Patents
Literature
172 results about "Logical disk" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
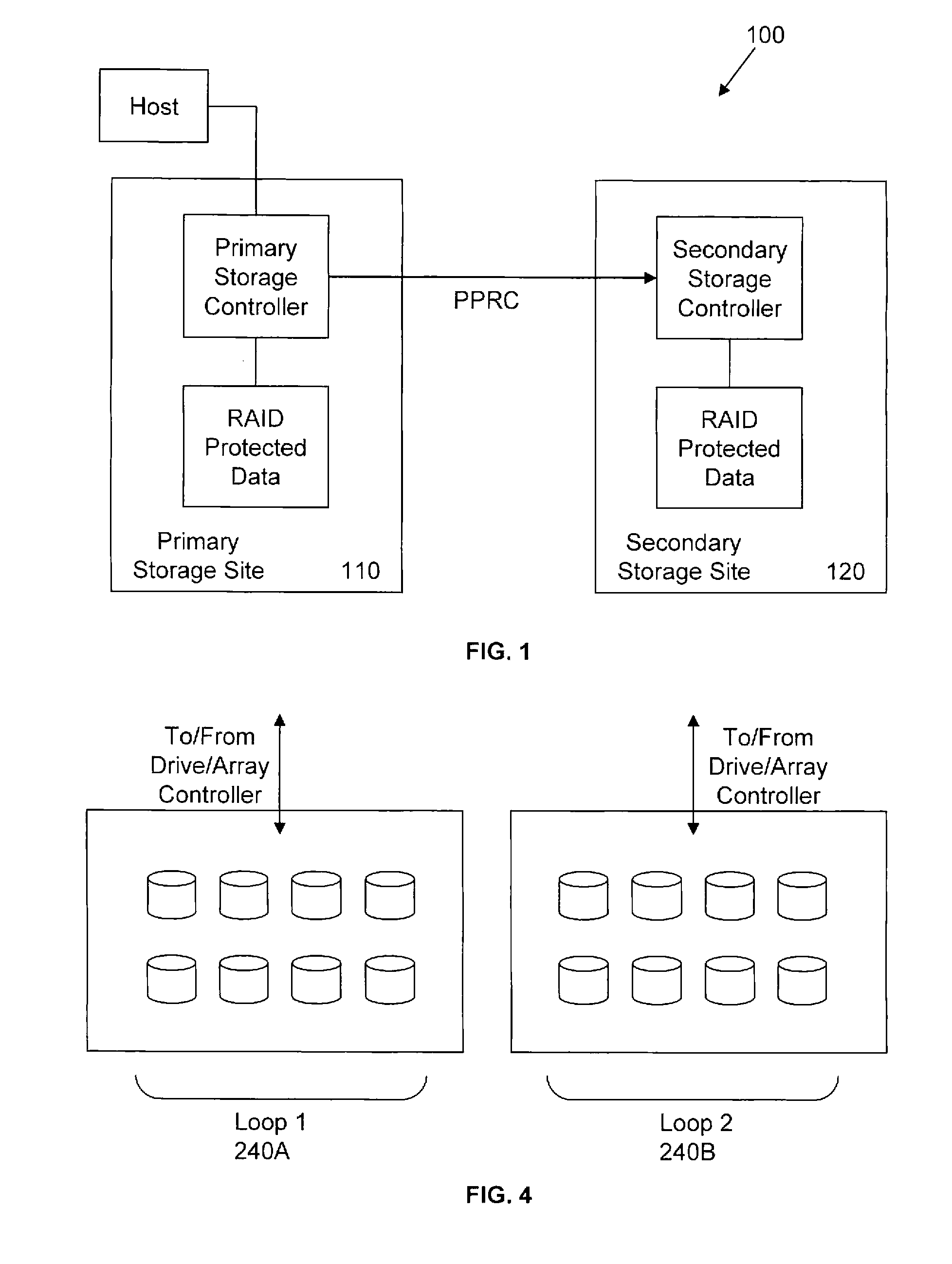
A logical disk, logical volume or virtual disk (VD or vdisk for short) is a virtual device that provides an area of usable storage capacity on one or more physical disk drive(s) in a computer system. The disk is described as logical or virtual because it does not actually exist as a single physical entity in its own right. The goal of the logical disk is to provide computer software with what seems a contiguous storage area, sparing them the burden of dealing with the intricacies of storing files on multiple physical units. Most modern operating systems provide some form of logical volume management.
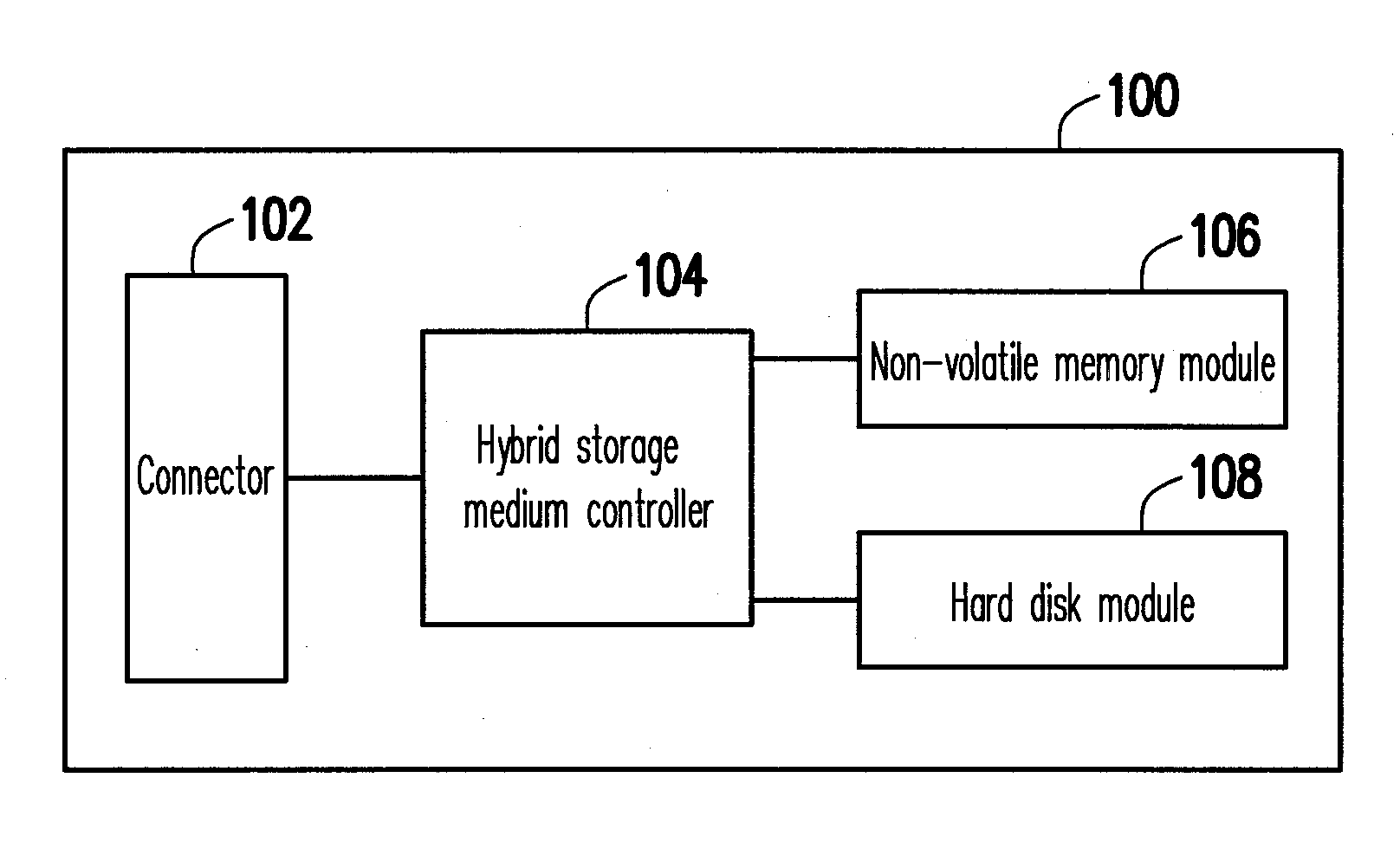
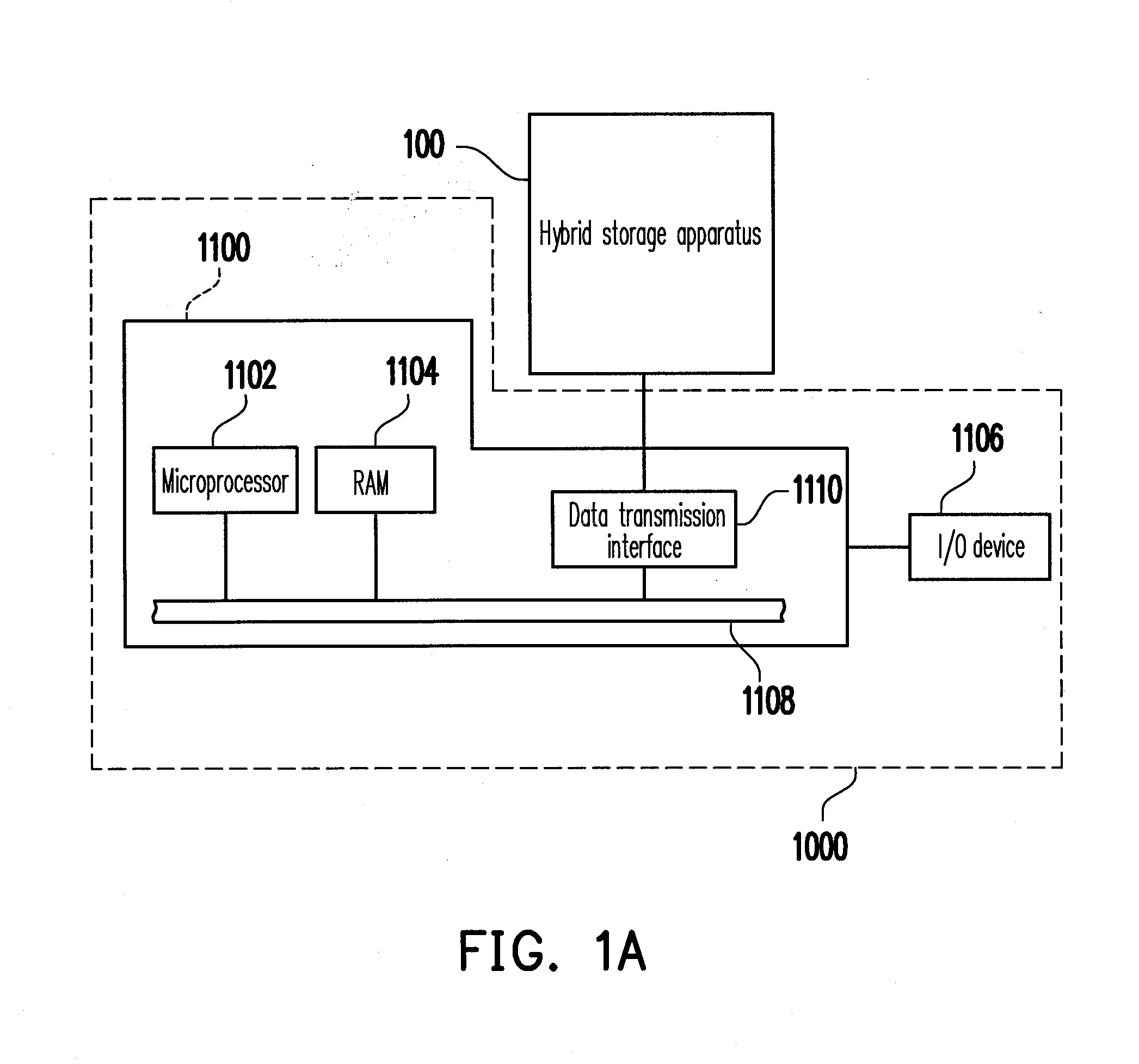
Hybrid storage apparatus and hybrid storage medium controlller and addressing method thereof
ActiveUS20120059972A1Improve data access speedExtend your lifeMemory architecture accessing/allocationInput/output to record carriersComputer hardwareLogical disk
A hybrid storage apparatus including a non-volatile memory module, a hard disk module, and a hybrid storage medium controller is provided. The hybrid storage medium controller groups physical bocks of the non-volatile memory module into at least a storage area and a replacement area, and the hybrid storage medium controller configures a plurality of logical blocks for mapping to the physical blocks in the storage area and configures a plurality of logical disk addresses for mapping to physical disk addresses of the hard disk module. The hybrid storage medium controller further configures a plurality of logical access addresses to be accessed by a host system and initially maps a portion of the logical access addresses to the logical blocks and the other logical access addresses to a portion of the logical disk addresses. Accordingly, the hybrid storage apparatus can have improved data access performance and prolonged lifespan.
Owner:PHISON ELECTRONICS
Disk striping method and storage subsystem using same
InactiveUS6327638B1Improve performanceImprove utilizationInput/output to record carriersMemory systemsControl electronicsDisk array
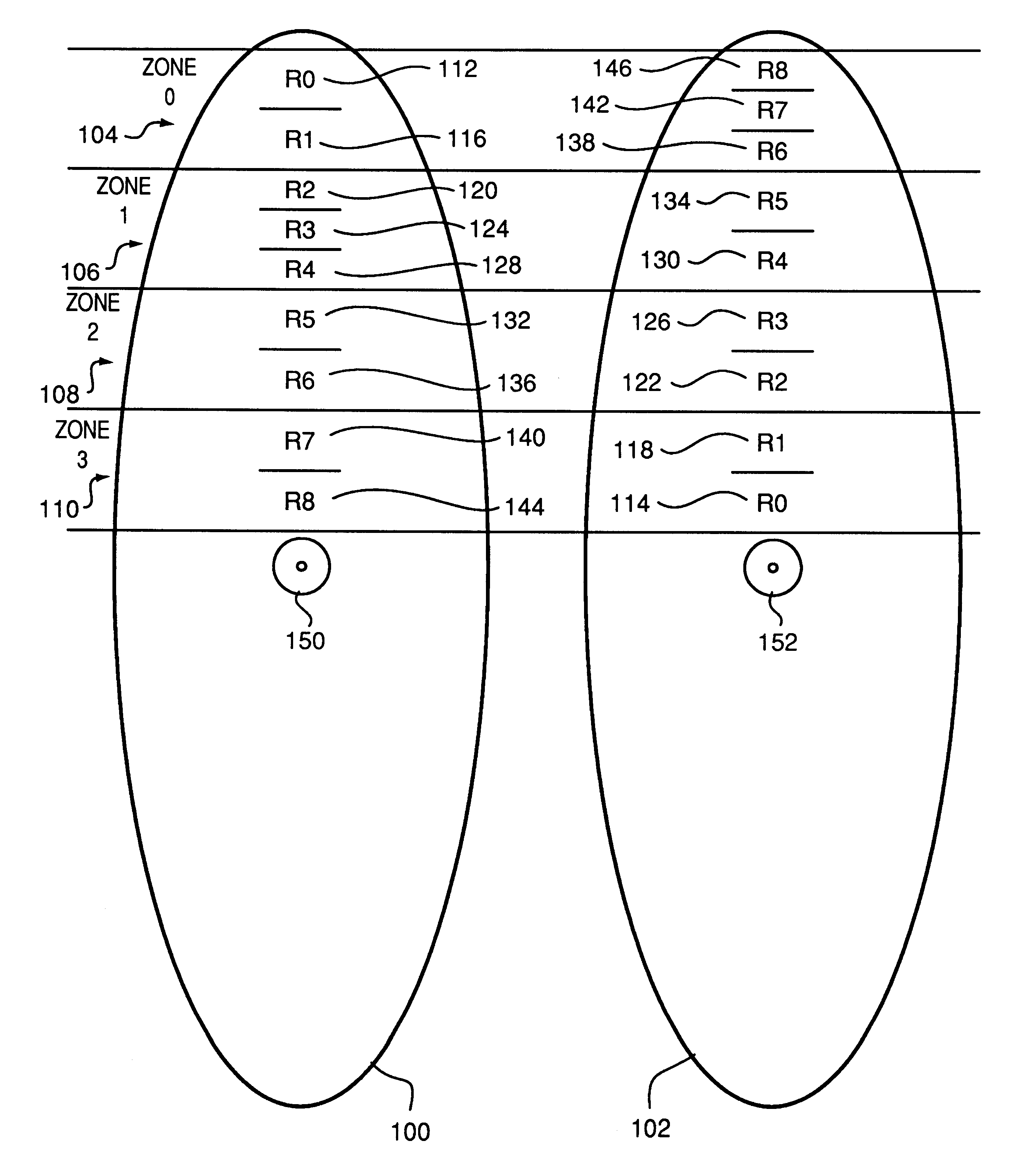
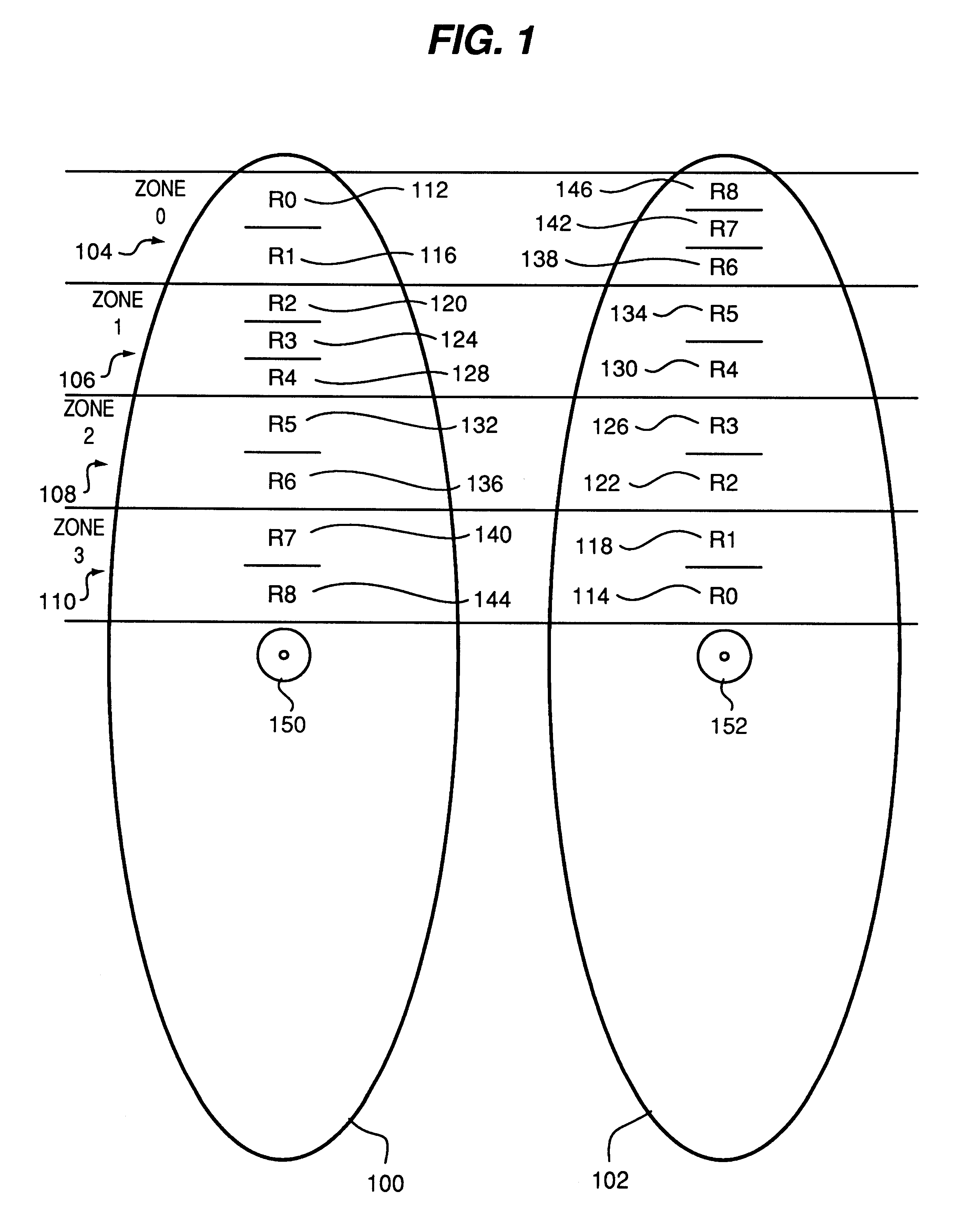
Methods and systems for mapping logical disk addresses to physical locations so as to achieve consistent sustained performance for a striped disk array I / O subsystem. Stripes (regions) are defined by a region mapping table. Zones are defined by the disk manufacturer as groups of cylinders having identical number of sectors per track. Outer zones store more data and therefore provide a higher level of sustained performance as compared to inner zones. Substantially half the disks in the array are mapped such that logical sequential blocks are allocated from outer most, higher performance, zones to inner, lower performance, zones. The other half of the drives in the array are mapped from inner zones to outer zones. Each region (stripe) therefore includes a mix of higher performance zones and lower performance zones. Each region therefore provides more consistent sustained performance as compared to prior techniques. Improved consistency in performance enables better utilization of storage system performance and storage capacity as compared to prior techniques. Alternate embodiments of the invention provide for striping such regions using multiple actuators within a single drive spindle and for providing such mapping functions within low level drive control electronics.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
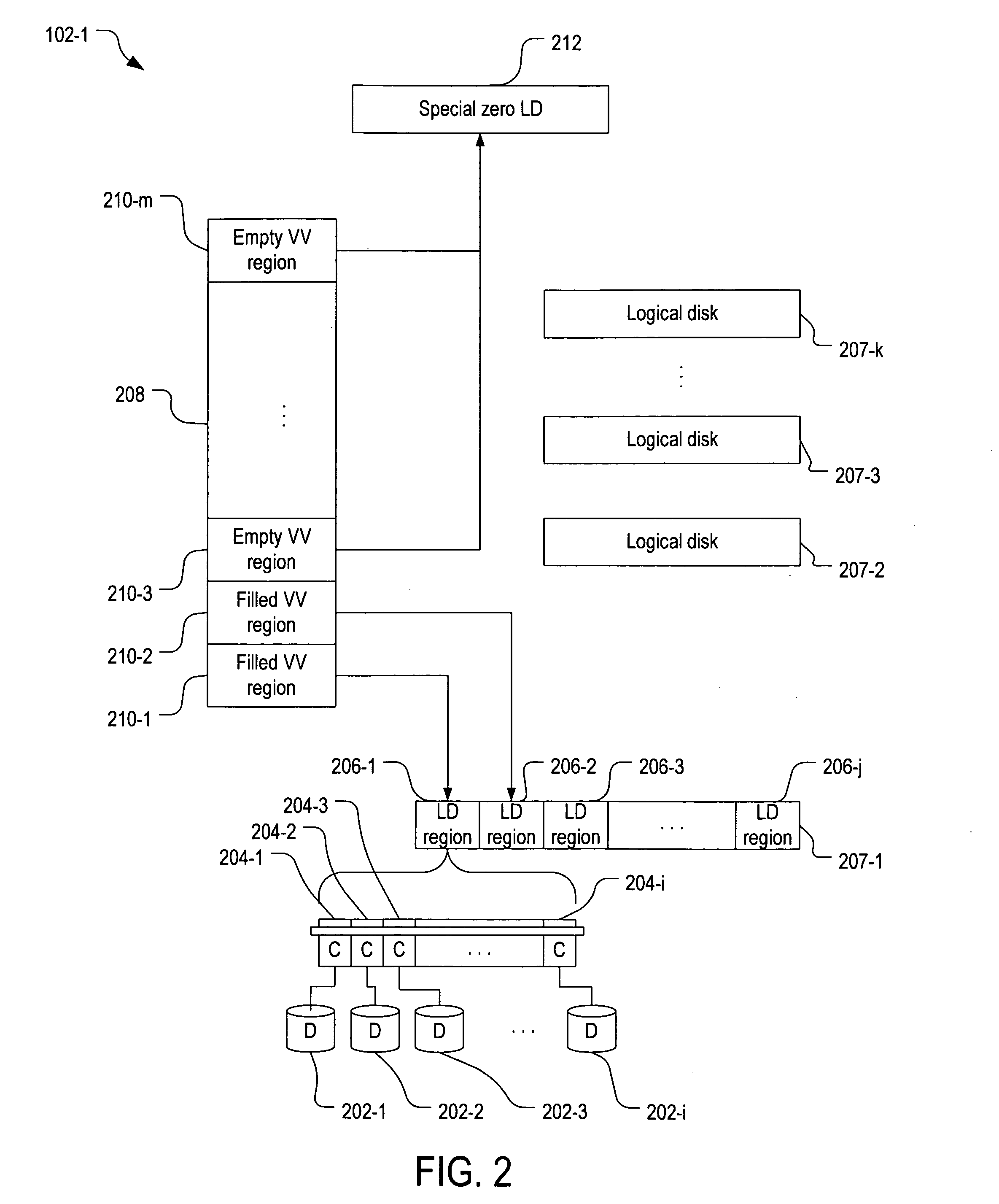
On-demand allocation of physical storage for virtual volumes using a zero logical disk
ActiveUS7032093B1Input/output to record carriersMemory adressing/allocation/relocationLogical diskOn demand
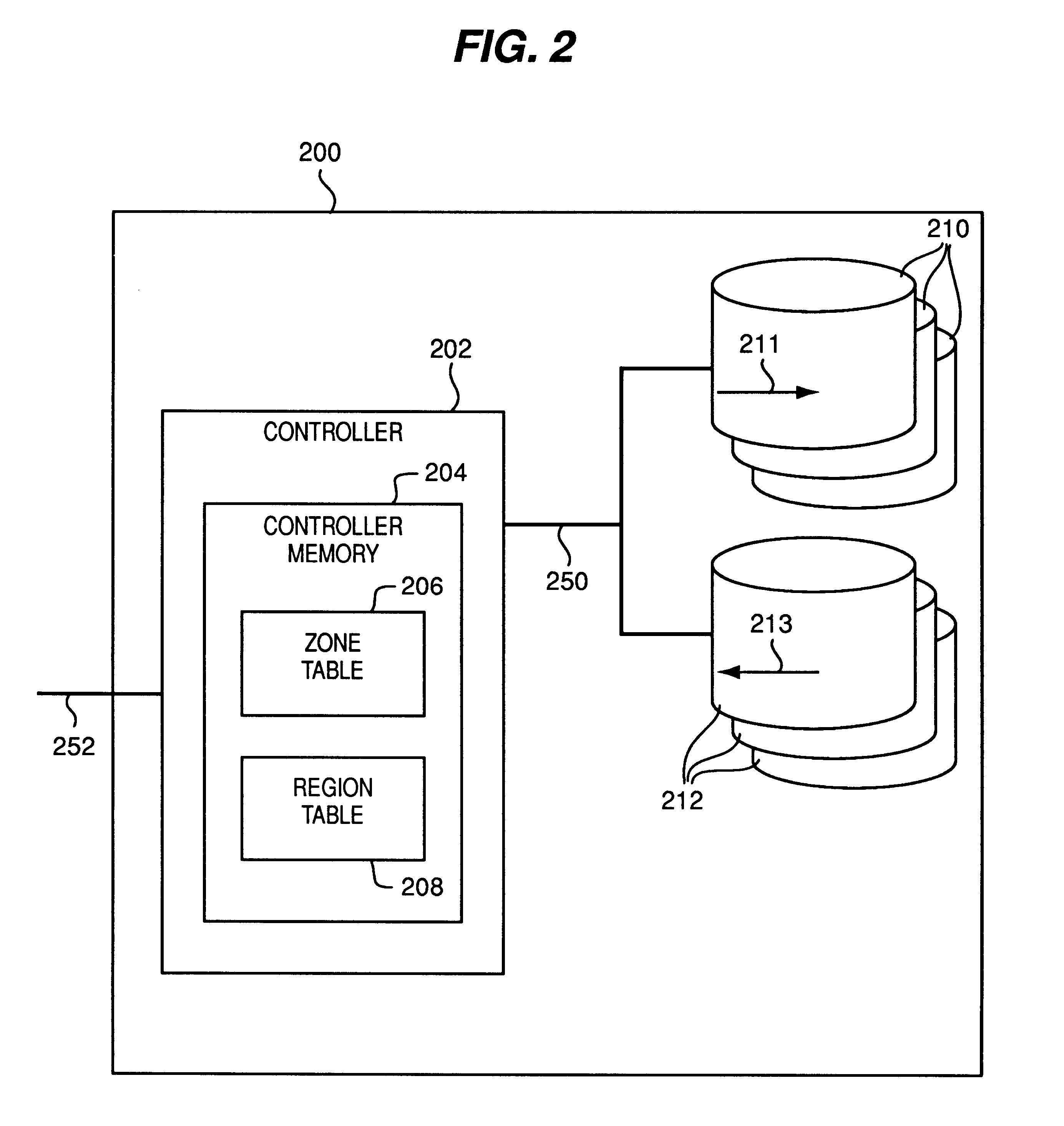
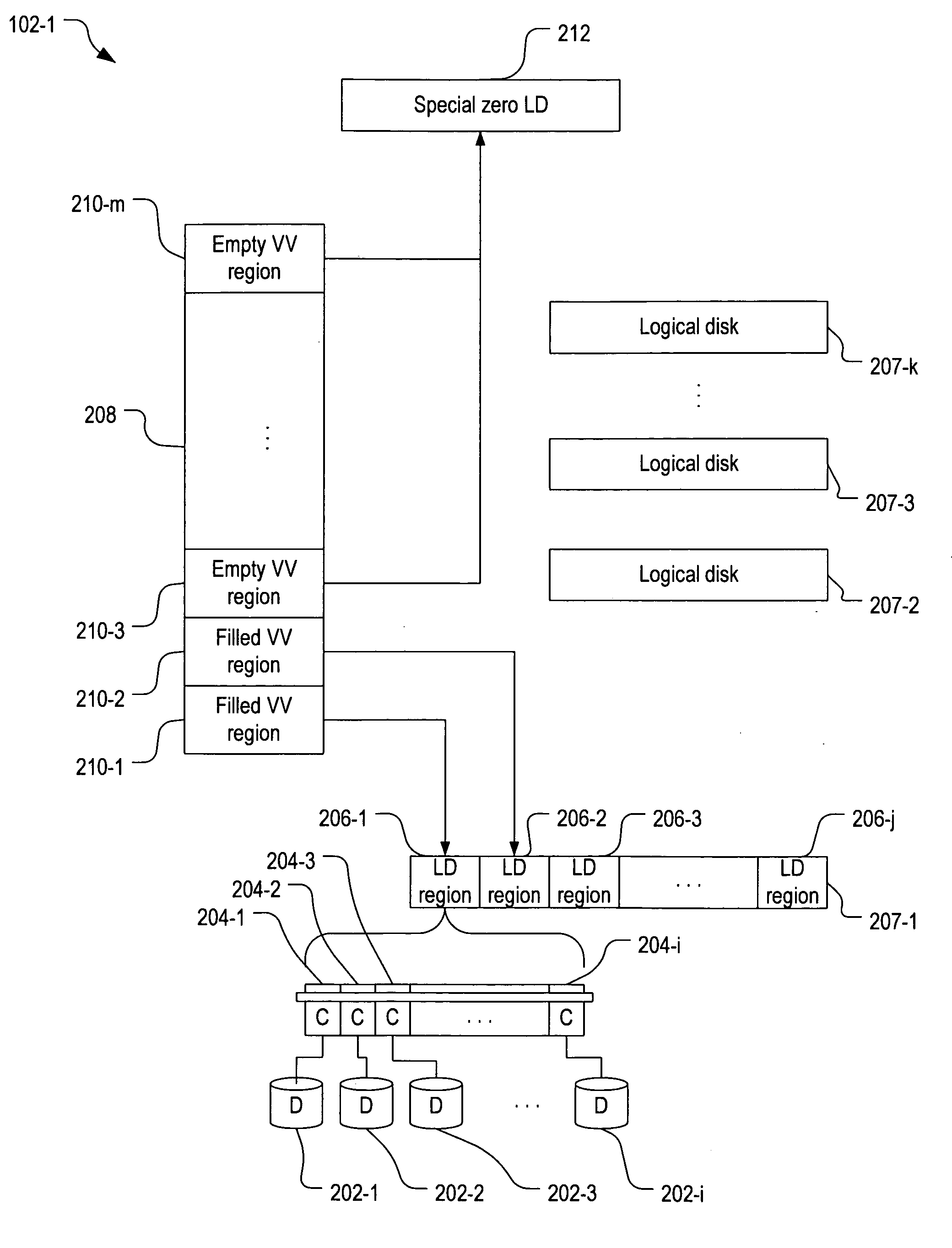
In one embodiment of the invention, a virtual volume is divided into “filled” and “empty” virtual volume (VV) regions. Empty VV regions are mapped to a special zero logical disk that does not consist of any physical disk regions. When a host writes to an empty VV region, a logical disk (LD) region is allocated to the empty VV region so the formerly empty VV region becomes a filled VV region mapped to the allocated LD region. If there are no LD regions available, a new logical disk is created. Additional physical storage can be added to the storage server to create new logical disks as the use of the virtual volume grows. Physical allocation warning points and limits allow the system administrator to be alerted to and to control physical allocation for each individual VV and the set of VVs drawing from the same data allocation control structure (DC).
