Terminal identification method and device
A terminal identification and identification technology, applied in the computer field, can solve the problem that the terminal identification method cannot meet the terminal identification with high precision, and achieve the effect of ensuring stability and uniqueness, and accurately identifying the terminal.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
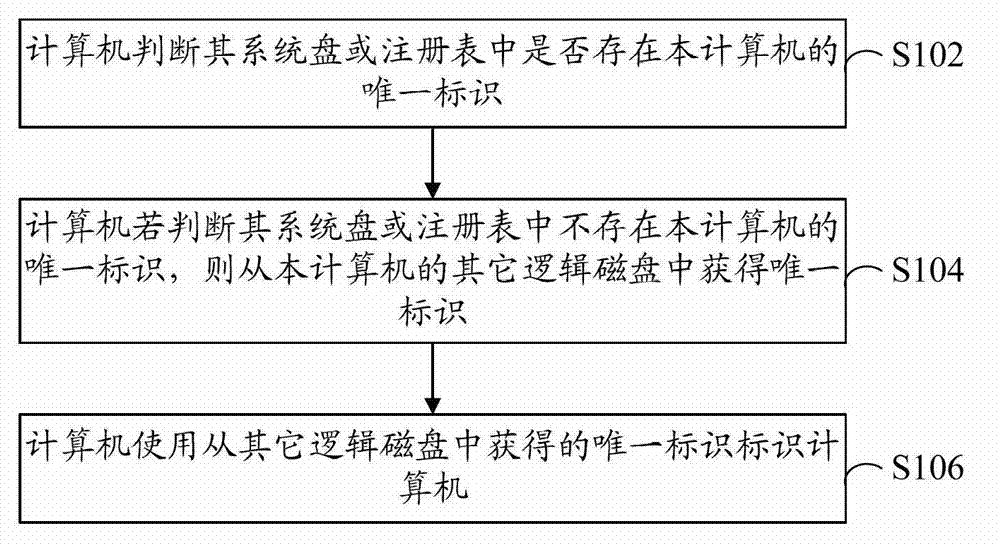
[0036] refer to figure 1 , shows a flow chart of steps of a method for identifying a terminal according to Embodiment 1 of the present invention.
[0037] The terminal identification method in this embodiment includes the following steps:
[0038] Step S102: The computer judges whether the unique identifier of the computer exists in its system disk or registry.
[0039] Wherein, the unique identifier of the computer is obtained by calculating the identifier calculation parameters, and the identifier calculation parameters include at least one of the following computer name, GUID (Globally Unique Identifier), and remaining disk size of the system disk. In addition to the above, the identification calculation parameters may also include random numbers.
[0040] Initially, the unique identifier of the computer exists in the registry, system disk and other logical disks of the computer. When something happens, such as after the system is reinstalled, the unique identifier of th...
Embodiment 2
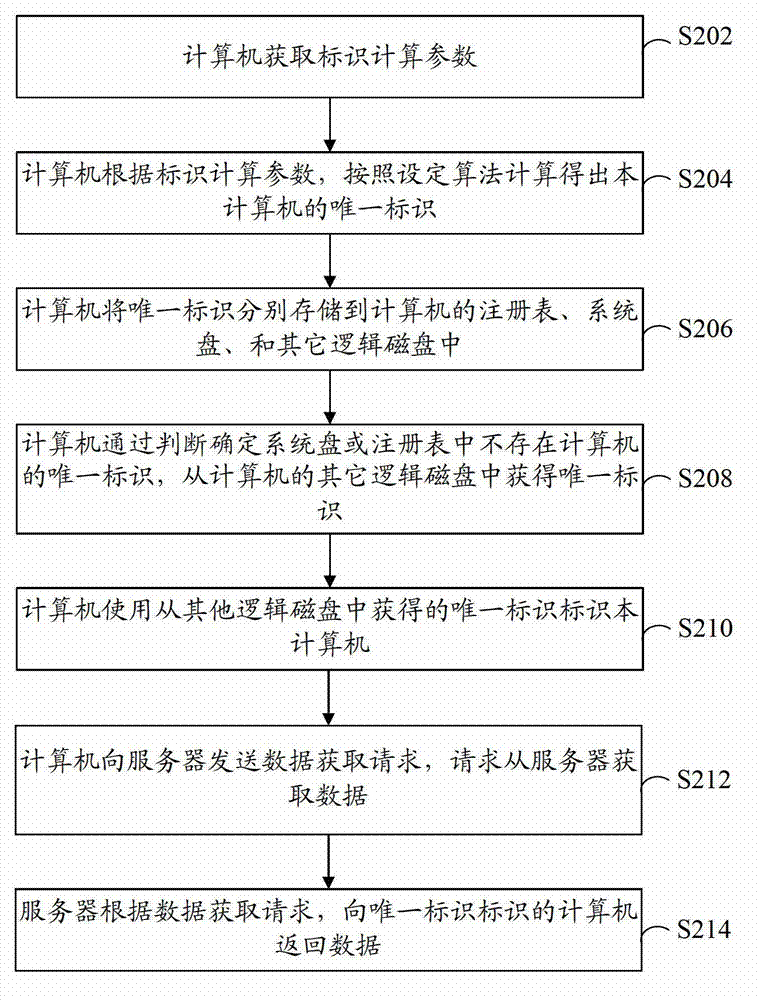
[0047] refer to figure 2 , shows a flow chart of steps of a method for identifying a terminal according to Embodiment 2 of the present invention.
