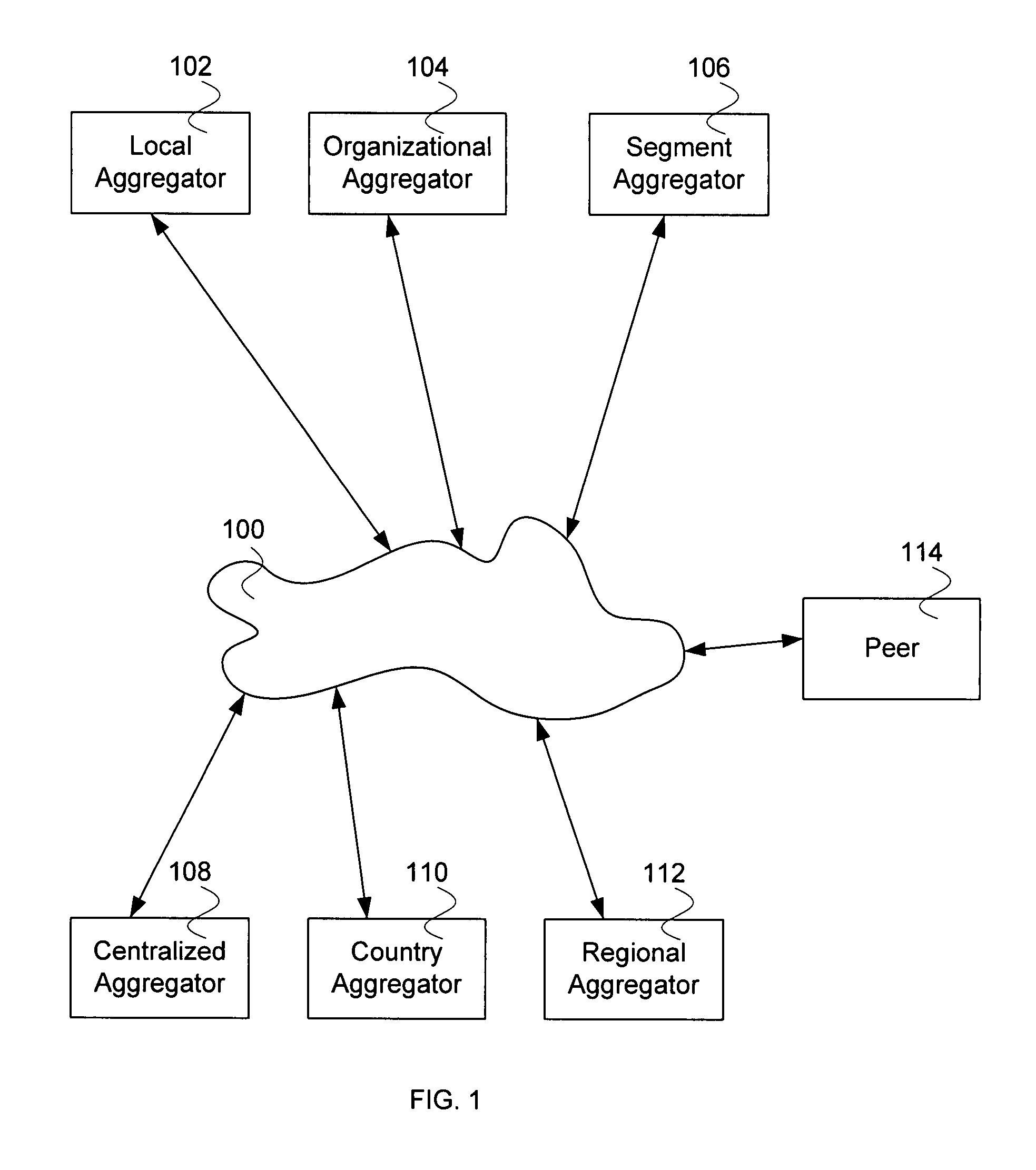
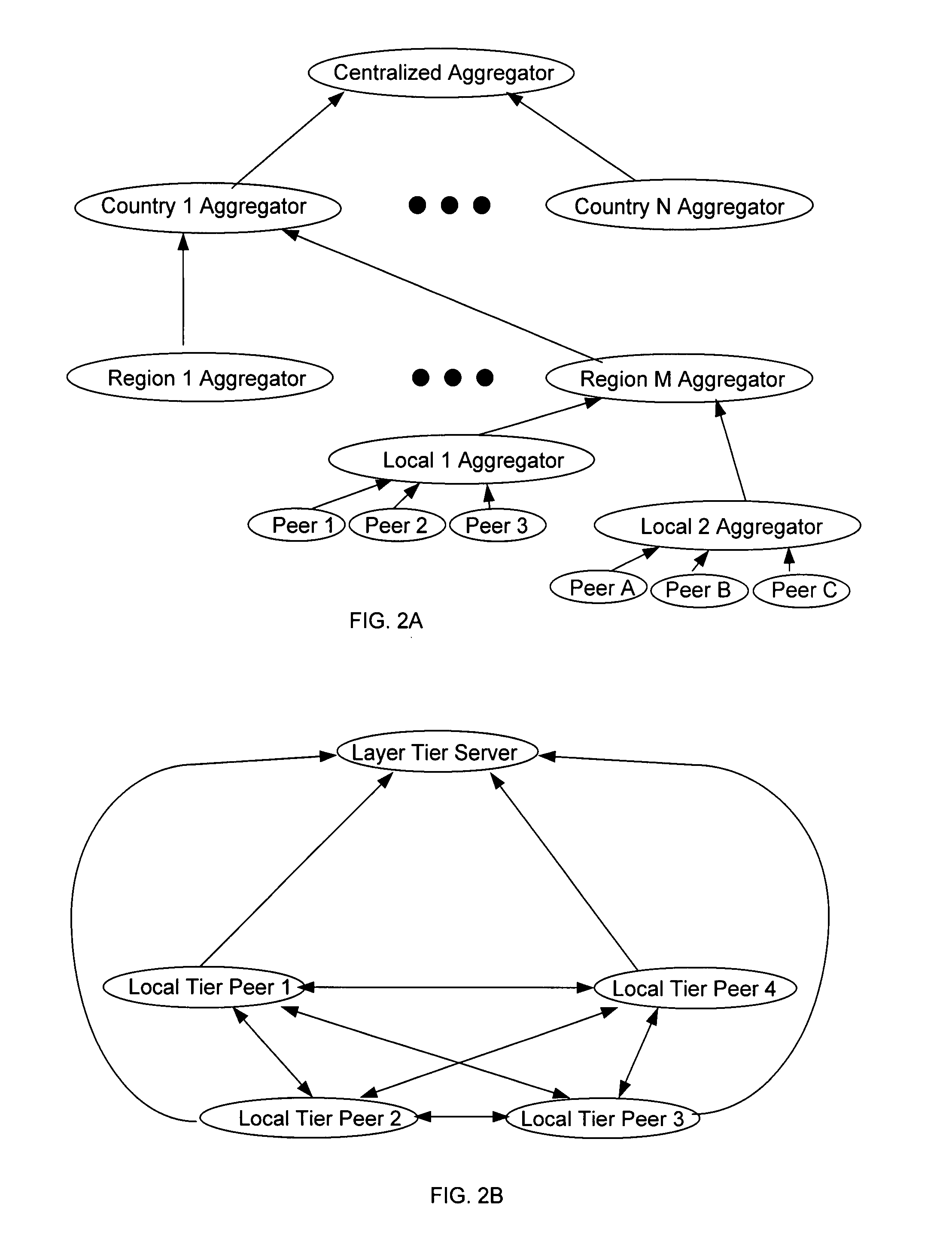
Patents
Literature
174 results about "News aggregator" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In computing, a news aggregator, also termed a feed aggregator, feed reader, news reader, RSS reader or simply an aggregator, is client software or a web application which aggregates syndicated web content such as online newspapers, blogs, podcasts, and video blogs (vlogs) in one location for easy viewing. The updates distributed may include journal tables of contents, podcasts, videos, and news items.
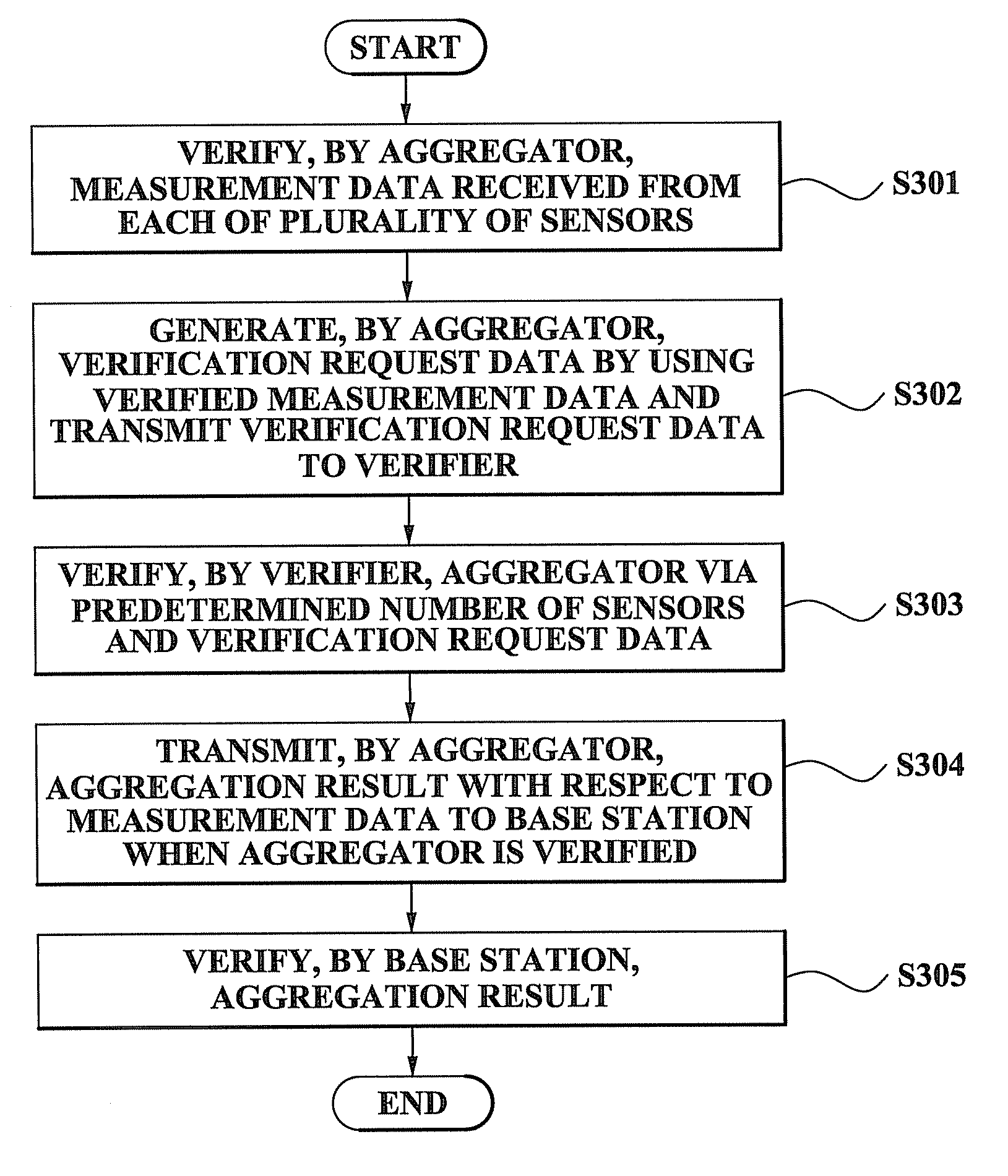
Method and system for performing distributed verification with respect to measurement data in sensor network
ActiveUS20080262798A1Efficient managementImprove securityAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceDigital data processing detailsData validationSource Data Verification
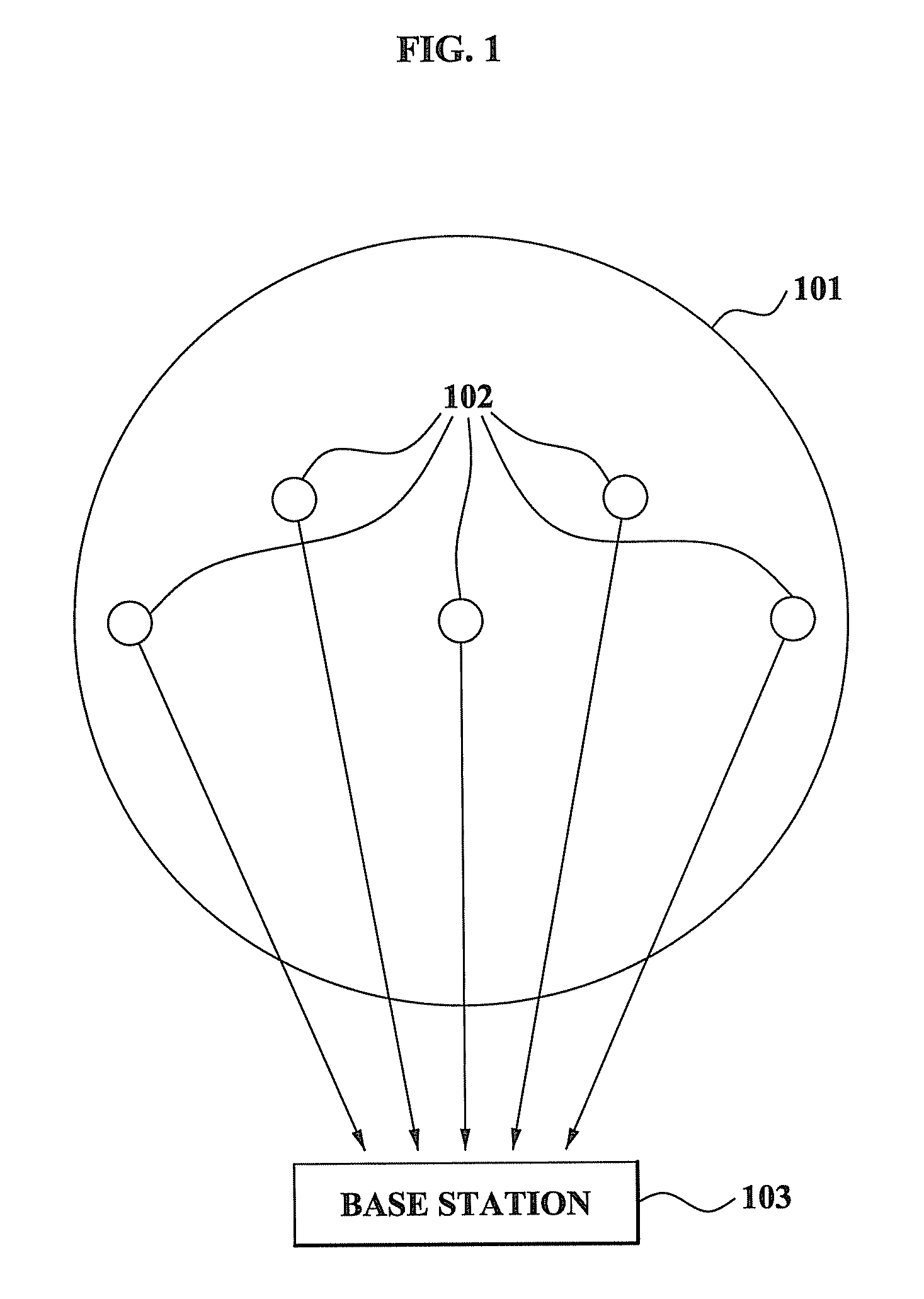
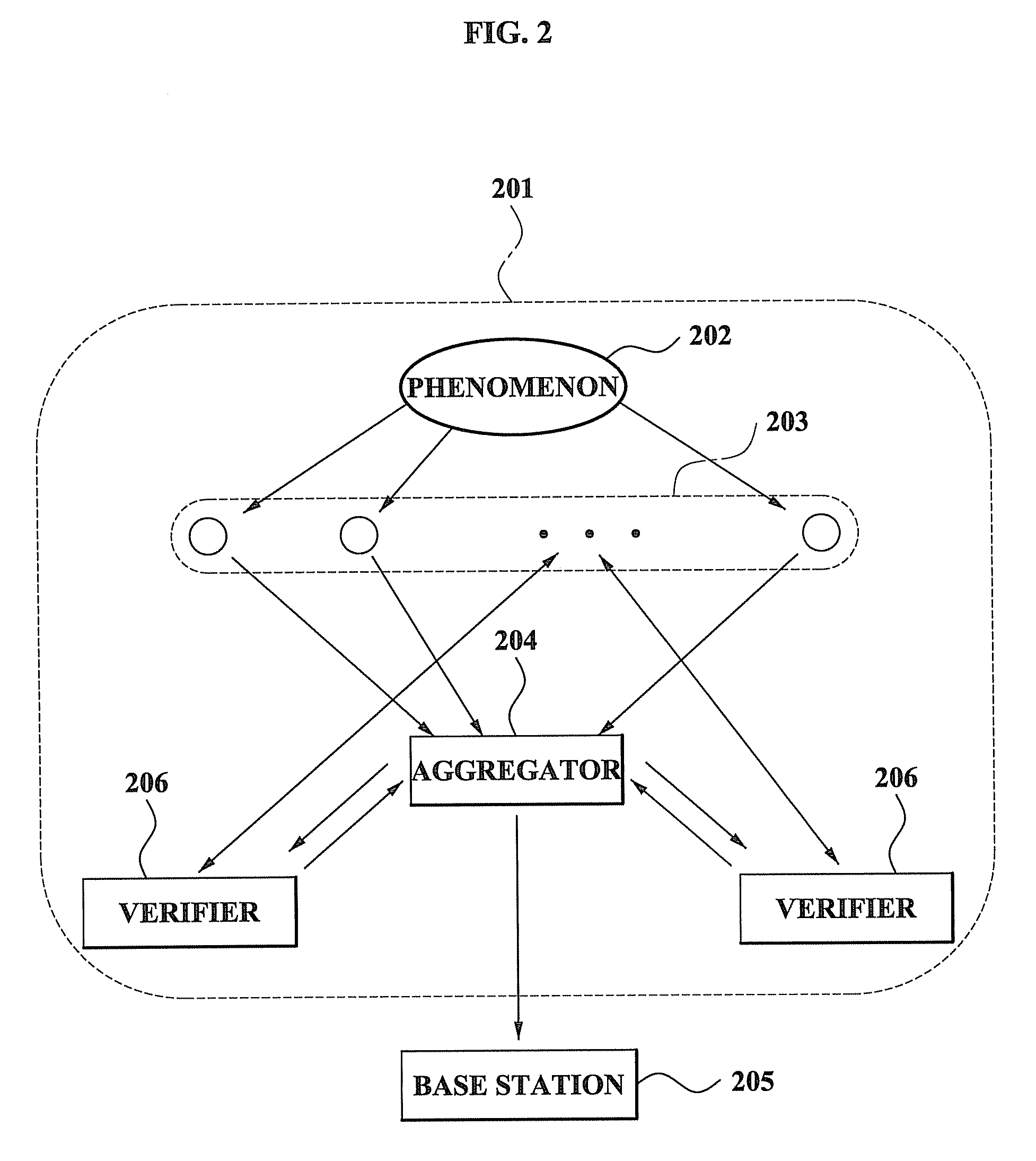
A method and system for performing a distributed verification with respect to measurement data in a sensor network. The method of performing the distributed verification with respect to measurement data in a sensor network includes: verifying, by an aggregator, the measurement data received from each of a plurality of sensors; generating, by the aggregator, verification request data by using the verified measurement data; transmitting the verification request data to a verifier; and verifying, by the verifier, the aggregator via a predetermined number of sensors of the plurality of sensors and the verification request data. The method of performing a distributed verification with respect to measurement data in a sensor network further includes transmitting, by the aggregator, an aggregation result with respect to the measurement data to a base station when the aggregator is verified; and verifying, by the base station, the aggregation result.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Data transfer for network interaction fraudulence detection
Transferring metadata is disclosed. Information about a network interaction is processed to generate metadata describing the network interaction. Based on the metadata it is determined whether the metadata is to be transferred to an aggregator. In the event that the metadata is to be transferred, one or more aggregators are determined to which the metadata is to be transferred. The metadata is transferred to the one or more aggregators.