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
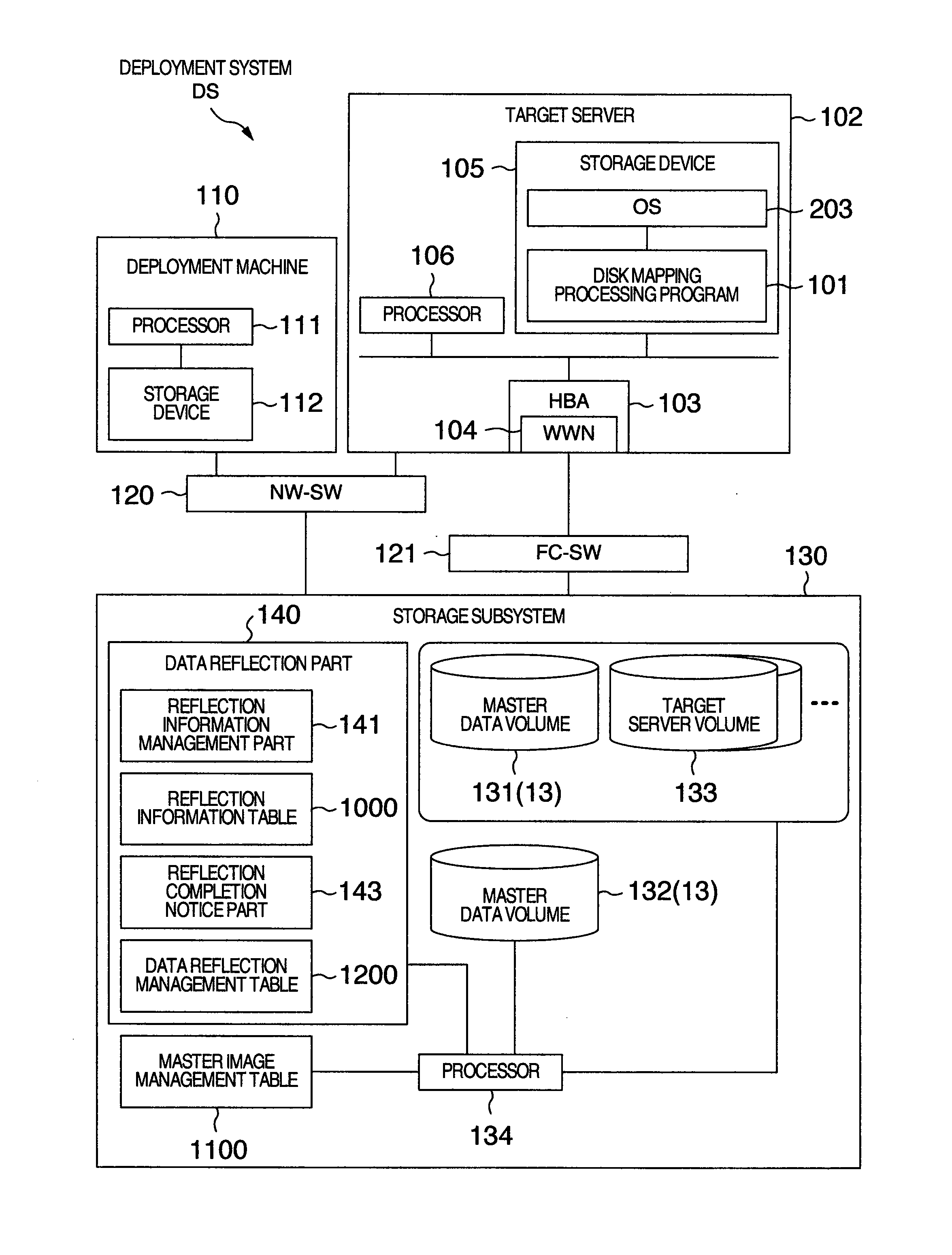
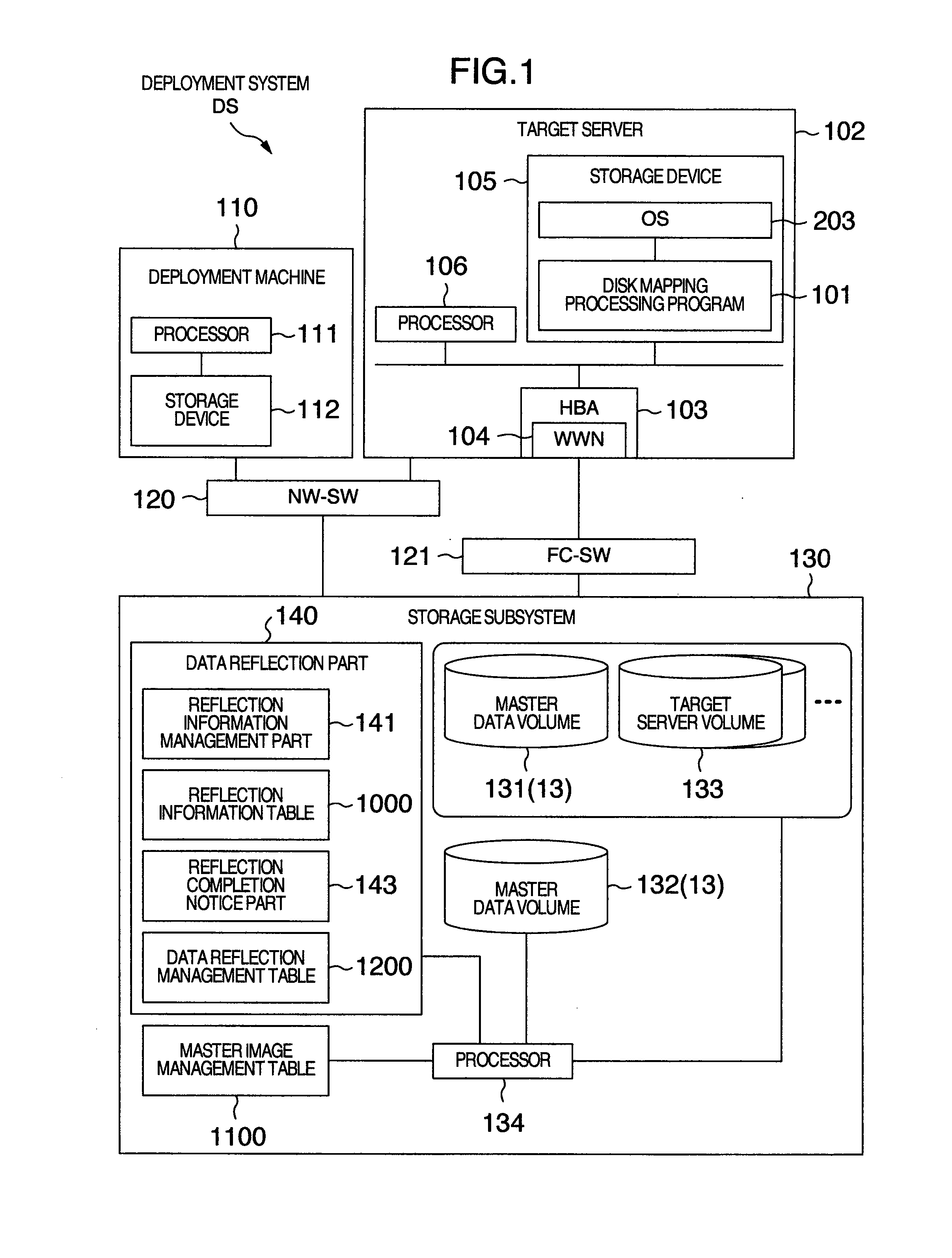
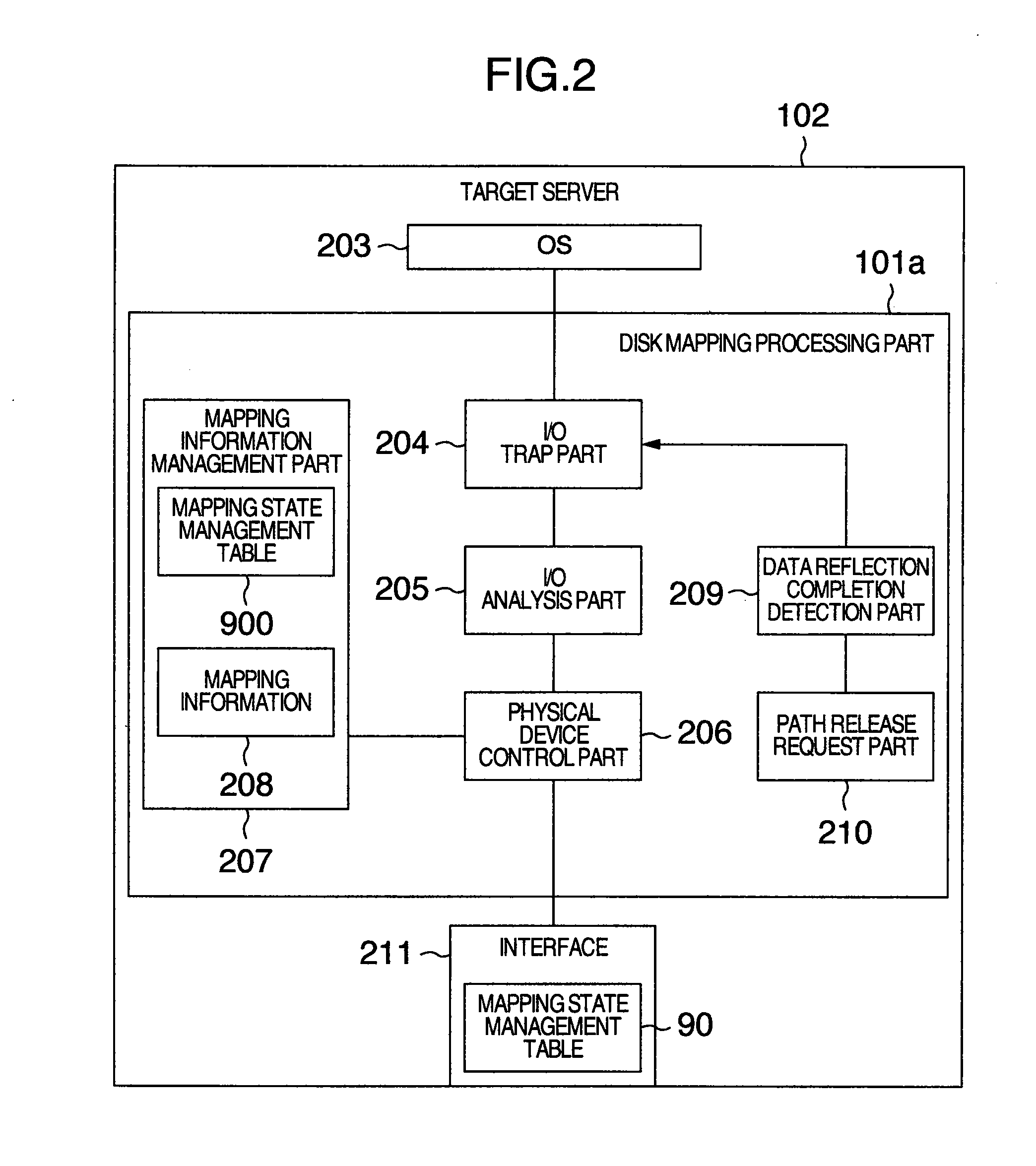
Deploy target computer, deployment system and deploying method
A deploy target computer is connected to a storage device including a replication source logical disk used to store a boot disk image. A disk mapping processing part in the deploy target computer changes over access destination so as to set the access destination to the replication source logical disk in the storage device when an I / O request is issued from the deploy target computer to the storage device and the I / O request specifies reading the boot disk image, and so as to set the access destination to a replication destination logical disk for conducting writing concerning the boot disk image when the I / O request specifies writing concerning the boot disk image.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
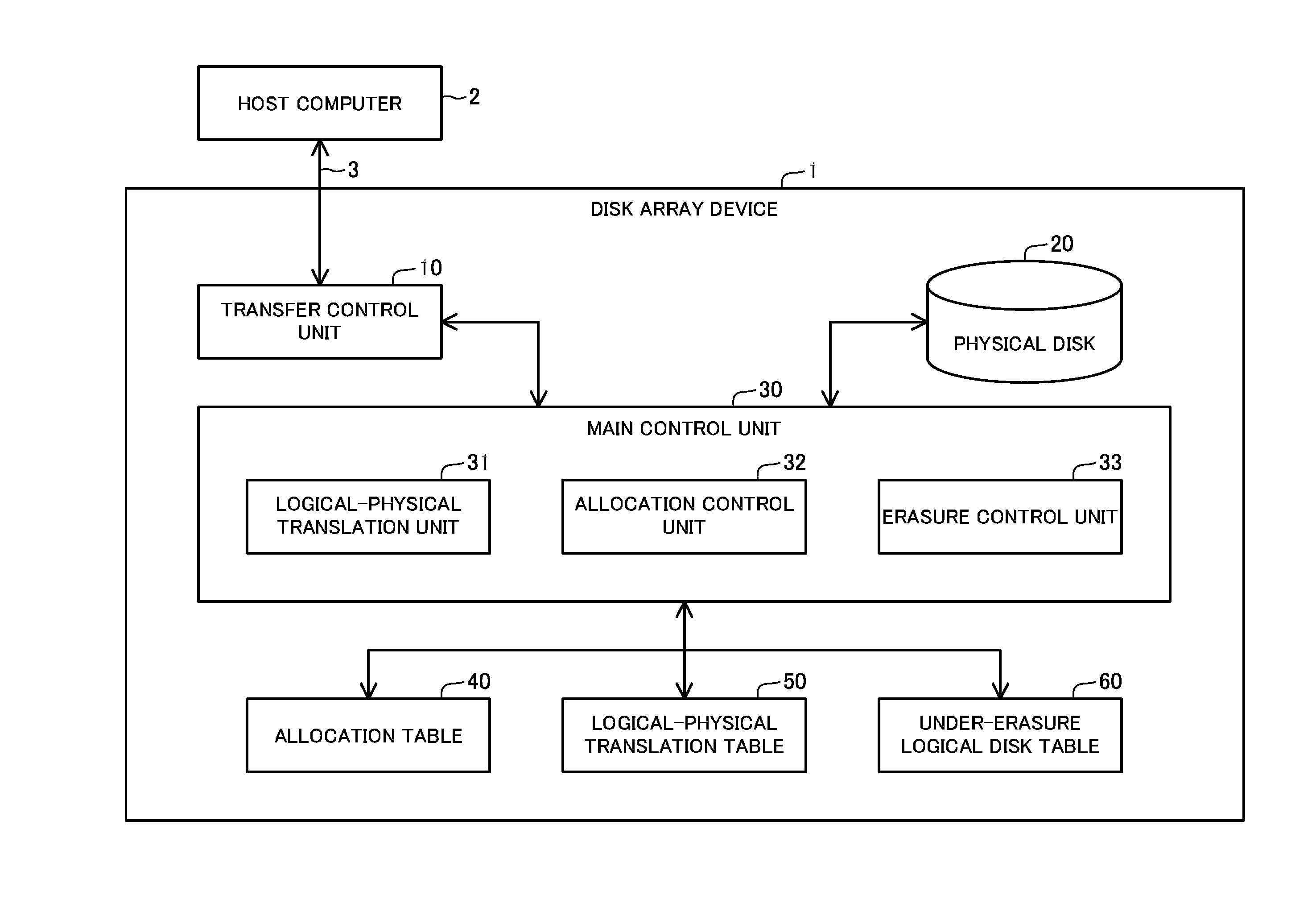
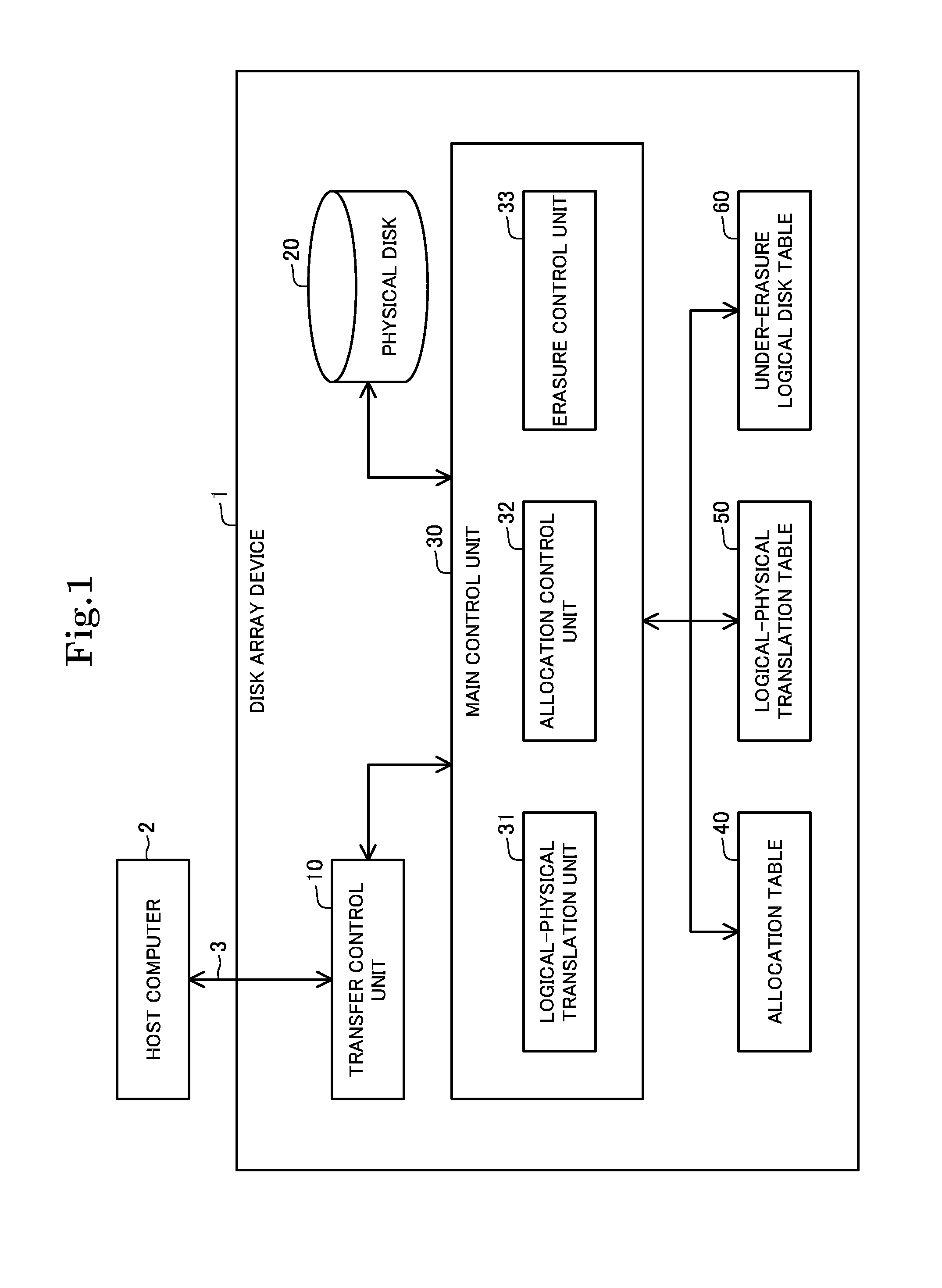
Disk array device
InactiveUS20140297949A1Increase speedMemory adressing/allocation/relocationInternal/peripheral component protectionDistribution controlDisk array
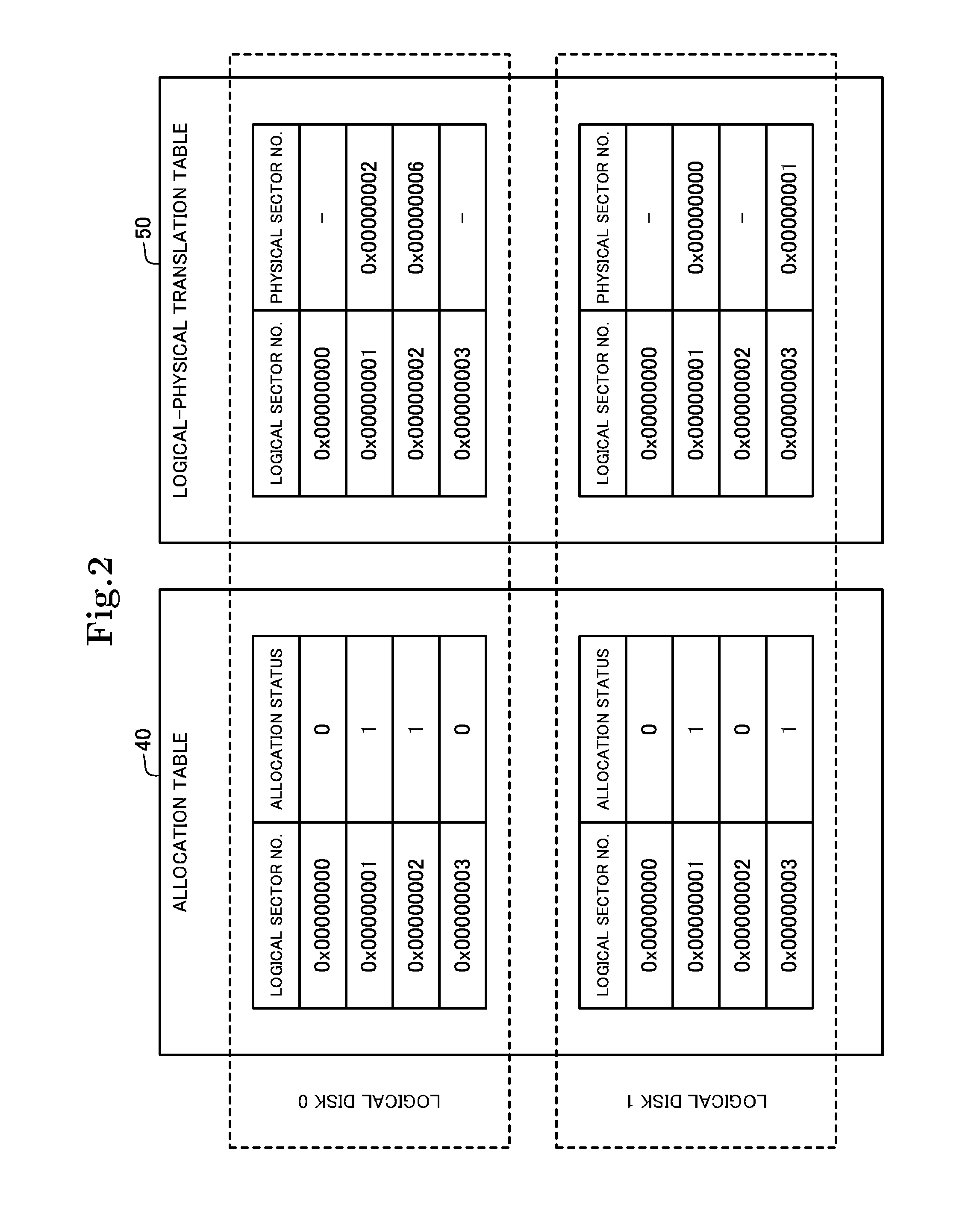
The disk array device includes an allocation control unit that allocates a physical sector to a logical sector, and an erasure control unit that erases data written on a logical sector. The allocation control unit stores a logical sector and a physical sector allocated thereto in a translation table in association with each other, and stores allocation information representing that the physical sector is allocated to the logical sector, in an allocation table. The erasure control unit registers logical disk information specifying a logical disk, to which an erasure request has been made, in an under-erasure table, specifies a physical sector allocated to a logical sector formed in the logical disk to which the erasure request has been made, based on the allocation table and the translation table, and performs erasure processing on the specified physical sector.
Owner:NEC CORP
Data protection via software configuration of multiple disk drives
InactiveUS20080168209A1Memory adressing/allocation/relocationComputer security arrangementsControl storeSystem configuration
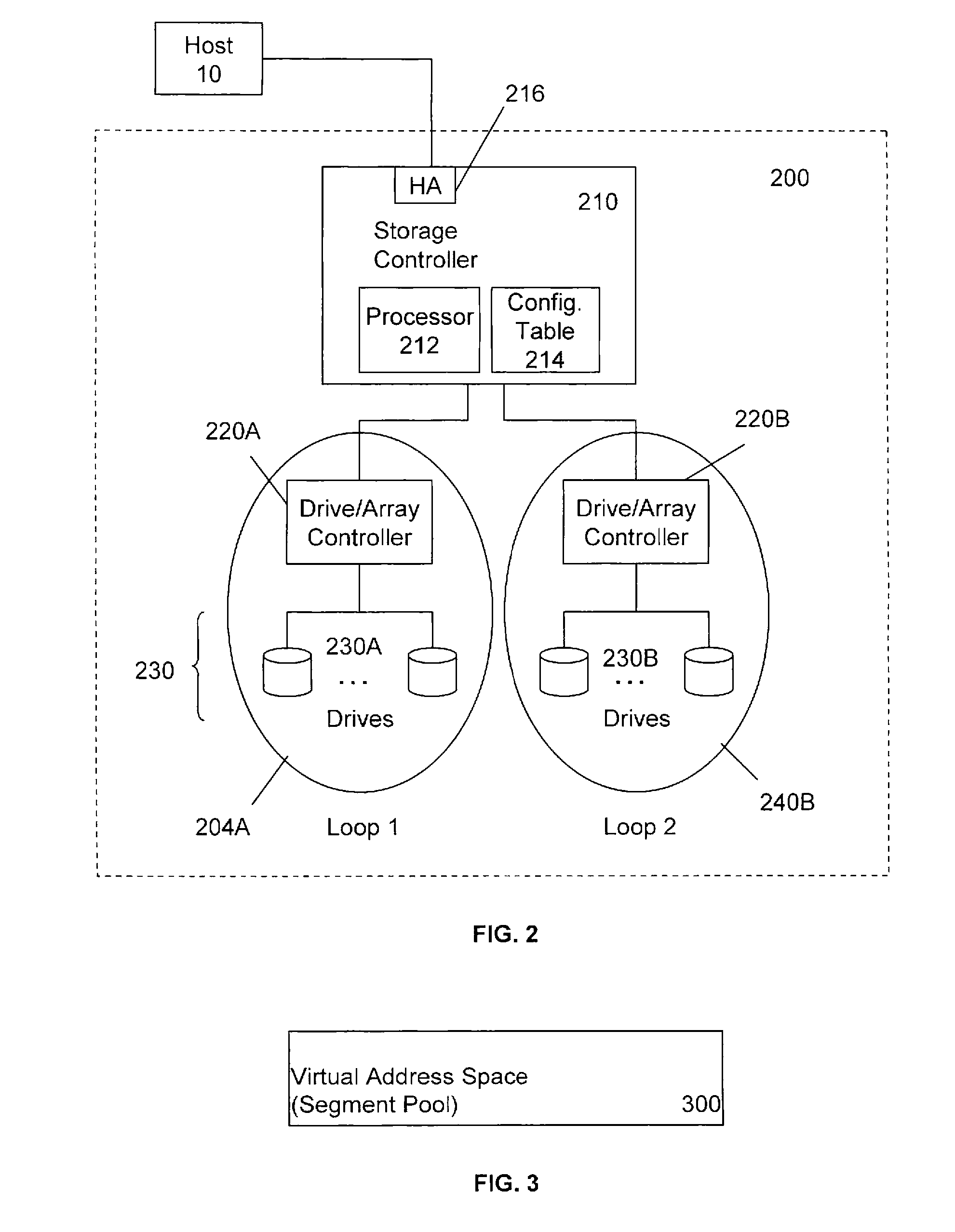
A data storage system and a method for managing a data storage system are provided. A storage controller is programmed with a disk configuration for each of one or more logical disk arrays and a protection level k. The available storage space from one or more disk drives in the data storage system is merged into a single virtual address space and the merged storage space is divided into storage segments. Next, the storage segments are allocated among the logical disk arrays and a configuration table is generated indicating the number of storage segments in each logical disk array and the physical location of each storage segment on a disk drive. The configuration table is stored in the storage controller and k copies of data may then be stored on the logical disk arrays.
