Space division multiplexing method and space division multiplexing device
A space division multiplexing and division multiplexing technology, applied in the field of communication, can solve the problems of low utilization rate of carrier resources and great difficulty in implementation, and achieve the effects of good income, increasing downlink throughput, and improving utilization rate of space division carrier resources.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
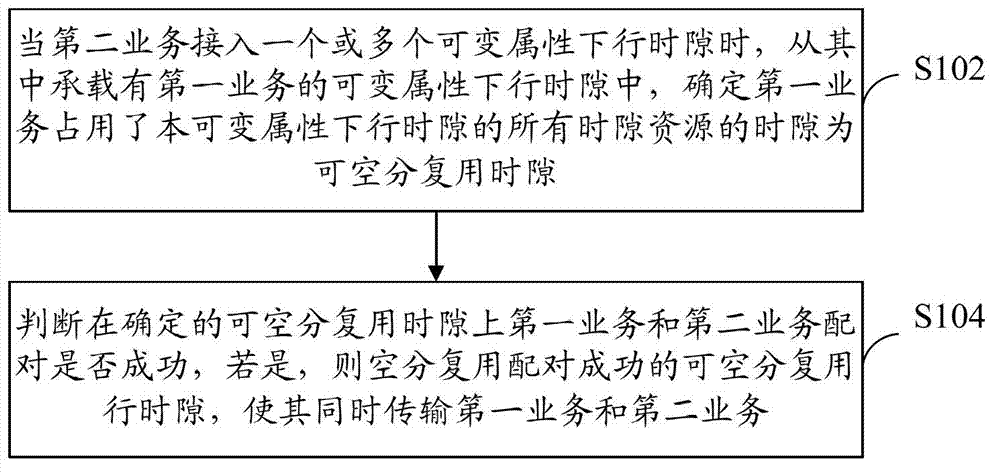
[0024] refer to figure 1 , shows a flow chart of steps of a space division multiplexing method according to Embodiment 1 of the present application.
[0025] The space division multiplexing method of the present embodiment comprises the following steps:
[0026] Step S102: When the second service accesses one or more variable-attribute downlink time slots, from which (that is, in the one or more variable-attribute downlink time slots accessed by the second service) can bear the first service In the variable attribute downlink time slot, it is determined that the first service occupies all the time slot resources of the variable attribute downlink time slot as the space division multiplexable time slot.
[0027] Taking the first service as H service and the second service as R4 service as an example, the variable attribute time slot technology supports setting the service time slots of some carriers under the cell as variable attribute time slots, and these time slots can carr...
Embodiment 2
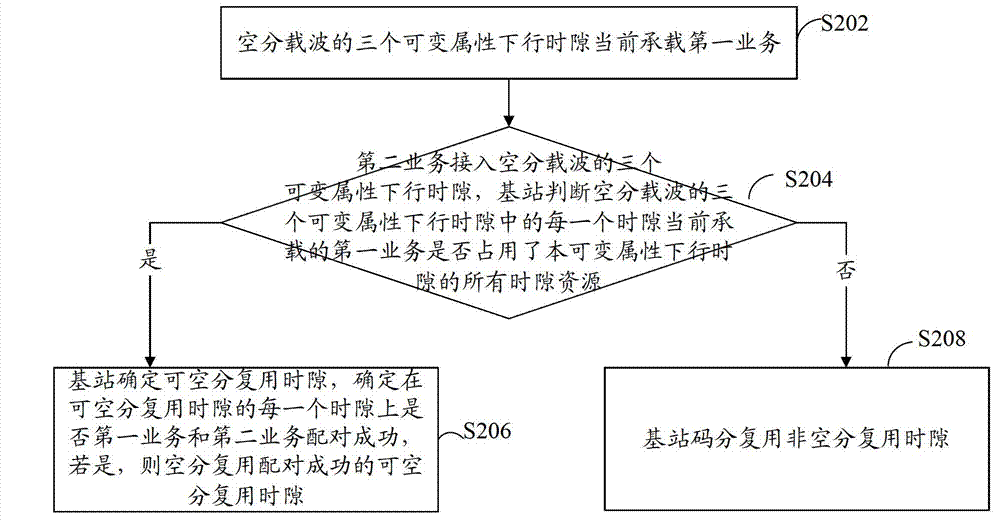
[0033] refer to figure 2 , shows a flow chart of steps of a space division multiplexing method according to Embodiment 2 of the present application.