Owner:ANCHOR INTELLIGENCE +1
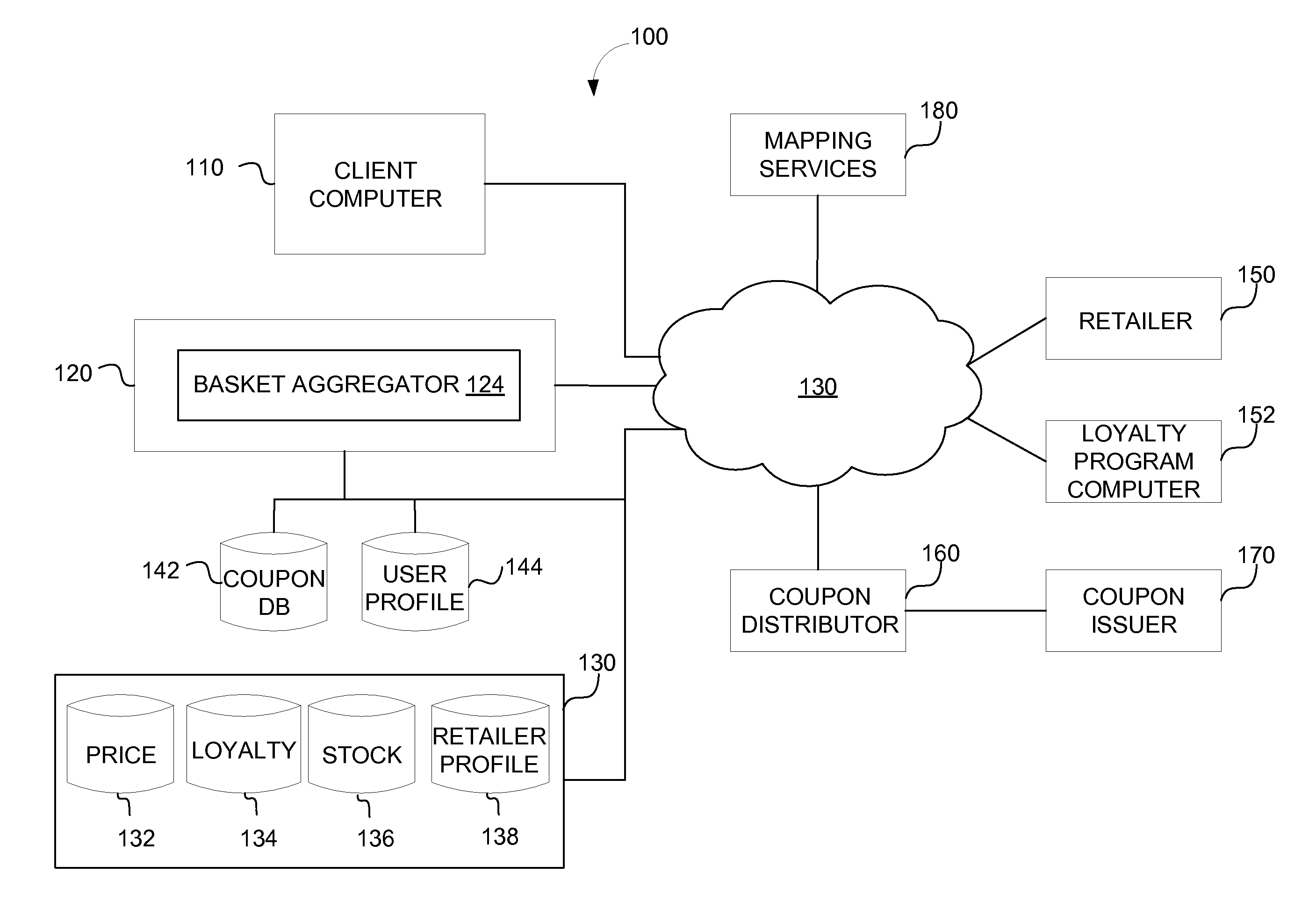
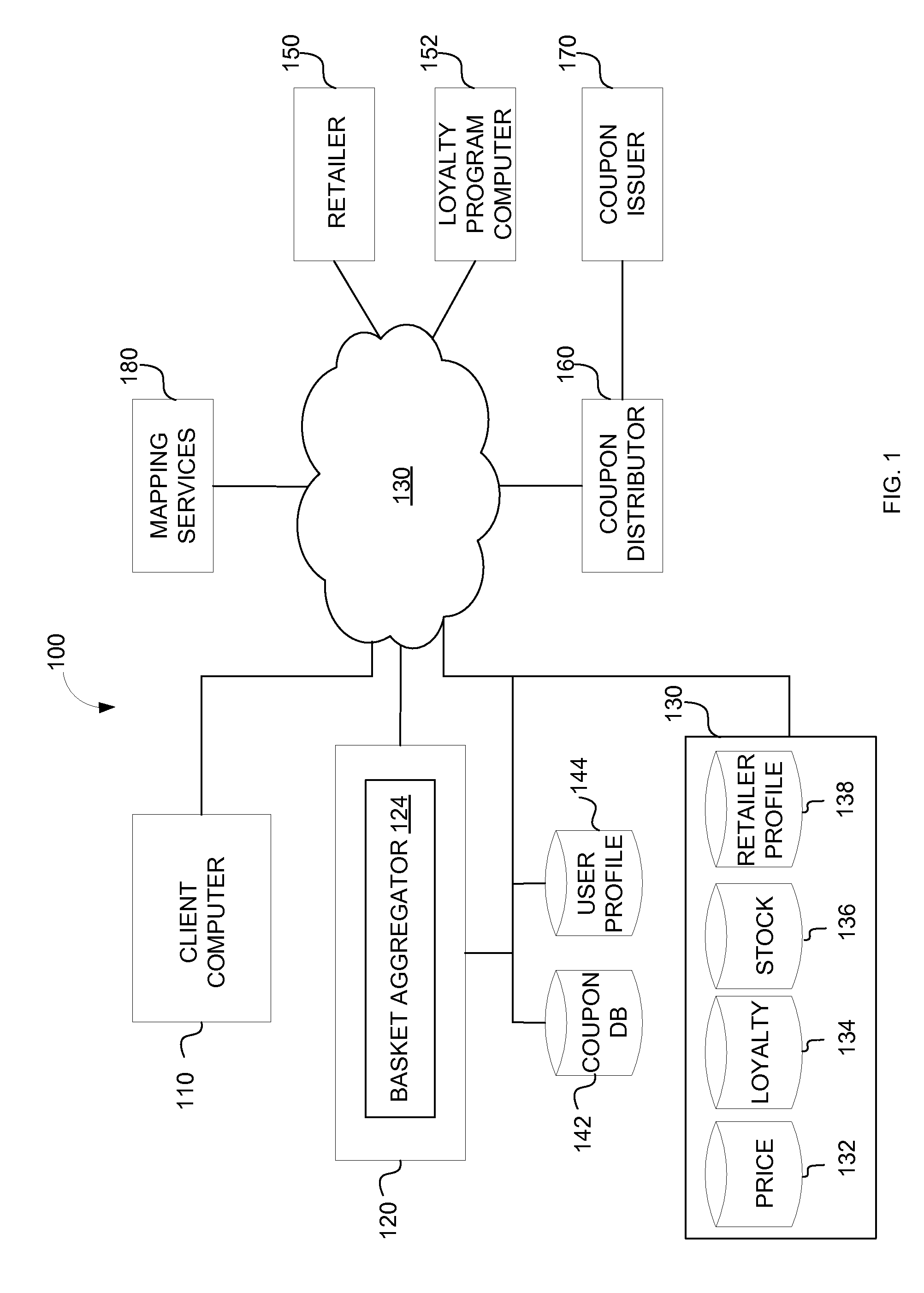
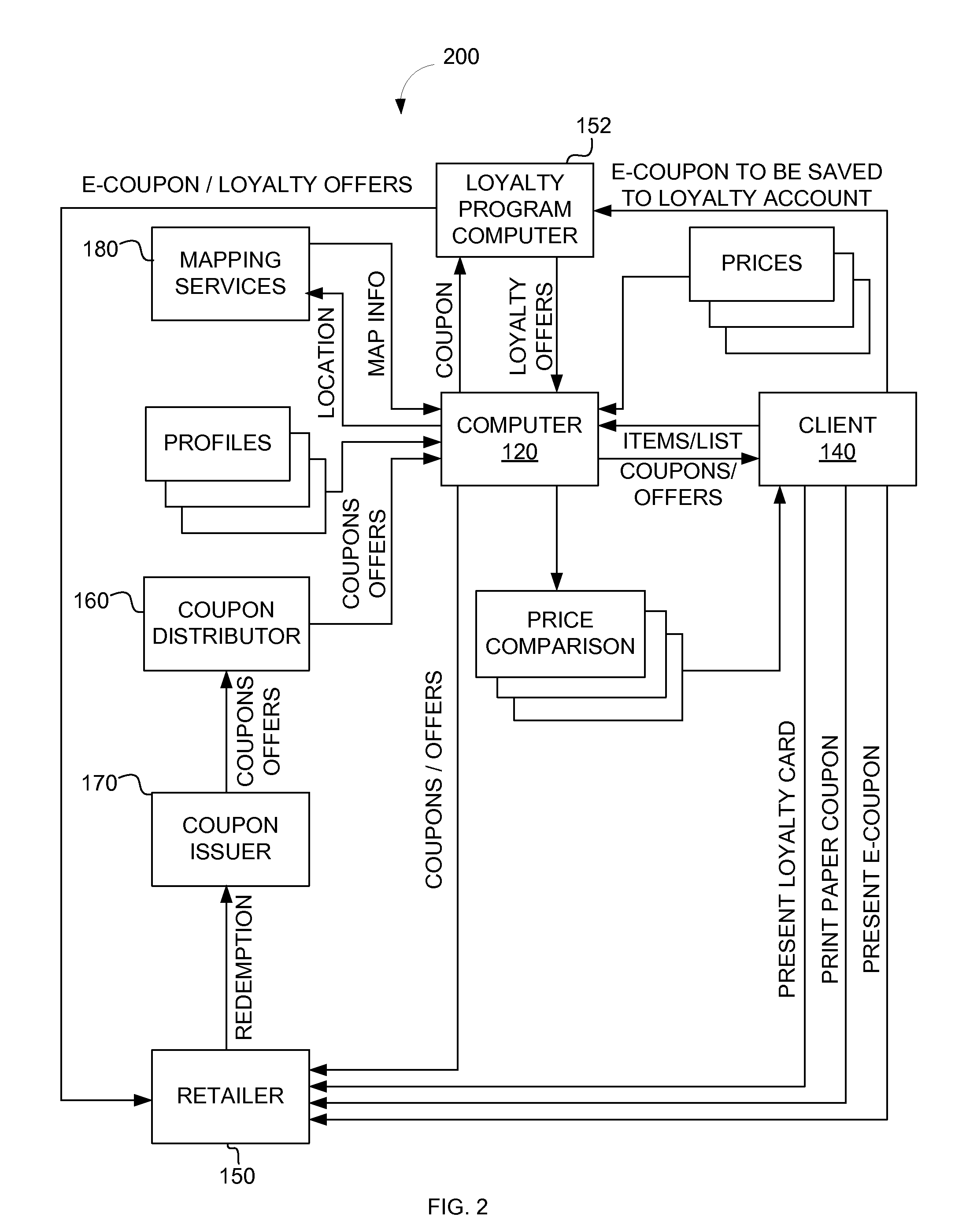
Basket aggregator and locator
A system and method for determining a basket, or total, price of items in a shopping list from various retailers is provided. Items may be added to the shopping list based on, for example, a coupon related to an item, items added to the shopping list by a user, items listed in a recipe, and items suggested for the user. The system may determine the price of the items from the various retailers and whether incentives are available for the items. If available and applicable, the incentives are applied to the total price for each retailer and a price comparison of total prices is generated. The price comparison results may be transmitted via various communication channels and may be displayed on a map.