Owner:IBM CORP
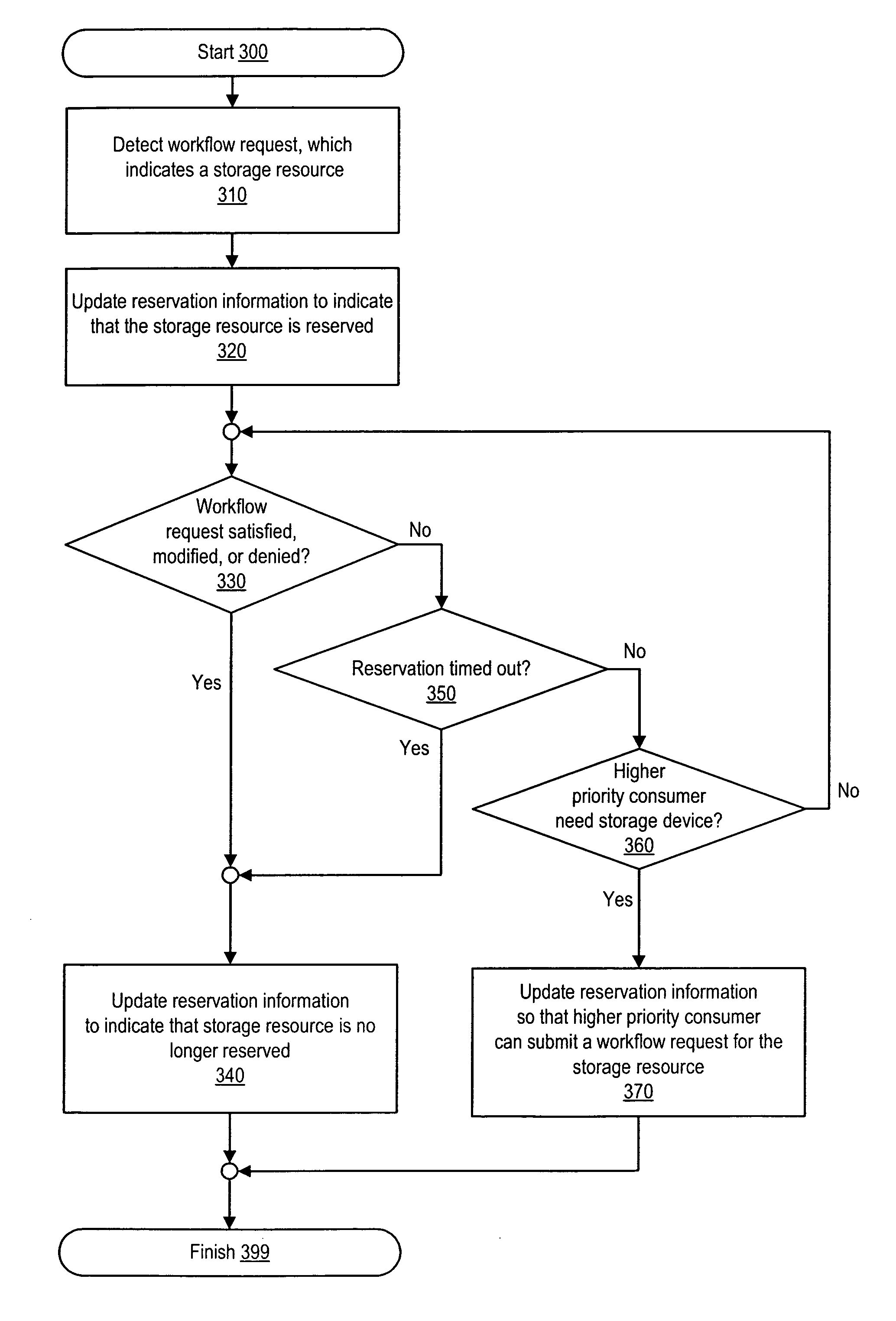
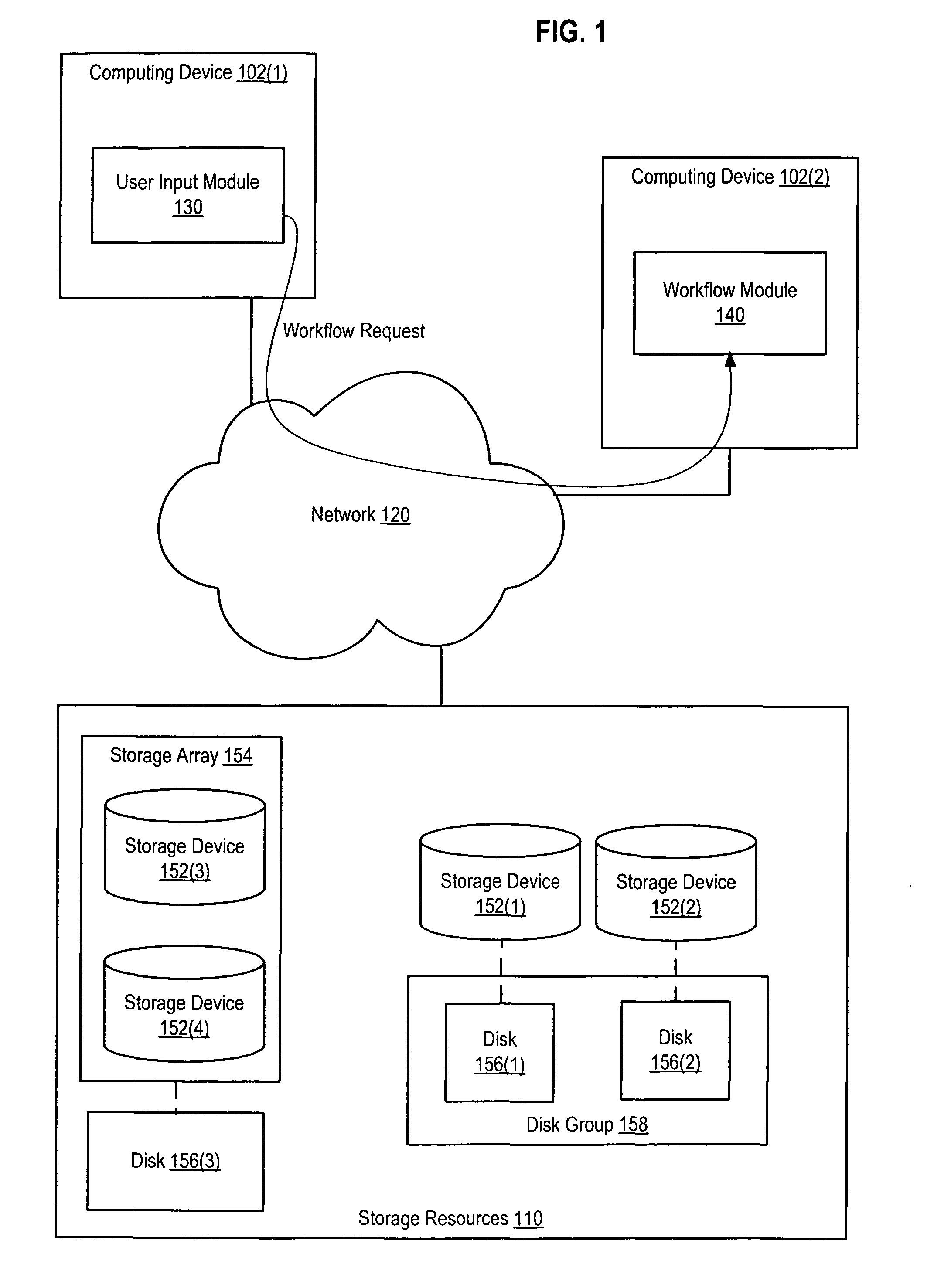
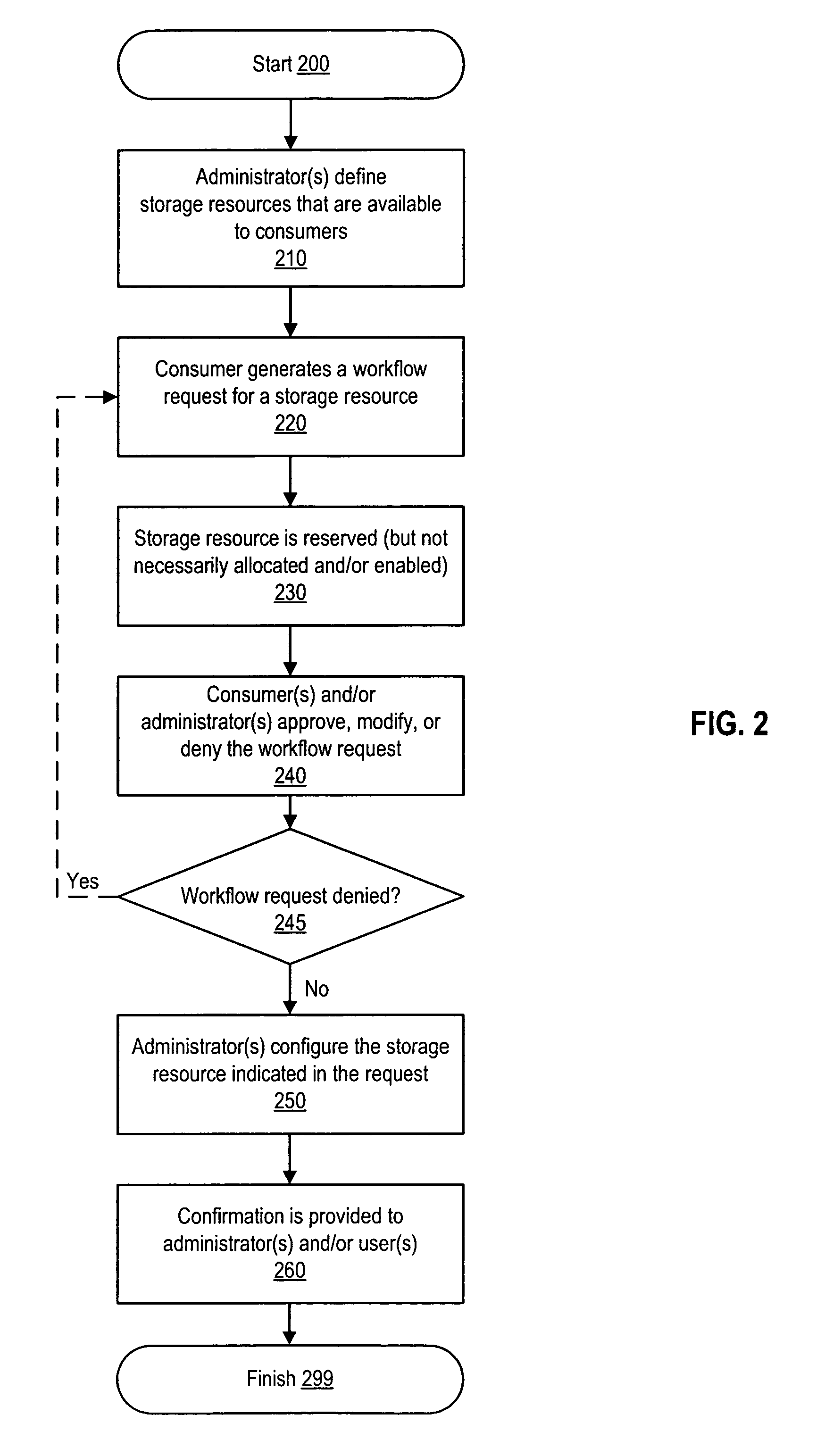
Workflow process with temporary storage resource reservation
A method involves: detecting a storage resource indication within a workflow request and, in response to the storage resource indication, generating an availability indication. The storage resource indication indicates a storage resource (e.g., by directly or indirectly identifying or selecting the storage resource). The availability indication indicates that the indicated storage resource is not available for subsequent workflow requests. The availability indication is generated prior to allowing the consumer that generated the workflow request to use the storage resource. The workflow request can include a request to allocate a logical storage structure (e.g., a volume or logical disk). The logical storage structure is allocated in response to the workflow request. If the workflow request is denied or expires, the logical storage structure is deleted.
Owner:SYMANTEC OPERATING CORP
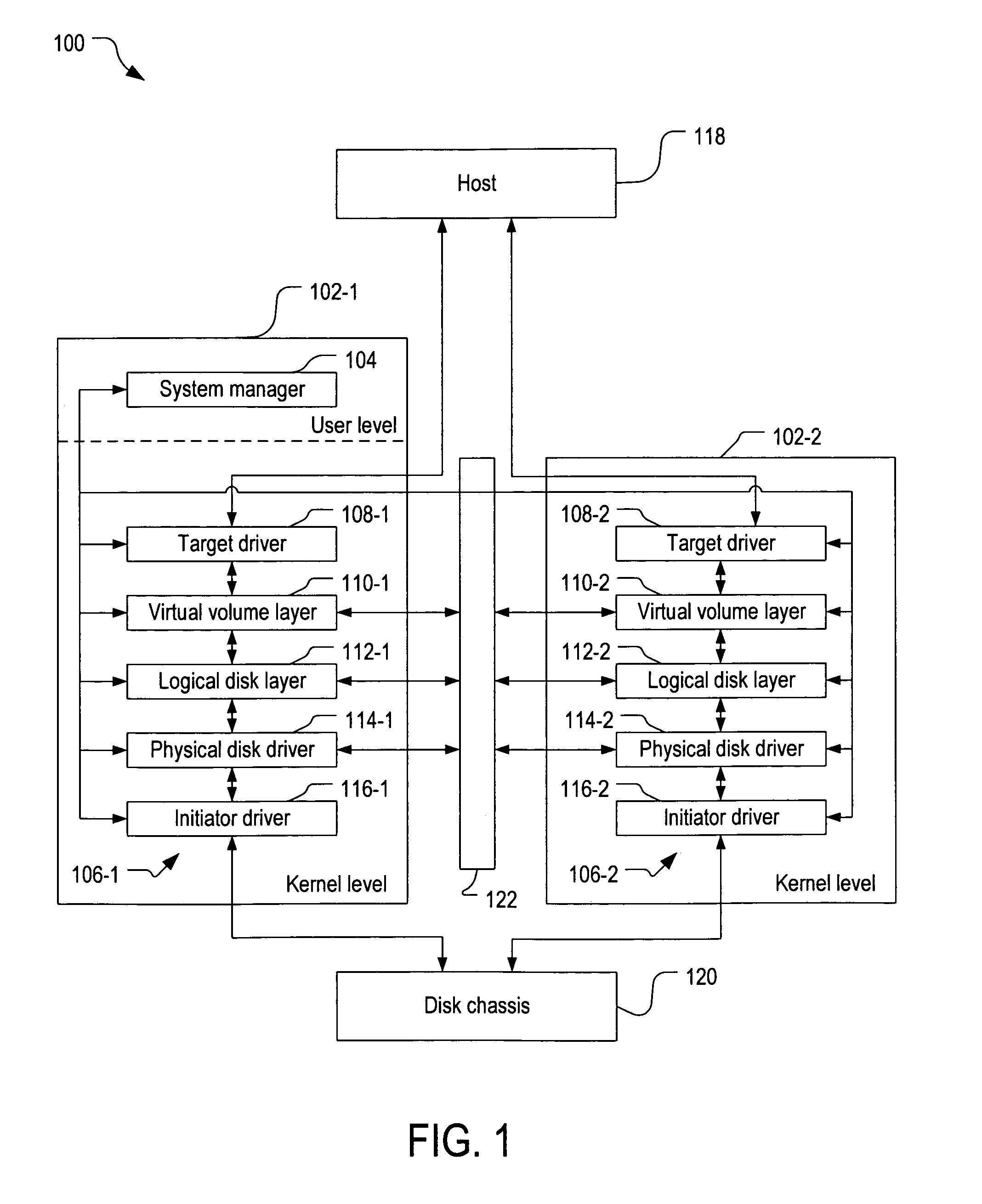
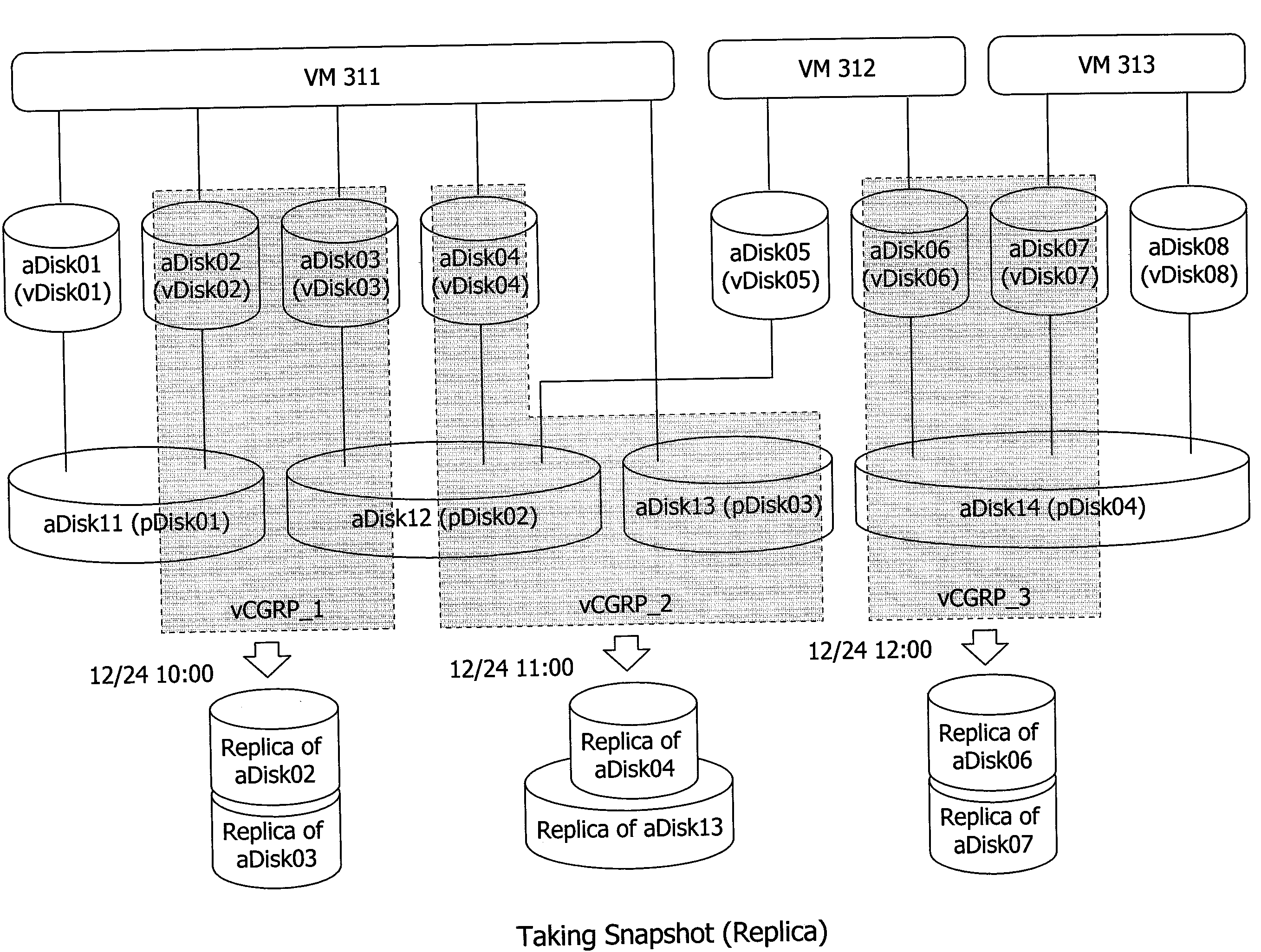
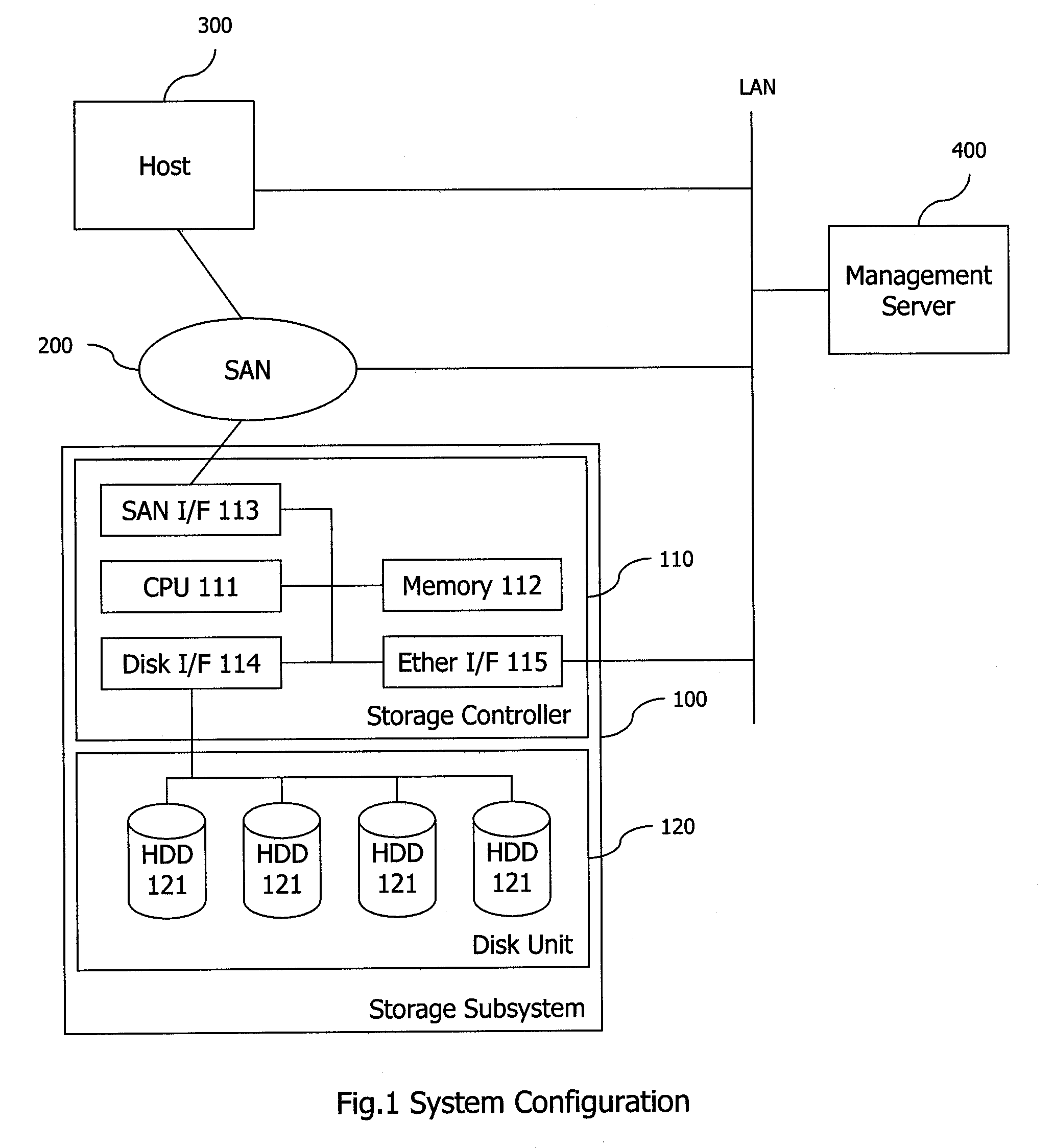
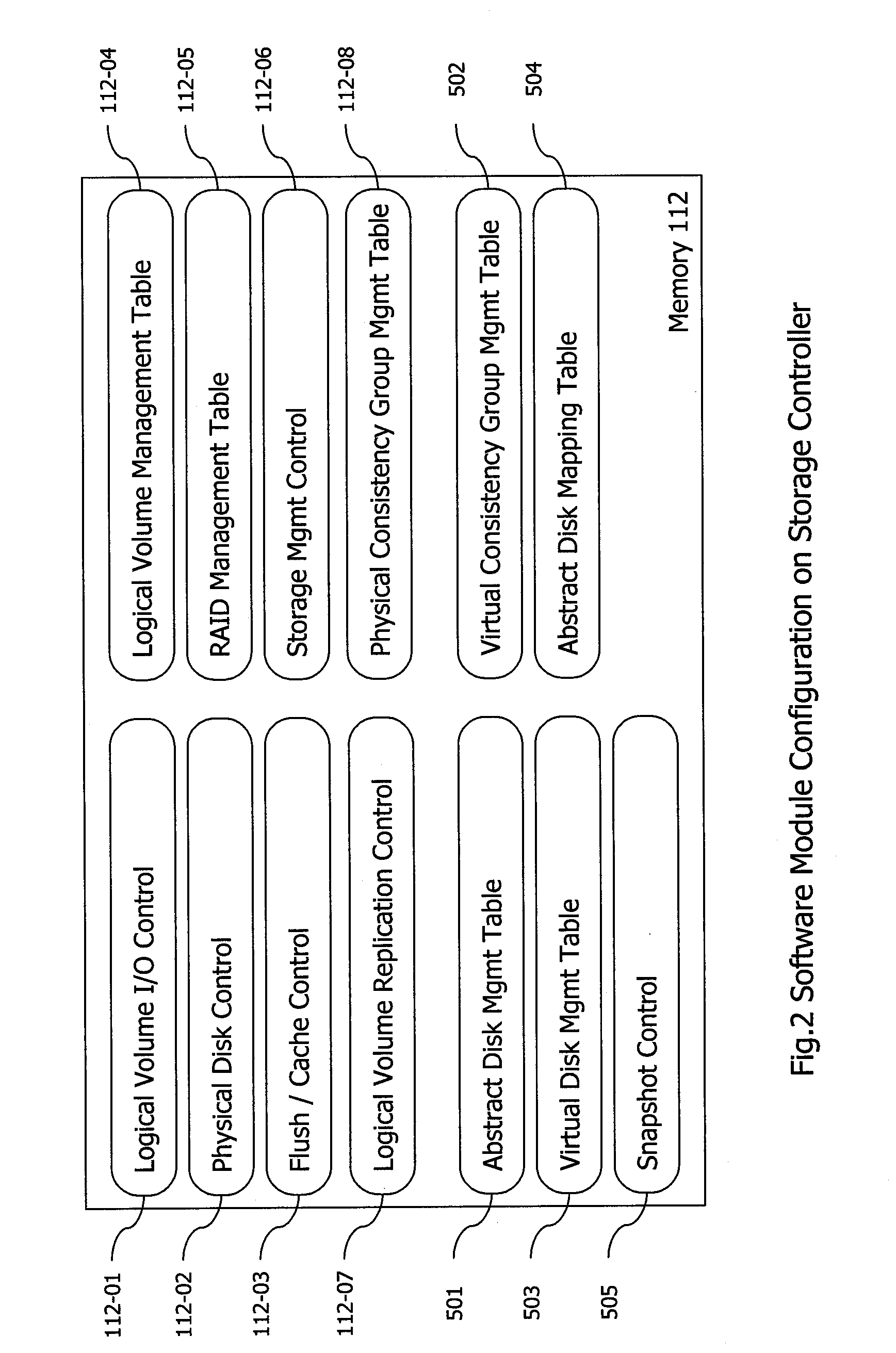
Method and apparatus for logical volume management for virtual machine environment
Exemplary embodiments of the invention provide logical volume management for a storage subsystem in a virtual machine environment. In one embodiment, a storage system comprises a storage subsystem including a processor, a memory, one or more virtual disks, and one or more logical disks each corresponding to a physical storage area in the storage subsystem; and a host computer connected with the storage subsystem via a network, the host computer including a plurality of virtual machines running thereon, the virtual machines each being connected to at least one of the virtual disks or logical disks in the storage subsystem. In the storage subsystem, abstract disks each represent one of the virtual disks or logical disks. An abstract disk management table is stored in the memory of the storage subsystem to manage a relationship between the abstract disks and the one or more virtual disks and between the abstract disks and the one or more logical disks.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
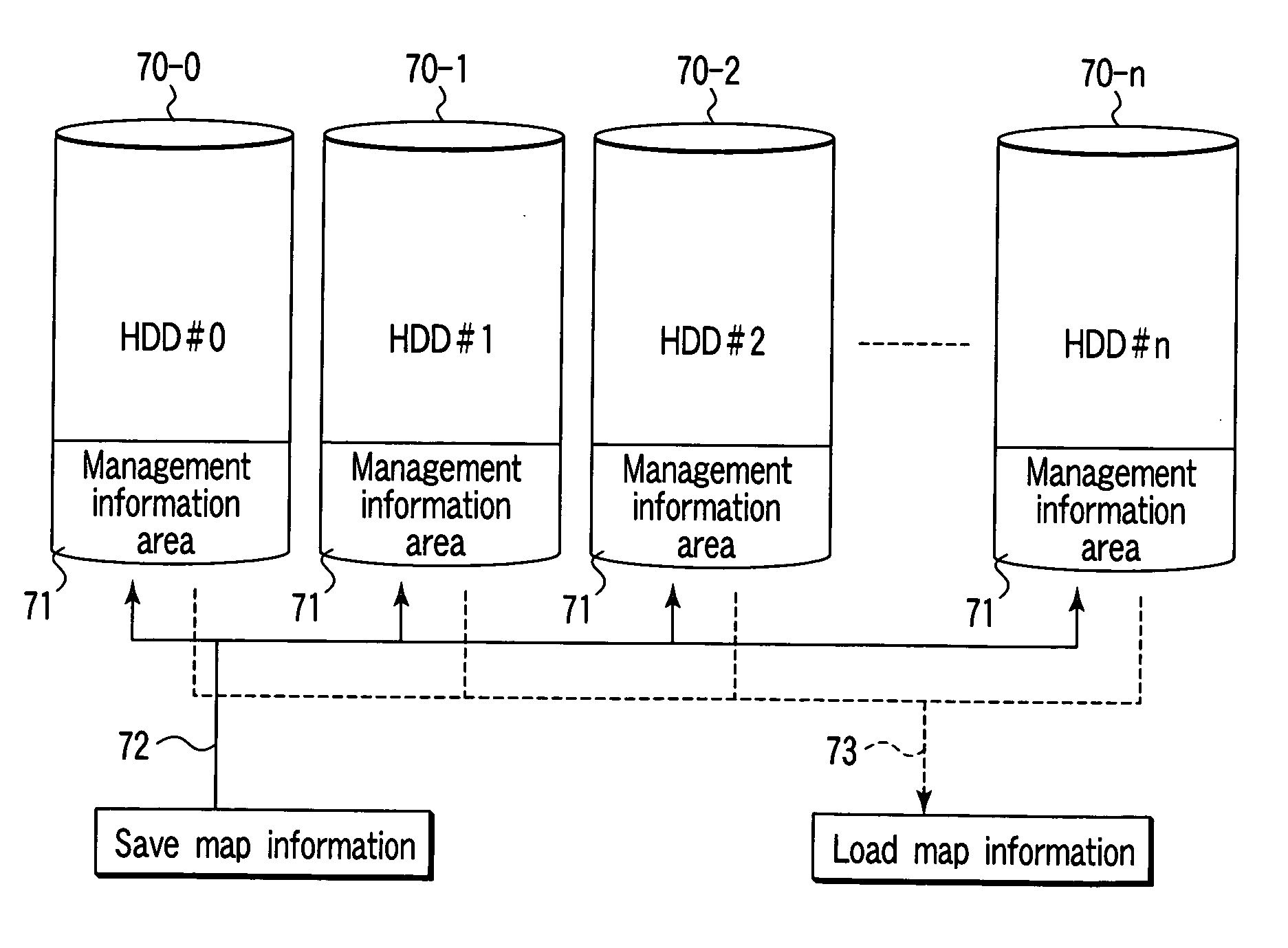
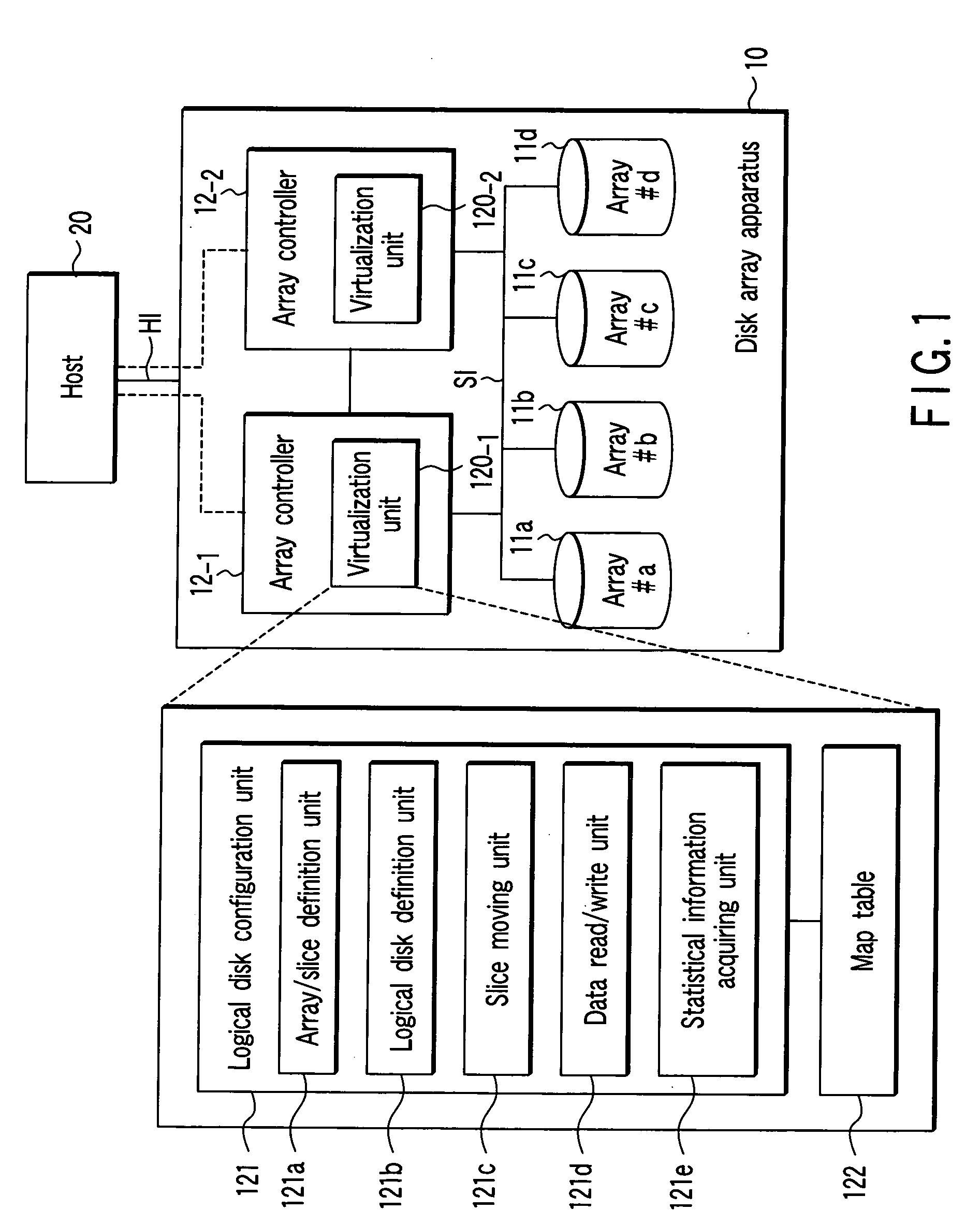
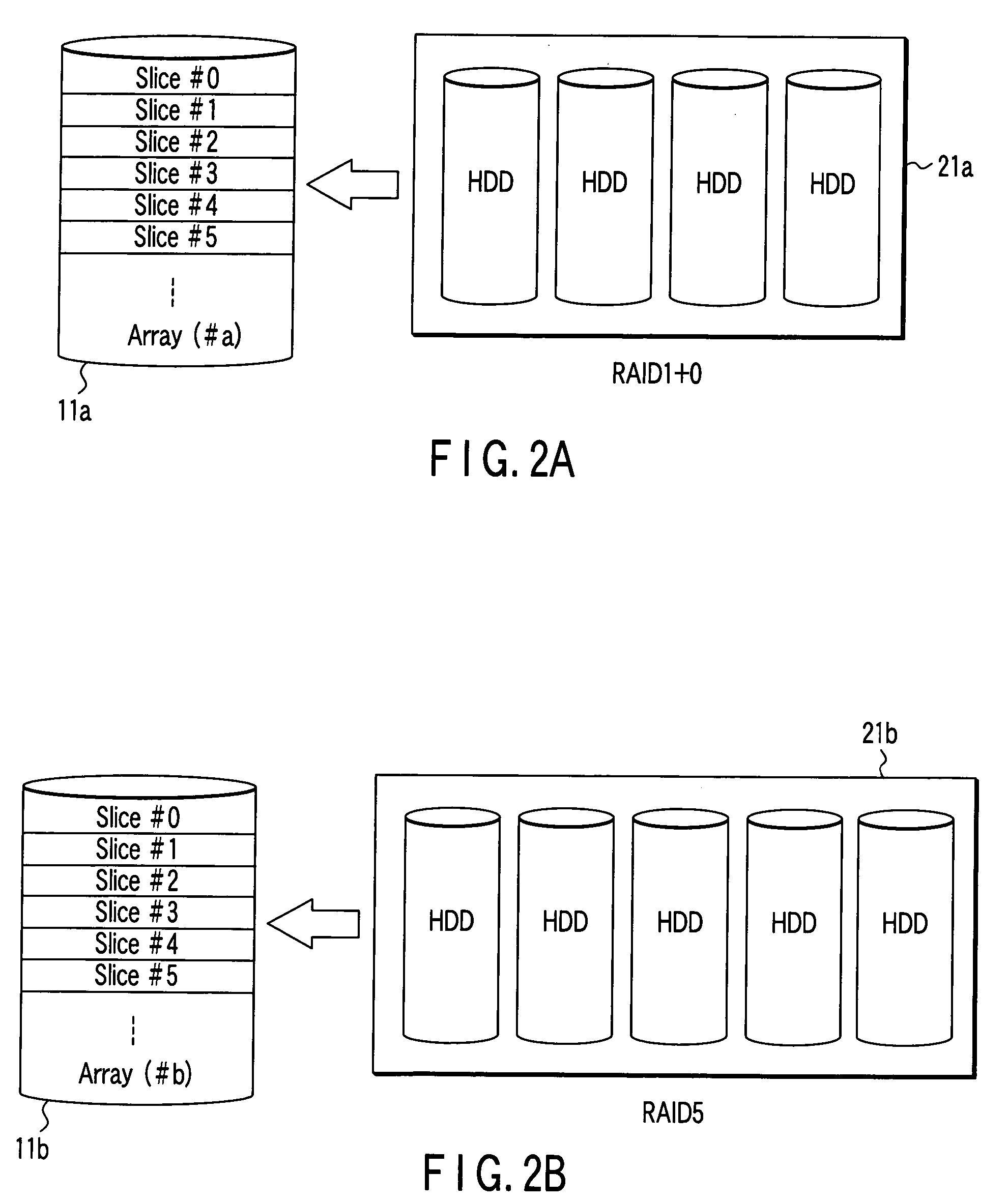
Logical disk management method and apparatus
InactiveUS20060010290A1Memory systemsInput/output processes for data processingLogical diskComputer engineering
An array / slice definition unit constitutes an array composed of a group of slices. The array is constituted by defining a storage area in a disk drive as a single physical array area of the array. The physical array area is divided to a plurality of areas under a certain capacity, and the divided areas are defined as the slices. A logical disk definition unit constitutes a logical disk by combining arbitrary plural slices of the slices contained in the array. A slice moving unit exchanges an arbitrary first slice entered into the logical disk and a second slice not entered into any logical disk including the logical disk.
