Collaborative transmission method based on distributed interweaved and group encoding
A cooperative transmission and block coding technology, applied in transmission systems, digital transmission systems, electrical components, etc., can solve problems such as departure, low utilization of system resources, and random changes in the number of nodes
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment
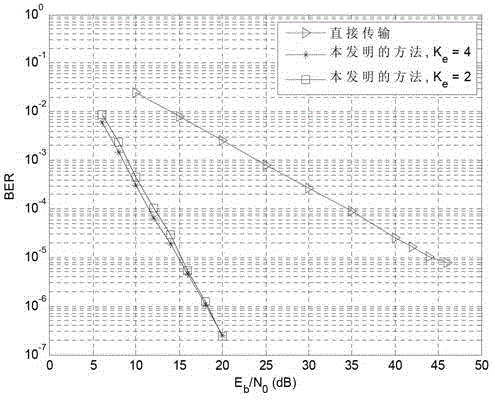
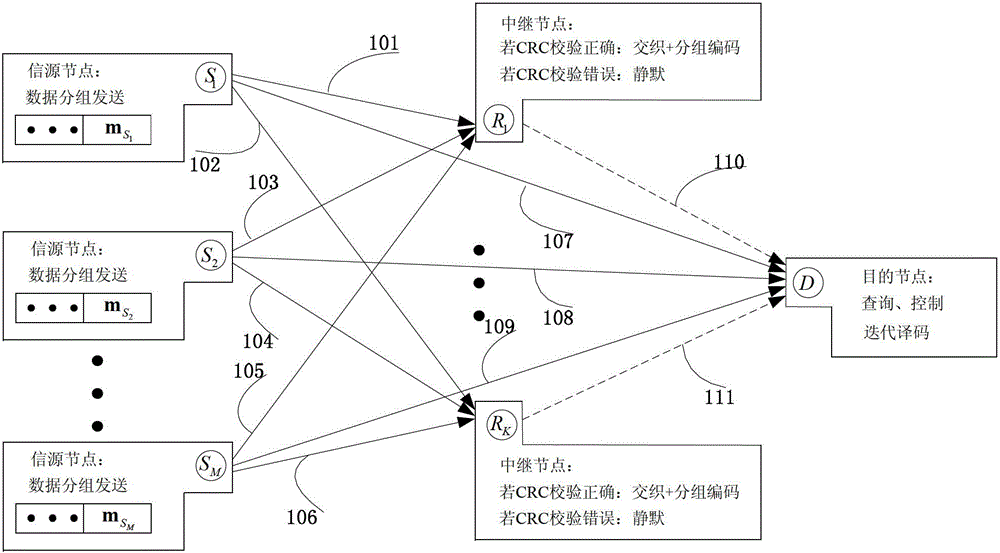
[0078] In the embodiment of the present invention, a cooperative network including M=11 source nodes is taken as an example, and the number of effective relay nodes is K e =2 or 4, the channels between all nodes are independent and identically distributed quasi-static Rayleigh fading channels. Combined with specific embodiments, the performance of the distributed interleaving and block coding-based cooperative transmission method designed in the present invention is verified.
[0079] The specific working method of the cooperative transmission method based on distributed interleaving and block coding proposed by the present invention is as follows:
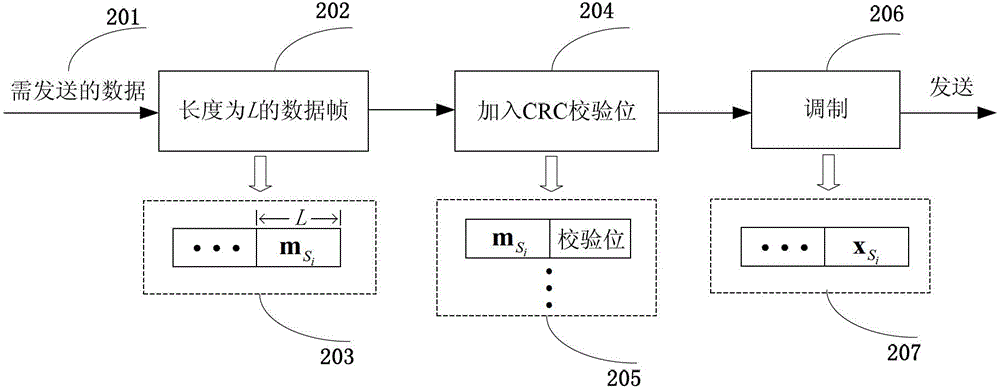
[0080] ■In the source broadcast stage, each source node divides the data to be sent into data frames with a length of L=22 bits, and broadcasts to the destination node and candidate relay nodes after modulation by binary phase shift keying (BPSK).
[0081] ■When the destination node cannot decode correctly based on the data broad...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com