Noncontact foot measurement and shoe tree matching method
A non-contact, matching technology, applied in the fields of image recognition, intelligent matching, and e-commerce, can solve problems such as inability to collect instep height data, inability to analyze space differences in shoes, single measurement data, etc., to achieve simple and practical data collection, The effect of wide application range and simple operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0143] The matching method provided by the present invention is described below through a specific embodiment. Using the method provided by the present invention, the specific steps are as follows:
[0144] The first step is to determine the eigenvalues of the first foot:
[0145] Take pictures of both feet from the front and side, or compare the feet with a ruler A4 paper.
[0146] A first foot feature value is obtained according to the foot image, and a three-dimensional model of the foot is established.
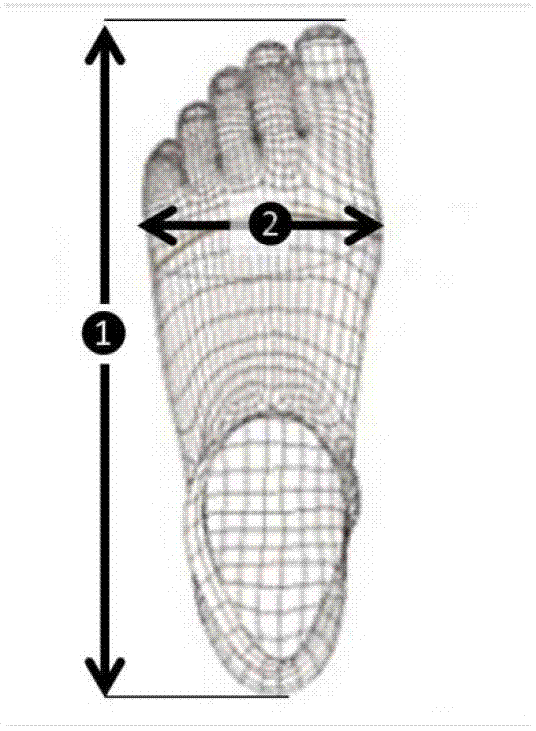
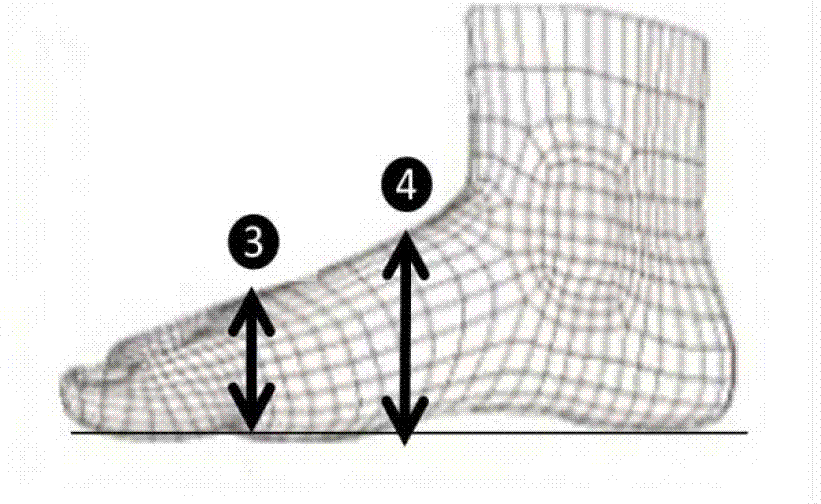
[0147] According to the foot image, the characteristic values of the first foot can be obtained: ①Length of the right foot: L1=24.143226cm ②Width of the right foot: L2=10.474839cm ③Height of the widest part of the foot: H1=3.456697cm ④The middle height of the instep : H2=7.856129cm. like figure 1 and figure 2 .
[0148] The second step is to convert the shoe last data of the pre-purchased new shoe B to obtain the most suitable foot characteristic data of the shoe...
Embodiment 2
[0158] The first step is to take the front and side photos of the foot with the coin as the reference scale to obtain the foot image. Data analysis is performed on the foot image to obtain a first foot feature value. L1=240mm, L2=85mm, H1=42mm, H2=80mm.
[0159] The second step is to measure the shoe last data of the pre-purchased shoe B, and convert the shoe last data to obtain the second foot characteristic value.
[0160] L1”=250mm, L2”=88mm, H1”=40mm, H2”=75mm.
[0161] The third step is to match the eigenvalues of the first foot with the eigenvalues of the second foot to obtain the degree of fit:
[0162] Q1=66.7%, Q2=96.6%, Q3=95%, Q4=93.3%, Q5=57.1%.
[0163] The fourth step is to get the feeling of trying on according to the degree of fit.
[0164] Combined with Table 1, the comprehensive evaluation is: it is not recommended to buy this shoe.
Embodiment 3
[0166] The first step is to measure the shoe last data of shoe A based on the user’s existing comfortable shoe A as an example, convert the shoe last data to obtain the corresponding second foot feature value, and assign the second foot feature value to The first foot eigenvalue.
[0167] LA1”=240mm, LA2”=85mm, HA1”=42mm, HA2”=80mm.
[0168] The second step is to measure the shoe last data of the pre-purchased shoe B, and convert the shoe last data to obtain the second foot characteristic value.
[0169] LB1”=250mm, LB2”=88mm, HB1”=40mm, HB2”=75mm.
[0170] The third step is to match the eigenvalues of the first foot with the eigenvalues of the second foot to obtain the degree of fit:
[0171] Q1'=66.7%, Q2'=96.6%, Q3'=95%, Q4'=93.3%, Q5'=57.1%
[0172] The fourth step is to get the feeling of trying on according to the degree of fit.
[0173] According to Table 2, the comprehensive evaluation is: it is not recommended to buy this shoe.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com