Owner:TOSHIBA SOLUTIONS +1
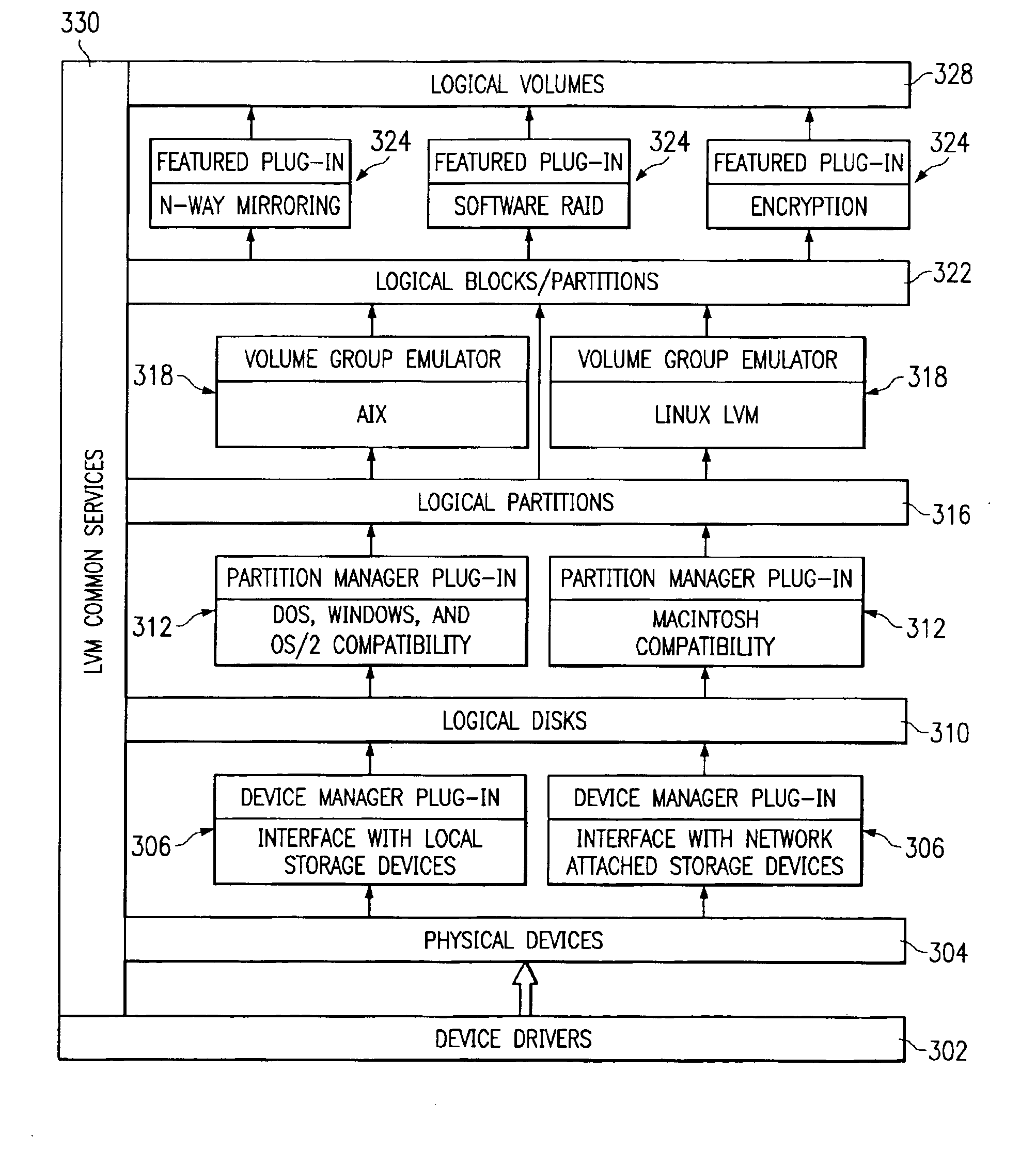
Method and an apparatus to extend the logic volume manager model to allow device management plug-ins
InactiveUS7003780B2Input/output to record carriersMemory adressing/allocation/relocationComputer hardwareLogical disk
Logical disks are provided, which are created by device managers. The logical volume manager is modified to use only logical disks. The device managers may be plug-in modules. This allows new device managers to be added to the logical volume manager at any time without changing the code in the logical volume manager. Anything that can be made to appear as a logical disk through the use of a device manager plug-in may then be used with the logical volume manager. A device manager for network attached storage may be written allowing network attached storage devices to be treated as local disk drives by the logical volume manager, thereby allowing all of the capabilities of the logical volume manager to be used with the network attached storage devices.
Owner:TWITTER INC
Method and apparatus for unified storage of data for storage area network systems and network attached storage systems
InactiveUS20050193021A1Input/output to record carriersSpecial data processing applicationsComputer hardwareStorage area network
A unified data storage apparatus for storing data for both storage area network and network attached storage system architectures on the same storage medium. The storage medium (50) is partitioned for storage of logical disk volumes and files (58), and is further partitioned for storage of pointers to logical disk volumes (59).
Owner:EXANET
File access method of Linux virtual machine disk under Windows platform
InactiveCN101944043AAvoid consumptionImprove performanceSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationSpecial data processing applicationsOperational systemAccess method
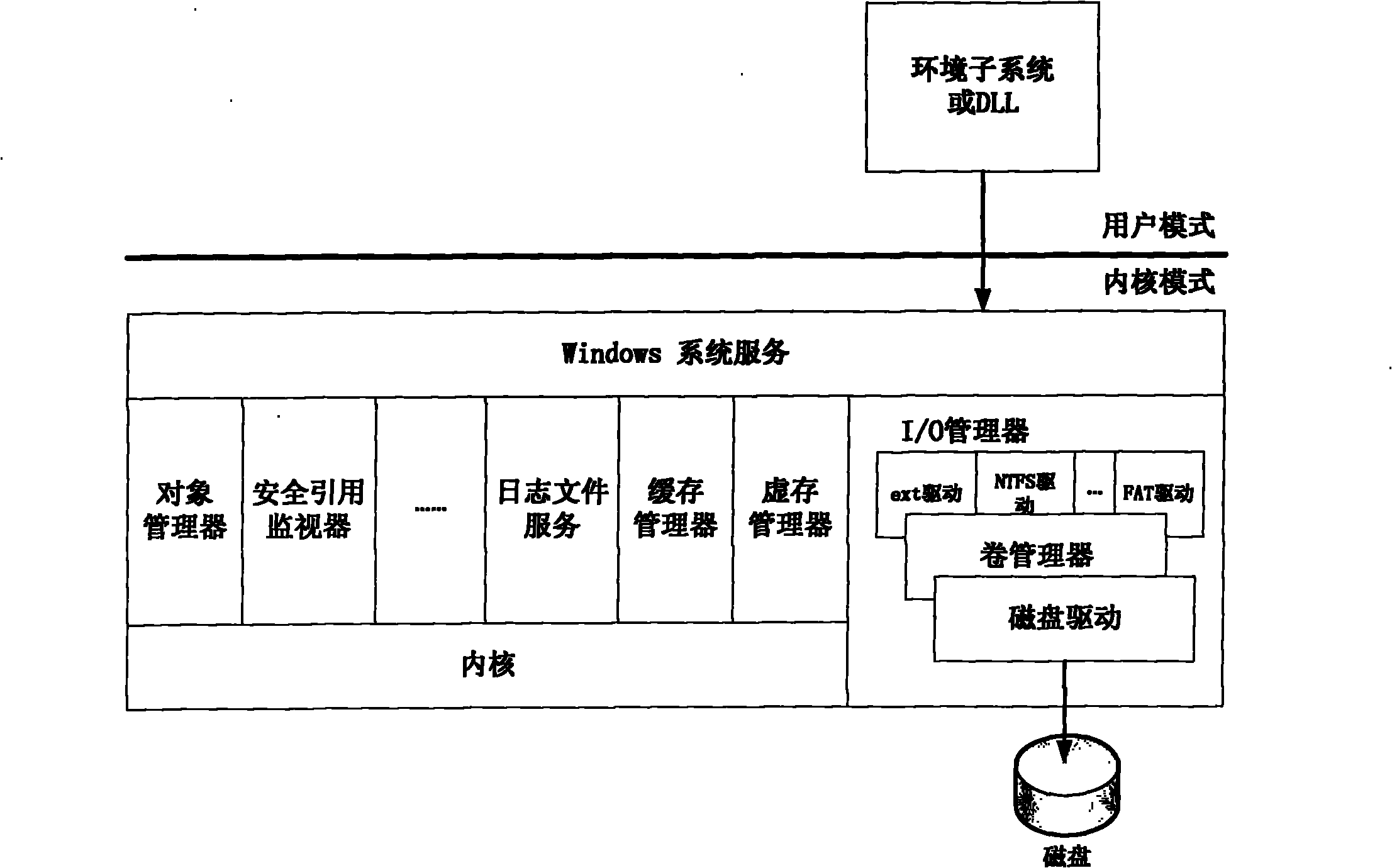
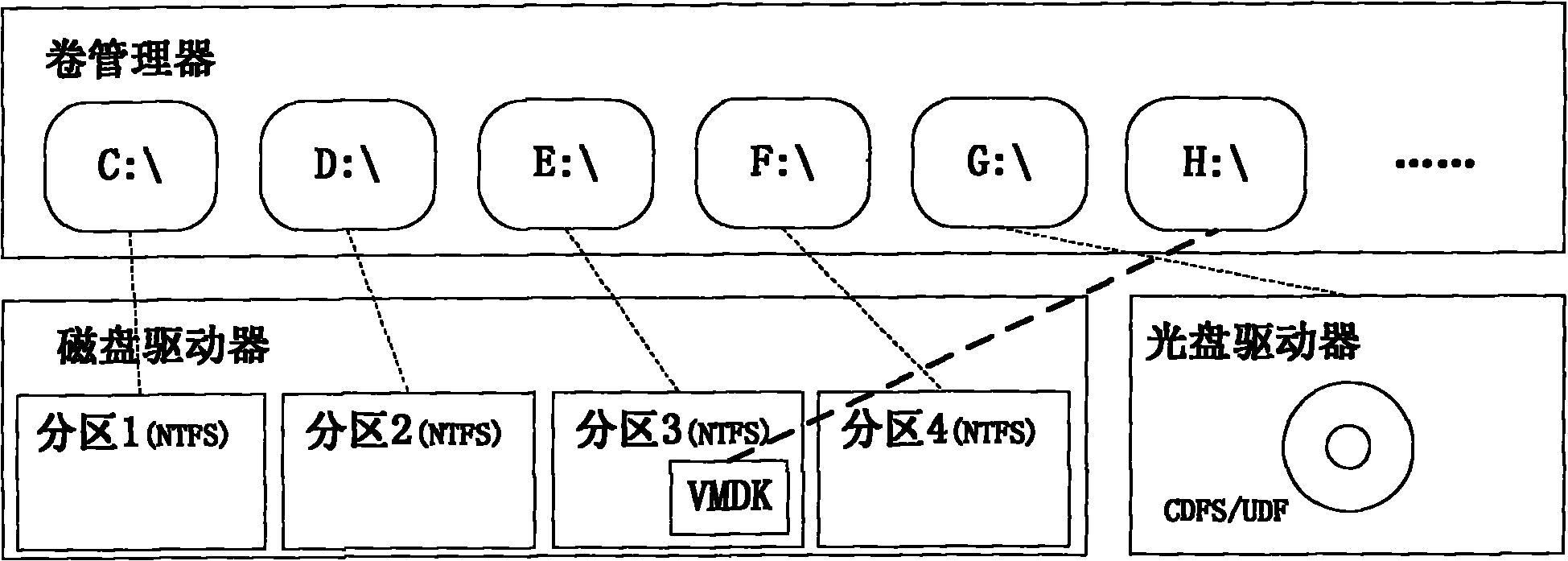
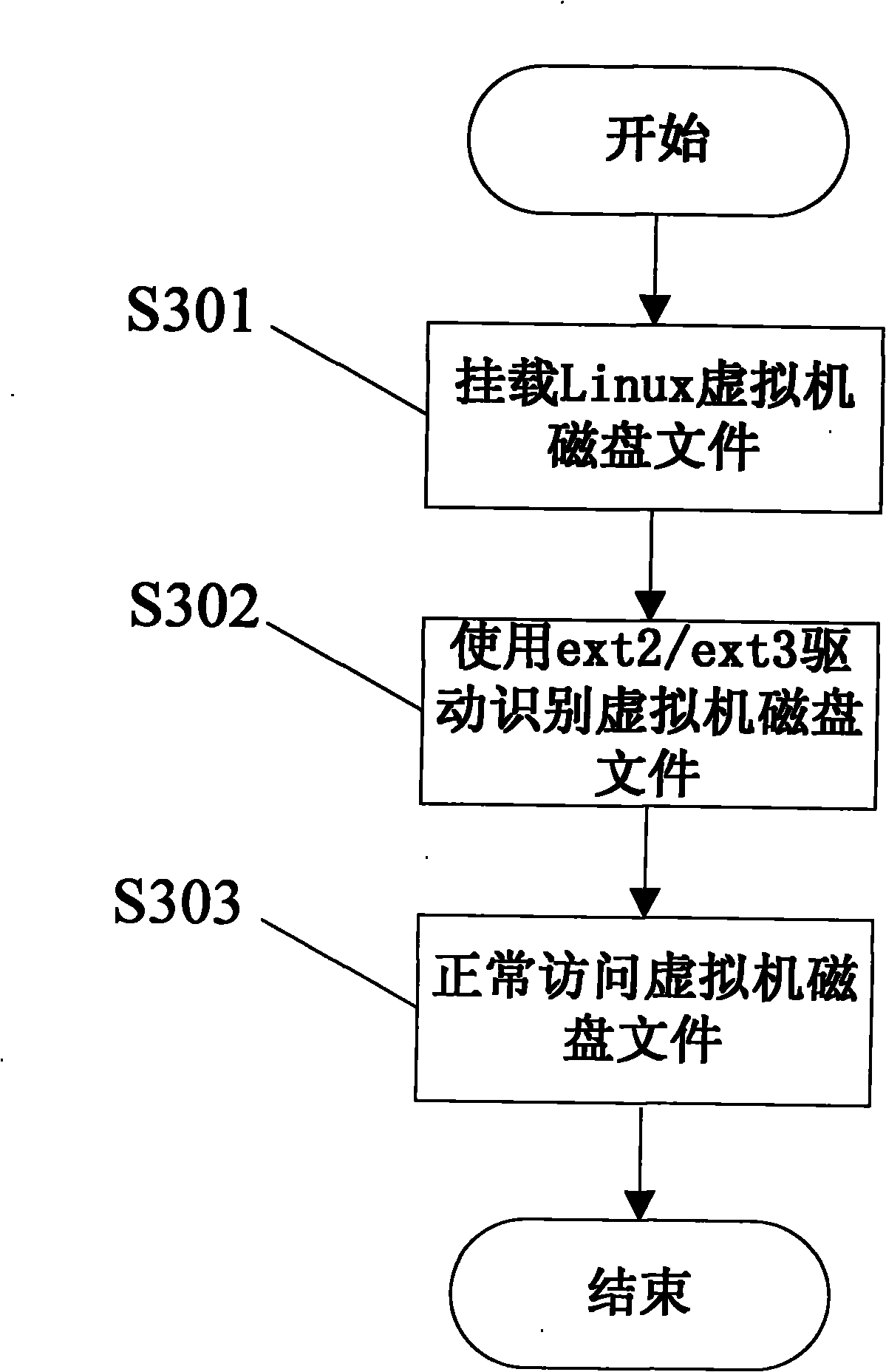
The invention discloses a file access method of a Linux virtual machine disk under a Windows platform, which comprises a mount program for the Linux virtual machine disk and a drive program for an ext2 / ext3 file system analysis. The file access method is characterized in that the mount program uses a VMware Mount Utility tool provided by the VMware company, creates a virtual volume by using a VMDK (Virtual Machine Disk Format) file in a host operating system and provides a new logic disk letter for a user; the realized ext2 / ext3 file system analysis creates a device object to an I / O manager of a Windows kernel and registers the file system so that the Windows operating system can access file systems besides FAT, NTFS, CDFS and UDF; and the drive program is installed in the catalog of \Windows\system32\drivers and is used by the Windows host (including but not limited to) operating system to analyze a file system in ext2 / ext3 format.
Owner:THE THIRD RES INST OF MIN OF PUBLIC SECURITY
Method for reading data with storage system, data managing system for storage system and storage system
InactiveUS20090125678A1Improve orderShorten and stabilize timeDigital data processing detailsMemory adressing/allocation/relocationData managementLogical disk
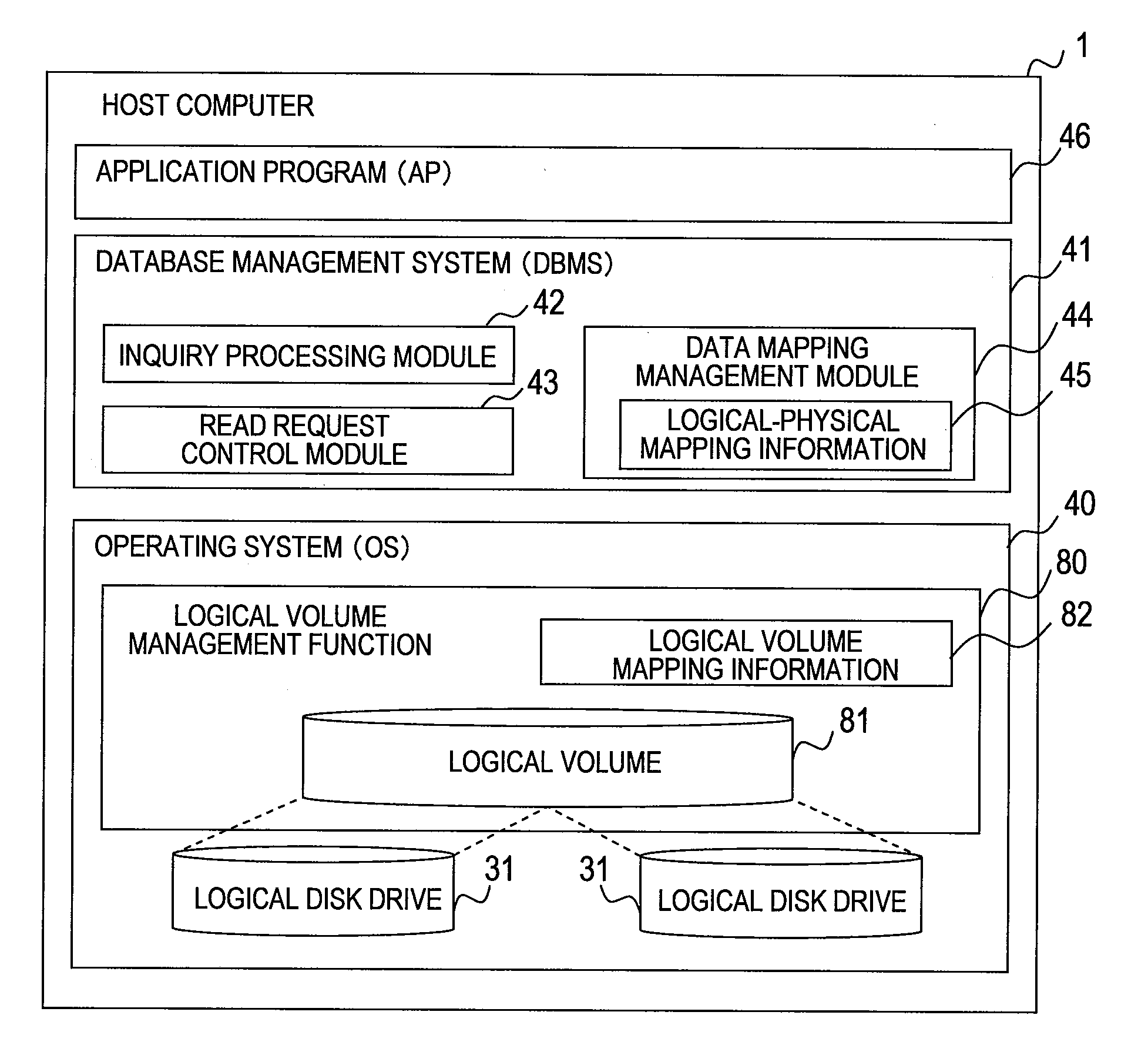
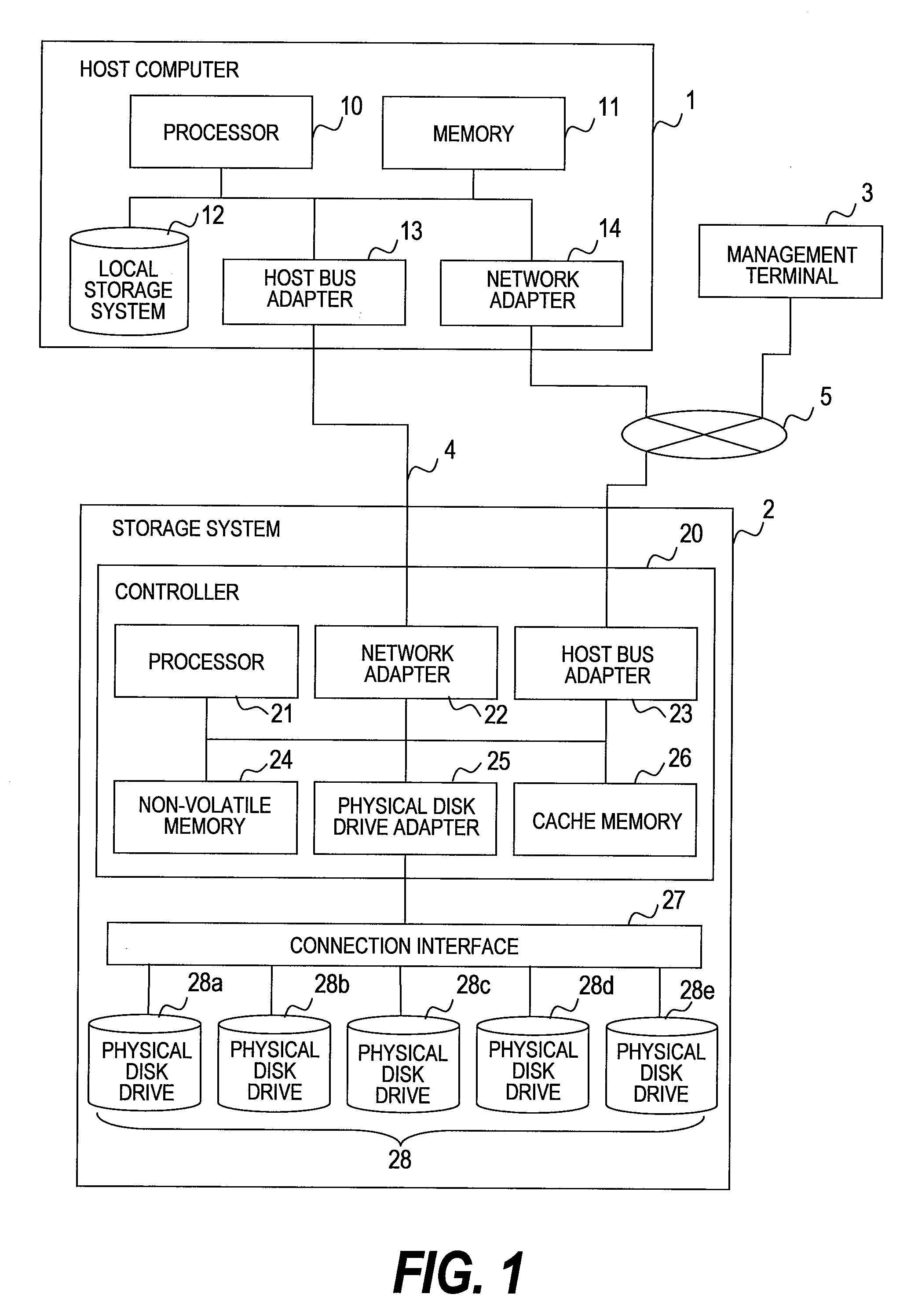
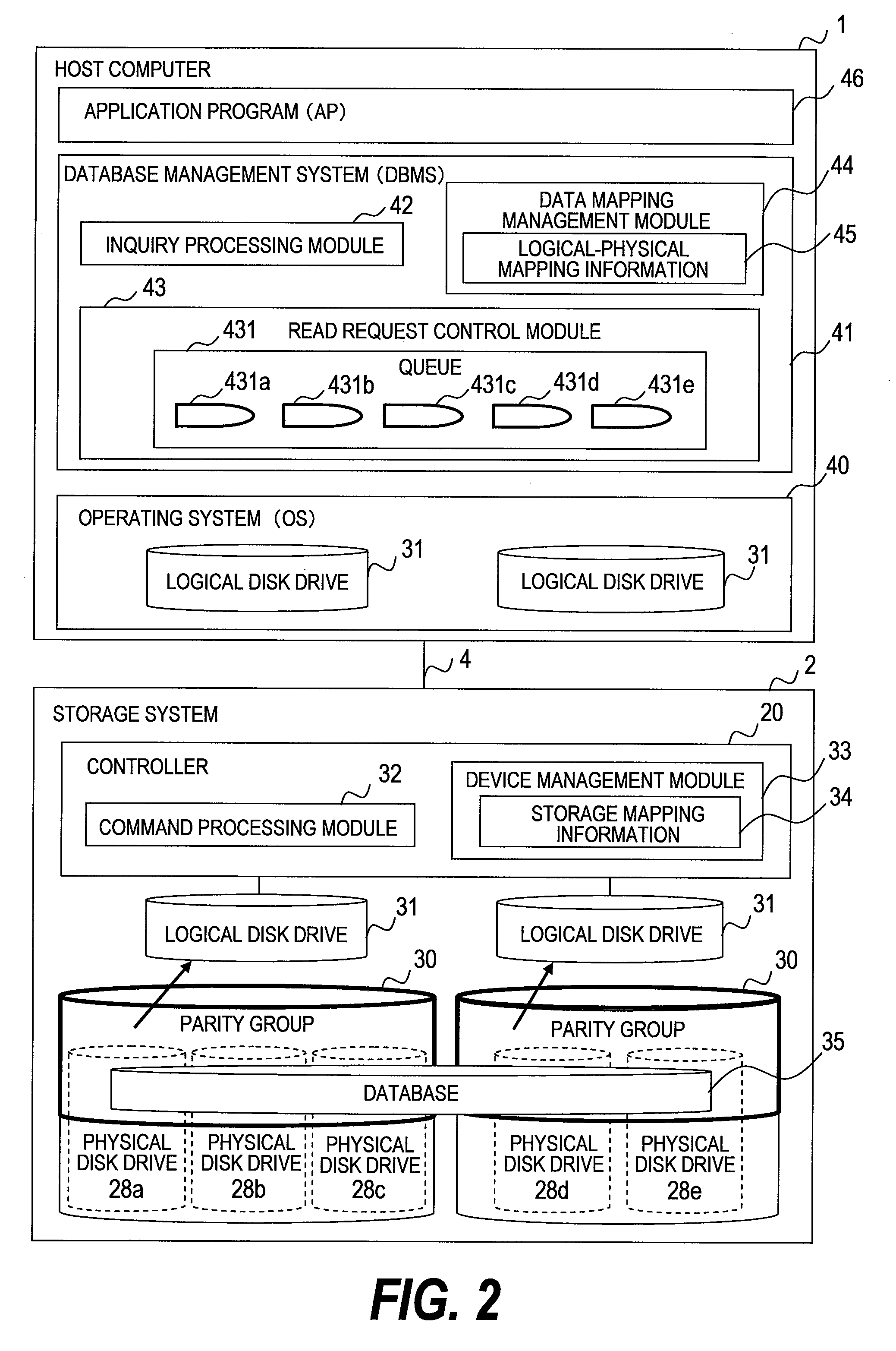
Provided is a database management system obtains storage mapping information which associates addresses in a plurality of physical disk drives within the storage system and addresses in logical disk drives including these physical disk drives, to create queues individually for each of the plurality of physical disk drives. The database management system receives a plurality of read requests which request to read data out of the physical disk drives via the logical disk drives provided by the storage system, sorts the read requests by their destination, and accumulates the read requests in the respective queues associated with the request destination physical disk drives. The database management system reallocates the accumulated read requests into an order that shortens the data read time in each physical disk drive, and then issues the read requests to the storage system.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
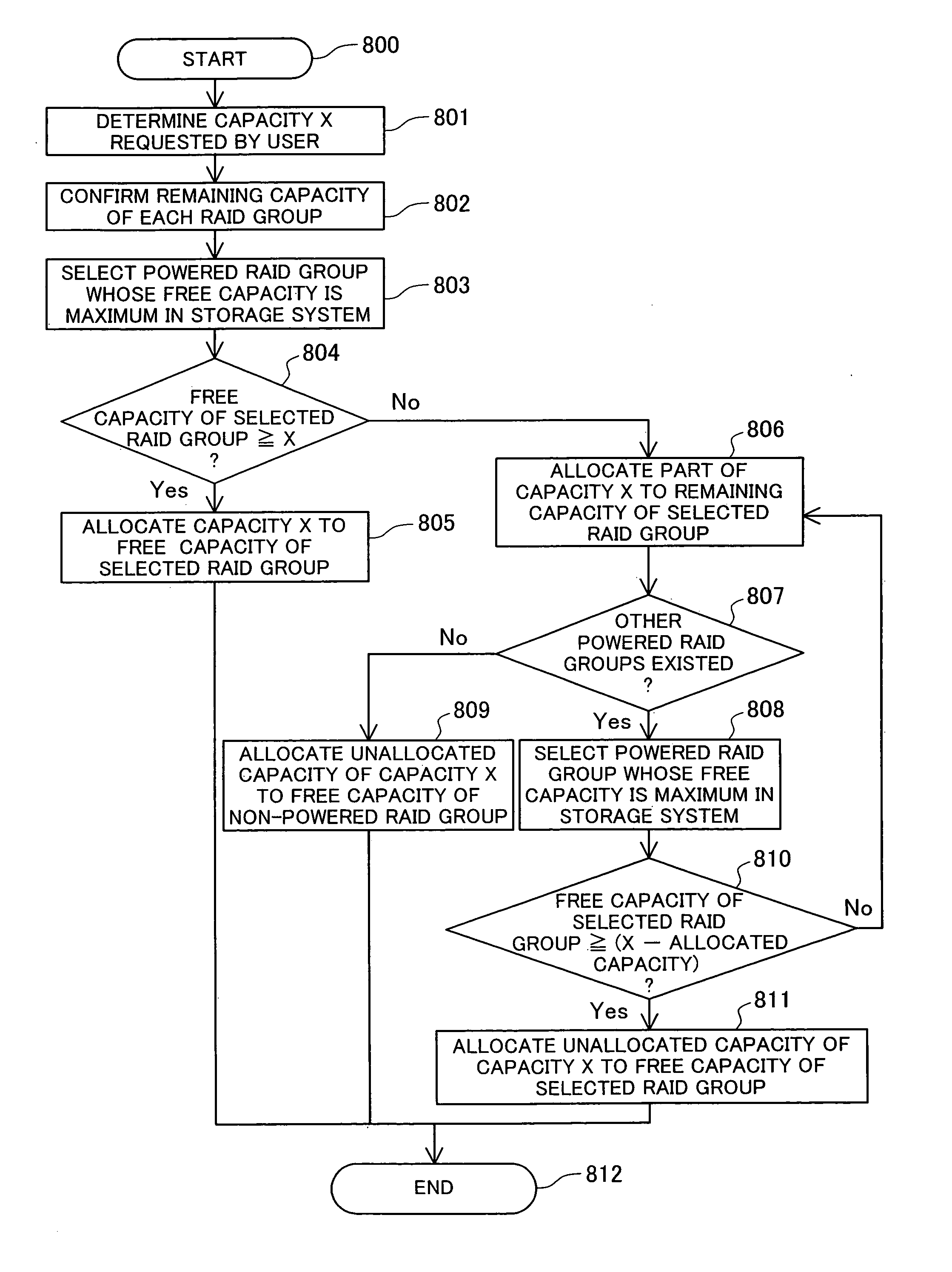
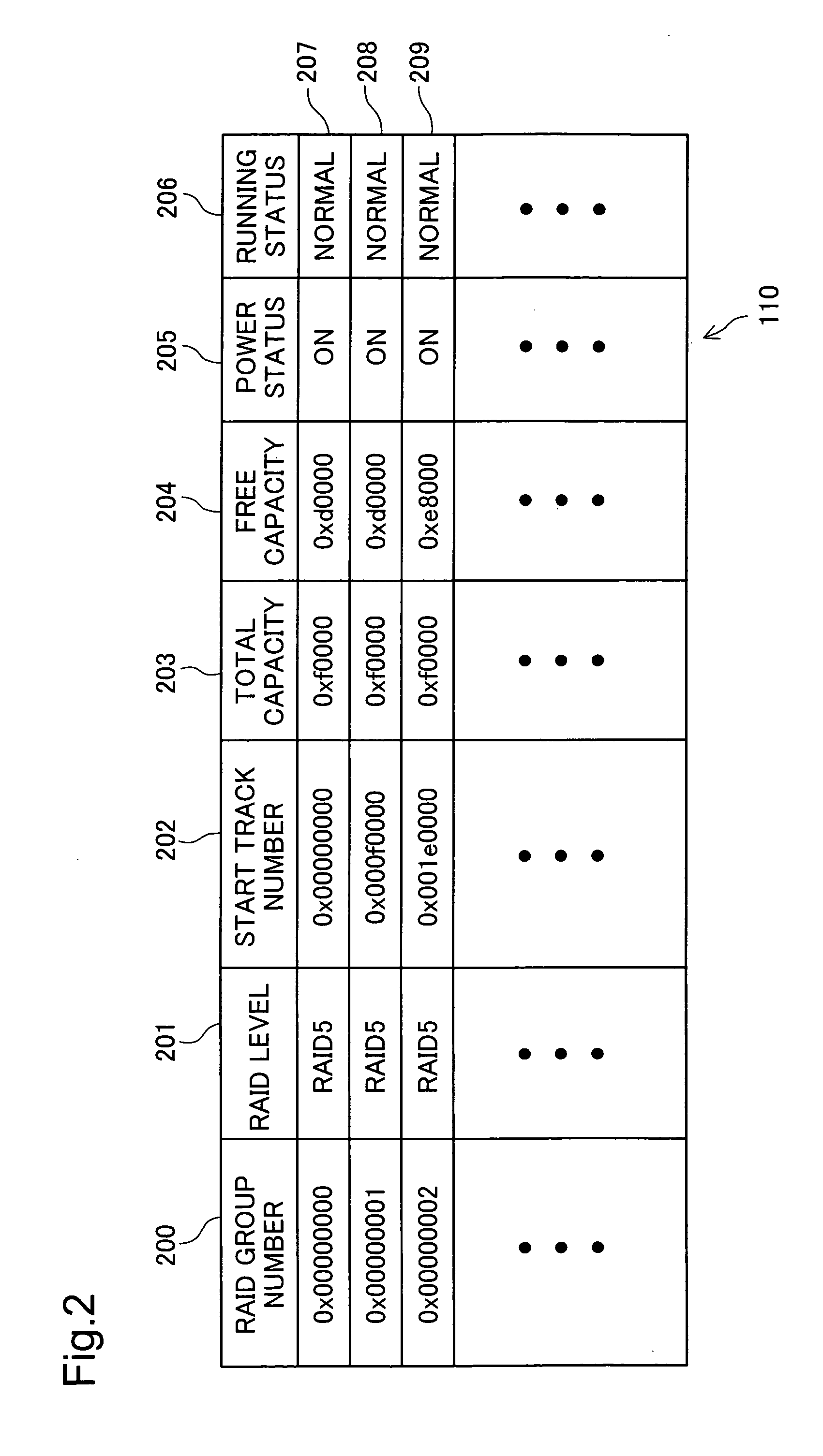
Storage system and capacity allocation method therefor
InactiveUS20070130424A1Increase consumptionEnergy efficient ICTMemory loss protectionRAIDDistribution method