[0034] In this embodiment, it is assumed that there are three variable attribute downlink time slots TS3, TS4 and TS5.
[0035] The space division multiplexing method of the present embodiment comprises the following steps:
[0036] Step S202: The three variable attribute downlink time slots of the space division carrier currently carry the first service.
[0037] In this embodiment, the first service is set to be the R4 service, and the second service that can be time-slot space-division multiplexed with the first service at this time is the H service. Of course, it is not limited thereto. In practical applications, the first service may also be an H service, and at this time, the second service that can be time-slot space-division multiplexed with the first service may be an R4 service or an H service.
[0038] In this ste...
Embodiment 3
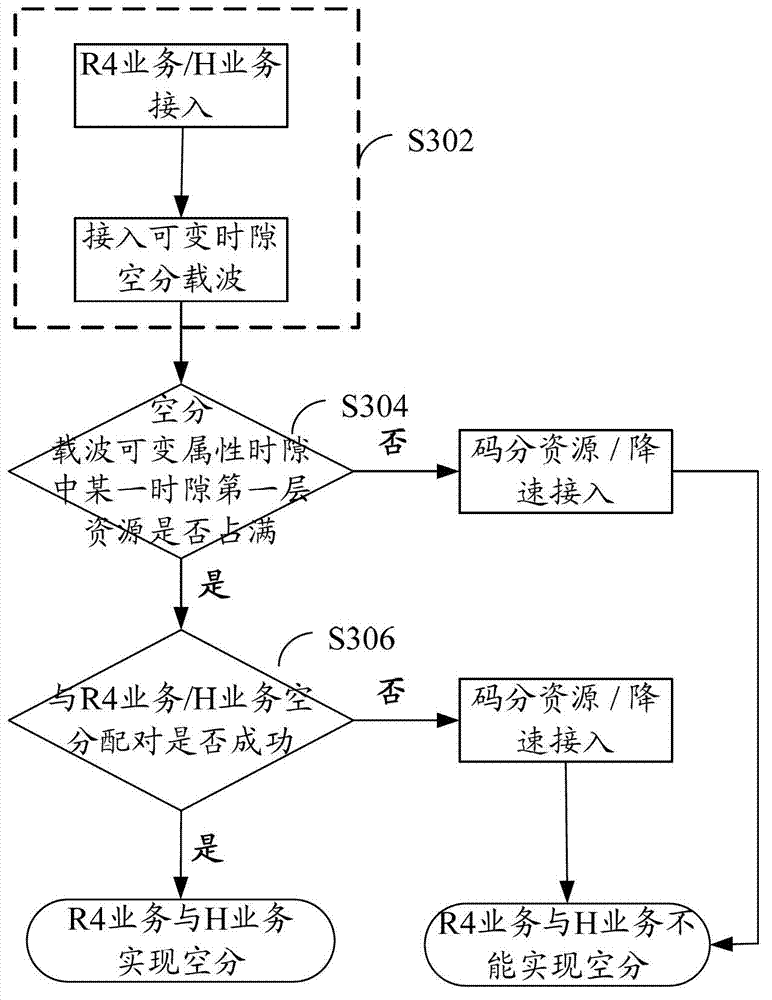
[0052] refer to image 3 , shows a flowchart of steps of a space division multiplexing method according to Embodiment 3 of the present application.
[0053] In this embodiment, an indoor distributed system multi-channel cell (a cell composed of multiple single-channel RRUs or multi-channel RRUs) is set, and a mixed-service HSPA (High-Speed Packet Access, high-speed packet access) cell is configured by default. 2:4 configuration, configure 1 HSPA carrier, TS2 is EPUCH (Enhanced-Physical Uplink Channel, enhanced uplink physical channel), TS3, TS4, TS5 are PDSCH (Physical Downlink Shared Channel, physical downlink shared channel), when the configuration is variable After the slot is switched, all downlink business time slots are HS-PDSCH (High Speed Physical Downlink Shared Channel) resources and DPCH (Dedicated Physical Channel, dedicated physical channel) resource variable attribute time slots. Access sequence: channel A accesses UE1 32 / 128k R4 services, channel B accesses...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com