Owner:CATALINA MARKETING CORP
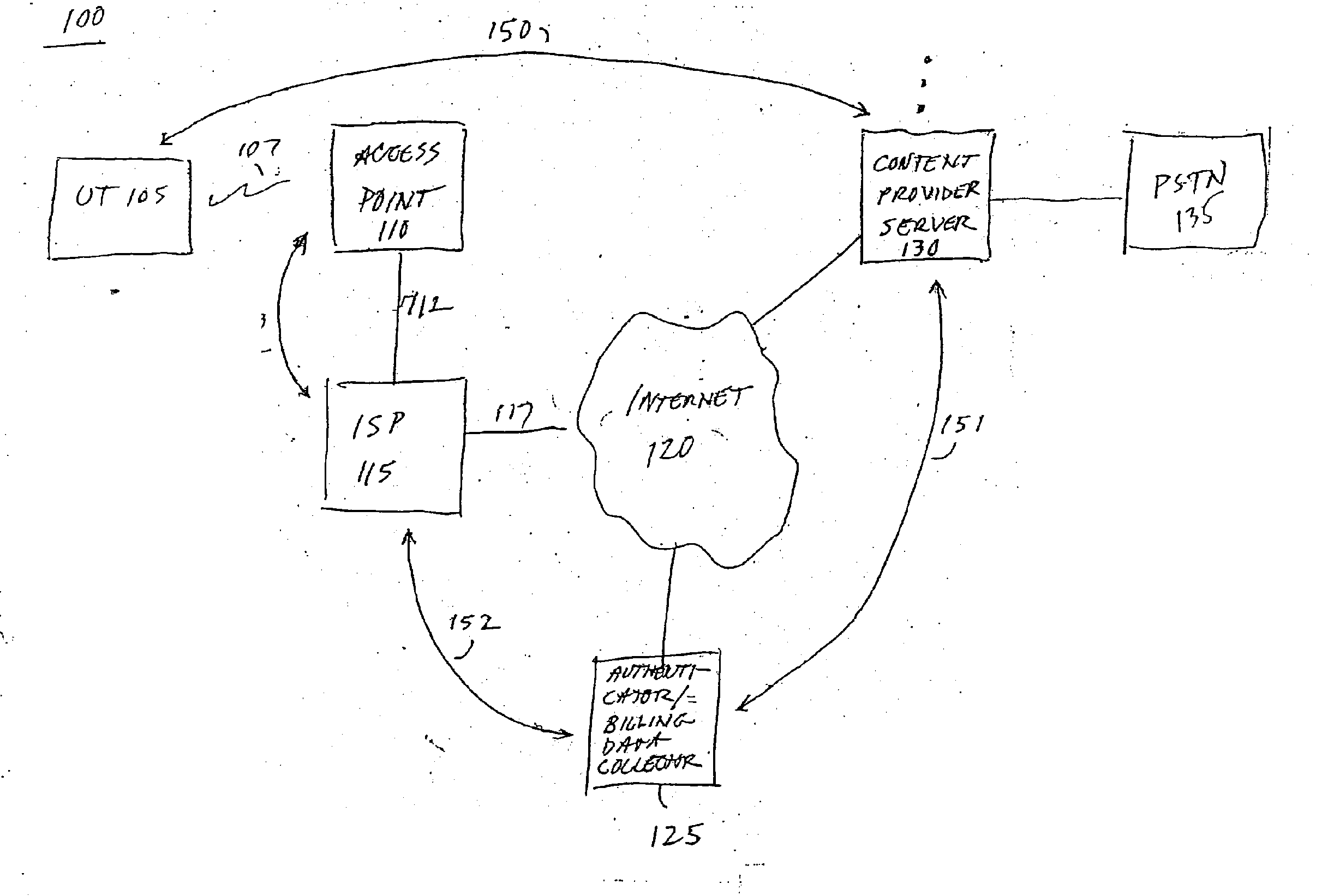
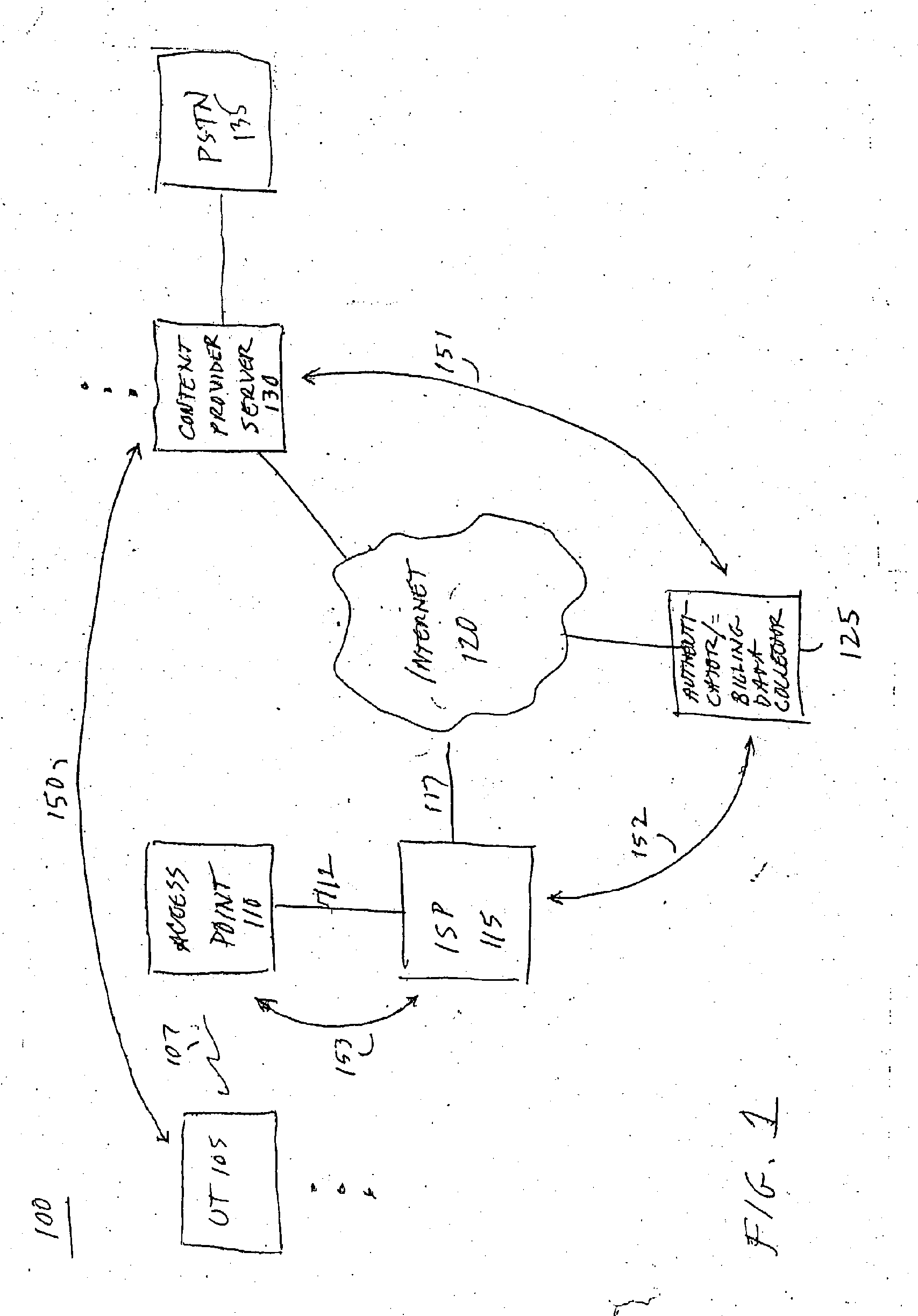
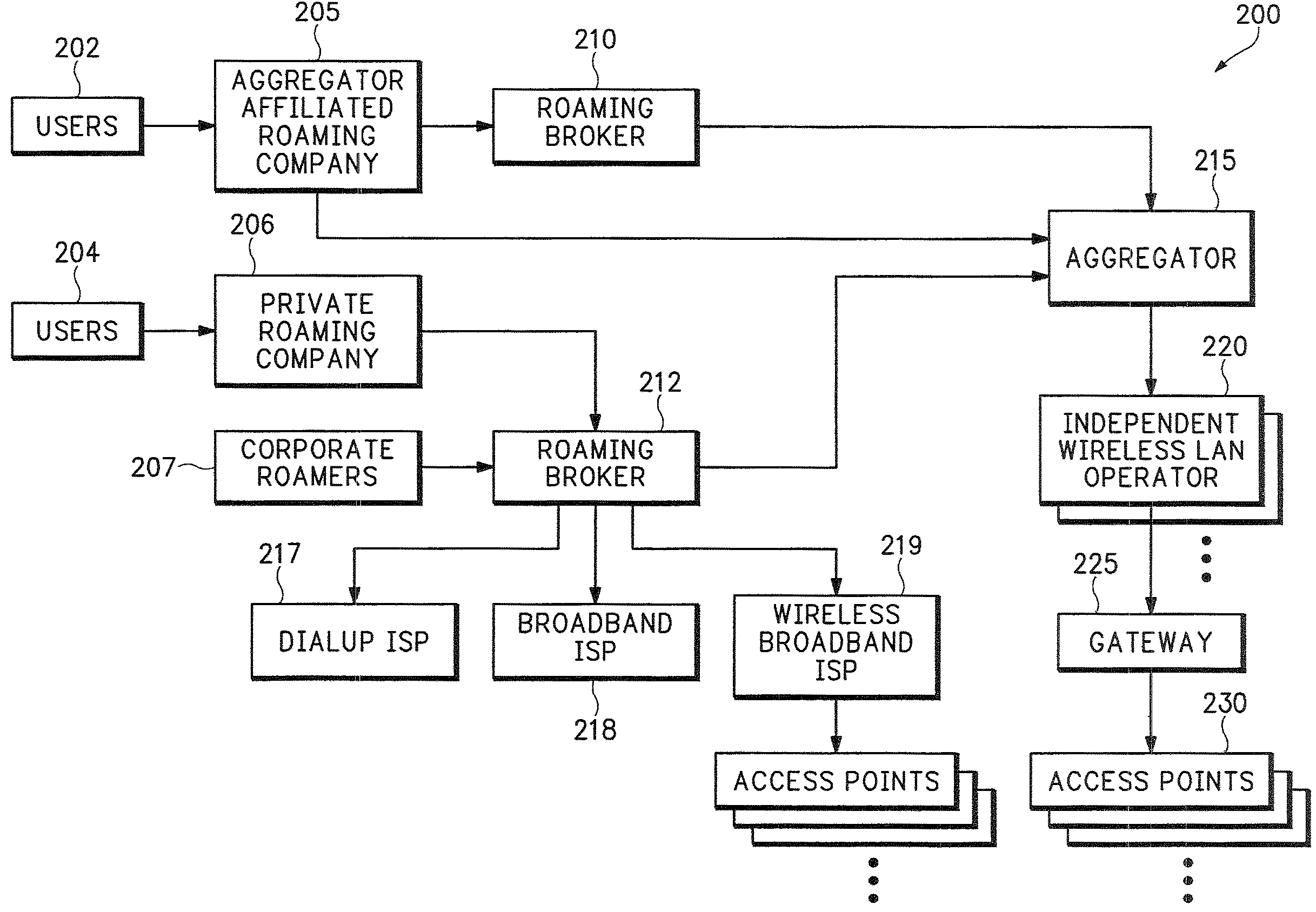
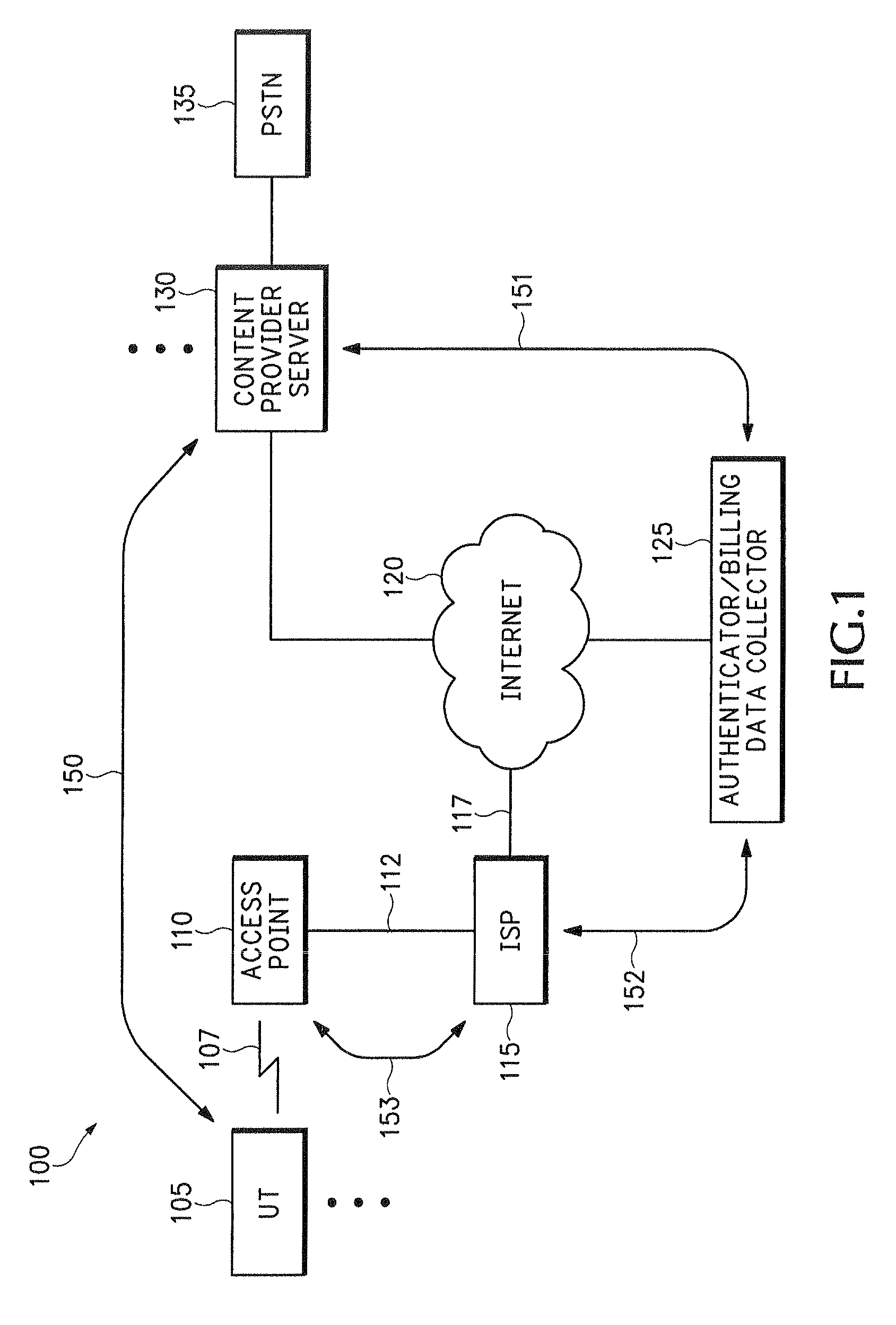
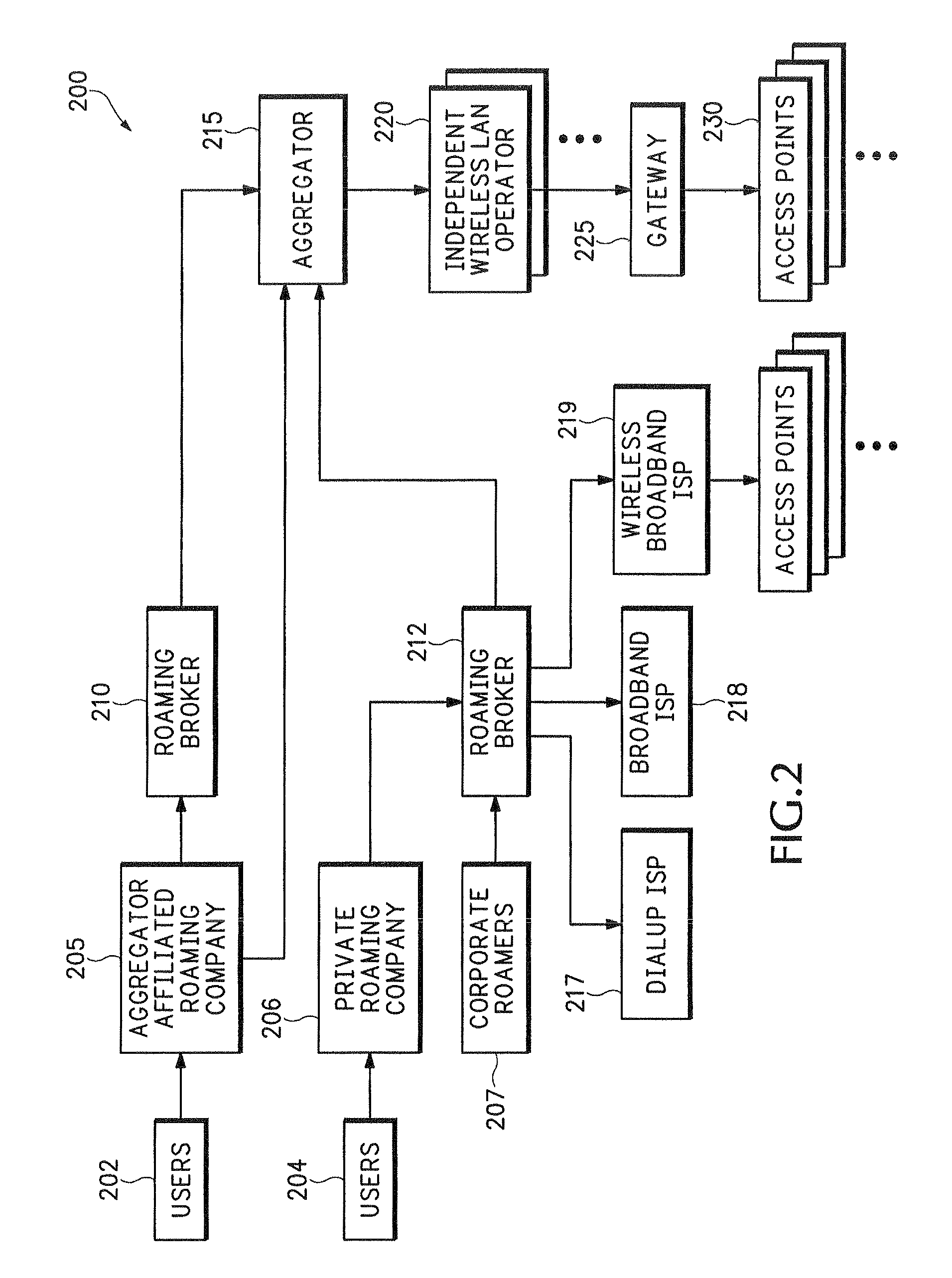
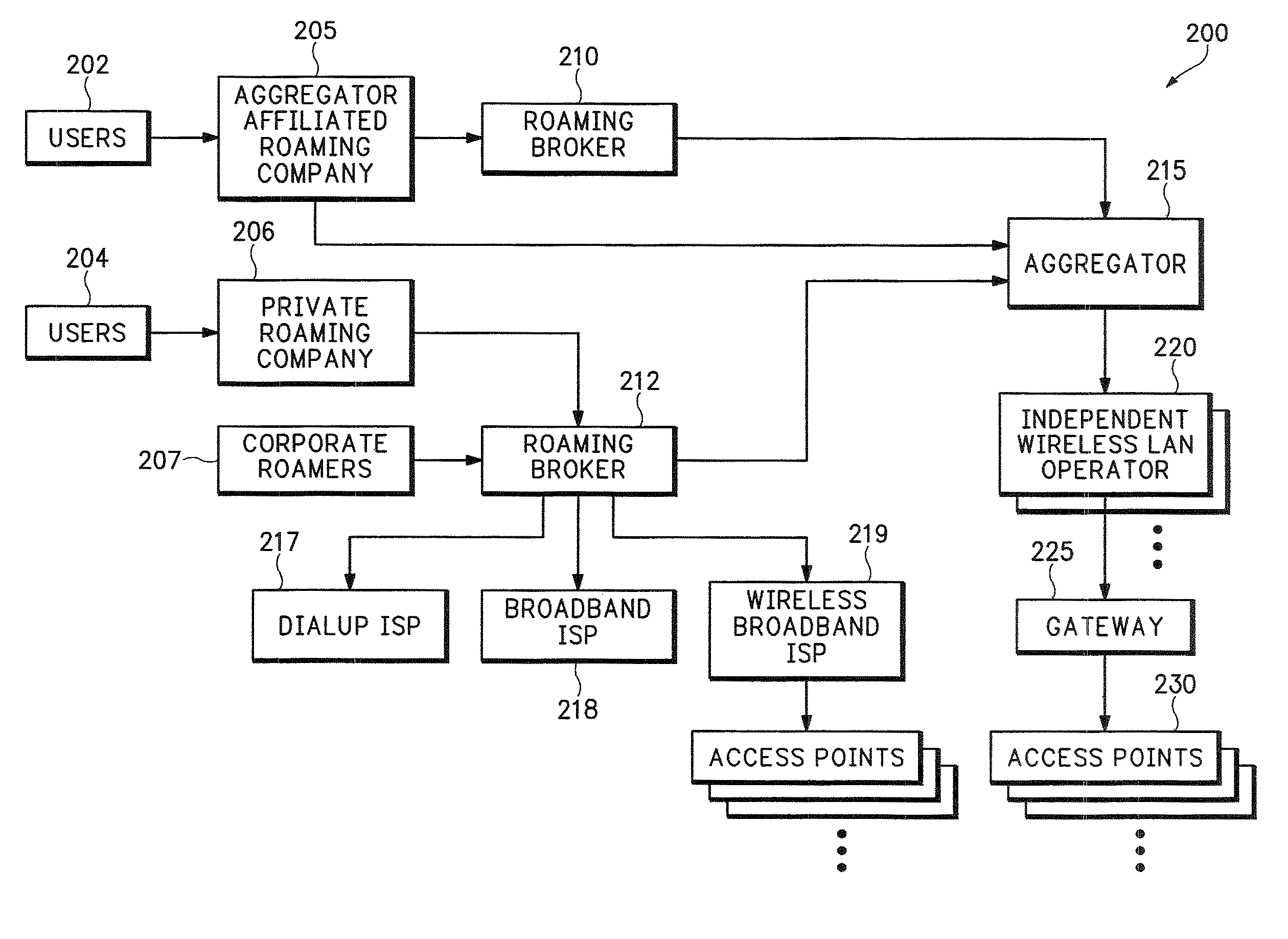
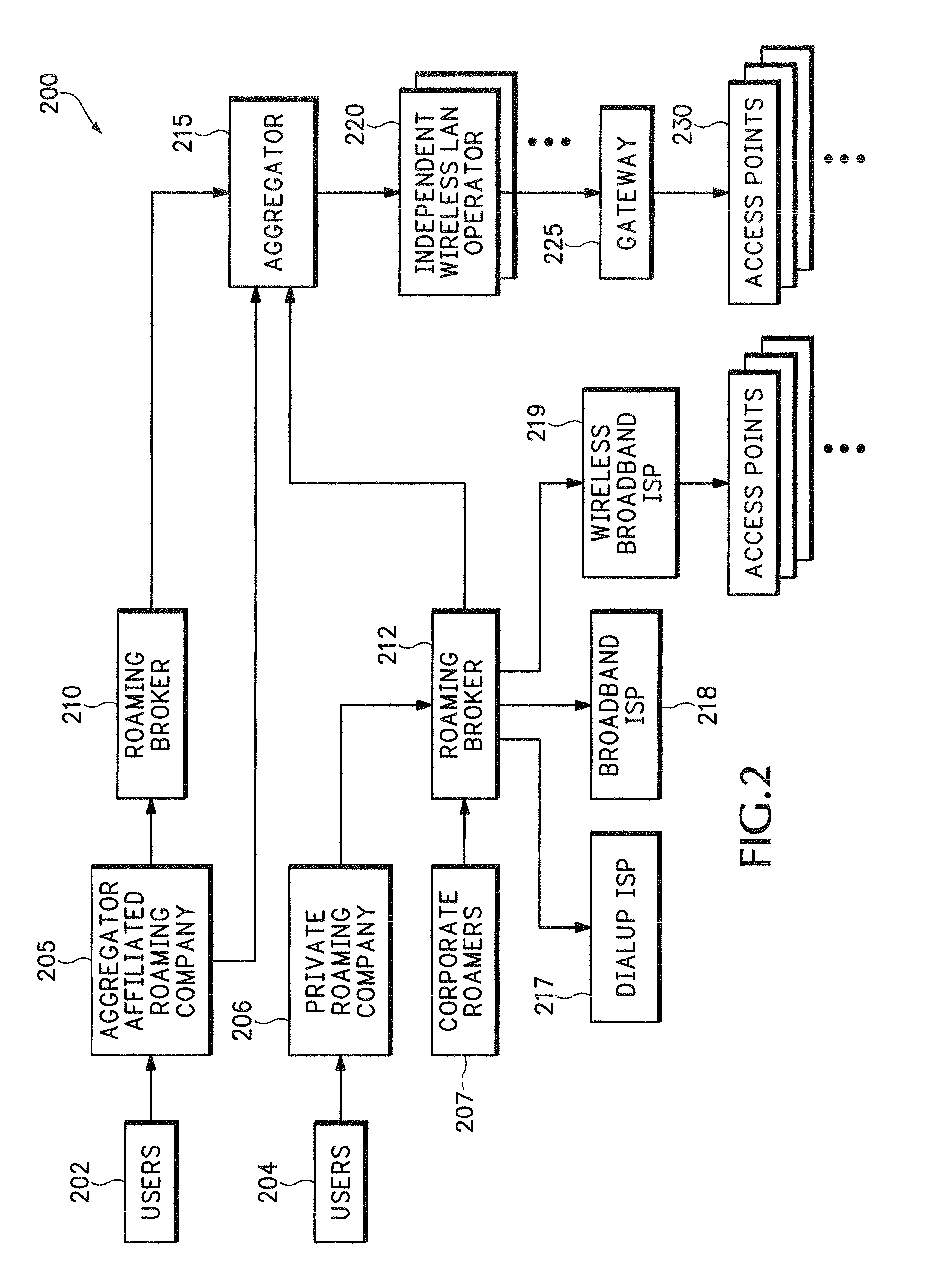
System for on-demand access to local area networks
ActiveUS20070112948A1Metering/charging/biilling arrangementsAssess restrictionPaymentTelecommunications
A roaming company makes payments to an aggregator of independent WLAN operators in exchange for providing Internet access services to subscribers of the roaming company. Independent WLAN operator accounts are maintained at the aggregation company.
Owner:XYLON LLC
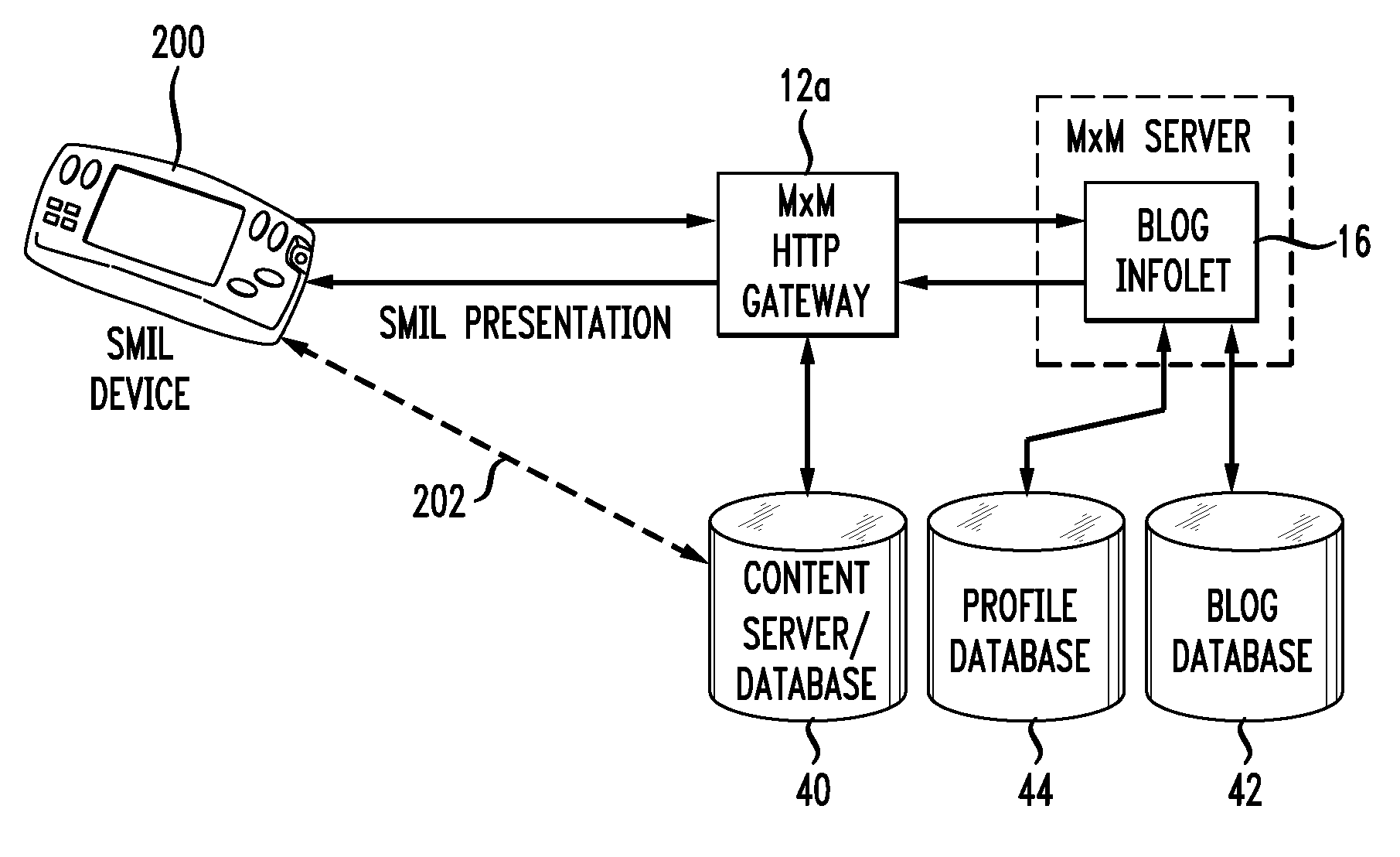
System for coordinating the presentation of digital content data feeds
A reader for obtaining a plurality of categorized digital content from a content aggregator framework over a communications network based on a content subscription with the aggregator framework, the reader configured for operation on a digital device. The reader includes an interface module configured for receiving content category selections from a user of the device and for identifying a profile of the user including one or more user definitions. A communications module communicates the profile and the content selections to the aggregator framework; and a generation module configured presents updated versions of the digital content to device user when the updated digital content becomes available from the aggregator framework, such that the digital content is assigned to one or more of the content categories as selected by the user. The user definitions of the profile and the content selections of the user are used to determine the contents of the updated digital content obtained by the reader. An aggregator framework is also provided that is configured to communicate with the reader.