A storage system connected to a terminal, the computer system includes: a plurality of drive devices that respectively drive a plurality of physical disks each having a physical storage area; a RAID configuration unit that configures a plurality of RAID groups by grouping two or more of the plurality of physical disks; a logical disk creation unit that creates, for the terminal through the RAID group, a logical disk having a logical storage area associated with the physical storage area; a memory for storing a RAID group control table showing, for each the RAID group, (i) a free capacity that is the amount of physical storage area remaining in the RAID group to be able to be associated with the logical disk and (ii) a power status of the RAID group; a receiver that receives a request for creating a new logical disk; and an area allocation unit that allocates to the new logical disk the physical storage area remaining in the RAID group selected by giving priority to a RAID group in a powered state over a RAID group in a non-powered state with reference to the RAID group control table.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
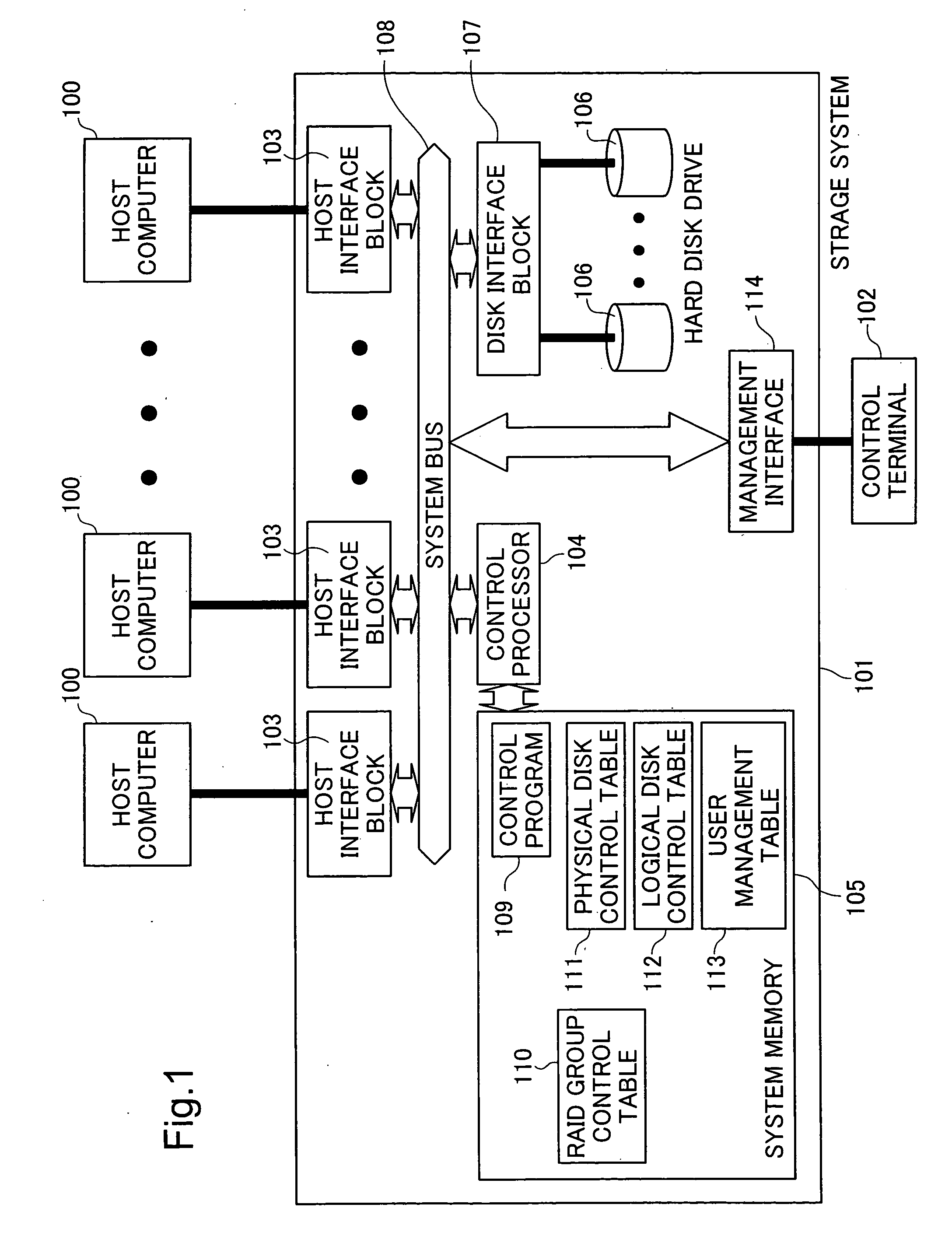
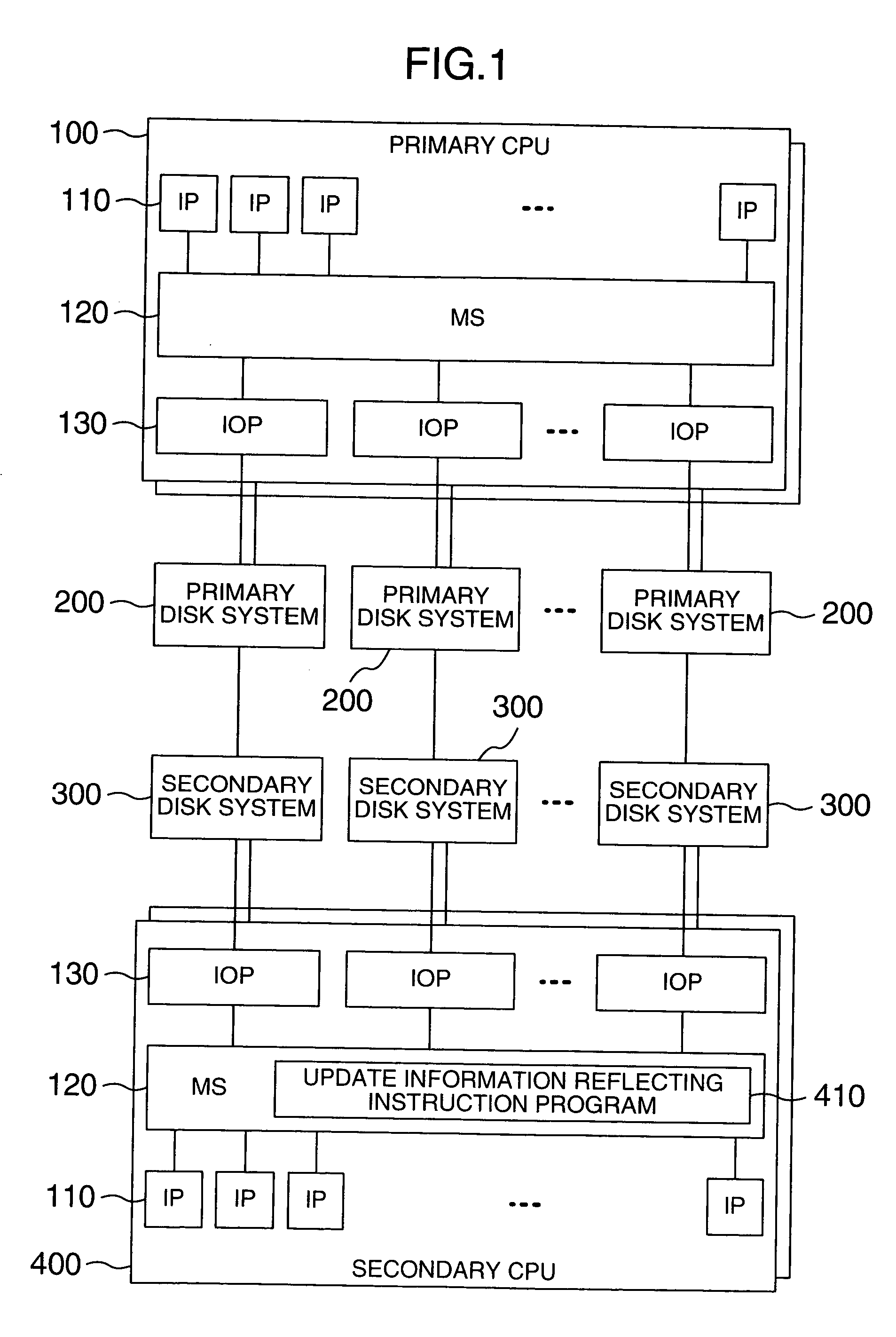
Storage control apparatus and storage control method
InactiveUS20050125617A1Improve responseData transfer overheadData processing applicationsInput/output to record carriersProcessing elementLogical disk
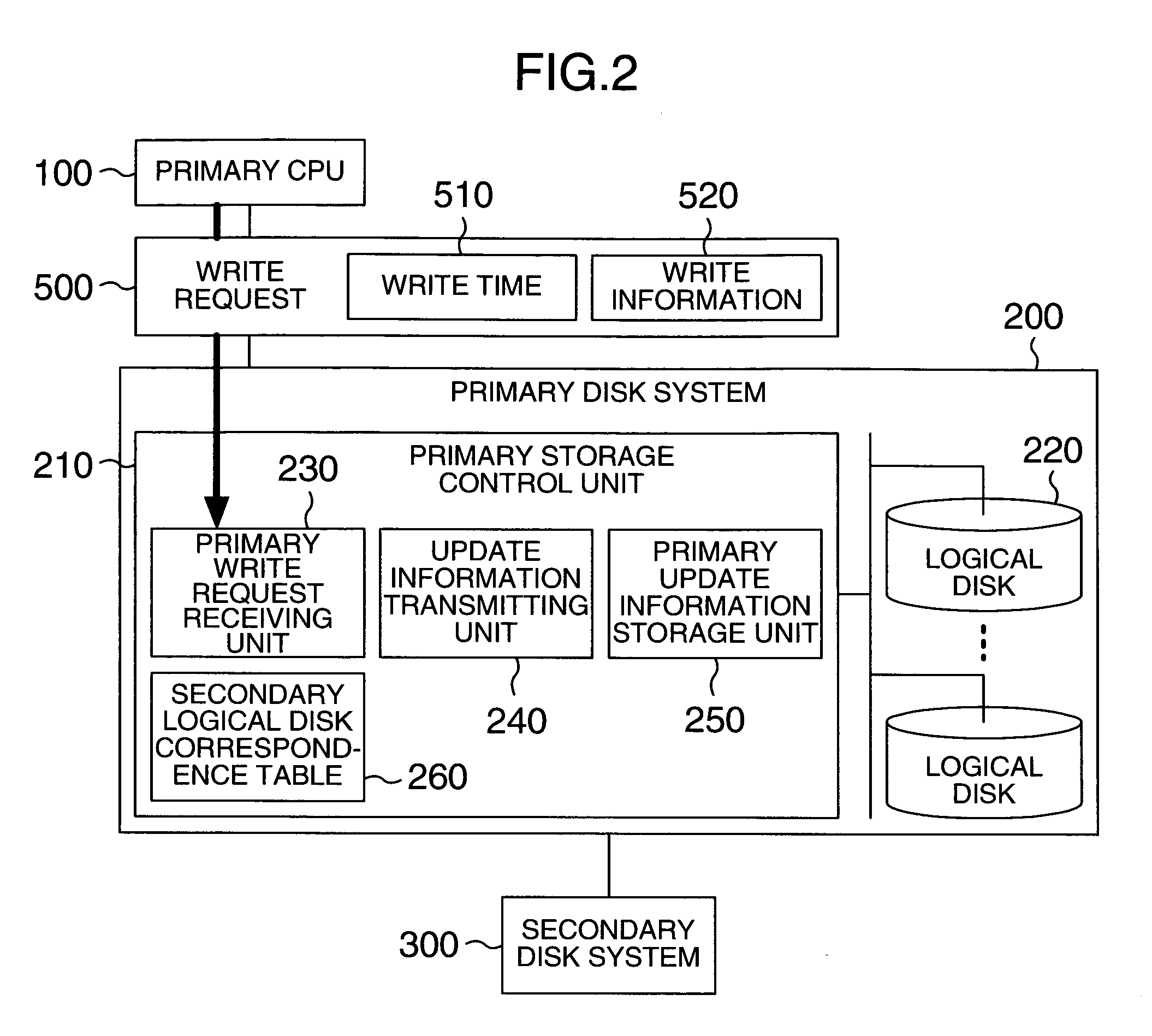
A storage control apparatus and a storage control method are provided wherein in a system having a plurality of disk systems and secondary disk systems at remote sites, the data transfer amount between a central processing unit and a disk system can be reduced when duplicate disk write is performed, the performance can be prevented from being degraded even if the distance between control units is elongated, and the intermediate results of a transaction are not left. A standard time is determined and a program is provided which instructs a secondary central processing unit to reflect only update information having a write time older than the standard time, upon a logical disk in the secondary disk system.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
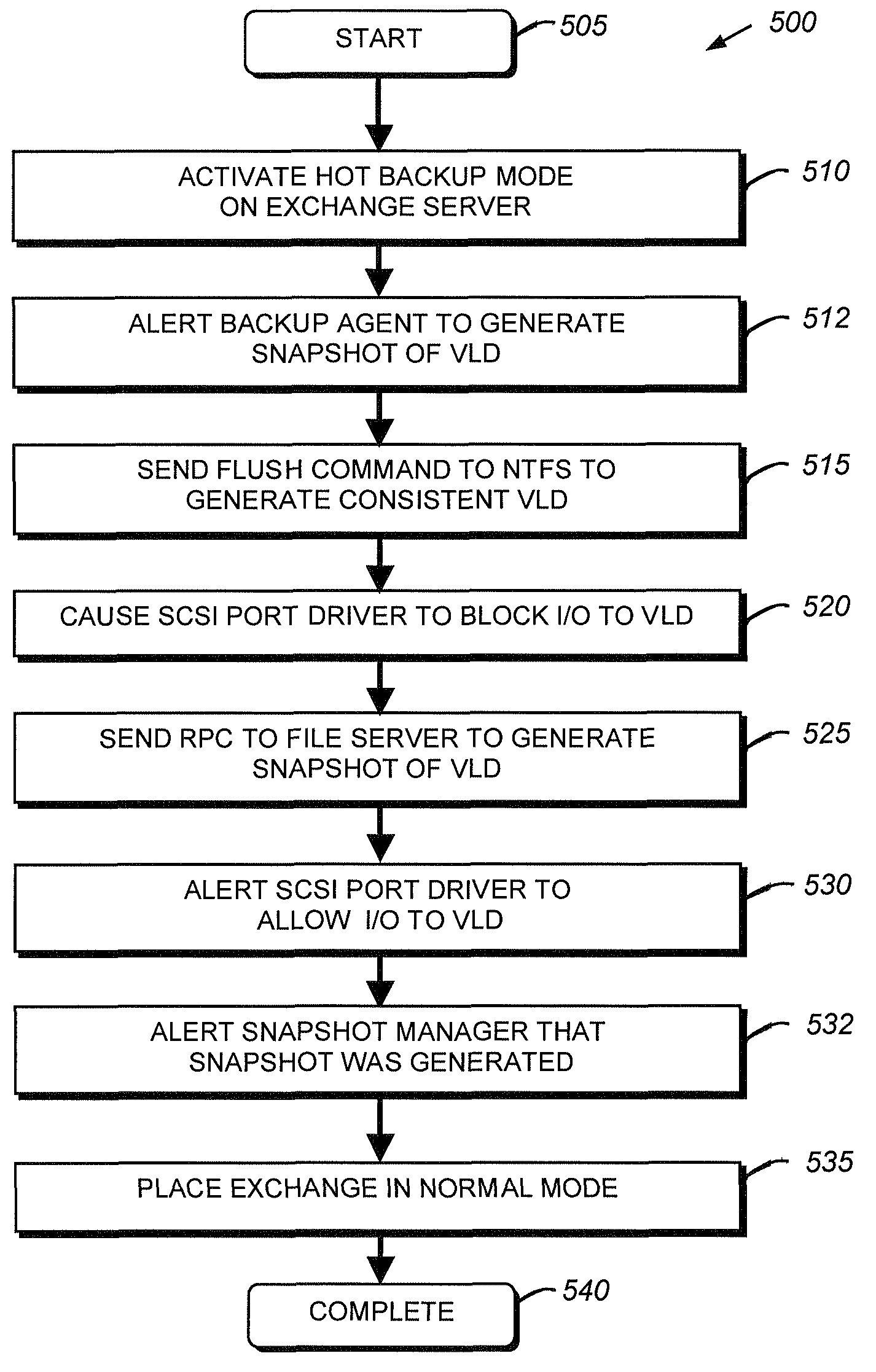
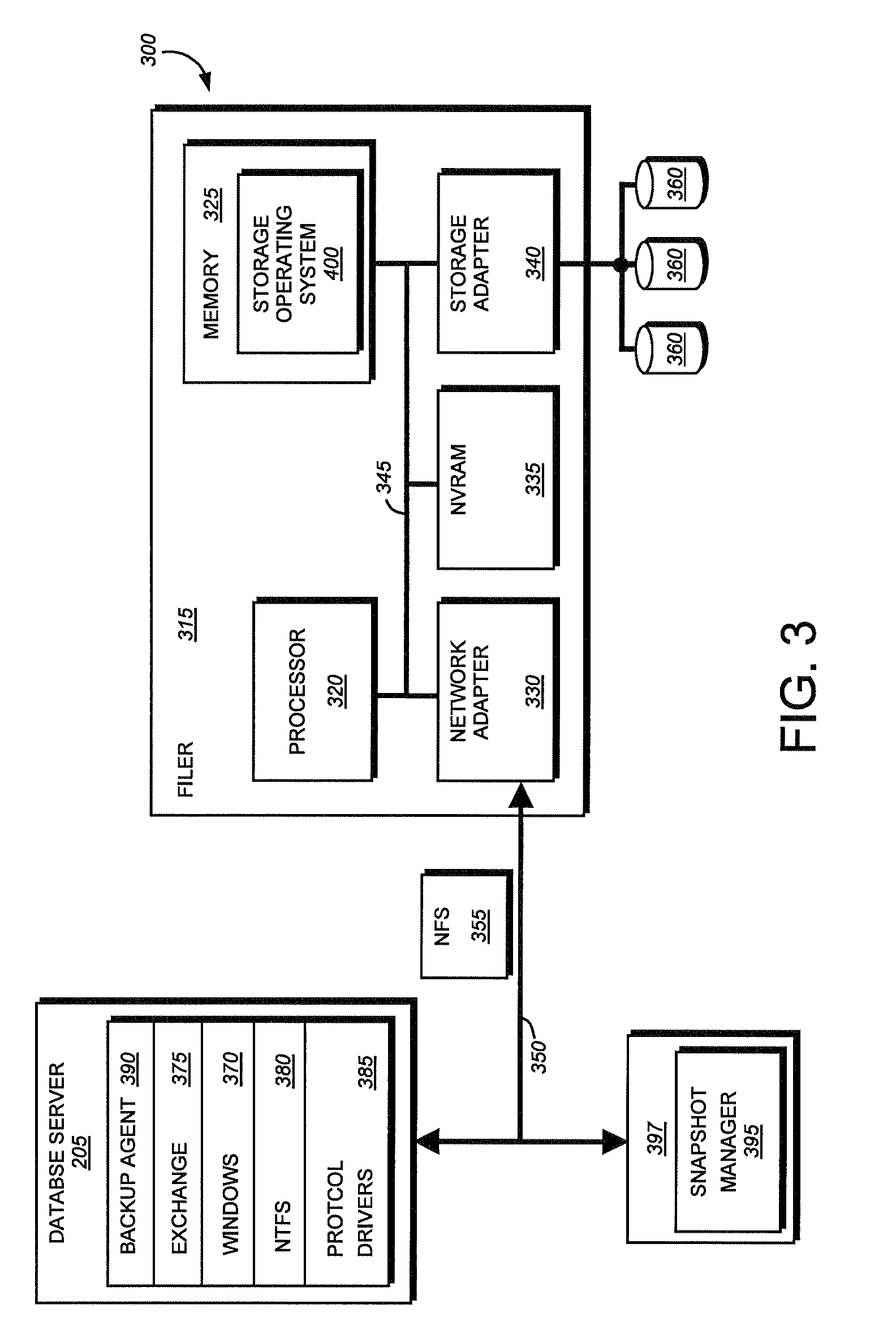
System and method for file system snapshot of a virtual logical disk
InactiveUS7925622B2Data processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsOperational systemFile system
A computer database system has one or more application buffers to use in performing input / output (I / O) operations. A file system receives contents of the application buffers. Contents of the file system are written into a nonvolatile memory. A backup command directed at the file system is received. A data contents of the one or more application buffers is moved to the file system in response to receiving the backup command, and the data contents are written to the nonvolatile memory. An operating system blocks I / O operations directed to the file system after the data contents of the one or more application buffers are moved to the file system. A snapshot of the nonvolatile memory is generated while the I / O operations directed to the file system are blocked.
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
Method, device and system for managing simply-configured memory array
InactiveCN101719106ANo schema changesLow costMemory adressing/allocation/relocationResource poolLogic cell
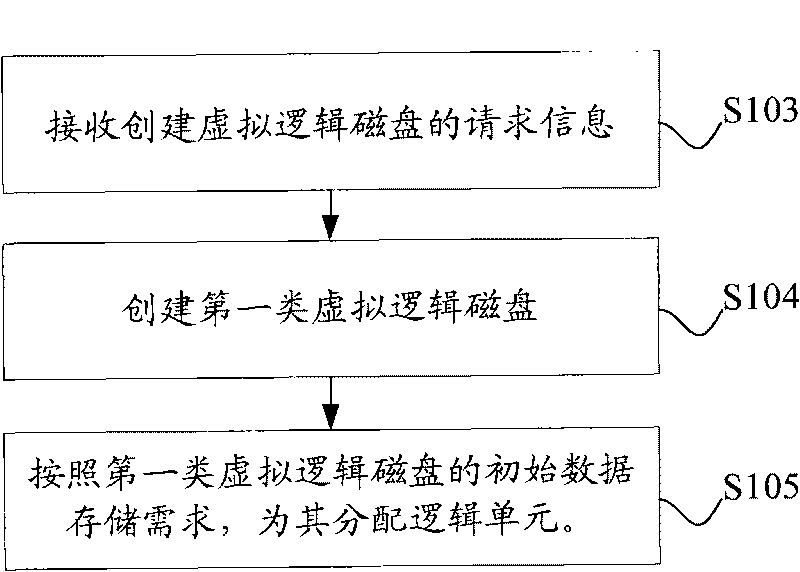
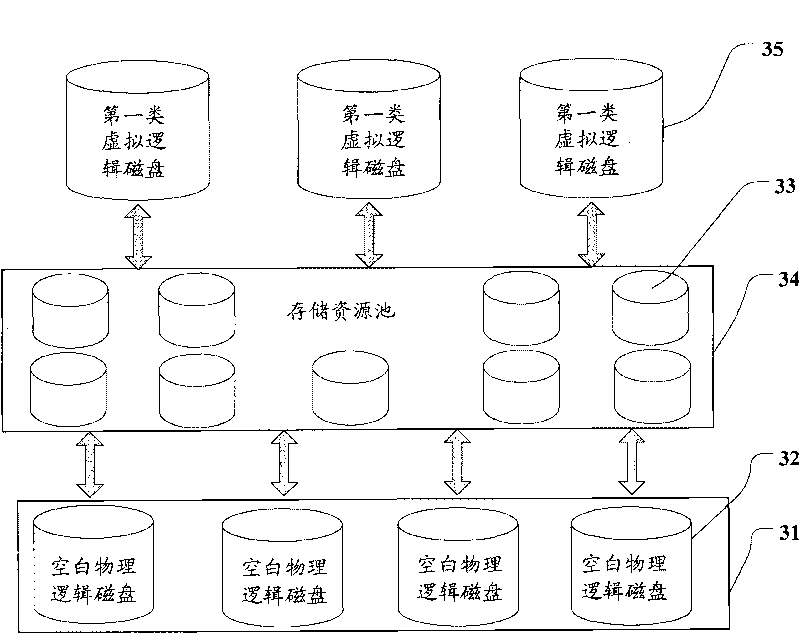
The embodiment of the invention discloses a method, a device and a system for managing a simply-configured memory array. The method for managing the simply-configured memory array comprises the following steps: receiving a request message for establishing a virtual logical disk, wherein the request message comprises the memory capacity of the request; establishing a first kind of virtual logical disks according to the request message; feeding back the size of the first kind of the virtual logical disks according to the memory capacity of the request; and allocating logical units for the first kind of the virtual logical disks in a memory resource pool. Through the scheme, the embodiment of the invention realizes the conversion from the memory array in traditional arrangement into the memory array supporting the simple configuration under the condition of not changing the framework of the original memory array and not influencing the original memory data and service, thereby reducing the cost for realizing the simple configuration.
