Vehicle control device
A technology for control devices and vehicles, which is applied in electrical control, power devices, exhaust devices, etc., and can solve problems such as decreased insulation resistance, inability to EHC, and energization.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 approach
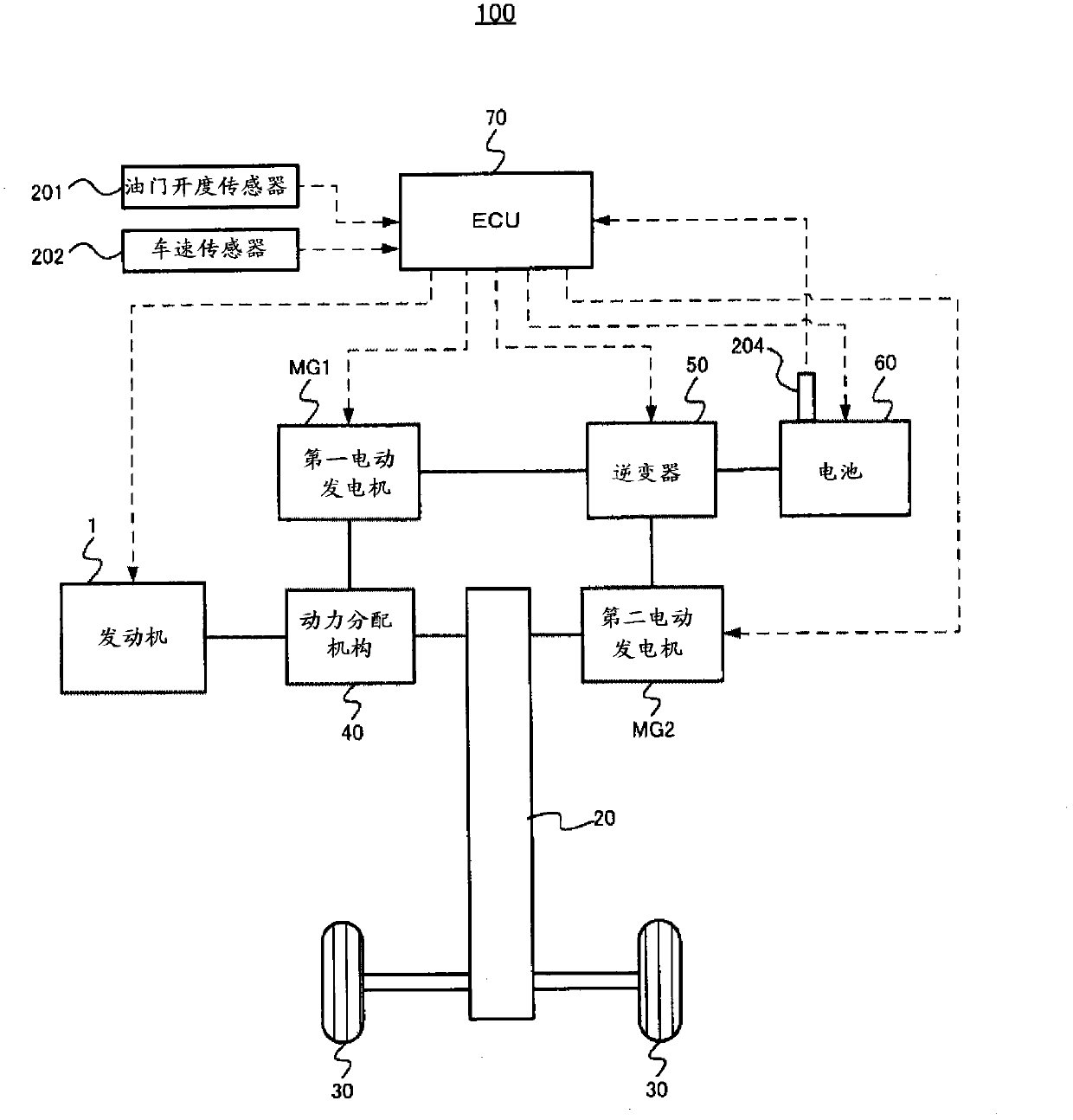
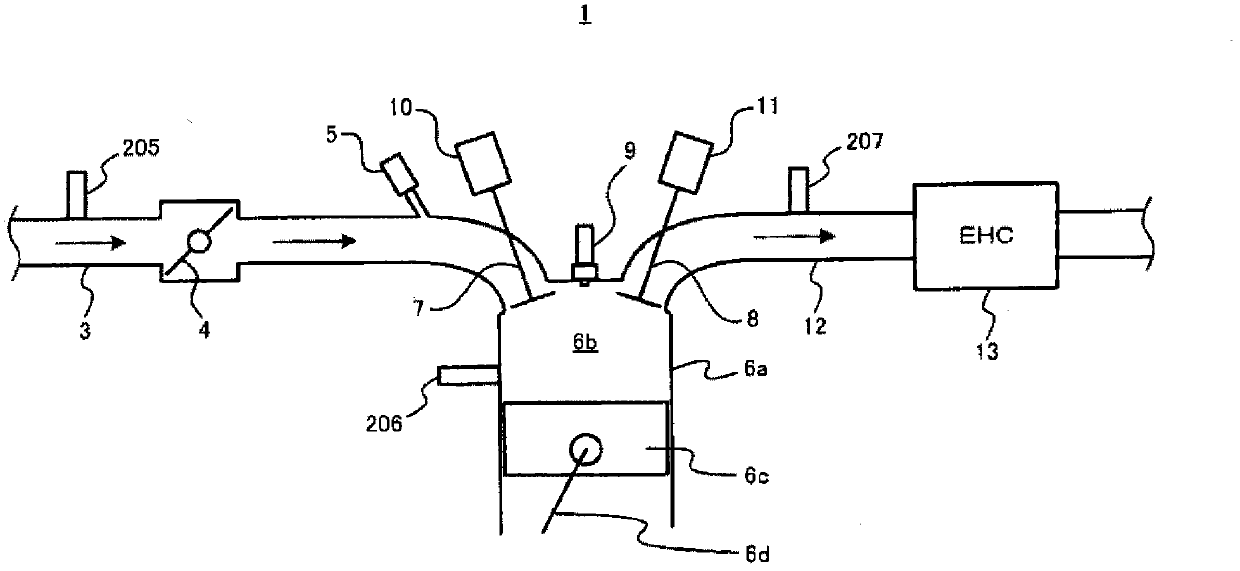
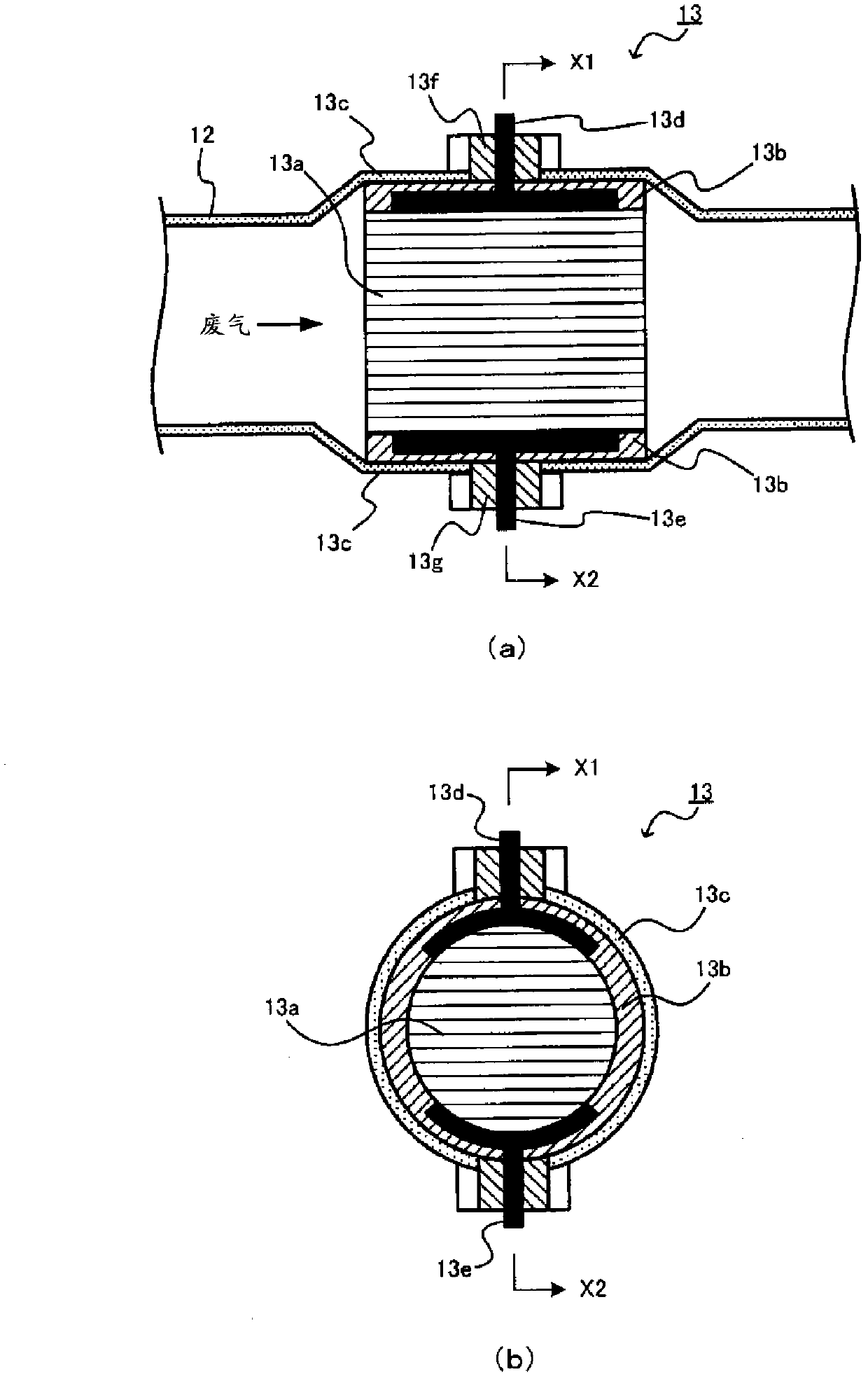
[0070] In the first embodiment, when the deceleration F / C condition is satisfied, the ECU 70 prohibits the execution of the F / C during deceleration to maintain the holding mat temperature at a temperature lower than the EHC bed temperature. That is, in the first embodiment, the execution of F / C at the time of deceleration is prohibited, and combustion is performed in the engine 1 to supply the combusted gas to the EHC 13 , thereby suppressing the supply of gas generated by the F / C to the EHC 13 . cold air.
[0071] More specifically, when the deceleration F / C condition is satisfied, the ECU 70 prohibits execution of the above-mentioned F / C when the temperature obtained by adding a predetermined temperature to the holding pad