Owner:MATHENY JOSEPH +1
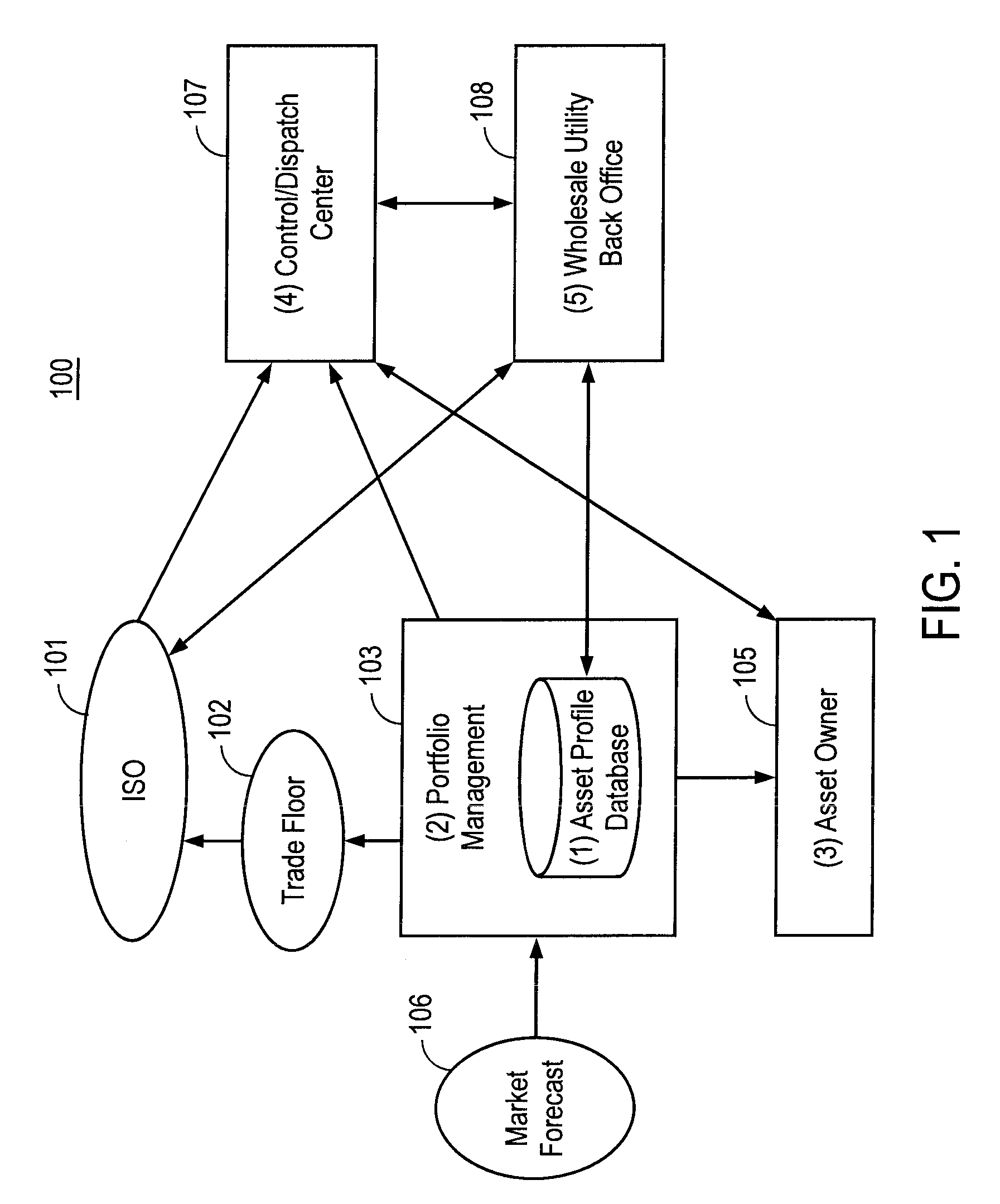
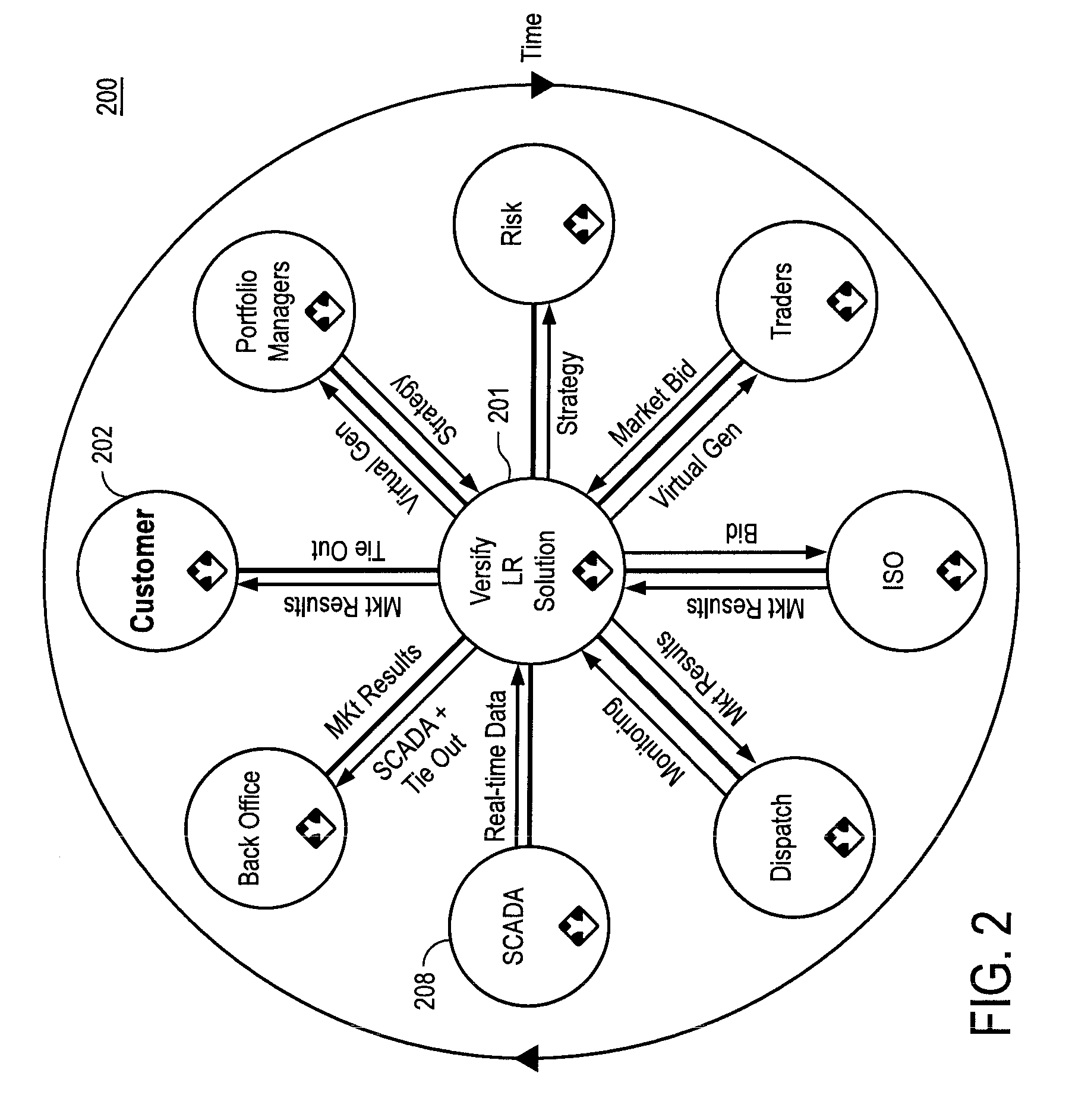
Aggregator, monitor, and manager of distributed demand response
ActiveUS8260468B2Facilitate power capacity to powerReduce loadMarket predictionsLevel controlPower gridNews aggregator
The invention broadly encompasses a system including a database to store demand response data, the demand response data including demand response agreement parameters, demand response load and energy demand characteristics of one or more demand response customers, the demand response load characteristics including power consumption capacity of each of one or more demand response loads, an aggregator to aggregate the demand response loads based on the demand response data and forecast data into a demand response portfolio, a monitor to monitor power demand of one or more demand response customers and one or more power grids, and a dispatcher to notify the one or more demand response customers of the demand response portfolio and to notify a utility of a response from the one or more demand response customers whether to control the demand response load to return the power consumption capacity of the demand response load back to the one or more power grids.
Owner:MCG VERSIFY ACQUISITION LLC
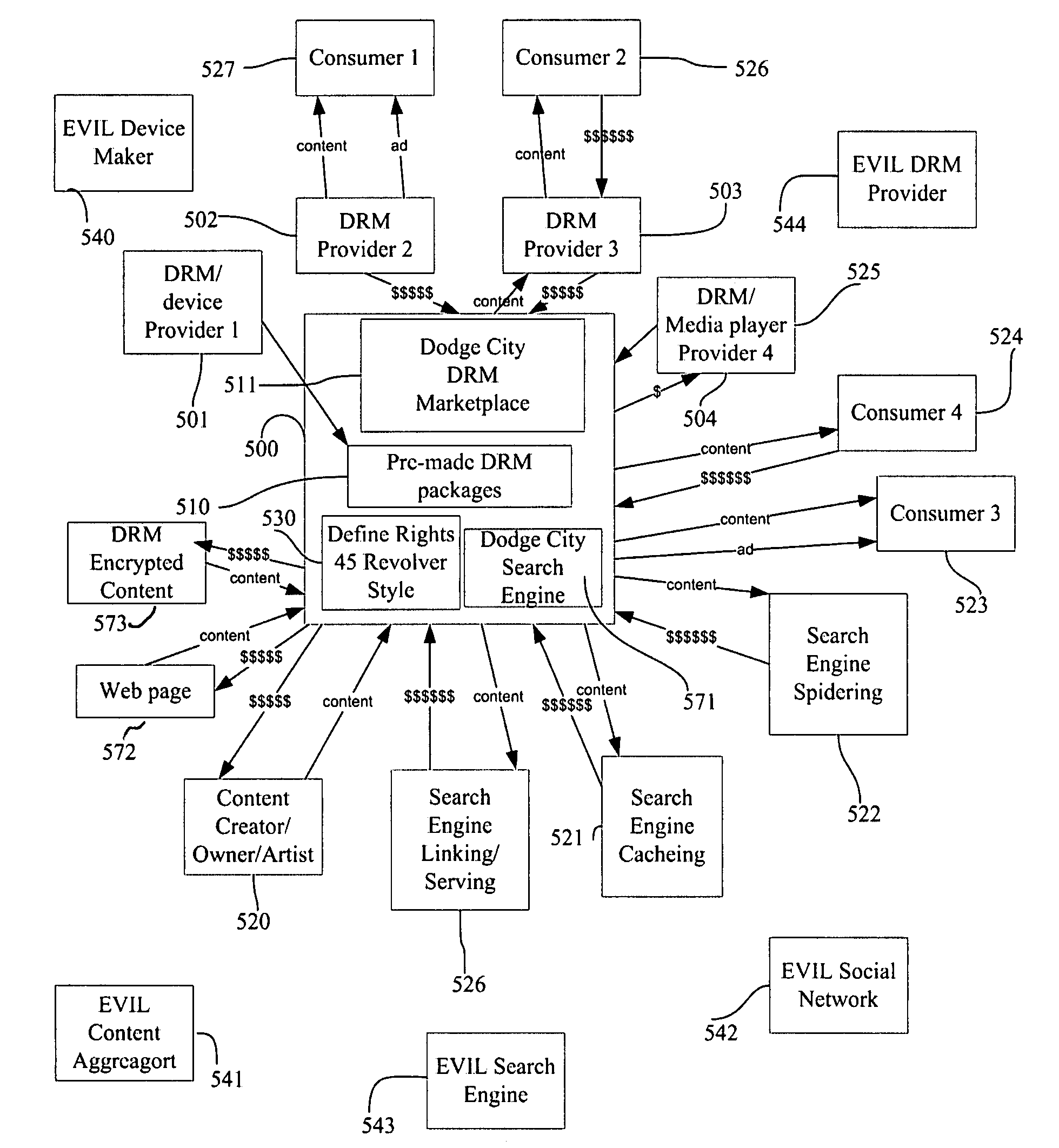
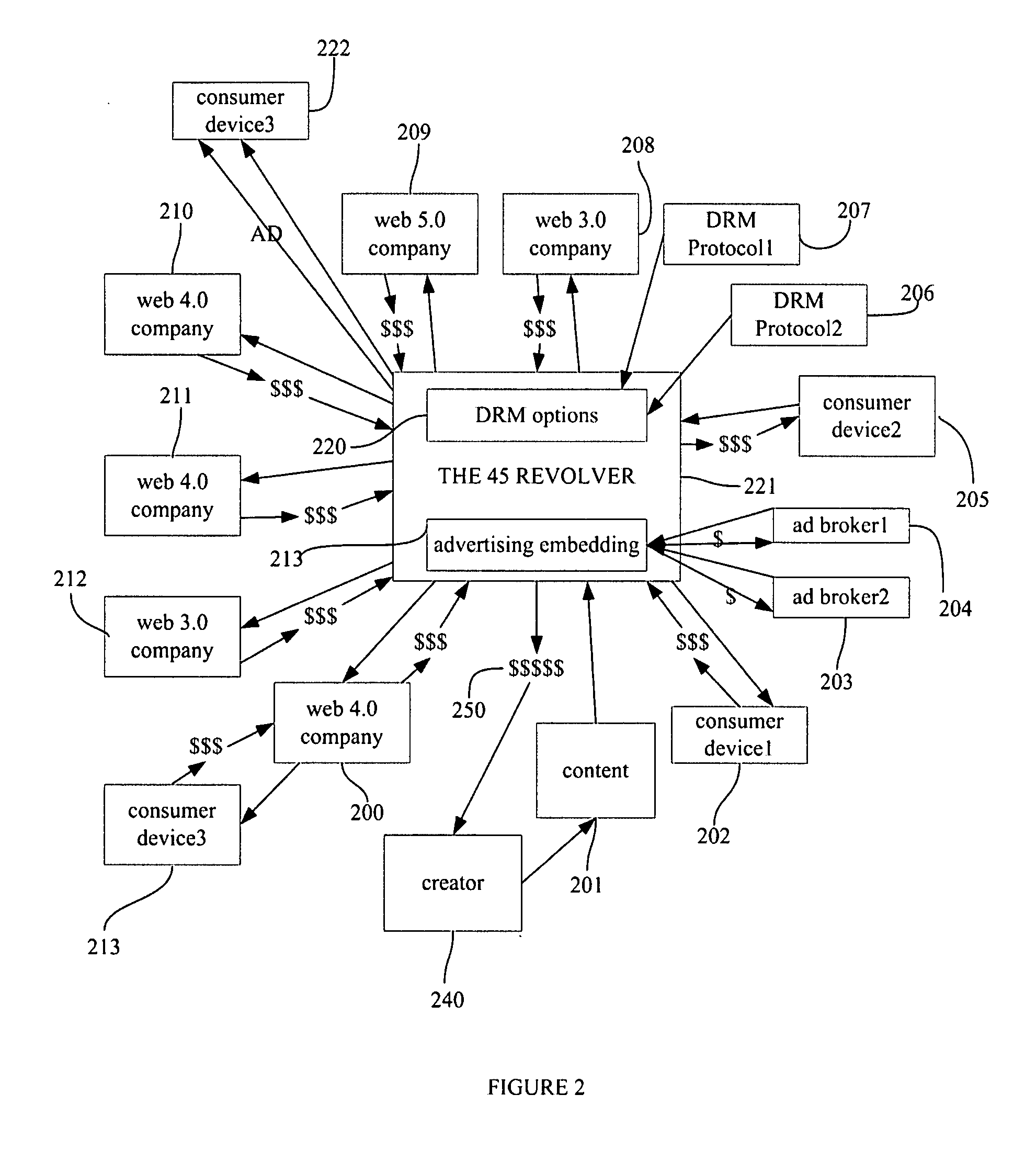
System and method for content marketplace, DRM marketplace, distribution marketplace, and search engine: the dodge city marketplace and search engine
InactiveUS20070255965A1Great dealGood wayUnauthorized memory use protectionHardware monitoringService provisionMarket place
The present invention offers novel and superior means for creating a content marketplace. The present invention allows technology companies to compete to meet and serve the creators' rights. Just as reverse auction systems allow consumers to name their price, with service providers competing to meet the price, the present invention allows artists, creators, and content owners to define their rights, whereupon content aggregators, record labels, social networks, DRM providers, device manufacturers, search engines, and others compete to bets meet the creators' needs. This innovation reflects the fact while technology companies are commodities, and thus artists ought declare their independence, and ascend to their natural place in the universe—those who take the risks and create the wealth on their Heroes' Journeys ought reap the rewards. The Dodge City Marketplace will lead to greater revenue and rights for artists, superior search engines, distribution, and art, and trusted standards for DRM.
