Calculating method of mirror field optical efficiency of tower type solar thermoelectric system
A tower solar and thermoelectric system technology, applied in computing, electrical digital data processing, special data processing applications, etc., can solve problems such as low efficiency, high difficulty, and increased computational complexity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
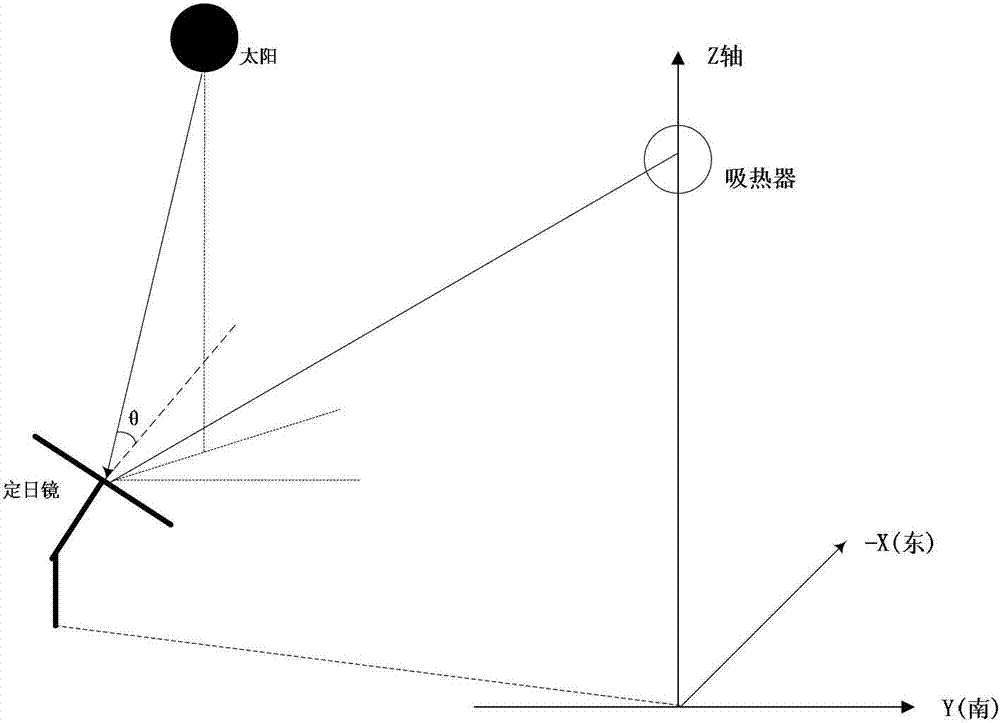
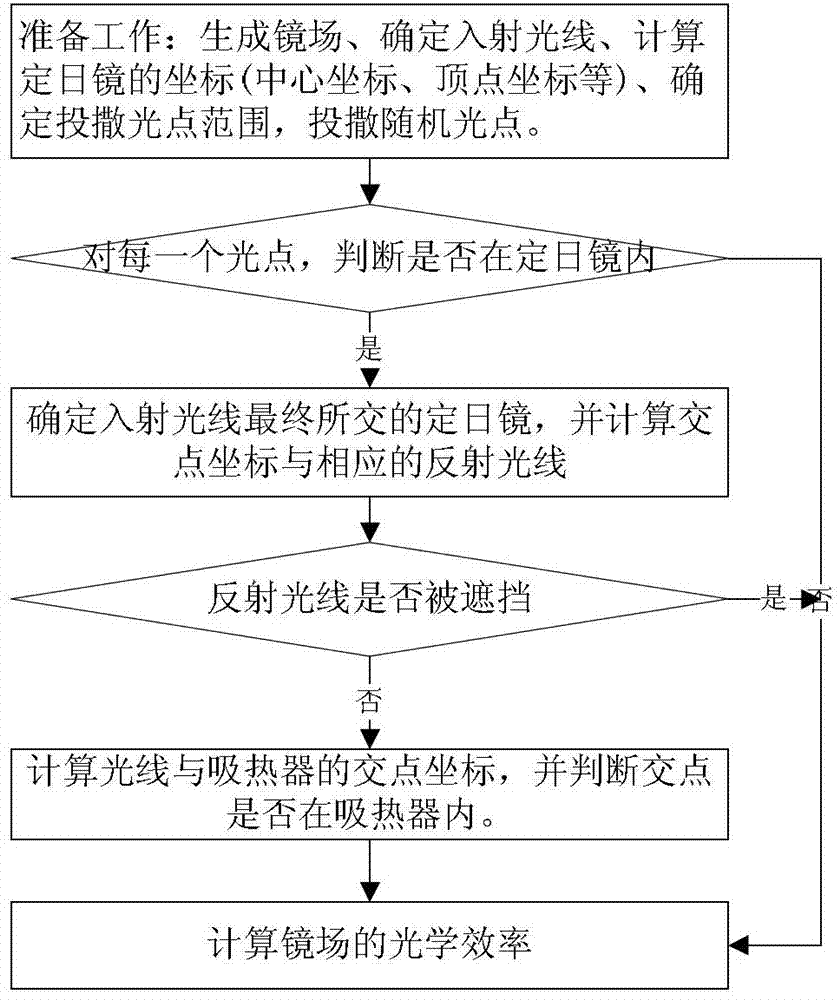
[0094] Such as image 3 As shown, the implementation steps of the calculation method for the optical efficiency of the mirror field of the tower solar thermoelectric system in this embodiment are as follows:
[0095] 1) Generate a mirror field and determine the incident light;
