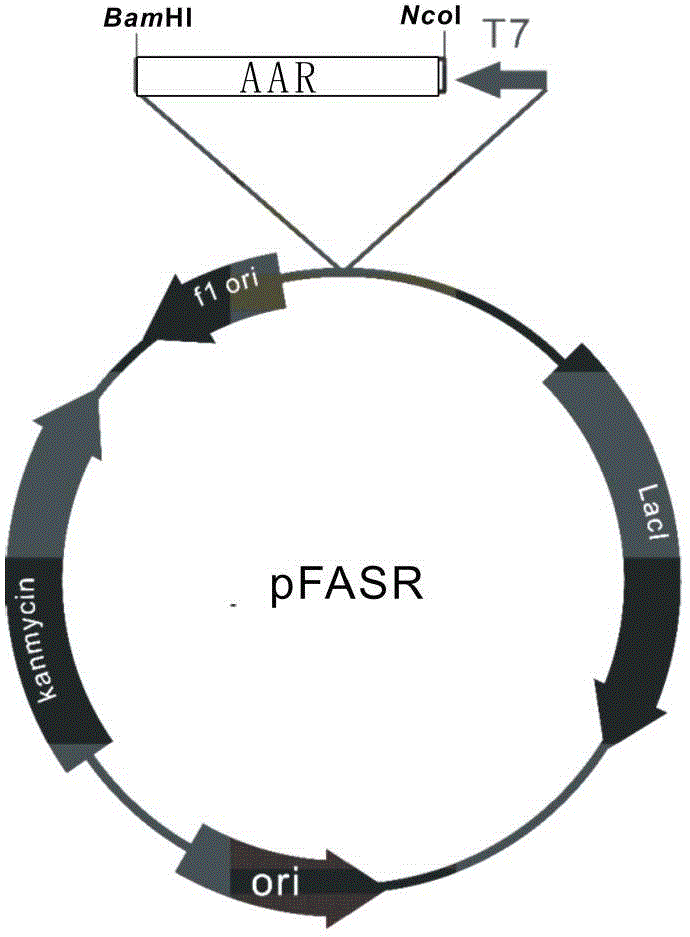
[0055] will be announced AAR The gene sequence was optimized and fully synthesized (SEQ ID No.3, synthesized by Jinweizhi Biotechnology Co., Ltd.), and passed Nco I and Bam HI two restriction sites to clone it into pET28 vector, and the constructed plasmid was named pFASR.
[0056] The pFASR was transformed into BL21(DE3), and a successful transformant was obtained by screening with kanamycin, which was named RL12.
[0057] Transformation of pFASR into MG1655(DE3) ΔRECAΔENDA , using kanamycin to select a successful transformant, which was named RL13.
[0058] The pFASR will be transformed into TL101, and the successful transformants obtained by kanamycin screening will be named RL14.
[0059] The pFASR was transformed into RL101, and a successful transformant was obtained by kanamycin screening, which was named RL15.
[0060] The pFASR and pMSD8 were co-transformed into TL101, and the successful transformant was screened by karimycin, which was named RL16.
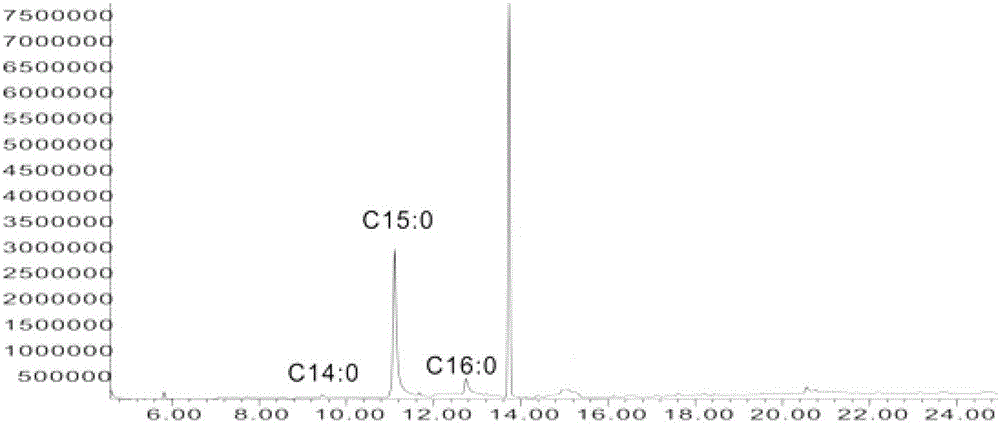
[0061] T...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com