Owner:MCGUCKEN ELLIOT
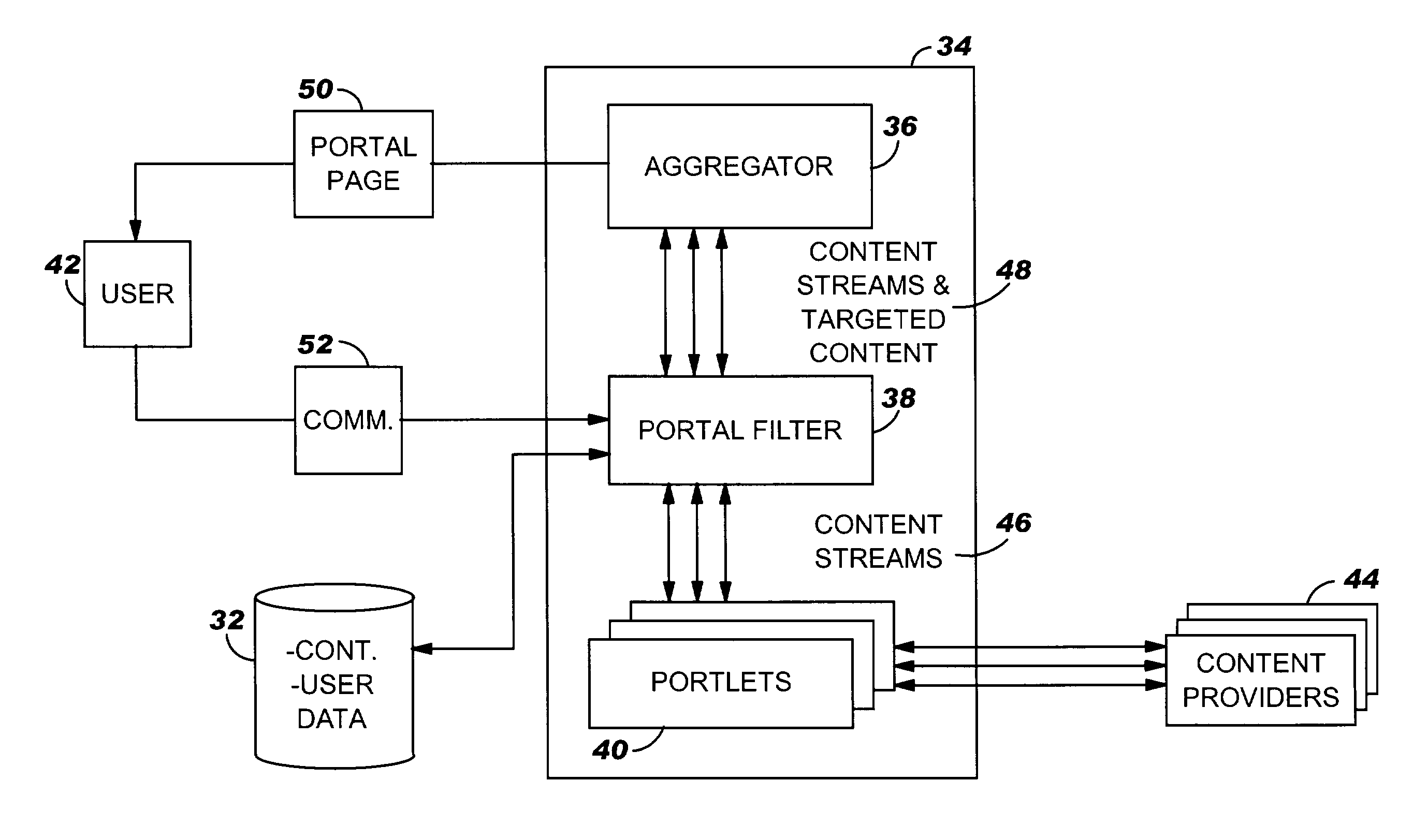
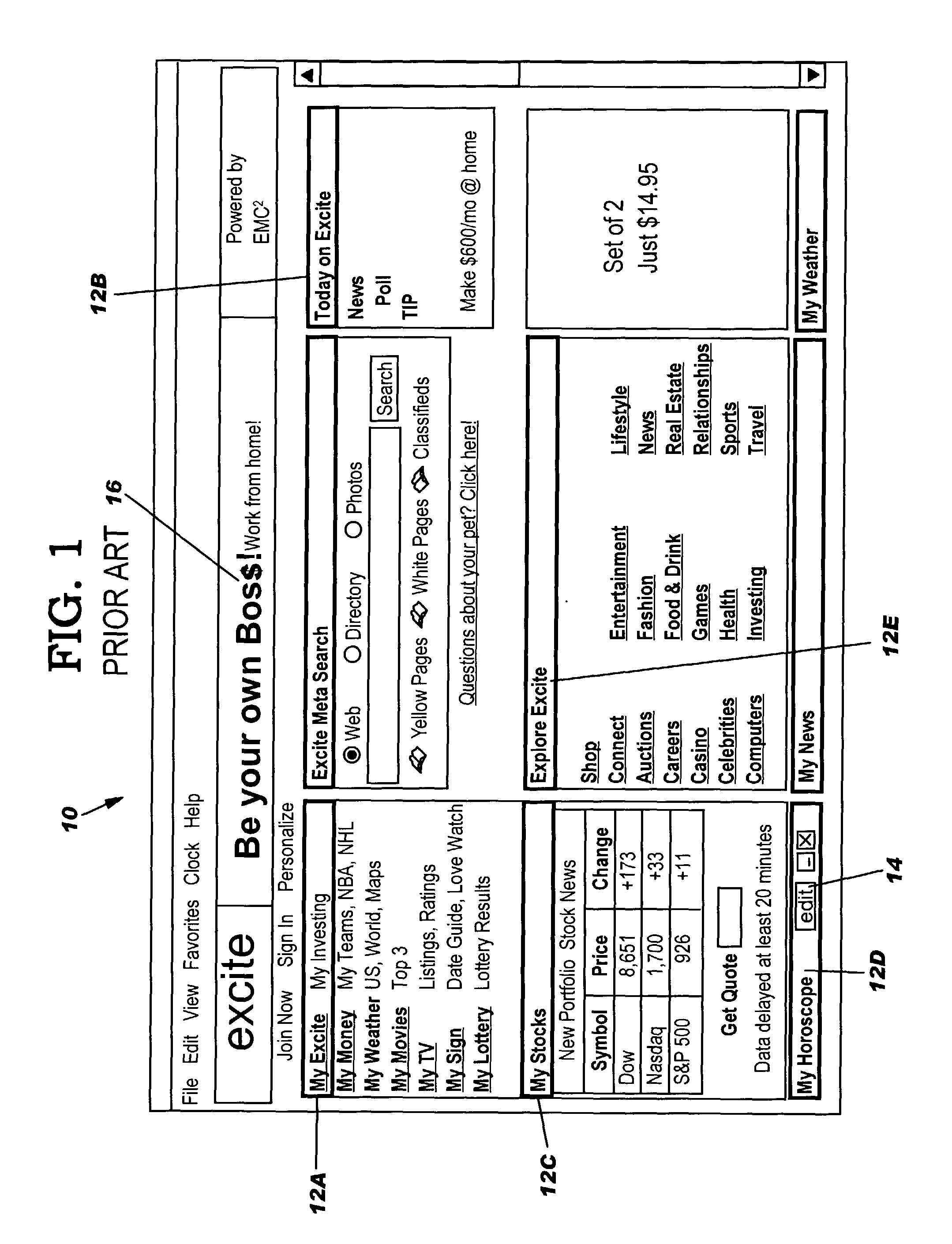
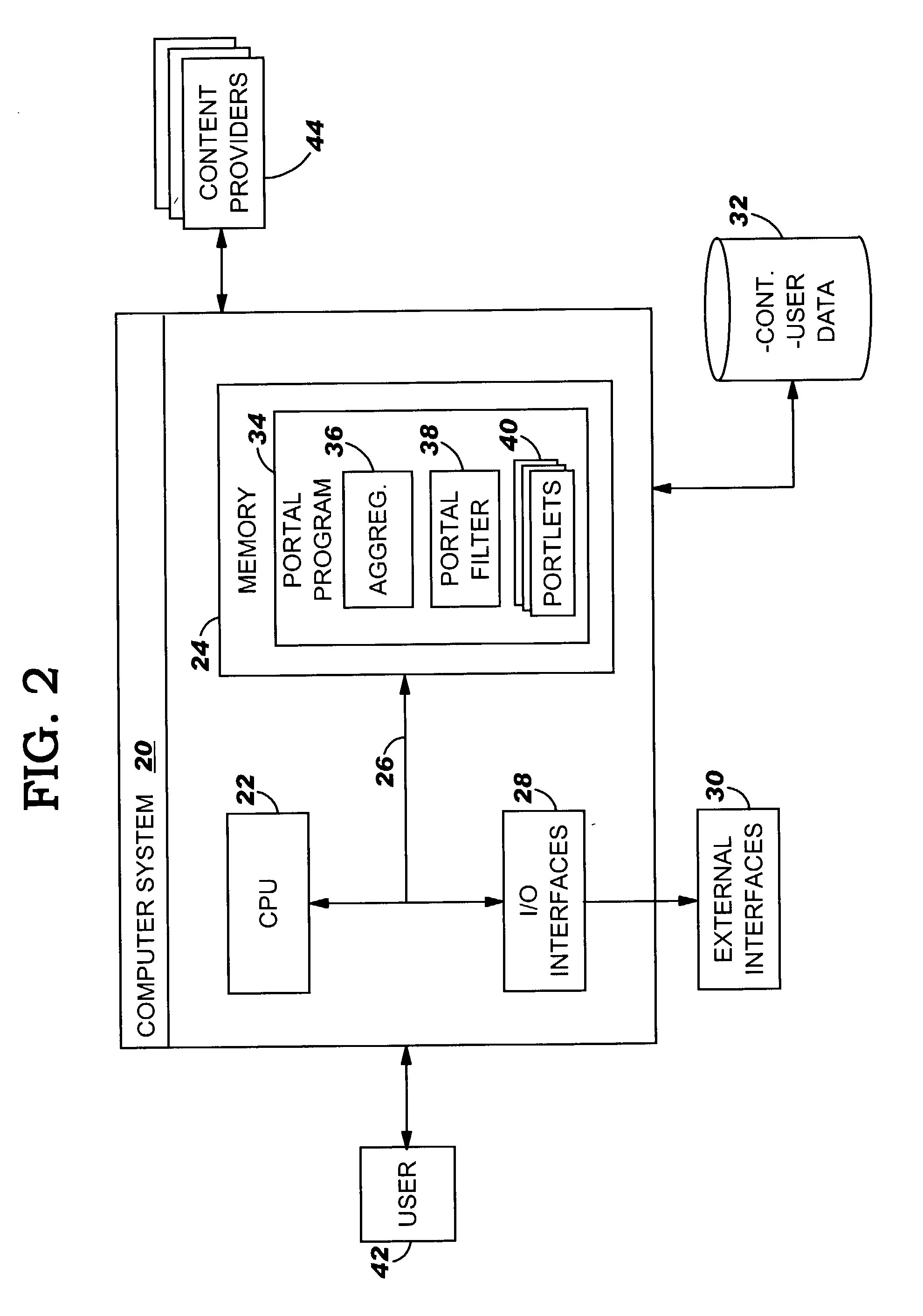
System, method and program product for inserting targeted content into a portlet content stream
A system, method and program product for inserting targeted content into a portlet content stream is provided. Specifically, the present invention provides a portal program that includes a container-managed portlet filter for inserting targeted web content into a portlet content stream based on a desired display mode of the portal user. Under the present invention, web content is obtained by a portlet from a content provider. Once obtained, the portlet outputs the web content as a portlet content stream to the portlet filter. The portlet filter then inserts the targeted content based on the desired display mode of the user. The combined targeted content and portlet content stream is then outputted to an aggregator where it is organized for display as a portal page.
Owner:SNAP INC
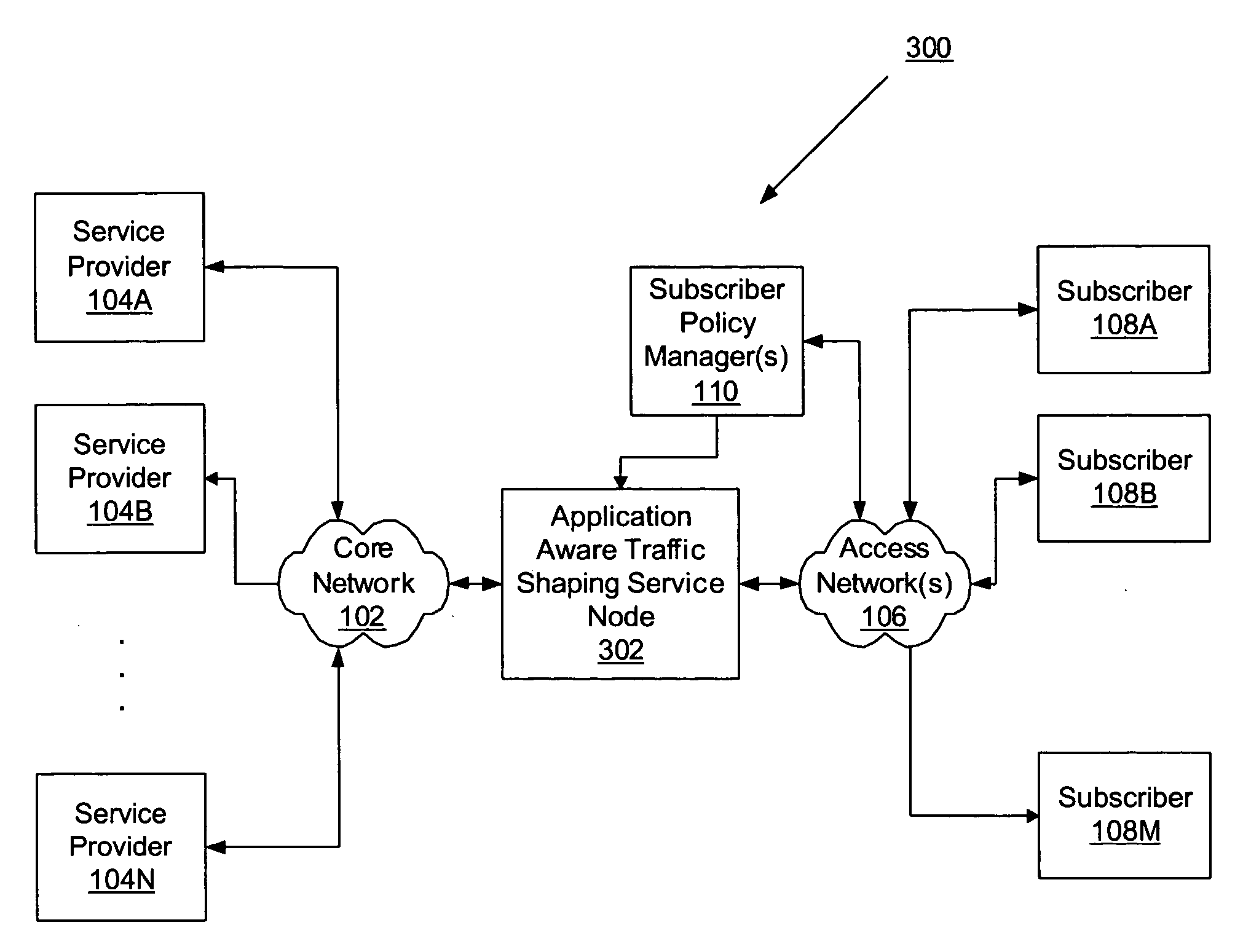
Application aware traffic shaping service node positioned between the access and core networks
ActiveUS20060233100A1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsGPRS core networkData traffic
A method and apparatus for an application aware traffic shaping service node positioned between the access and core networks is described. One embodiment of the invention enforces a per subscriber, per application traffic policy for network traffic between one or more subscribers communicatively connected through an access network and a set of one or more service providers communicatively connected through a core network. According to another embodiment of the invention enforcement of the per subscriber, per application traffic policy comprises classifying the network traffic into application level subscriber flows, maintaining real-time statistics on the application level subscriber flows and overall network element congestion, updating, in real-time, the per subscriber, per application traffic policy based on the real-time statistics and restricting bandwidth and dropping packets on the application level subscriber flows as necessary to enforce the per subscriber, per application traffic policy. Another embodiment of the invention is a passthrough mode where the data traffic is transmitted by the traffic in the same manner as received by the traffic shaping service node. Yet another embodiment of the invention is a combined service node with integral edge routing and traffic aggregator.