[0096] 2) Determine the casting range according to the mirror field, incident light and the coordinates of the heliostat;
[0097] 3) Randomly cast light spots in the heliostat field within the casting range;
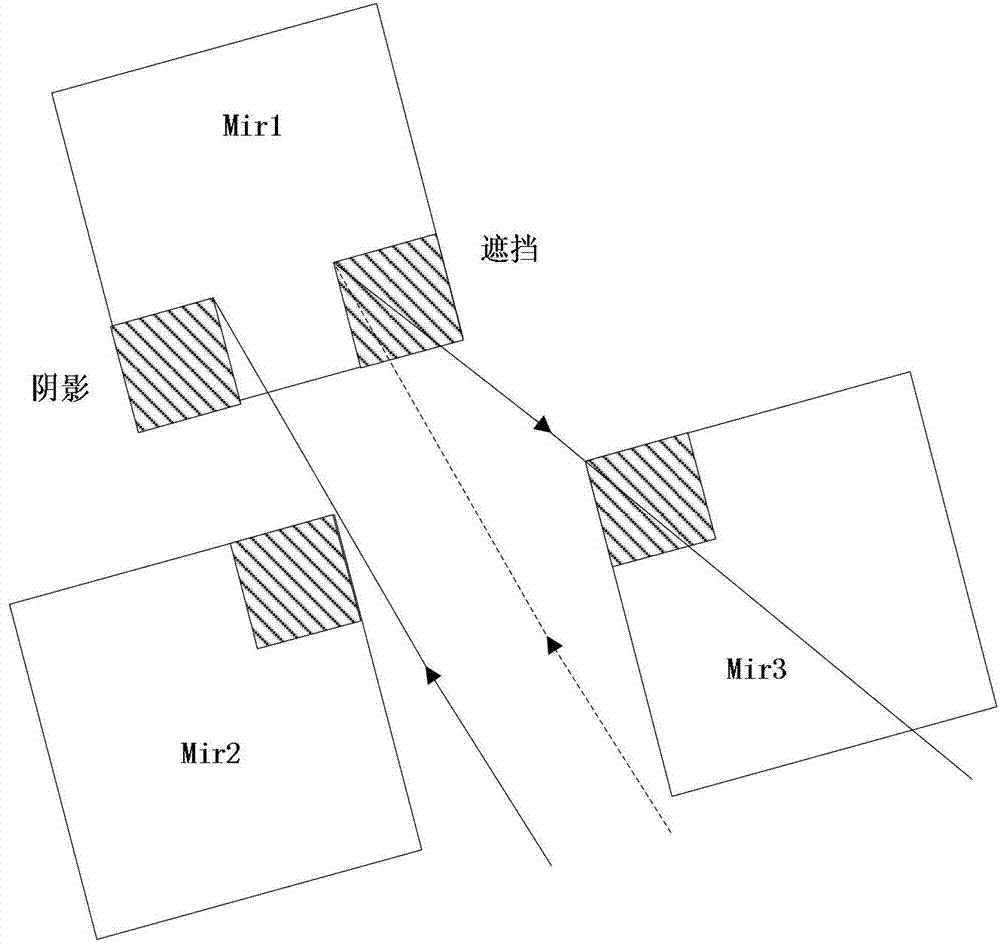
[0098] 4) Use the CUDA computing platform to perform ray tracing for each ray in the form of multi-threading, from the light spots randomly scattered on the ground and the four vertices of the heliostat along the projection coordinates of the incident ray on the ground Determine the intersection of the incident ray and each heliostat. If the projection of the light point is not in any heliostat, the ray corresponding to the light point is an invalid incident ray, and then consider the next lig...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com