Detection and mitigation of interference in a receiver
A technology of receiving equipment and receiving method, applied in receiver monitoring, shaping network in transmitter/receiver, space transmit diversity, etc., can solve the problems of indistinguishable, inability to fully optimize receiver performance, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0023] This description of exemplary embodiments is intended to be read in conjunction with the accompanying drawings, which are to be considered a part of the entire specification as written.
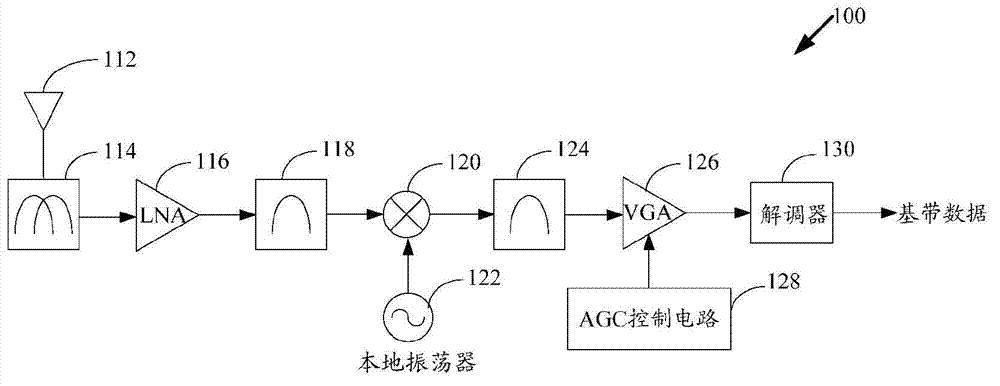
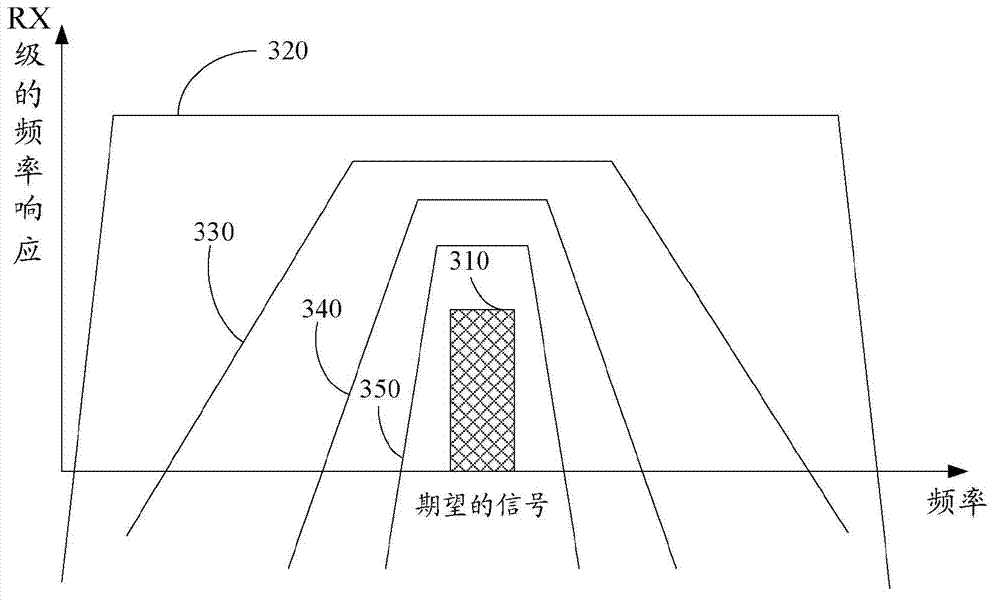
[0024] Embodiments of the present disclosure provide a novel receiver architecture to optimize receiver performance in the presence of interference. In various embodiments, the estimation circuit is used in a variable selective manner to determine the exact nature of the interference and to optimize performance accordingly. Variable selectivity is achieved by using multiple stages of filtering with progressively narrower bandwidths. Furthermore, the novelty of the actual method of optimizing receiver performance compared to the prior art is that the gain setting and baseband filter order (to be used class).
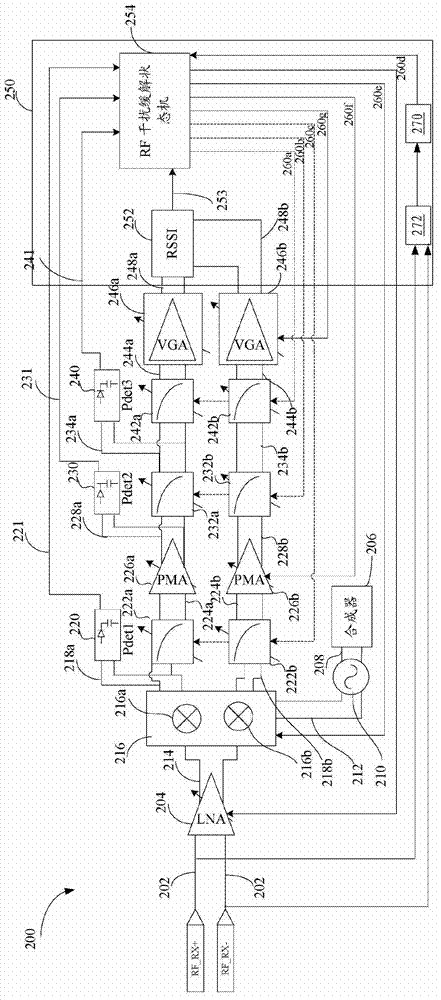
[0025] figure 2 is a block diagram of the system architecture of the receiver 200 according to some embodiments of the present disclosure. An input signal 202 is received, fo...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com