Owner:TELLABS COMM CANADA
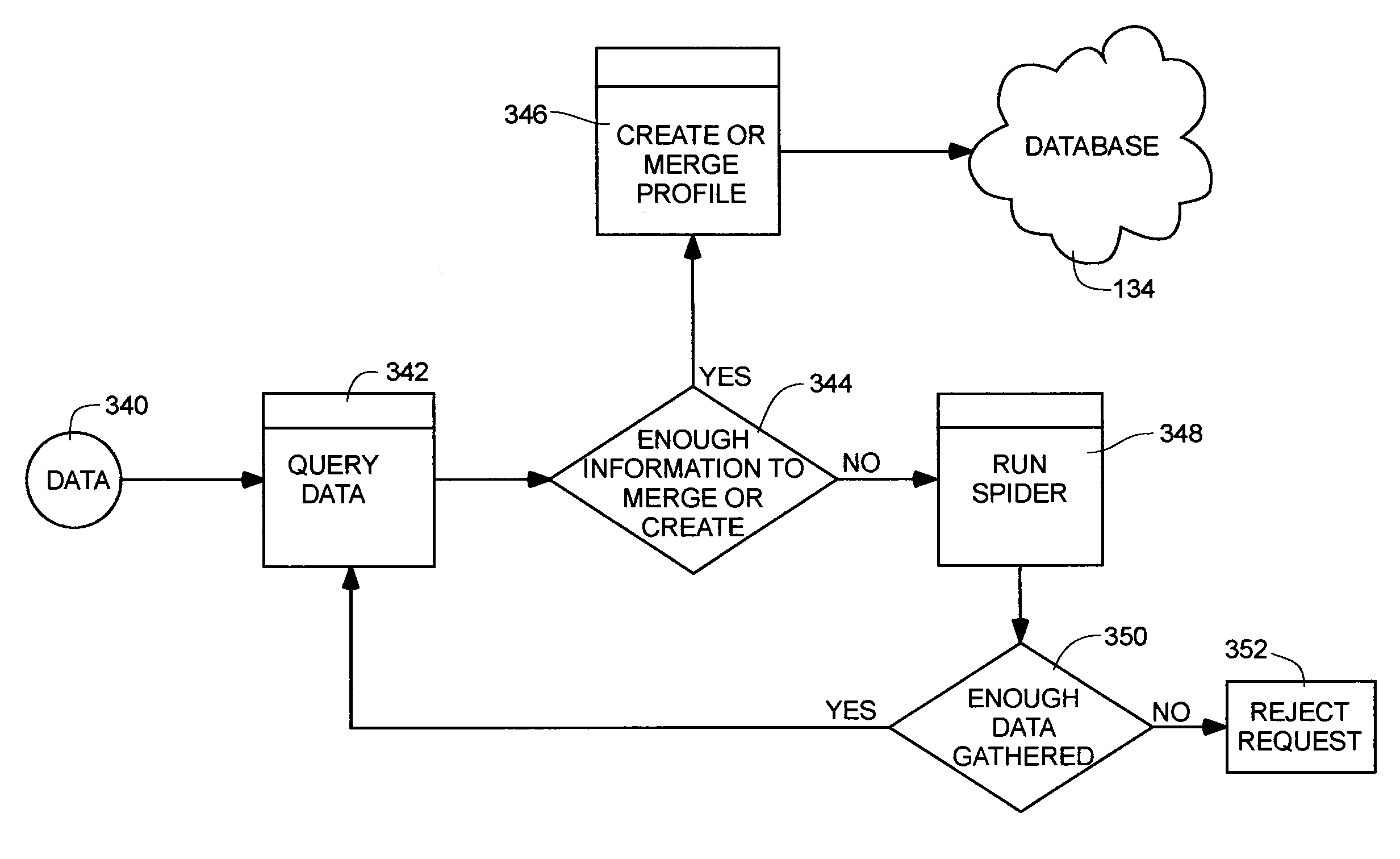
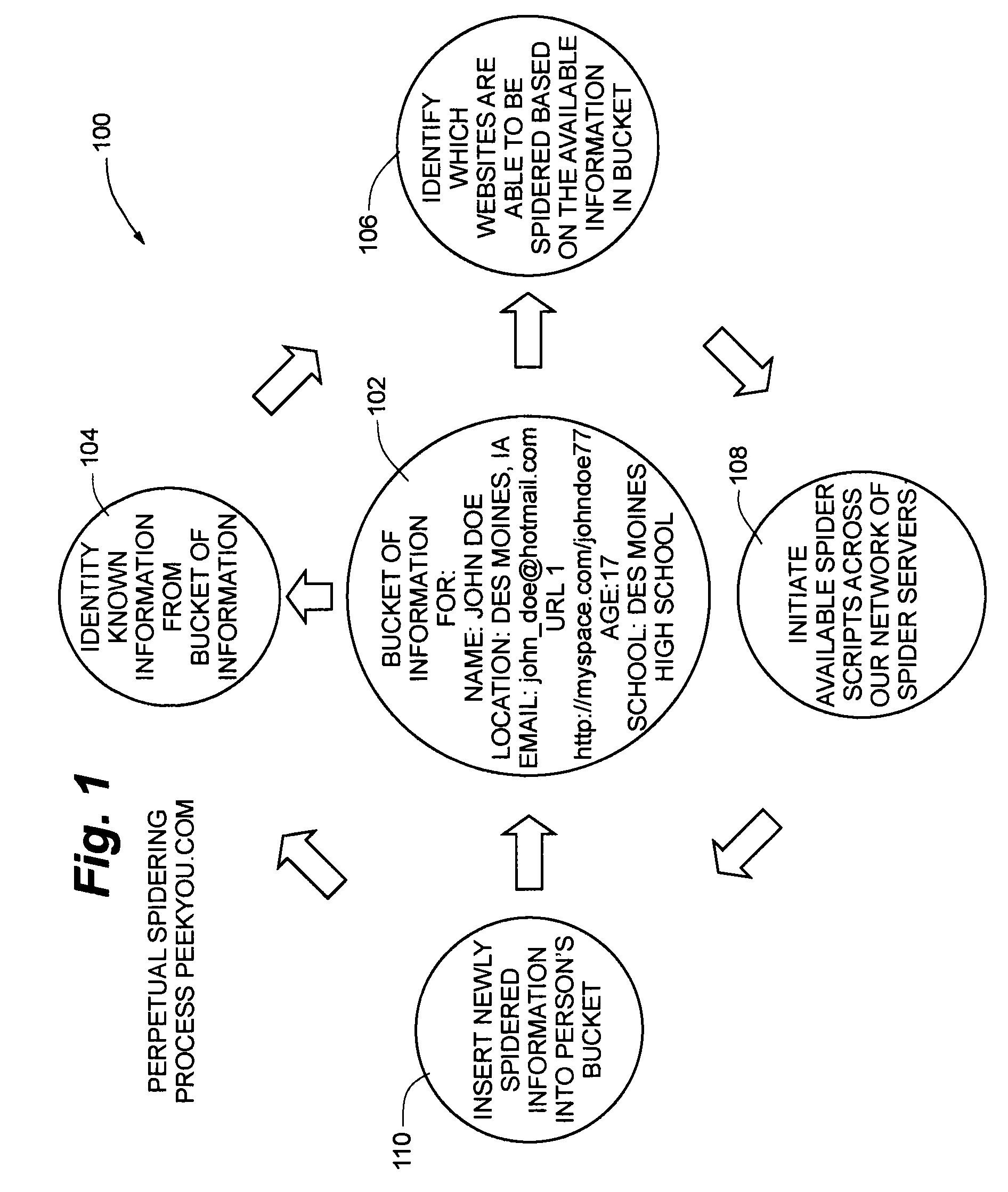
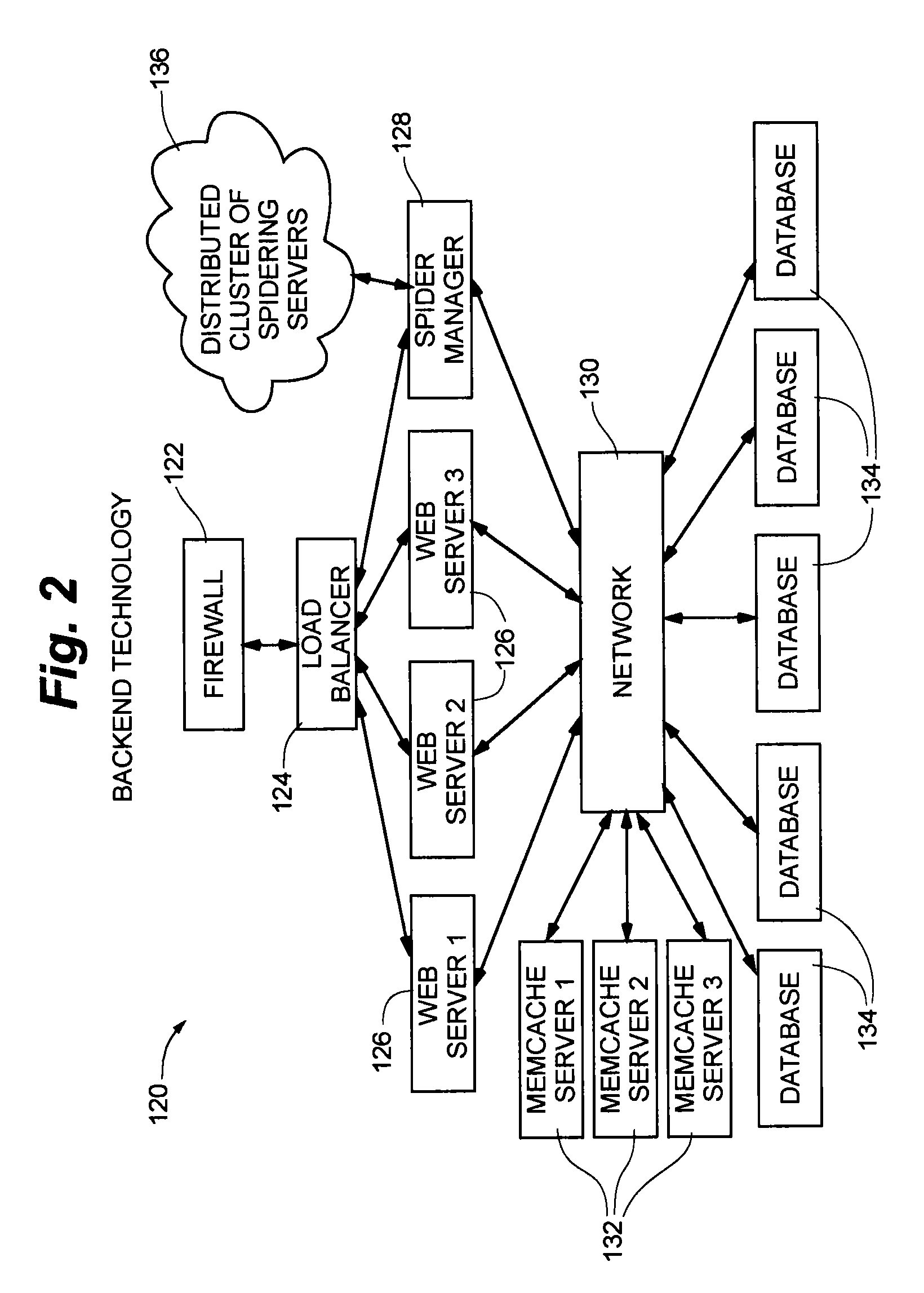
Distributed personal information aggregator
ActiveUS20100010993A1Digital data information retrievalSpecial data processing applicationsNews aggregatorData science
A method of aggregating personal information available from public sources over a network. The method includes the steps of receiving at a computer server, data associated with a person, the data being publicly available over a network, and including at least a first name and a last name; using a processor to compare the received data to a plurality of data profiles stored in a database of one or more memory devices, each profile corresponding to a previously-profiled person and containing data associated with the previously-profiled person; determining whether the received data sufficiently matches data associated with the previously-profiled person of the data profile; and merging the received data with the data associated with the previously-profiled person.
Owner:PEEKANALYTICS
Aggregation of social network data
InactiveUS20110179161A1Multiple digital computer combinationsOffice automationApplication softwareNetwork data
A method, system, and computer program product for aggregation of social network data on a user's local system are provided. The system at the user's local system includes: a processor; a private social network data collector for collecting private social network data relating to a user from applications on a user's local system; a receiver for receiving public social network data at the user's local system; and a local aggregator for combining the private social network data with the public social network data on the user's local system. The combined private and public social network data is only accessible by or with the permission of the user on the user's local system. The receiver may receive aggregated public social network data relating to the user from a public aggregator on a server system, wherein the aggregated public social network data is collected from public sources.