Owner:HUAWEI DIGITAL TECH (CHENGDU) CO LTD
Automatic thin-provisioning method for optimizing space management
ActiveCN104317742AReduce random distributionReduce the degree of random distributionInput/output to record carriersMemory adressing/allocation/relocationData segmentThin provisioning
The invention discloses an automatic thin-provisioning method for optimizing space management. The method comprises the following steps: forming a storage pool through a plurality of logical disks; forming a logic volume space by crossing the plurality of logical disks; dividing the storage pool space into two stages, namely, dividing the logical disk space into a plurality of data sections; dividing each data section into a plurality of data blocks; distributing the data sections to a logical volume through the storage pool; maintaining the distributed data section by each logical volume; distributing the space for storing the written data from the maintained data section through the logical volume while the upper application writes data to the logical volume; applying to the storage pool for distribution of a new data section through the logical volume in case that the data section maintained by the logical volume does not have enough space for distributing. Compared with the prior art, the automatic thin-provisioning method for optimizing the space management, the random distribution degree of the data in a physical disk can be effectively reduced; meanwhile, the storage space utilization rate is high; in addition, the load balance of a storing device is ensured while distributing the storage space.
Owner:LANGCHAO ELECTRONIC INFORMATION IND CO LTD
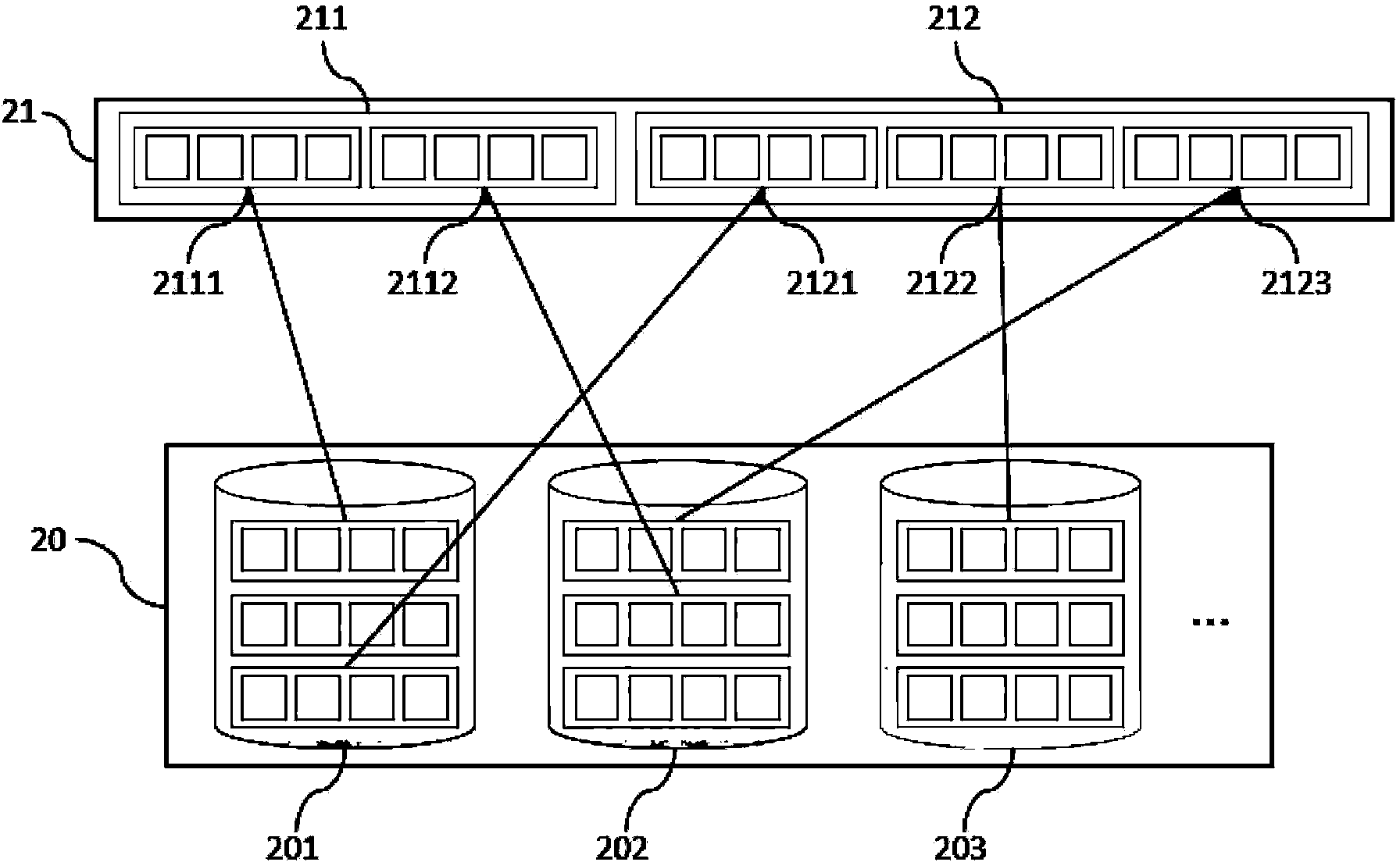
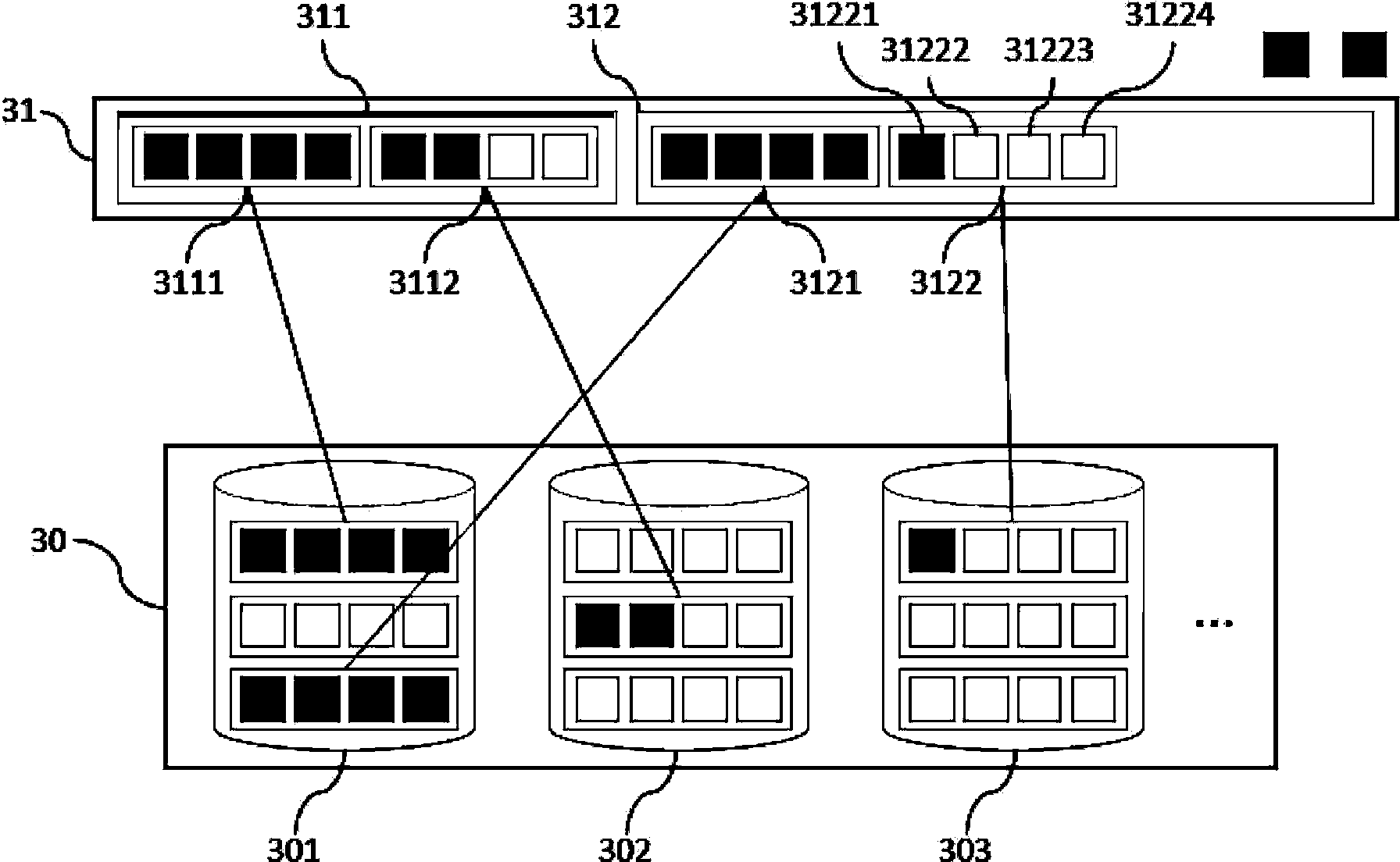
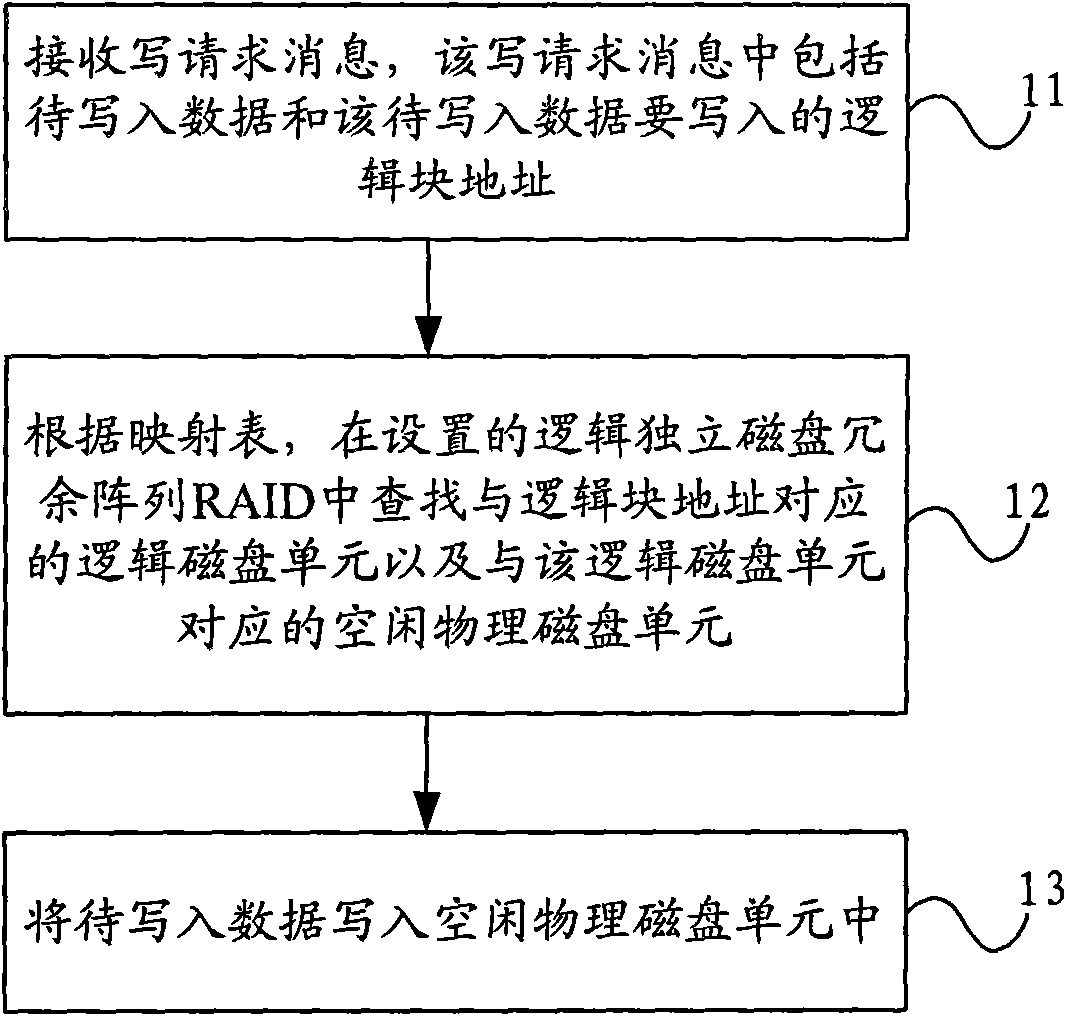
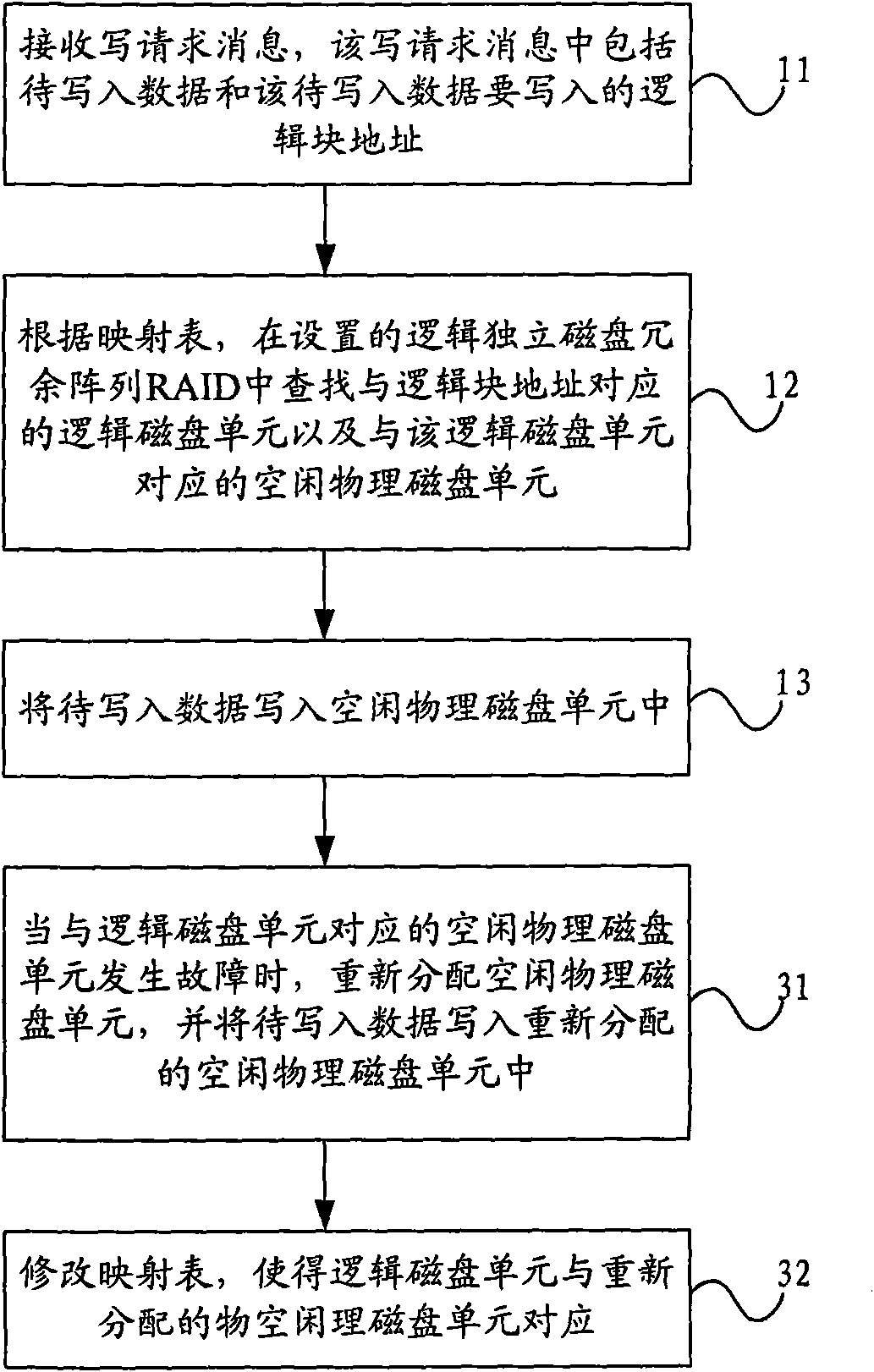
Data read-in method, disc redundant array and controller thereof
ActiveCN101625627AImprove space utilizationInput/output to record carriersRAIDLogical block addressing
The embodiment of the invention relates to a data read-in method, a disc redundant array and a controller thereof, wherein the data read-in method comprises the following steps: receiving a read-in request message comprising data to be read in and a logical block address to be read in by the data; looking up a logical disc unit corresponding to the logical block address and an idle physical disc unit corresponding to the logical disc unit in a set logical independent disc redundant array RAID according to a mapping table; and reading the data to be read in into the idle physical disc unit. The embodiment of the invention can effectively improve the utilization rate of the disc.
Owner:CHENGDU HUAWEI TECH
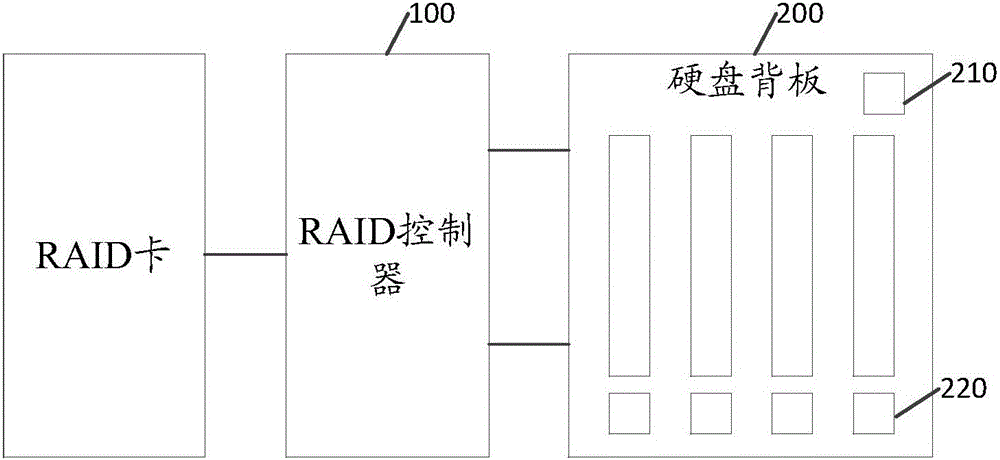
Server hard disk condition monitoring method and system
The invention discloses a server hard disk condition monitoring method and system. The system comprises a main control chip, a hard disk back plate of LED lights and a RAID controller. The RAID controller is connected with a RAID card through a port to acquire preset parameter information of the hard disk in the RAID card, wherein the preset parameter information comprises hard disk information, logic magnetic disk information and hard disk current using condition. Corresponding SGPIO signals are sent to the main control chip of the hard disk back plate based on the hard disk current using condition. The hard disk back plate is connected with the RAID controller through a MINISAS line, and controls the corresponding LED lights to display corresponding conditions to indicate the conditions of the hard disk based on the content of the SGPIO signals. The system determines the hard disk conditions based on the SGPIO signals of the RAID card, namely, achieving the hard disk condition analysis through the SSF8489 protocol, and therefore the checking of the hard disk information is more convenient. The invention further discloses a server hard disk condition monitoring method which has the advantages.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU YUNHAI INFORMATION TECH CO LTD
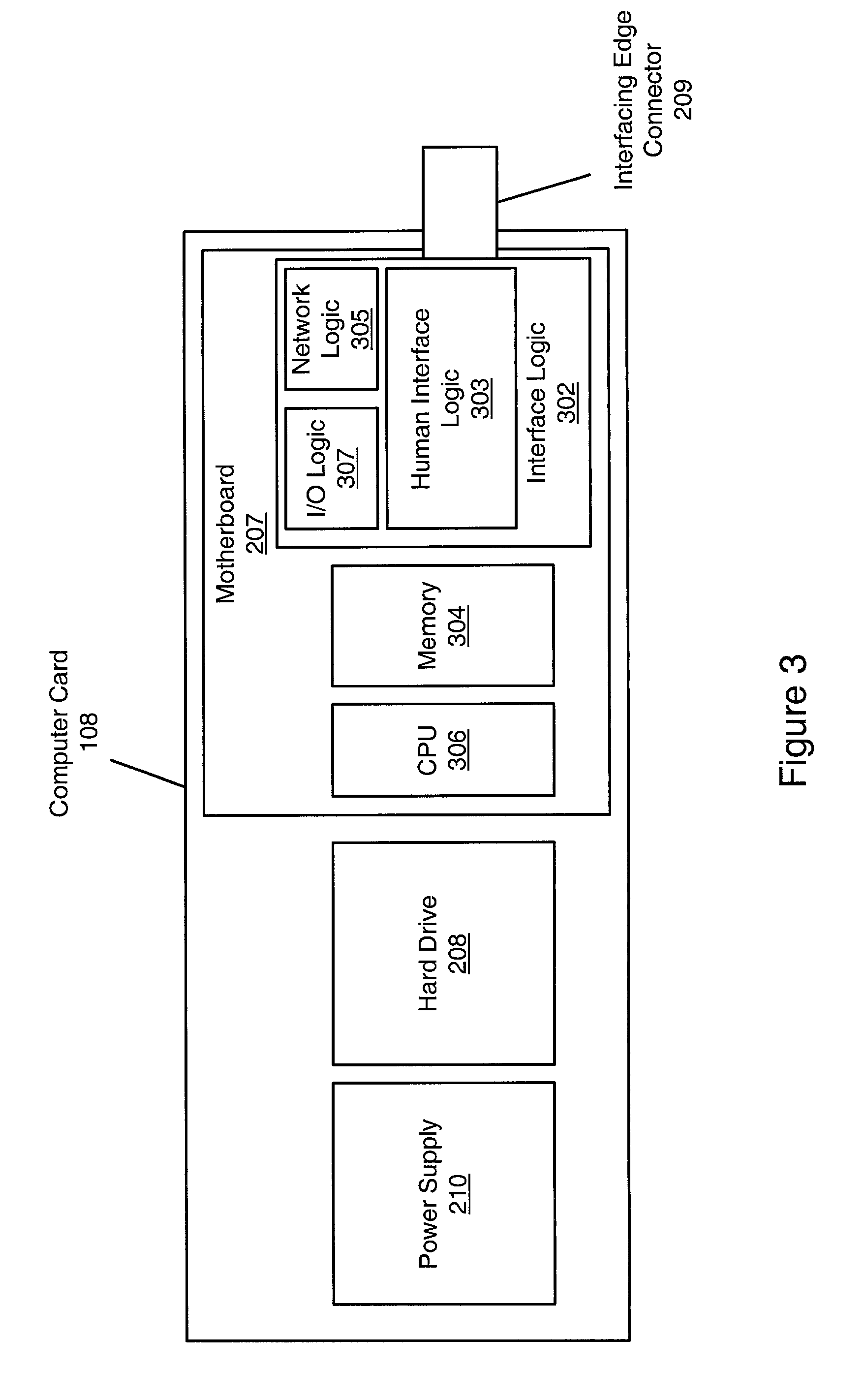
Computer on a card with a remote human interface
InactiveUS20010000539A1Cathode-ray tube indicatorsMultiple digital computer combinationsHuman–machine interfaceNetwork communication
A computing system in which a human interface (HI) is located remotely from a computer. The HI includes a keyboard, mouse, and monitor. The computer includes a motherboard with CPU, memory, network and interface logic, disk drives, and a power supply, configured on a single card, and communicates with the HI by sending and receiving encoded HI signals. The computer card includes an interfacing edge connector for communicating with the HI and networks. The HI logic receives HI signals from the interface logic and encodes the signals into a format suitable for transmission to the HI. The HI logic receives and decodes incoming encoded HI signals from the HI, and transmits the decoded HI signals to the interface logic for use in the computing system. The network logic encodes network signals into a format suitable for transmission to the network, and receives and decodes encoded network signals from the network.
Owner:CLEARCUBE TECHNOLOGY INC
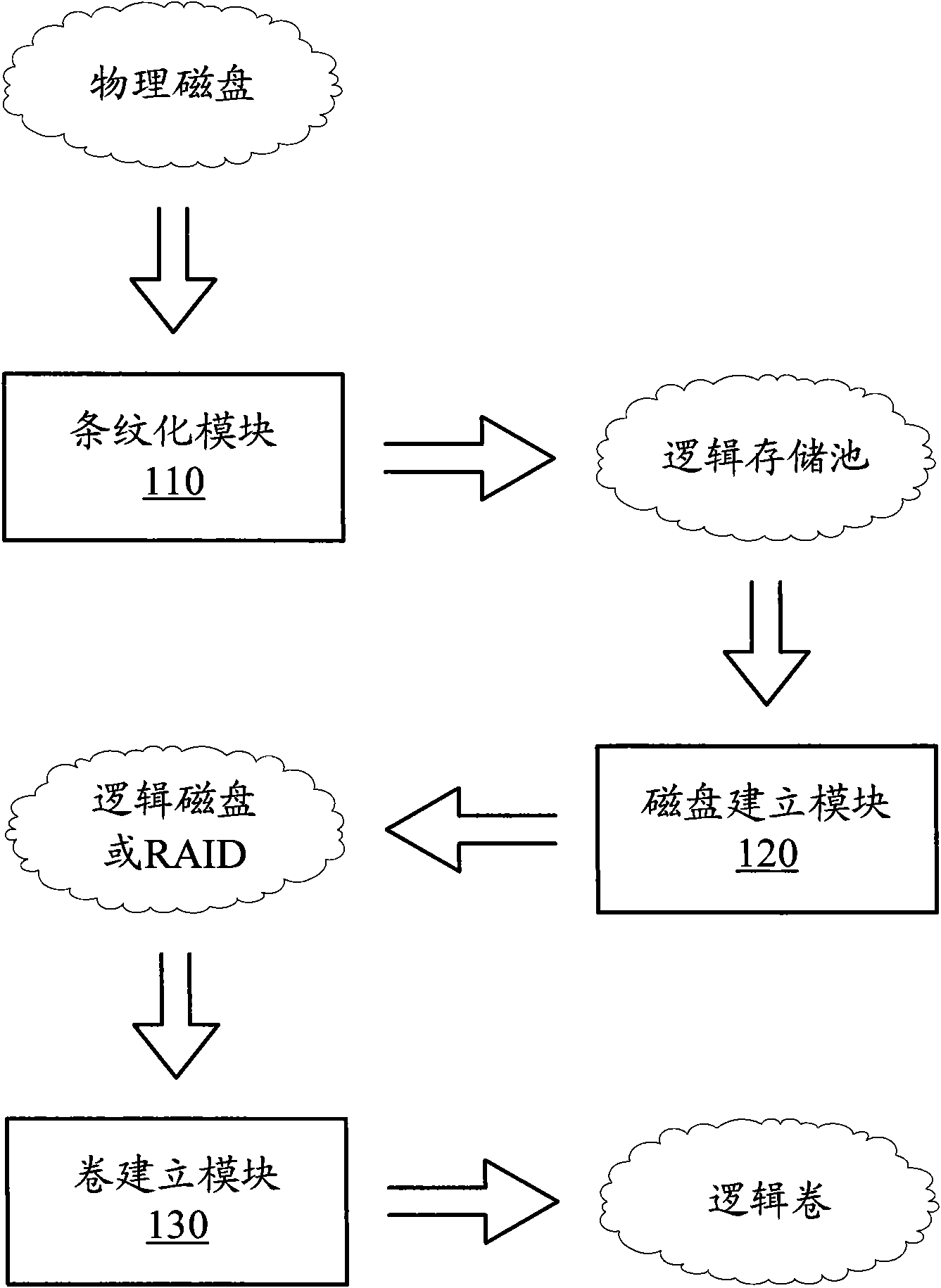
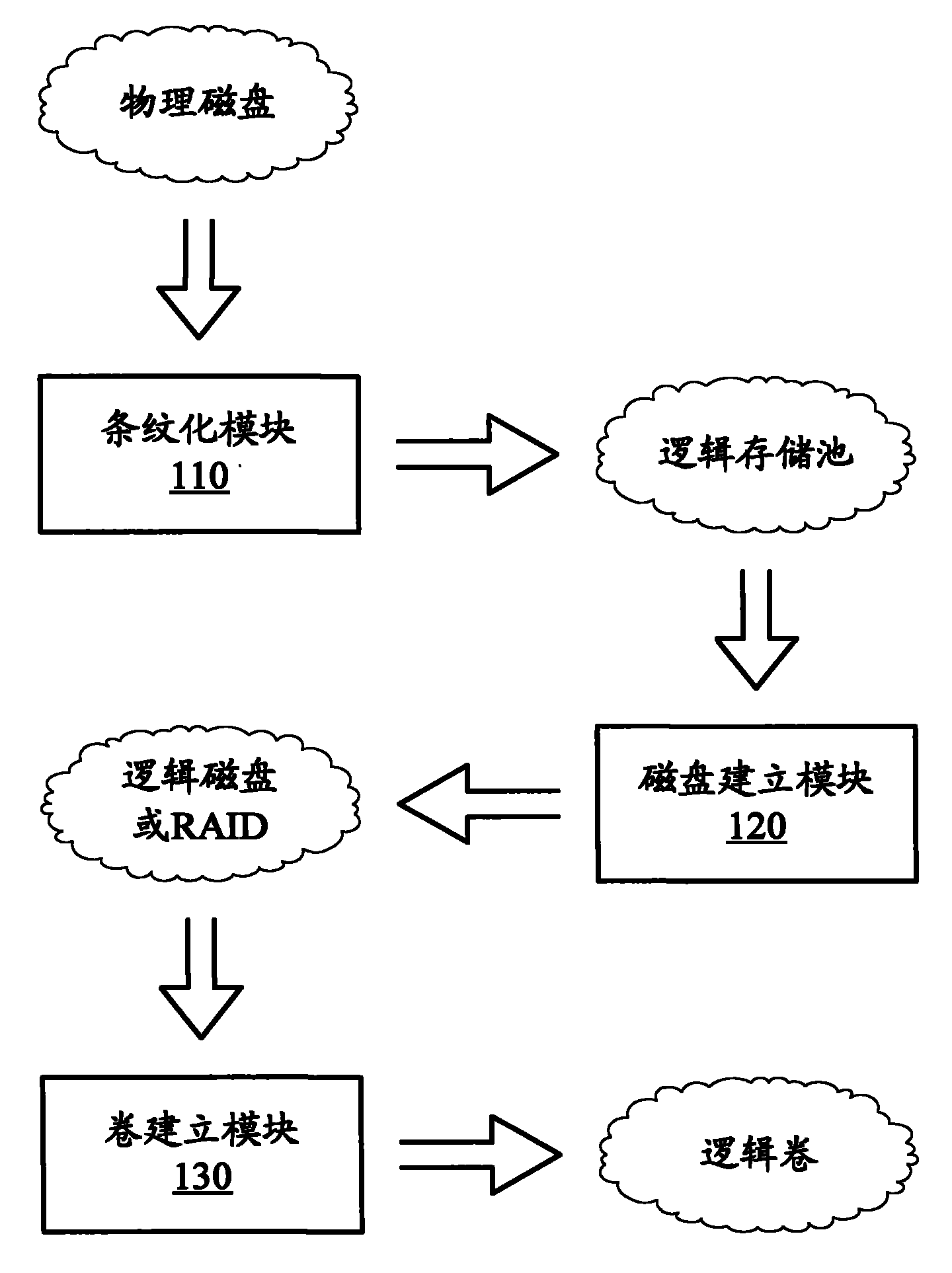
Memory virtualization system and method
ActiveCN101788889ABalance I/O loadAvoid overall overheatingInput/output to record carriersVirtualizationMemory virtualization
The invention discloses a memory virtualization system and a method to balance IO load of physical disks. In the system, a striping module processes the physical disks by means of striping data to build a logic pond; a disk-building module builds a logic disk or a logic disk array on a logic memory pond; and a volume-building module builds a logic volume on the logic disk or the logic disk array. With the three layers of virtualization process, a read and write request of a customer is performed by being dispersed to the plurality of physical disks, and compared with the prior art that the read and write request of the customer is performed by being concentrated on one physical disk, the invention balances the IO load of the physical disks, effectively prevents some date of the physical disks from over heating, and improves the security and the performance of the memory system.