temperature is equal to or higher than the EHC bed temperature. That is, the execution of F / C during deceleration is prohibited only when the relationship of "retaining mat temperature + specified temperature ≥ EHC bed temperature" is established, and when...
no. 2 approach
[0084] Next, a second embodiment will be described. In the second embodiment, when the deceleration F / C condition is satisfied, when the temperature obtained by adding a predetermined temperature to the holding pad temperature is equal to or higher than the EHC bed temperature, the intake valve 7 is closed and the F / C is executed. The control of the exhaust valve 8 is different from the first embodiment in this point. That is, in the second embodiment, the execution of F / C during deceleration is not prohibited, and the control of setting the intake valve 7 and the exhaust valve 8 to fully close (in other words, making the intake valve 8 fully closed) is performed during execution of F / C. valve 7 and exhaust valve 8 stop control). Specifically, in the second embodiment, the intake valve 7 and the exhaust valve 8 are forcibly set fully closed during execution of F / C, thereby blocking the flow of gas from the engine 1 to the EHC 13 when F / C is generated. The supply of cold air ...
no. 3 approach
[0092] Next, a third embodiment will be described. In the third embodiment, when the deceleration F / C condition is satisfied, when the temperature obtained by adding a predetermined temperature to the holding pad temperature is equal to or higher than the EHC bed temperature, the throttle valve 4 is controlled to be closed when F / C is executed. (hereinafter referred to as "throttle closing control"), this point is different from the first embodiment and the second embodiment. That is, in the third embodiment, the execution of the F / C is not prohibited during deceleration as in the second embodiment, but when the F / C is executed, instead of the control to close the intake valve 7 and the exhaust valve 8, the throttling is performed. Valve closing control is different from the second embodiment in this point. Specifically, in the third embodiment, throttle closing control is performed when F / C is executed, thereby reducing the amount of other supply generated when F / C is direct...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com