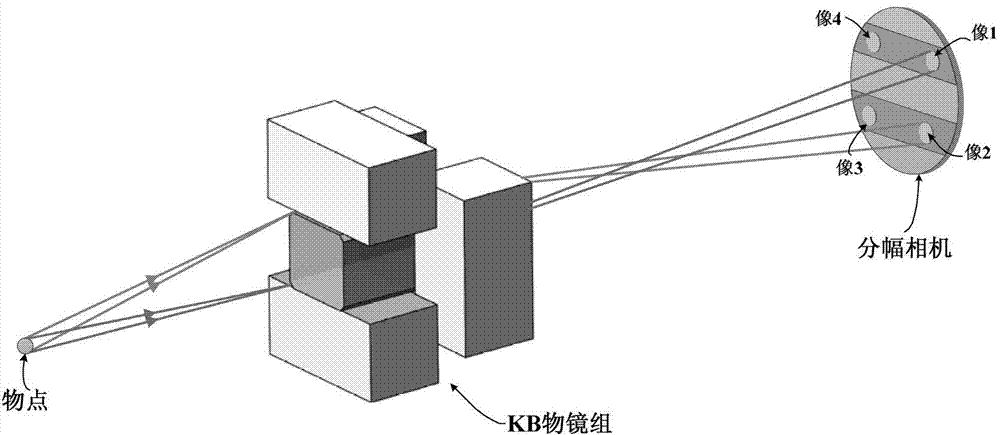
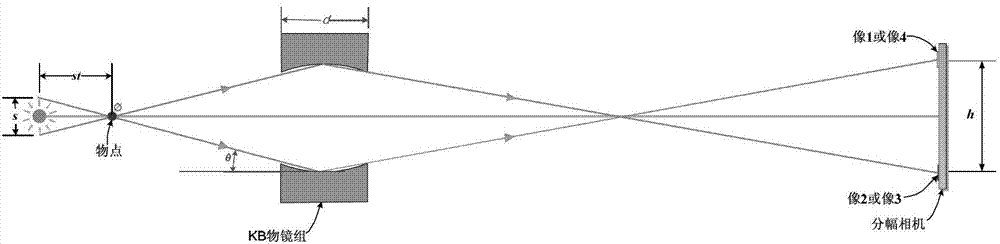
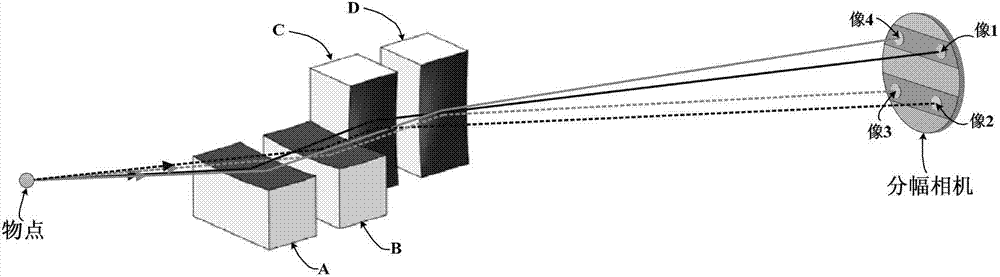
Four-channel KB microimaging system working under small-size backlight
A microscopic imaging, four-channel technology, used in γ-ray or X-ray microscopy, nuclear engineering, etc., can solve the problems of inability to meet the requirements of backlight X-ray flux, high X-ray intensity, and reduced backlight X-ray intensity. It can achieve the effect of great difficulty in installation and adjustment, reduce the difficulty of installation and adjustment, and improve the intensity of backlight X-rays
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0028] A four-channel KB microscopic imaging system operating under a small size backlight, such as image 3 As shown, it includes two KB objective lenses arranged in sequence in the meridional direction (namely objective lens A and objective lens B) and two KB objective lenses arranged in sequence in the sagittal direction (namely objective lens C and objective lens D). The X-rays emitted by the object point are respectively reflected by two KB objective lenses (namely objective lens A and objective lens B) in the meridional direction to form two-channel one-dimensional imaging, and then the two-channel one-dimensional imaging passes through the sagittal direction The two KB objective lenses (namely objective lens C and objective lens D) reflect and form four-channel two-dimensional imaging on the receiving surface of the framing camera. The specific imaging relationship is as follows: objective lens A and objective lens C participate in forming image 1; objective lens A and ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com