Owner:INSPUR SUZHOU INTELLIGENT TECH CO LTD
Storage space configuration and management method applied to cloud computing
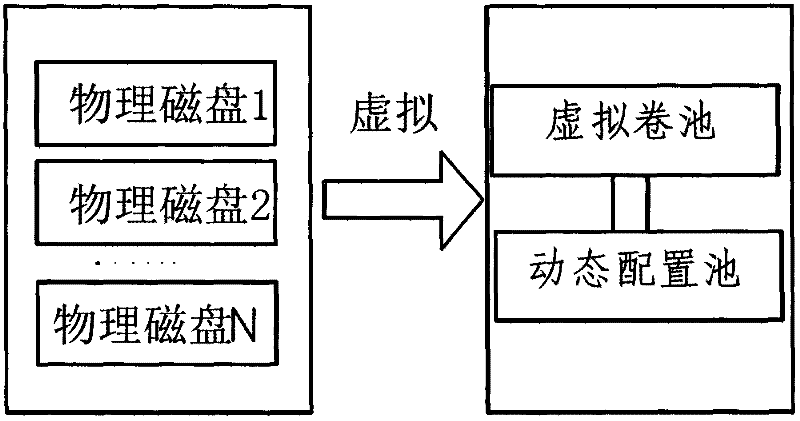
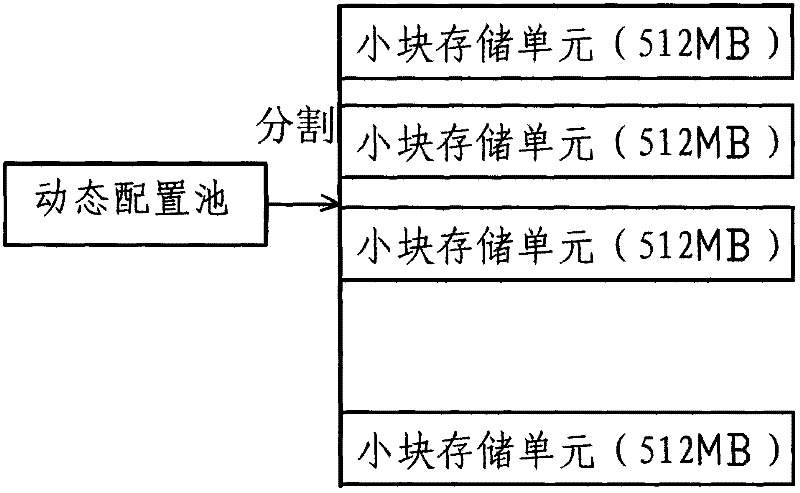
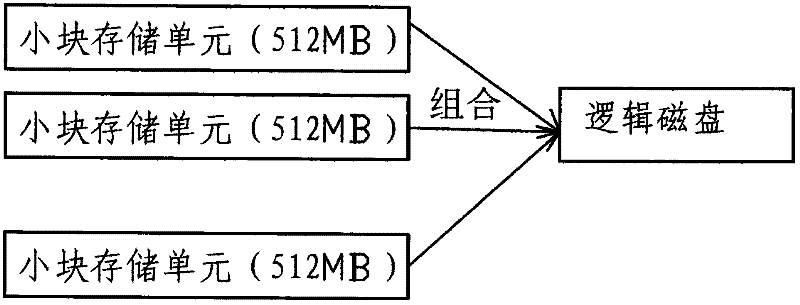
The invention discloses a storage space configuration and management method applied to cloud computing, which is characterized by including the following steps that a) a storage controller enables a heterogeneous storage physical disk to be integrated with a virtual volume pool and virtualizes storage capacity in the virtual volume pool into a dynamic configuration pool; b) the storage controller divides the dynamic configuration pool into one or more than one small block storage units which form a logic disk; c) the storage controller distributes logic unit number for each logic disk which is divided into a preposition type and a special service type, and the logic unit number of the special service type logic disks correspond to all services and identification of the services; and d) the storage controller utilizes the preposition type logic disk to distribute unit storage units for task writing in each time and transfers and stores metadata in the unit storage units to the corresponding special service type logic disk.
Owner:ZHONGSHAN IKER DIGITAL TECH
Memory management method, memory management device and memory device
ActiveCN104536909AShorten the timeReduce occupancyMemory adressing/allocation/relocationProgram controlLogical diskMemory management unit
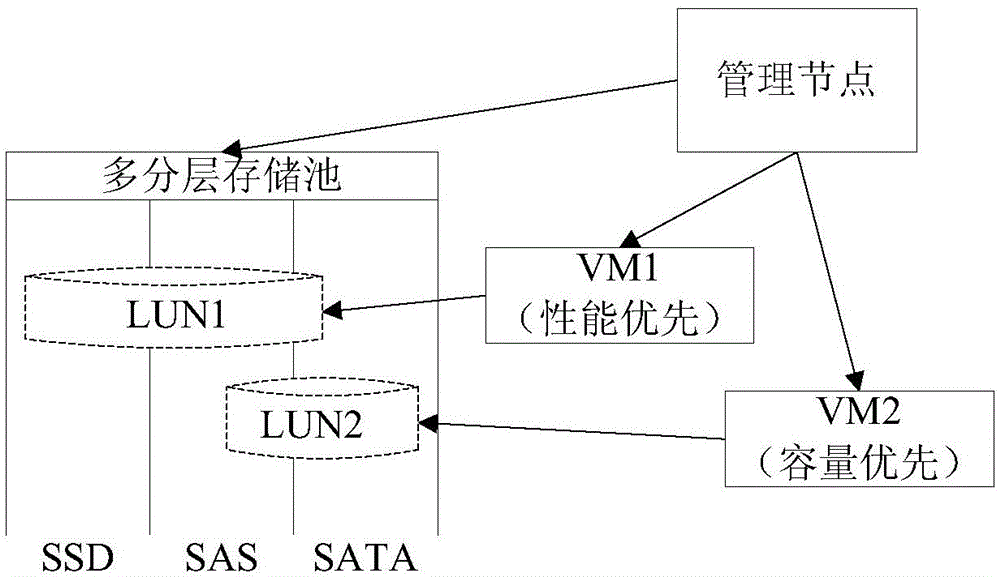
The embodiment of the invention discloses a memory management method, a memory management device and a memory device. A virtual machine system is applied in the memory management method, and a logic disk is allocated for a virtual machine of the virtual machine system and comprises at least two types of physical disks. The memory management method comprises the steps of obtaining composing information of the logic disk of the virtual machine, wherein the composing information of the logic disk of the virtual machine is used for indentifying the distribution situation of memory space of the logic disk of the virtual machine in each type of physical disks; adjusting the composing information of the logic disk of the virtual machine by taking preset load equilibrium strategy. A new logic disk is not needed to be established by adopting the composing information of the logic disk of the virtual machine, so that mainframe migration is not needed to be conducted on the logic disk. Therefore, the time for solving the hot spot access problem can be shortened, and resources occupied by the hot spot access problem can be decreased.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
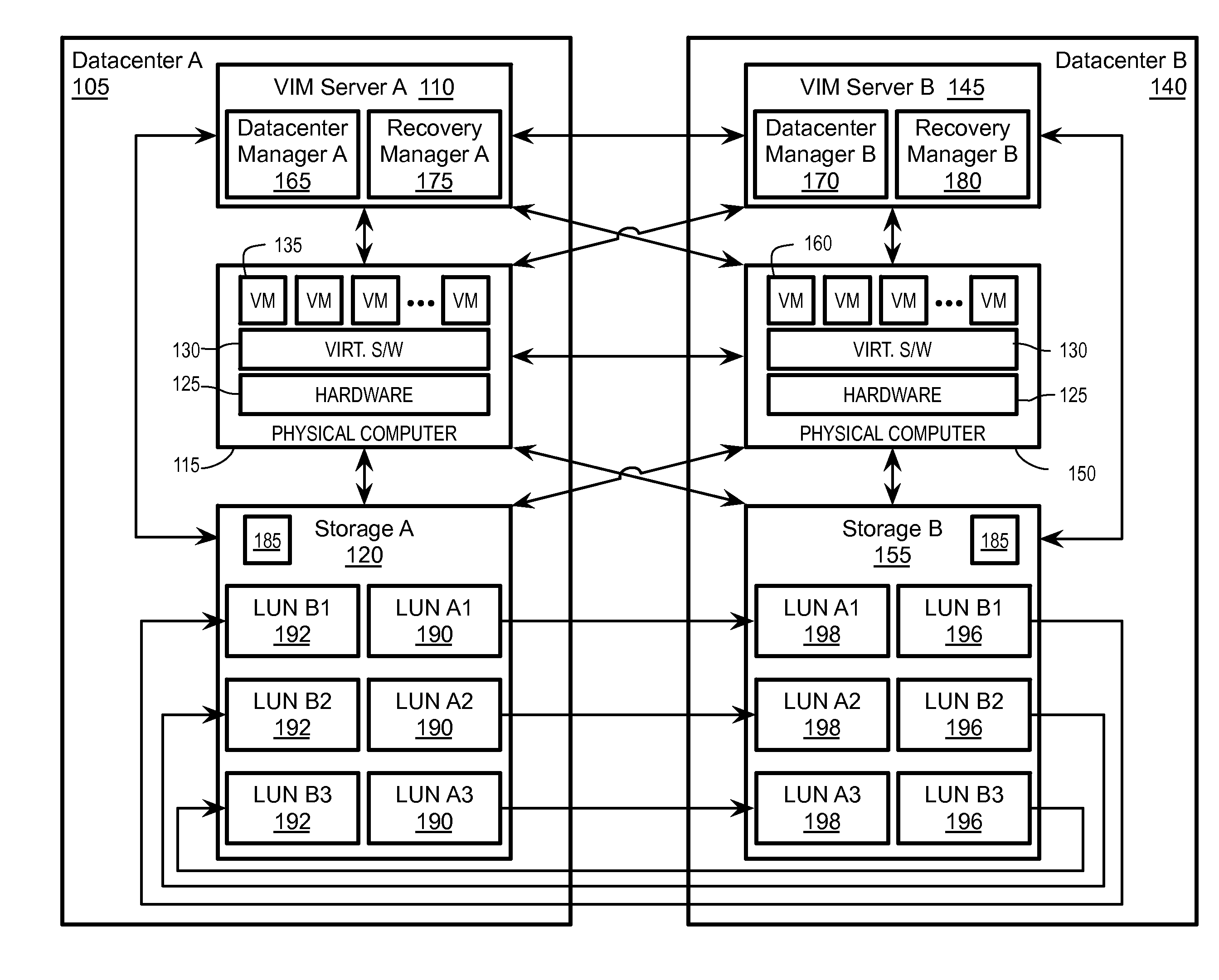
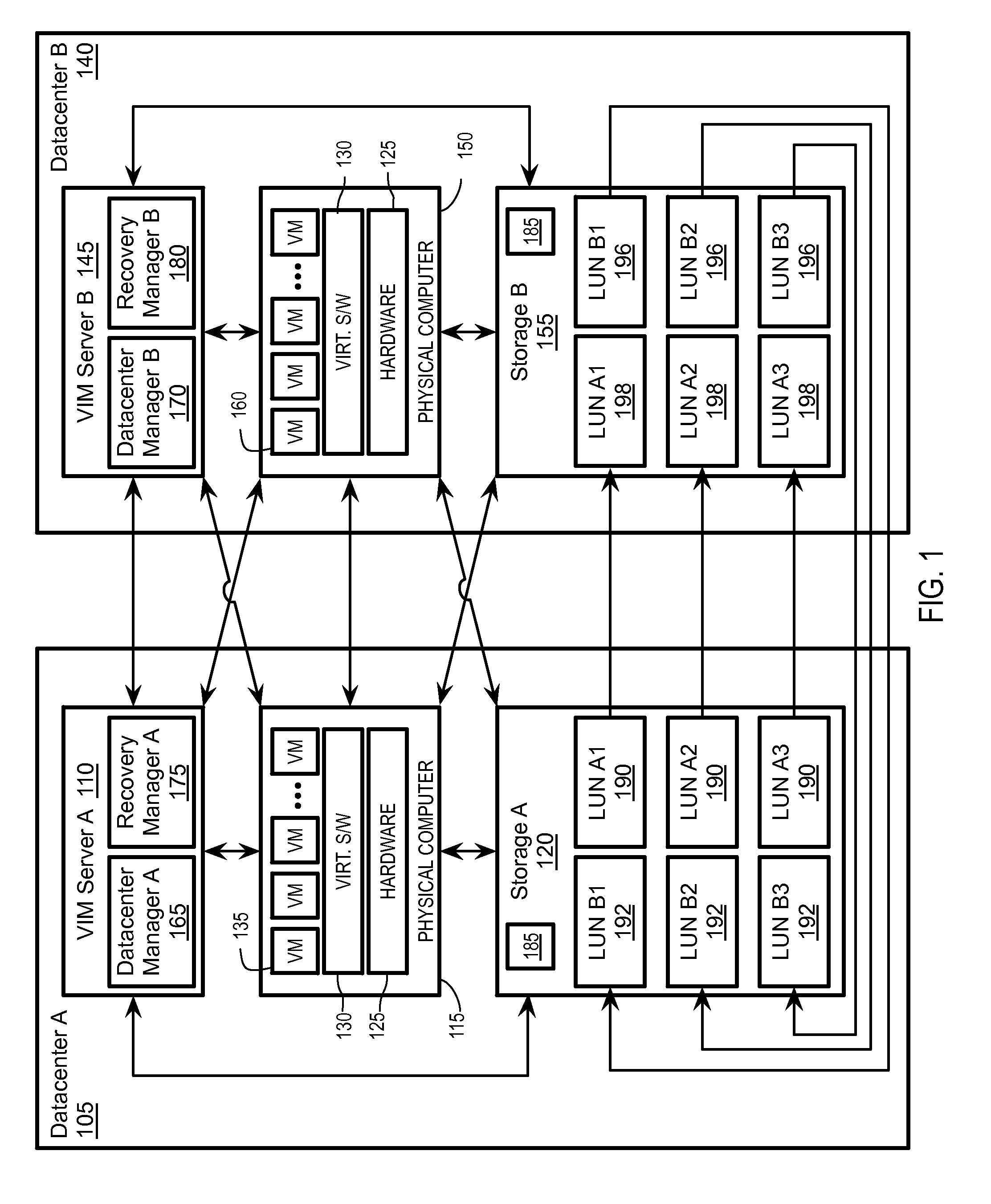
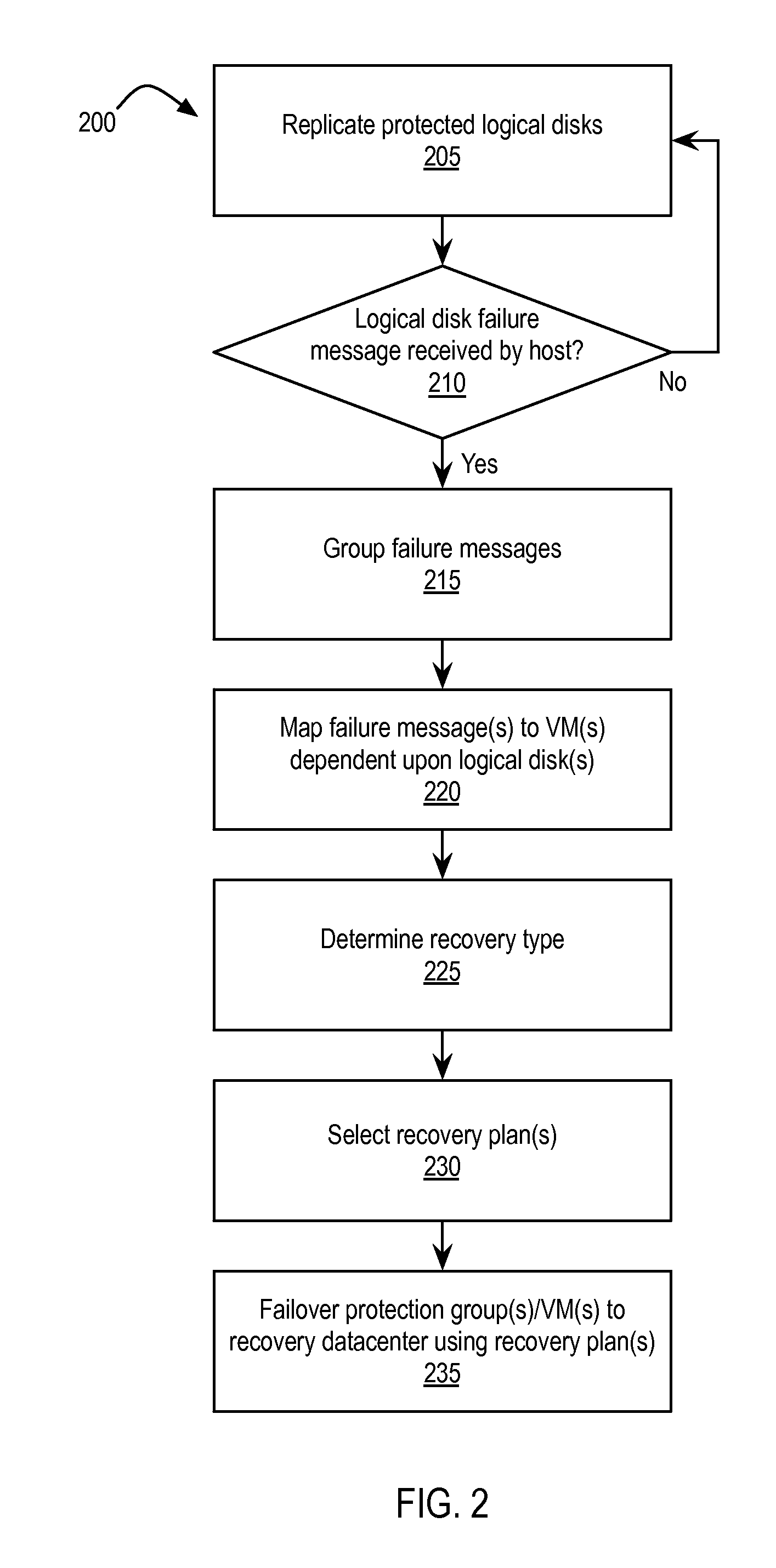
High availability across geographically disjoint clusters
ActiveUS20150212910A1Redundant operation error correctionRedundant hardware error correctionFailoverData center
Exemplary methods, apparatuses, and systems include a first virtual infrastructure management (VIM) server monitoring a first host device to determine if the first host device receives one or more messages within an interval of time from a first storage device indicating a failure of one or more logical disks within the first storage device. The first VIM server manages a first virtual datacenter including the first host device and the first storage device. A second VIM server manages a second virtual datacenter including a second host device and a second storage device. The logical disk is replicated on the second storage device. The first VIM server determines, that a plurality of virtual machines running on the first host device is dependent upon the logical disk(s). The first VIM server performs, in response to the dependency upon the logical disk, a failover of the virtual machines to the second host device.
Owner:VMWARE INC
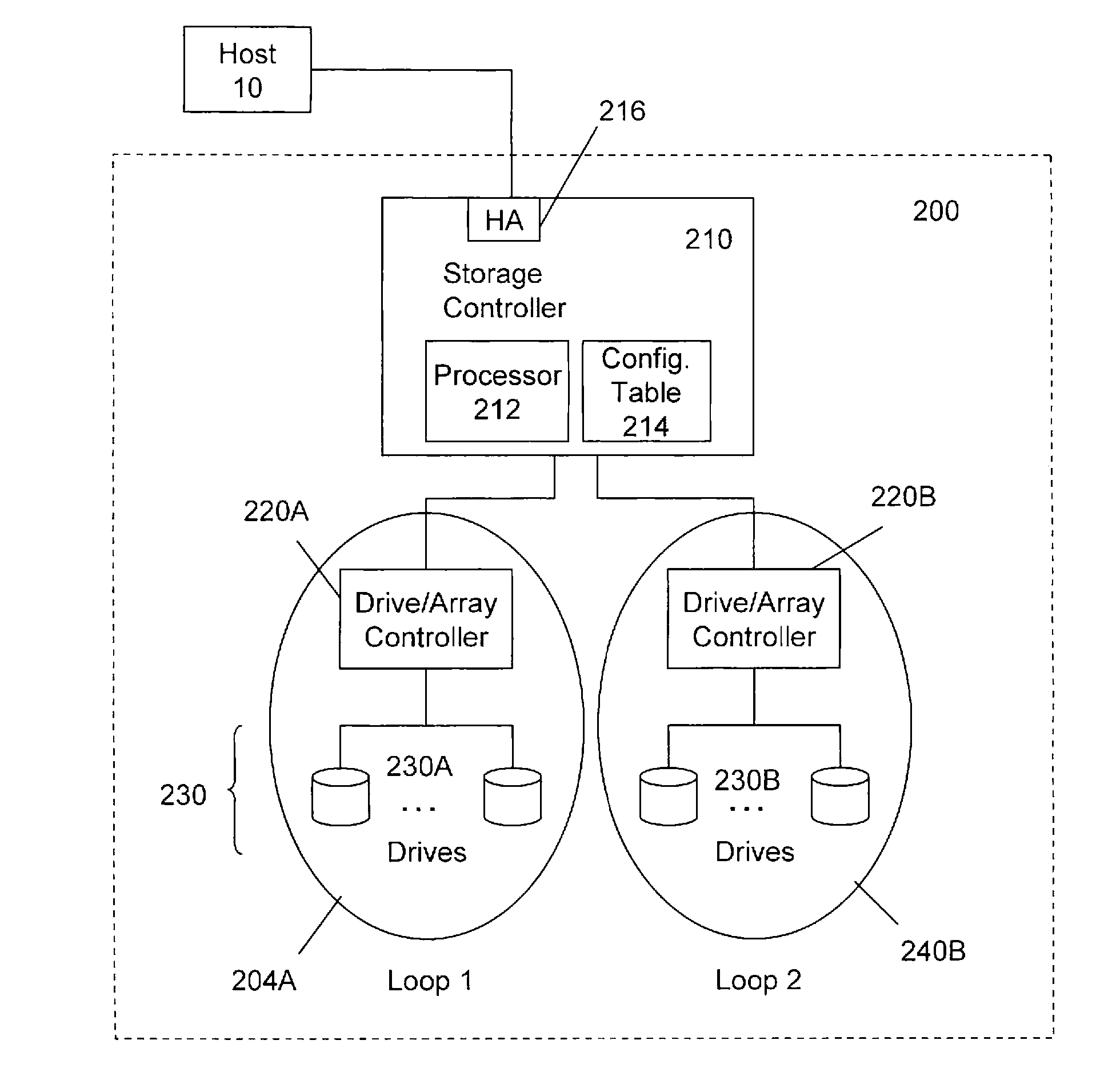
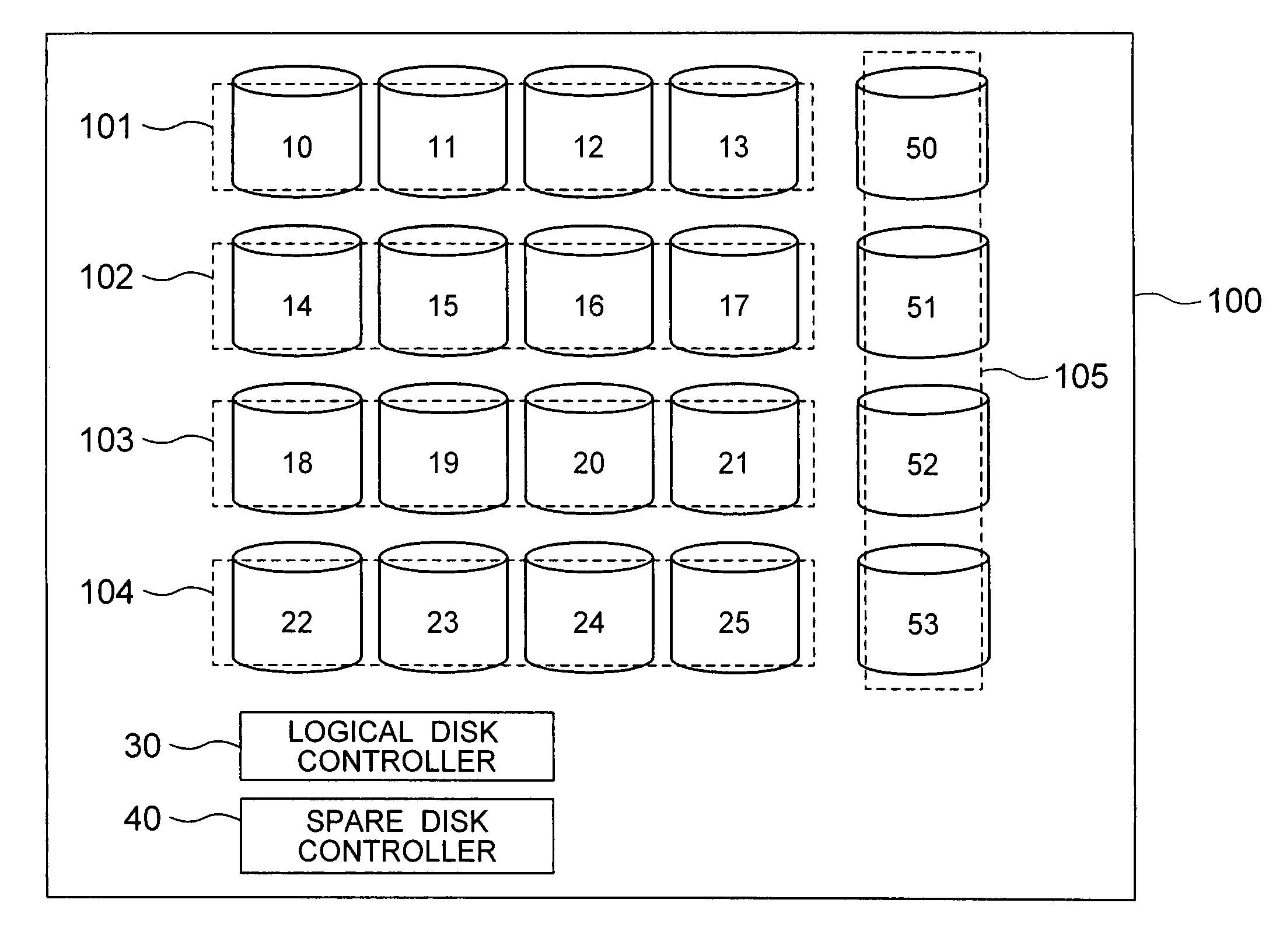
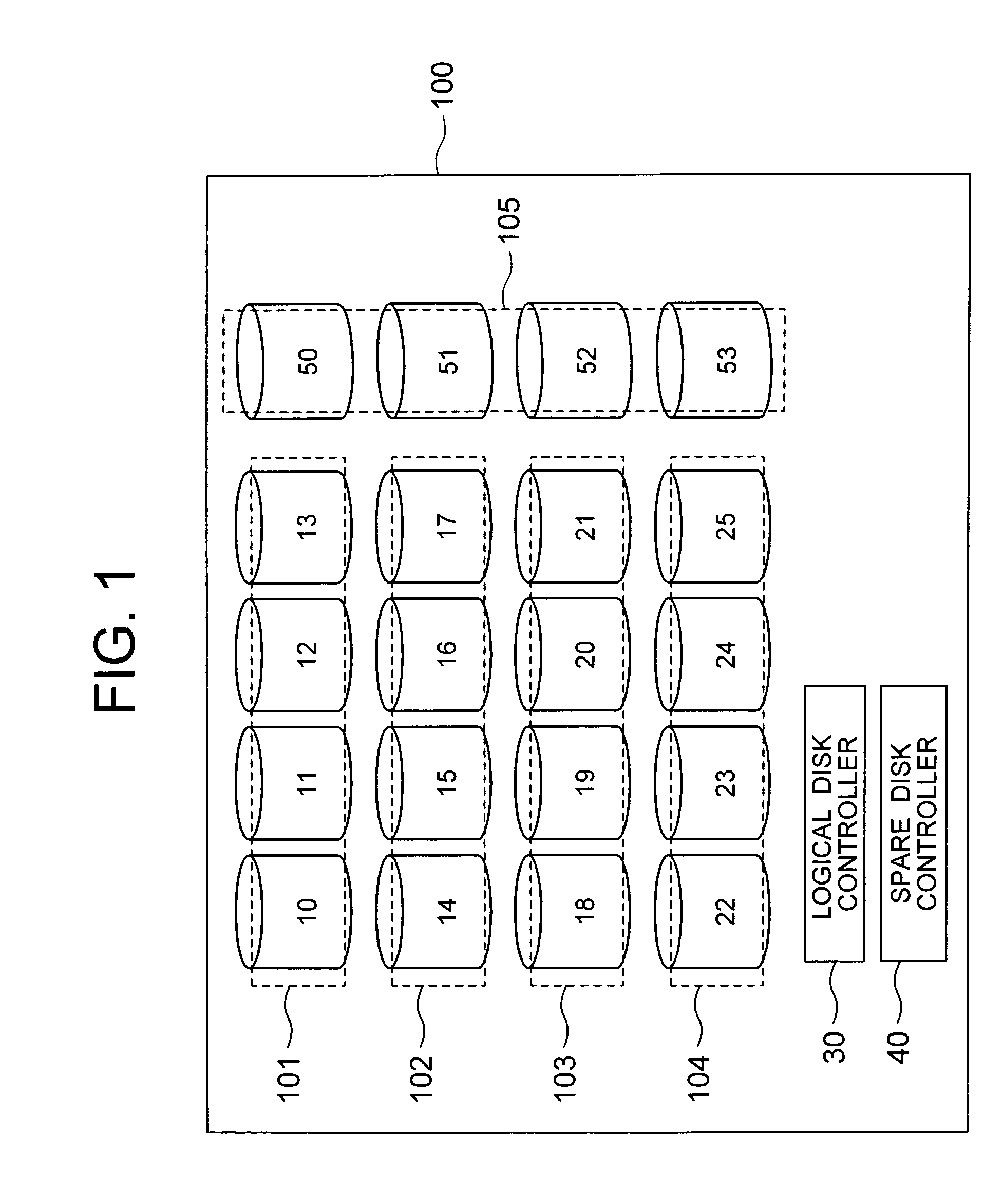
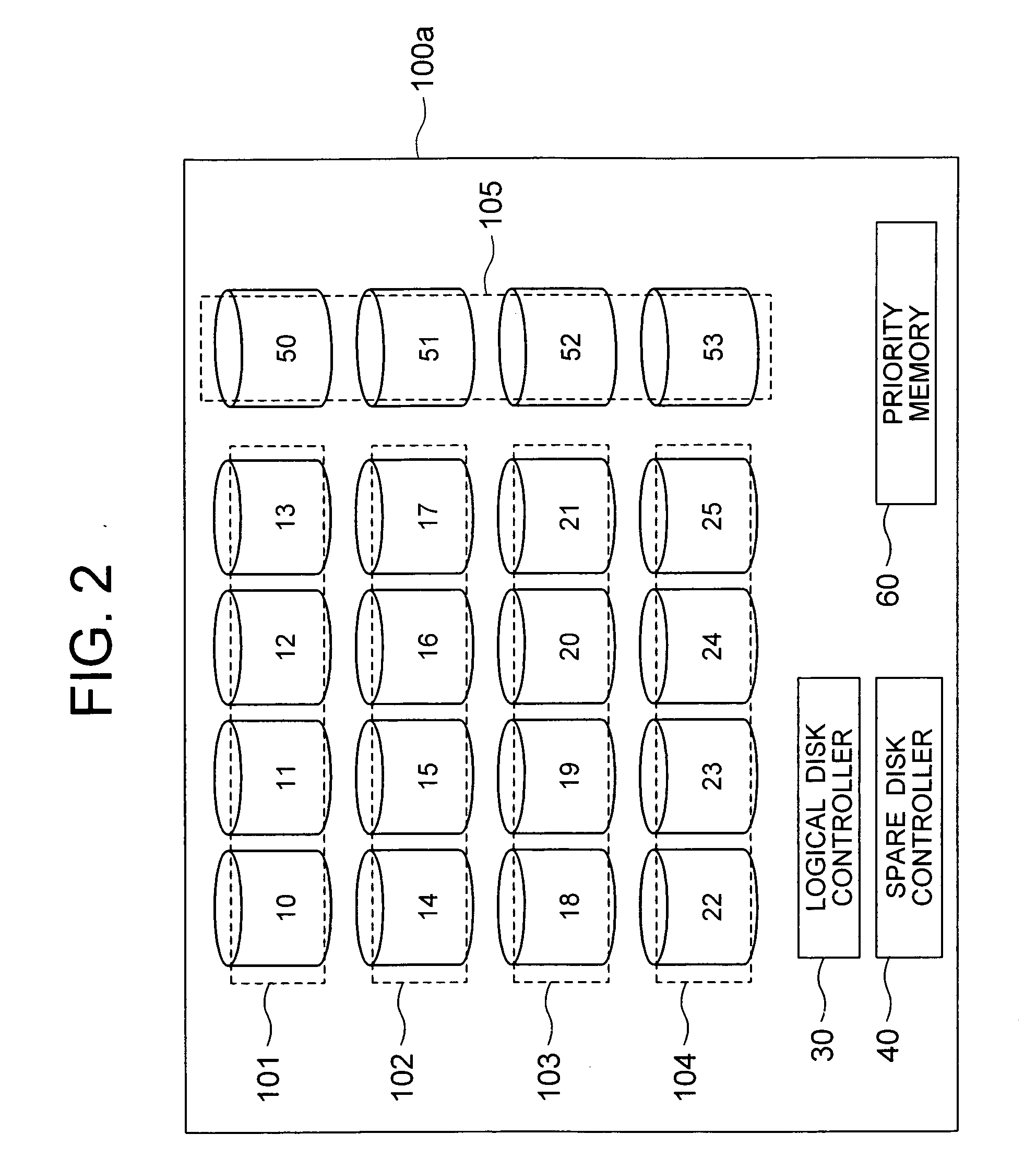
Disk array system configuring a logical disk drive having a redundancy function
InactiveUS20060161823A1Improve reliabilityShorten the length of timeError detection/correctionRecord information storageDisk controllerDisk array
A disk array system includes a plurality of physical disks (10 to 25) configuring a logical disk (101 to 104) having a redundancy function, and a plurality of spare disks (50 to 53) for storing recovered data recovered from the physical disks (10 to 25) by the redundancy function upon occurring of a failure of one of the logical disks (10 to 25). A spare disk controller (40) writes the recovered data into the spare disks (50 to 53) in parallel for a high-speed redundancy recovery.