[0048] The terminal identification method in this embodiment includes the following steps:
[0049] Step S202: The computer obtains the identification calculation parameters.
[0050] In this embodiment, the identification calculation parameters include one or more of computer name, GUID, remaining disk size of the system disk of the computer, and may also include random numbers and the like.
[0051] Step S204: The computer calculates the unique identifier of the computer according to the set algorithm according to the identifier calculation parameters.
[0052] For example, by combining the identification calculation parameters and random values, a unique identification is calculated according to the set algorithm, so that the possible repetition rate of the identification is extremely low.
[0053] Preferably, the unique ide...
Embodiment 3
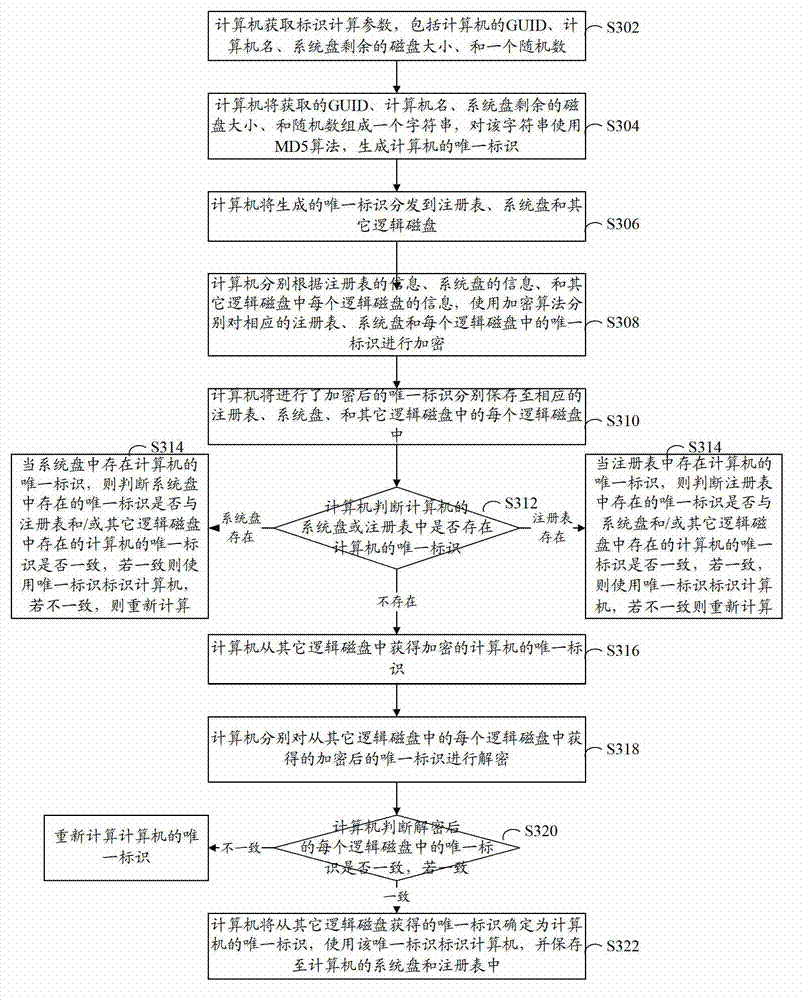
[0071] refer to image 3 , shows a flow chart of steps of a method for identifying a terminal according to Embodiment 3 of the present invention.
[0072] The terminal identification method in this embodiment includes the following steps:
[0073] Step S302: The computer acquires identification calculation parameters, including computer GUID, computer name, remaining disk size of the system disk, and a random number (pseudo-random number calculated by the computer).
[0074] Step S304: The computer forms a character string with the obtained GUID, computer name, remaining disk size of the system disk, and random numbers, and uses the MD5 algorithm on the character string to generate a unique identifier of the computer.
[0075] Step S306: The computer distributes the generated unique identifier to the registry, system disk and other logical disks.
[0076] Step S308: According to the information of the registry, the information of the system disk, and the information of each ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com