Owner:NEC CORP
Method and apparatus for managing data volumes in a distributed computer system
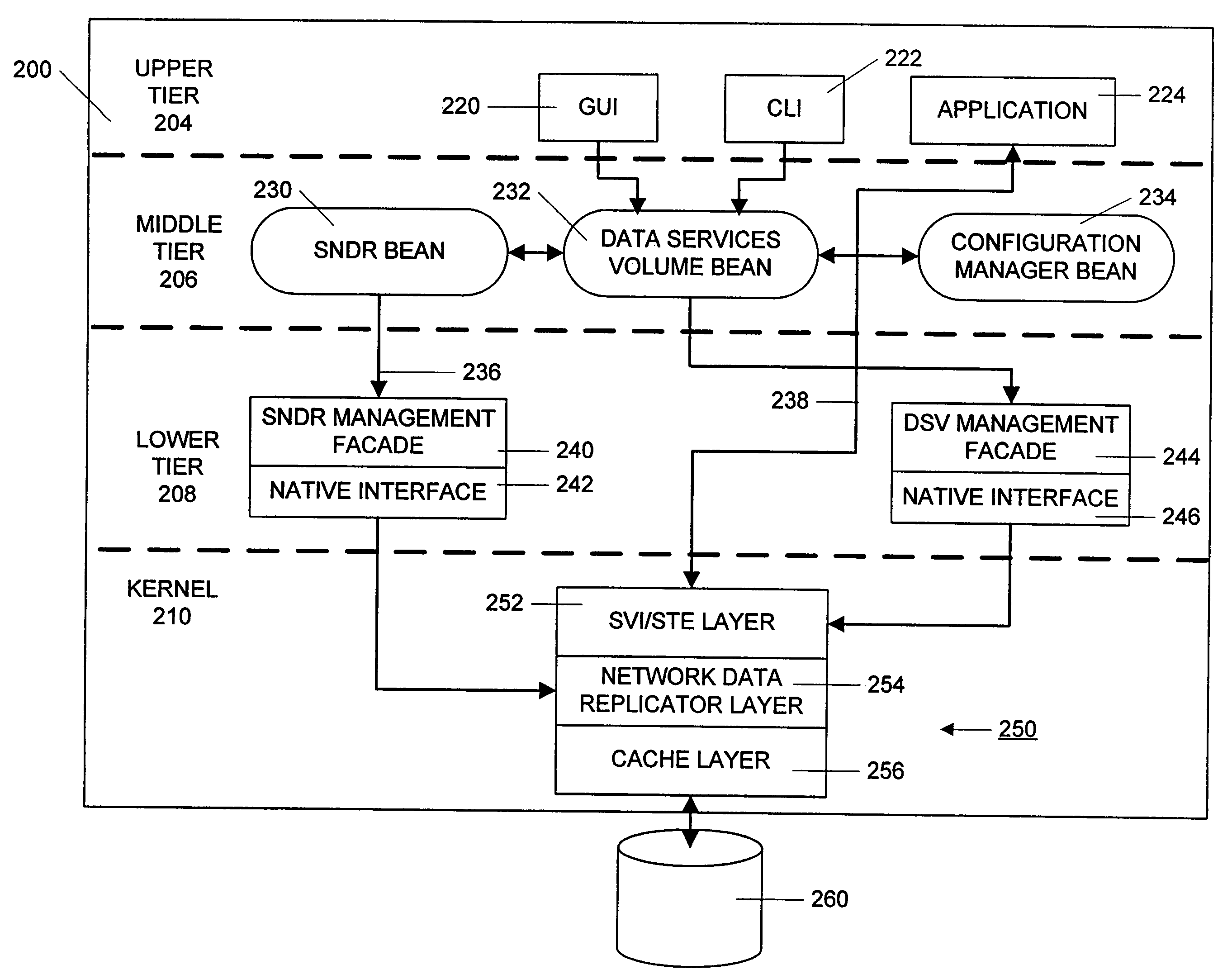
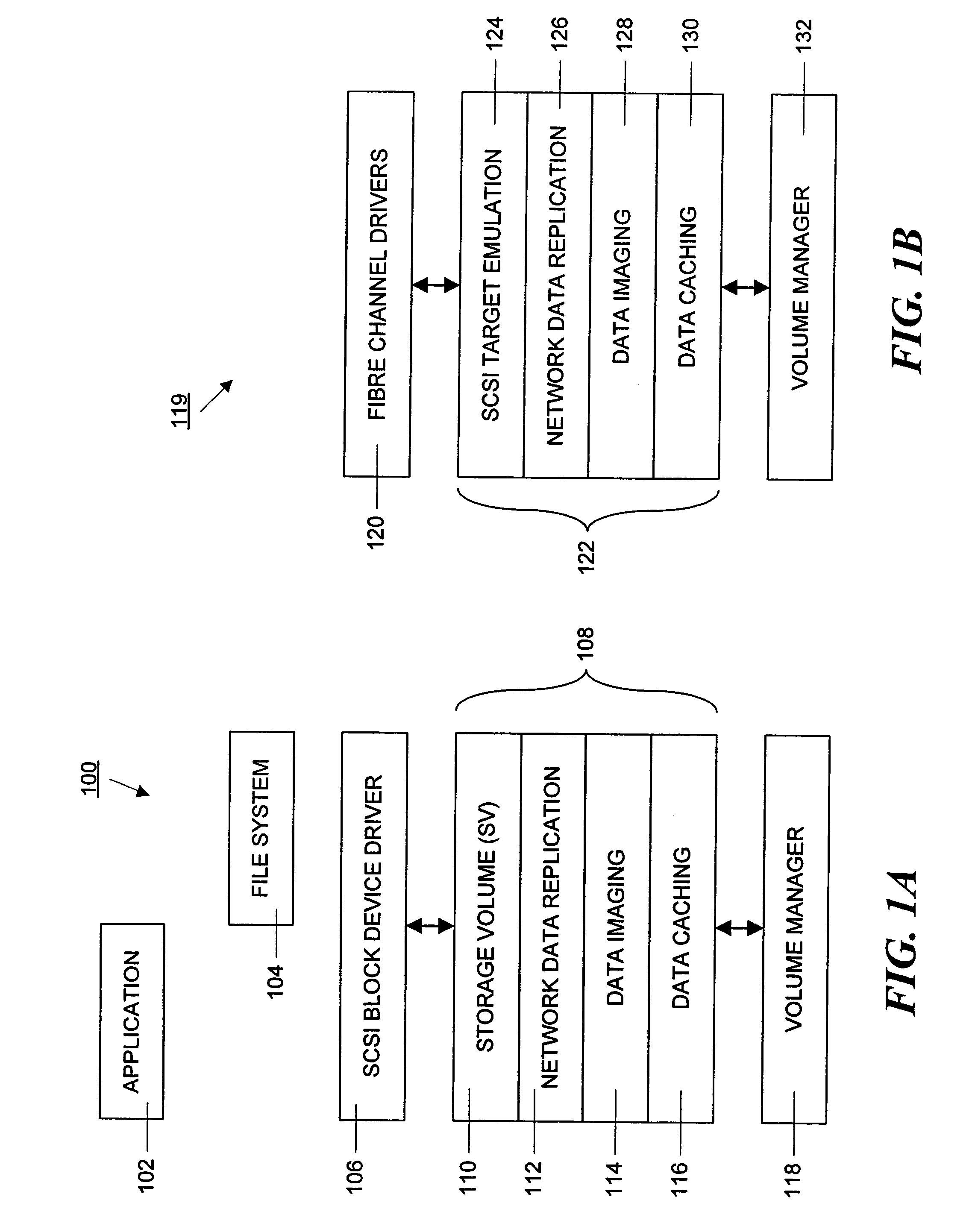
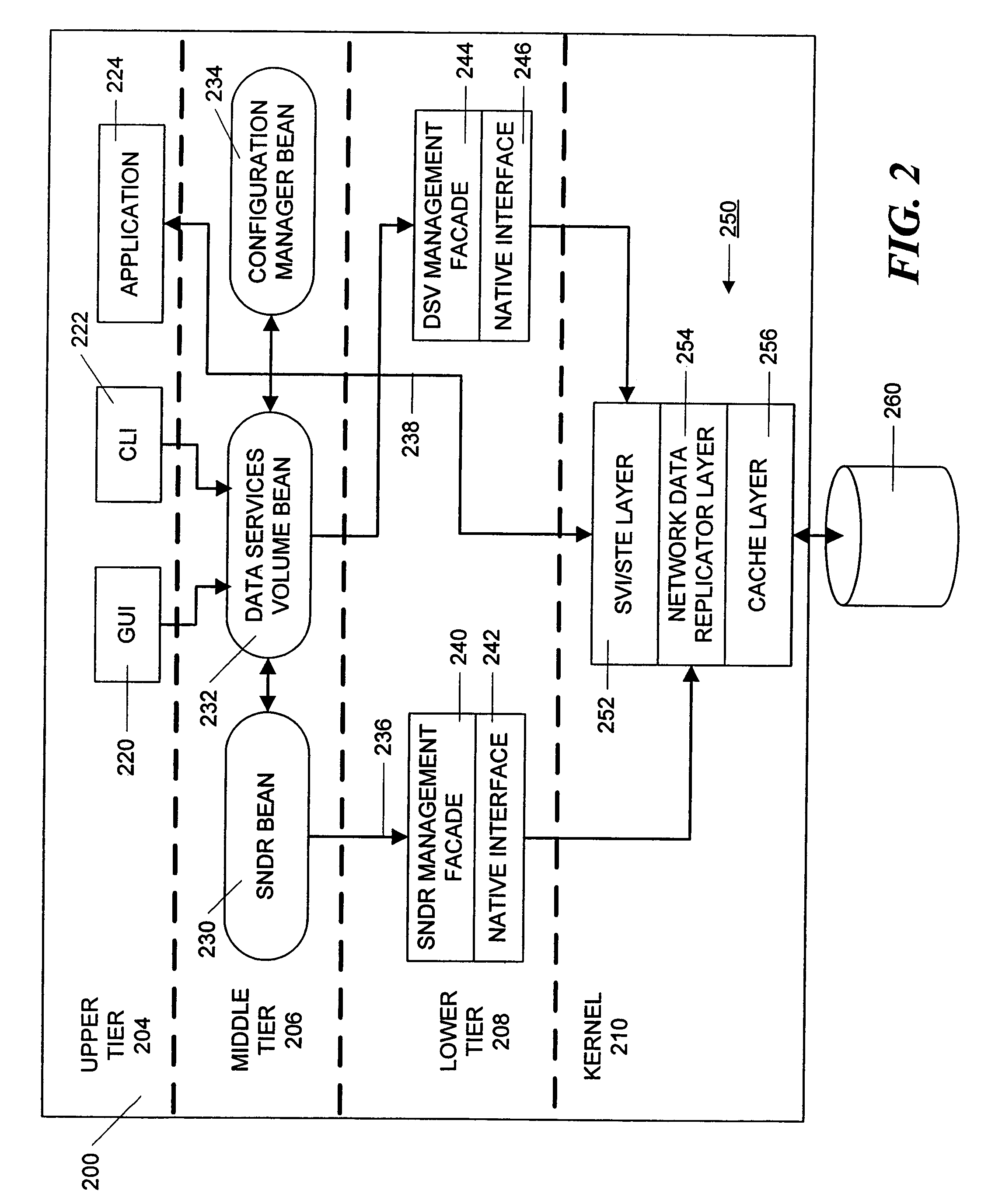
Data volumes on local hosts are discovered and managed by federated Java beans that run on each host. The Java beans form part of a three-tiered data services management. The lowest tier comprises management facade software running on each machine that converts platform-dependent interface written with the low-level kernel routines to platform-independent method calls. The middle tier is a set of federated Java beans that communicate with the management facades and with the upper tier of the system. The upper tier of the inventive system comprises presentation programs that can be directly manipulated by management personnel to view and control the system. The federated beans can configure and control data volumes with either a SCSI terminal emulation interface or a storage volume interface and use a logical disk aggregator to present all volumes available on a local host as a single “logical volume” in which all information regarding the various volumes is presented in a uniform manner.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
System and method for file system snapshot of a virtual logical disk
InactiveUS20080147755A1Data processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsOperational systemFile system
A computer database system has one or more application buffers to use in performing input / output (I / O) operations. A file system receives contents of the application buffers. Contents of the file system are written into a nonvolatile memory. A backup command directed at the file system is received. A data contents of the one or more application buffers is moved to the file system in response to receiving the backup command, and the data contents are written to the nonvolatile memory. An operating system blocks I / O operations directed to the file system after the data contents of the one or more application buffers are moved to the file system. A snapshot of the nonvolatile memory is generated while the I / O operations directed to the file system are blocked.
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
Recording medium storing control program for decentralized data, storage management program, control node, and disk node
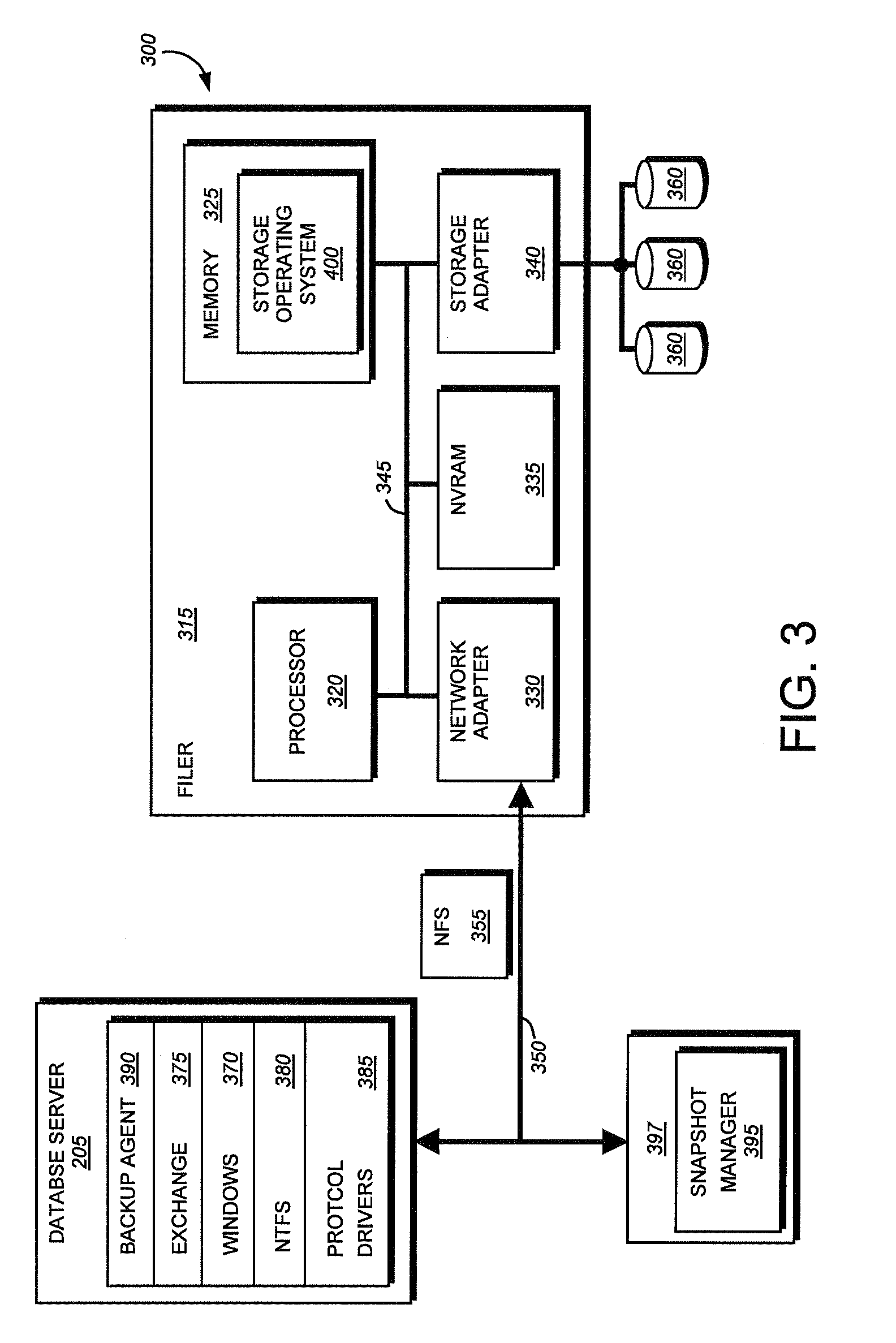
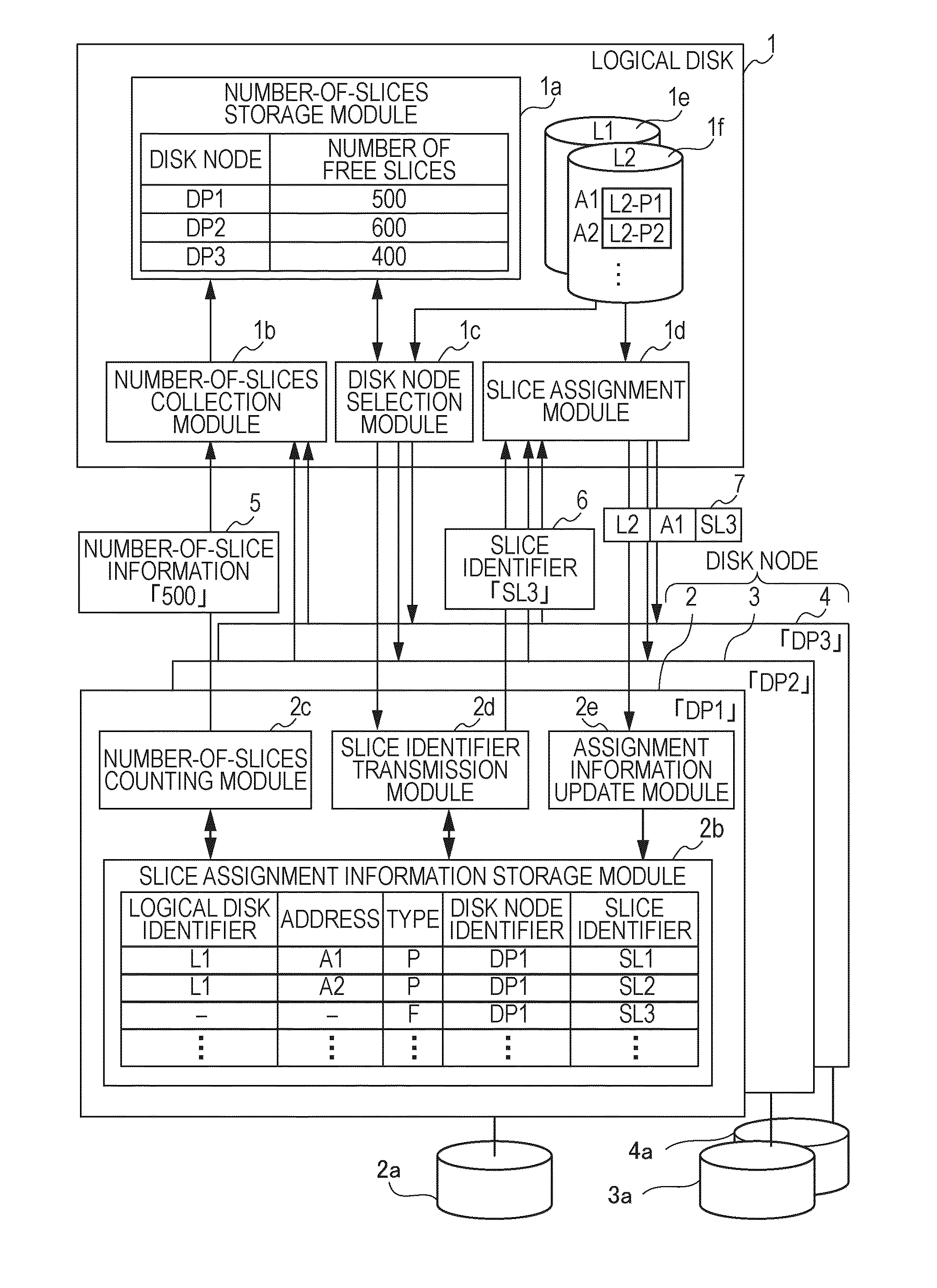
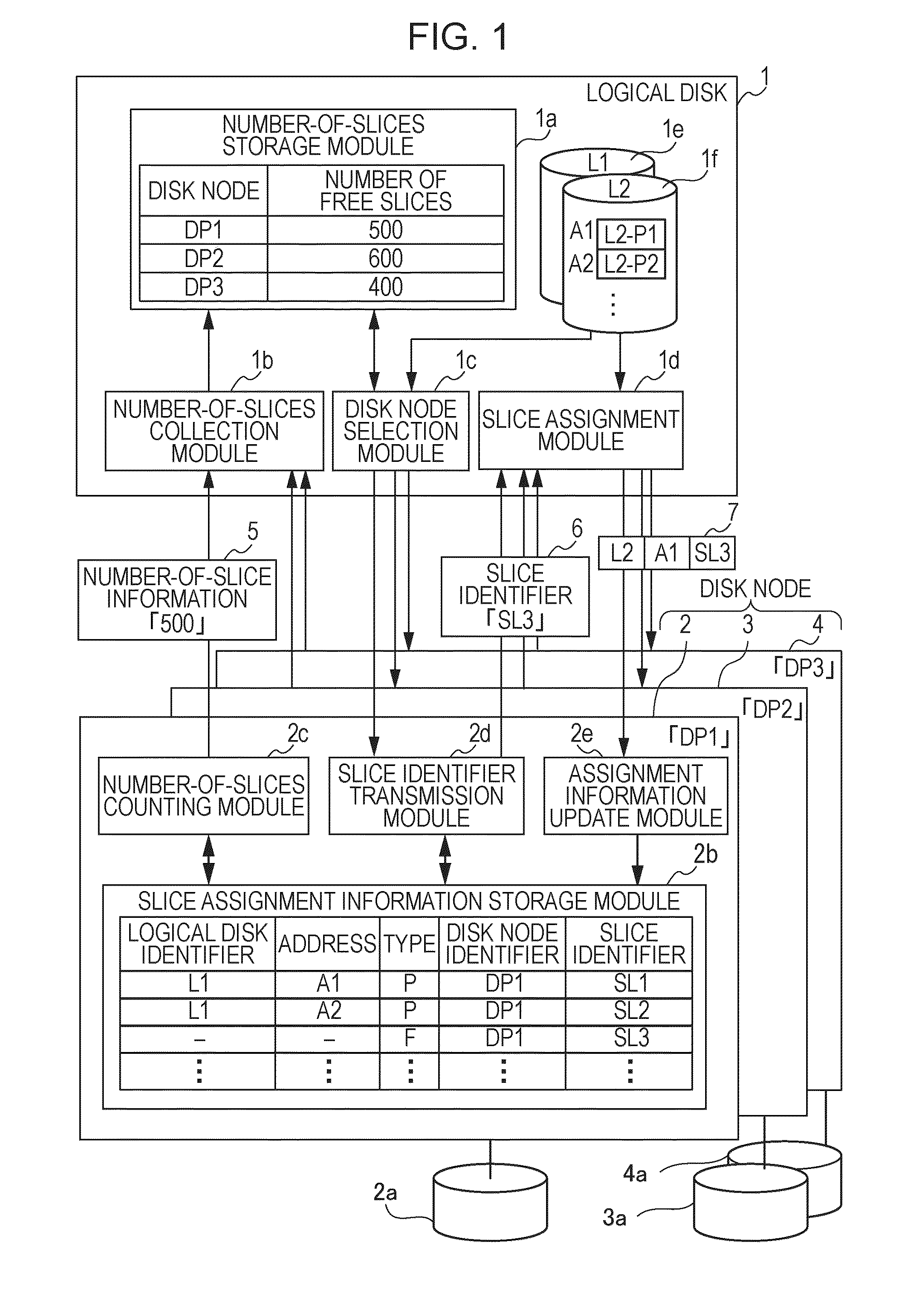
A number-of-slices collector collects number-of-slices information indicating the number of free slices, which are not assigned to a storage areas of a logical disk, from each of a plural disk nodes, divides the storage area of the corresponding storage device in units of slice, and stores an assignment relation of the slices with respect to the storage areas of the logical disk. A disk node selector selects a source disk node from among the disk nodes having the free slices, and requests a slice identifier to identify the free slice for the selected source disk node. The source disk node serves as a source providing the slice to be assigned. A slice assigner receives the slice identifier from the source disk node, and determines an assignment relation of the free slice, which is denoted by the received slice identifier, with respect to the storage areas of the logical disk.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
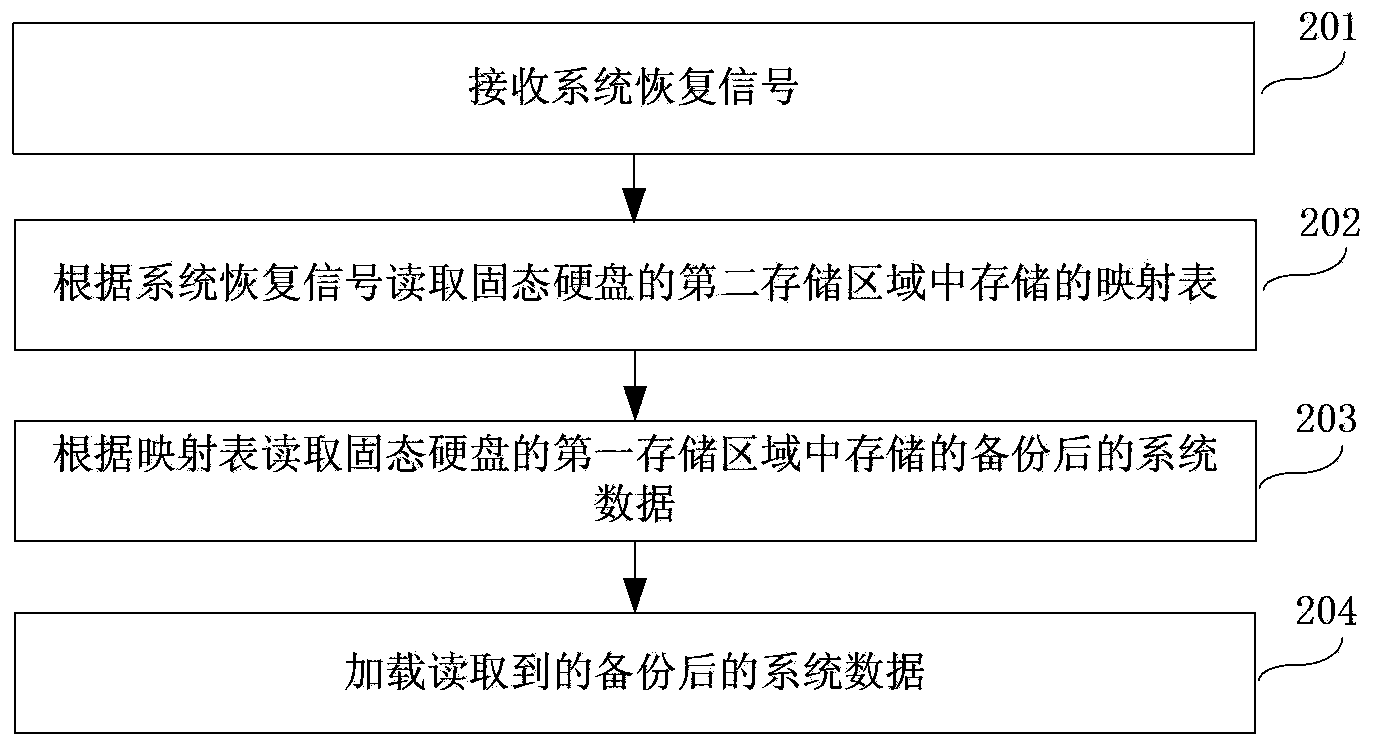
System recovery method, system recovery device, solid state disk and electronic equipment
ActiveCN104077197AResolution timeSolve space problemsRedundant operation error correctionRecovery methodSystem recovery
The invention belongs to the technical field of computers, and discloses a system recovery method, a system recovery device, a solid state disk and electronic equipment. The system recovery method includes: receiving a system recovery signal; reading a mapping table stored in a second memory region of the solid state disk according to the system recovery signal, wherein the mapping table includes corresponding relation between a physical disk address and a logical disk address corresponding to backed-up system data; reading the backed-up system data stored in a first memory region of the solid state disk according to the mapping table; loading the read-out backed-up system data. The problems of long system recovery time and waste of disk space in the prior art are solved; system recovery can be realized only by reading the mapping table stored in the solid state disk and reading and operating the backed-up system data according to the mapping table, so that the effect of short system recovery time is achieved.
Owner:SHENZHEN YILIAN INFORMATION SYST CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com