Owner:IBM CORP
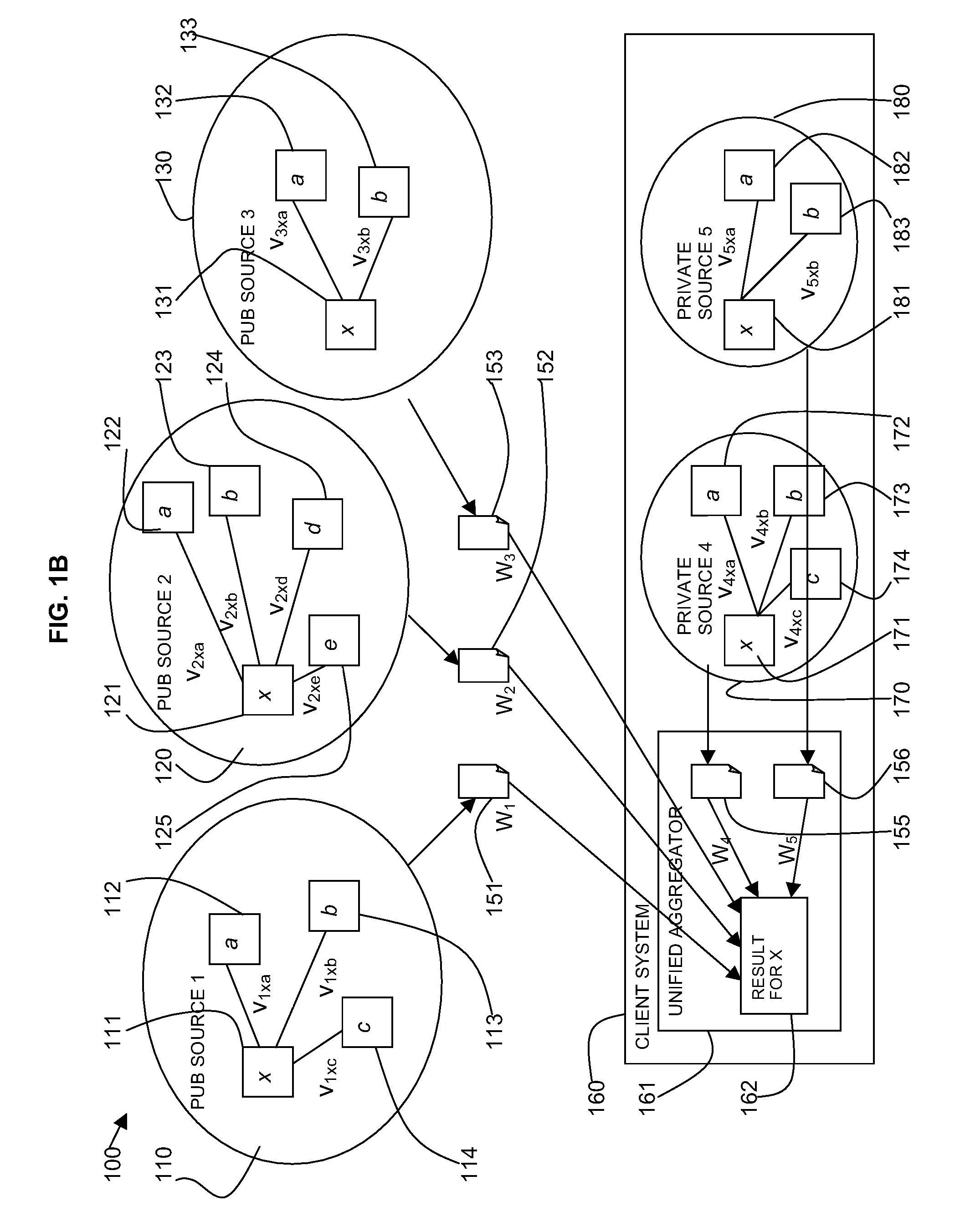
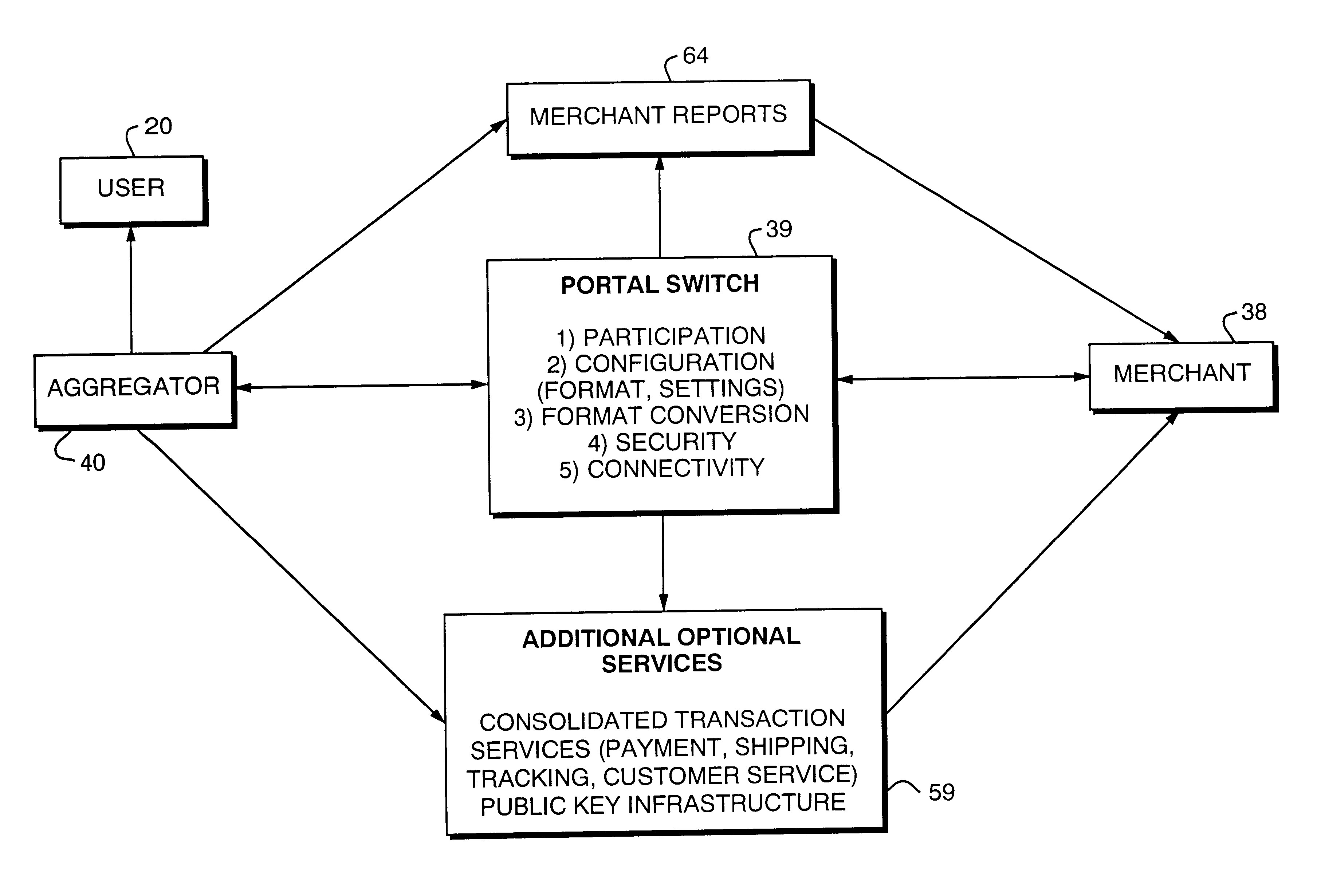
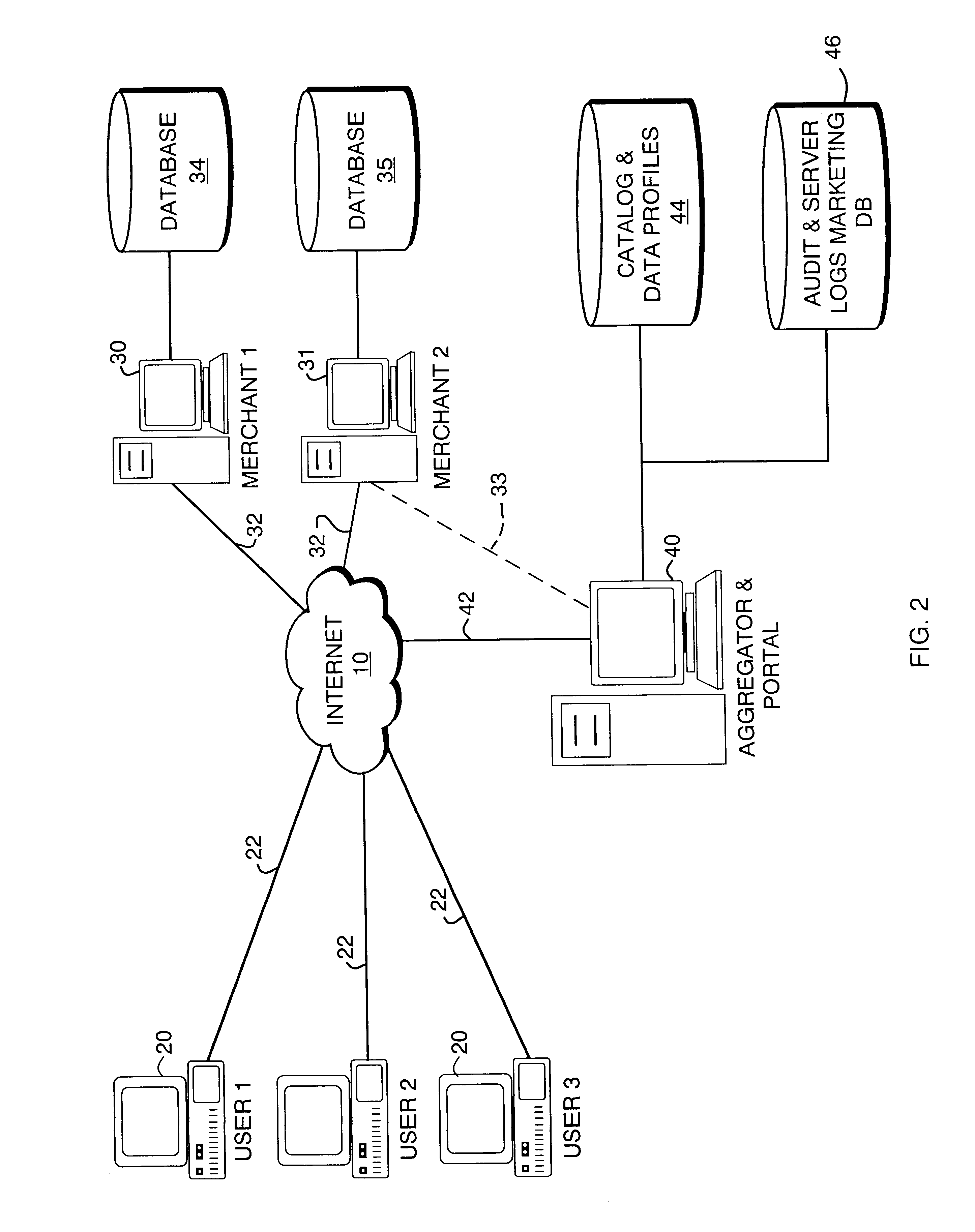
Portal switch for electronic commerce
InactiveUS6907401B1Easy to useBuying/selling/leasing transactionsSpecial data processing applicationsE-commerceNews aggregator
A portal switch is provided that controls participation of merchants in on-line aggregators, such as portals, used for buying and selling goods and services. Merchants may enable or disable participation in an aggregator site by turning on or off software settings. When participation is enabled, the merchant's site makes its catalog entries and merchant profile available to the aggregator. By enabling or disabling the switch, the merchant actively expresses a willingness to participate in (or, conversely, a desire to be excluded from) the aggregator.
Owner:LEVEL 3 COMM LLC +1
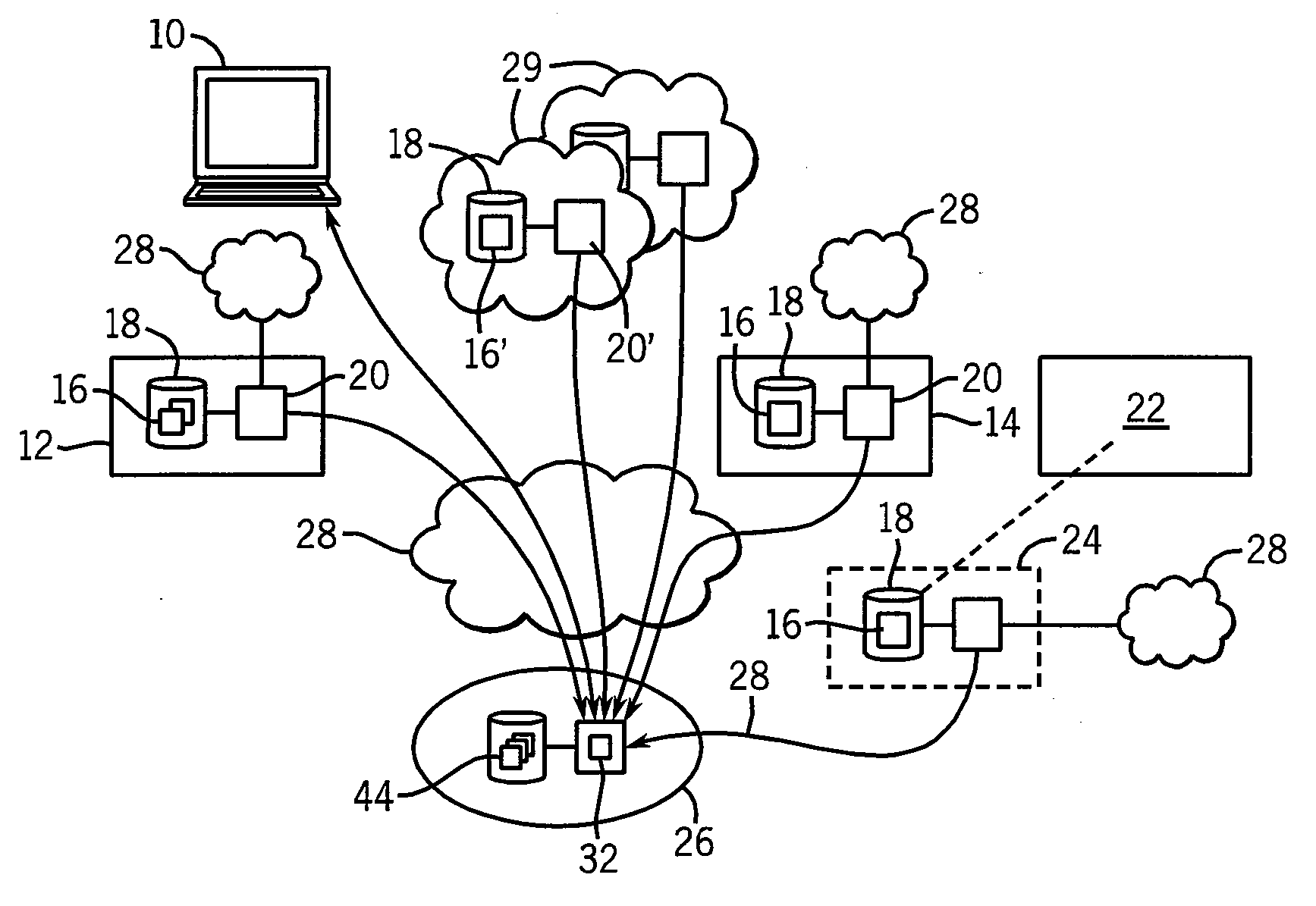
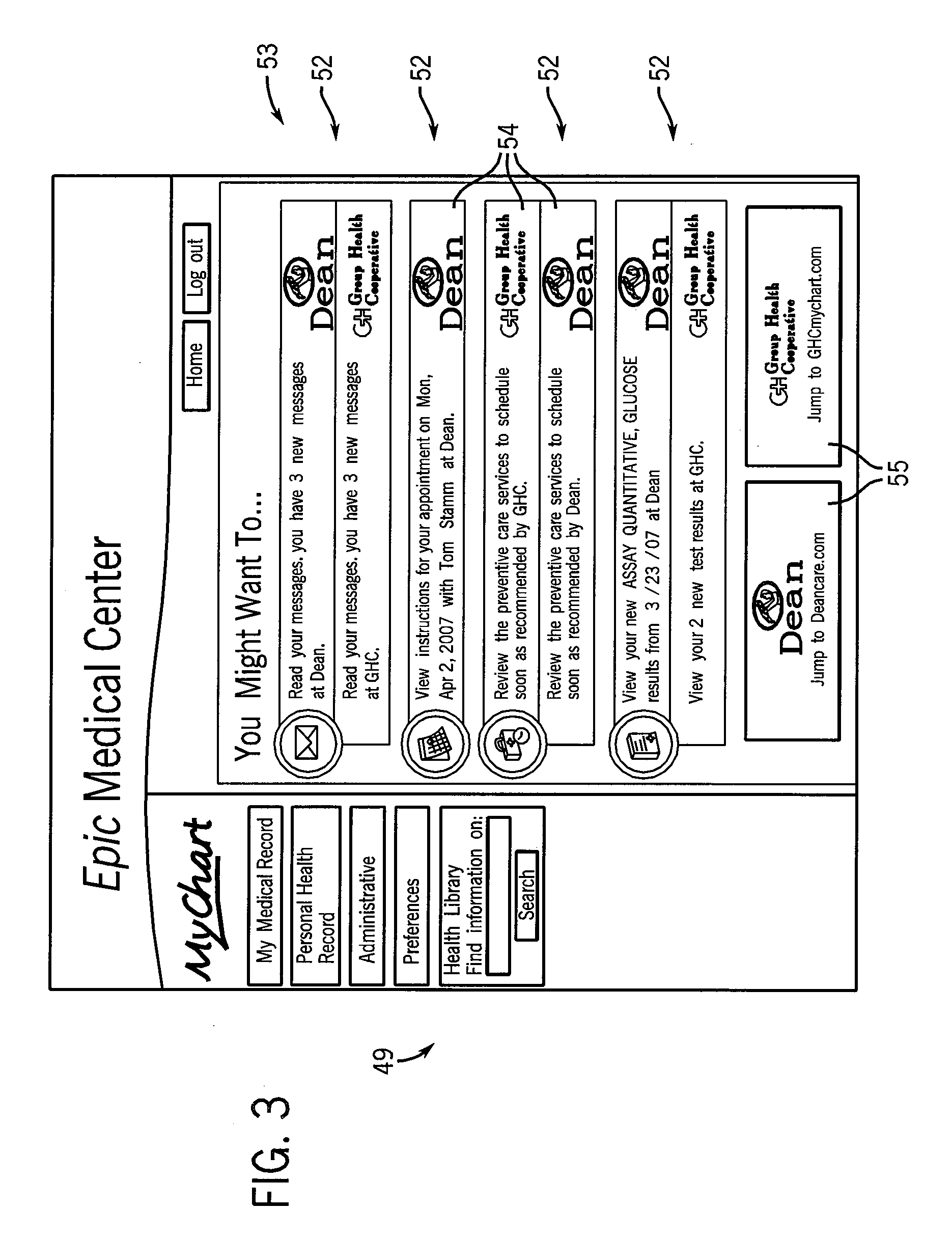
Method and apparatus for accommodating diverse healthcare record centers
InactiveUS20090216562A1Preserving an incentive structure for accurate and complete recordkeepingMinimal disruptionMedical data miningData processing applicationsMedicineSimultaneous visualization
Owner:EPIC SYST CORP (US)
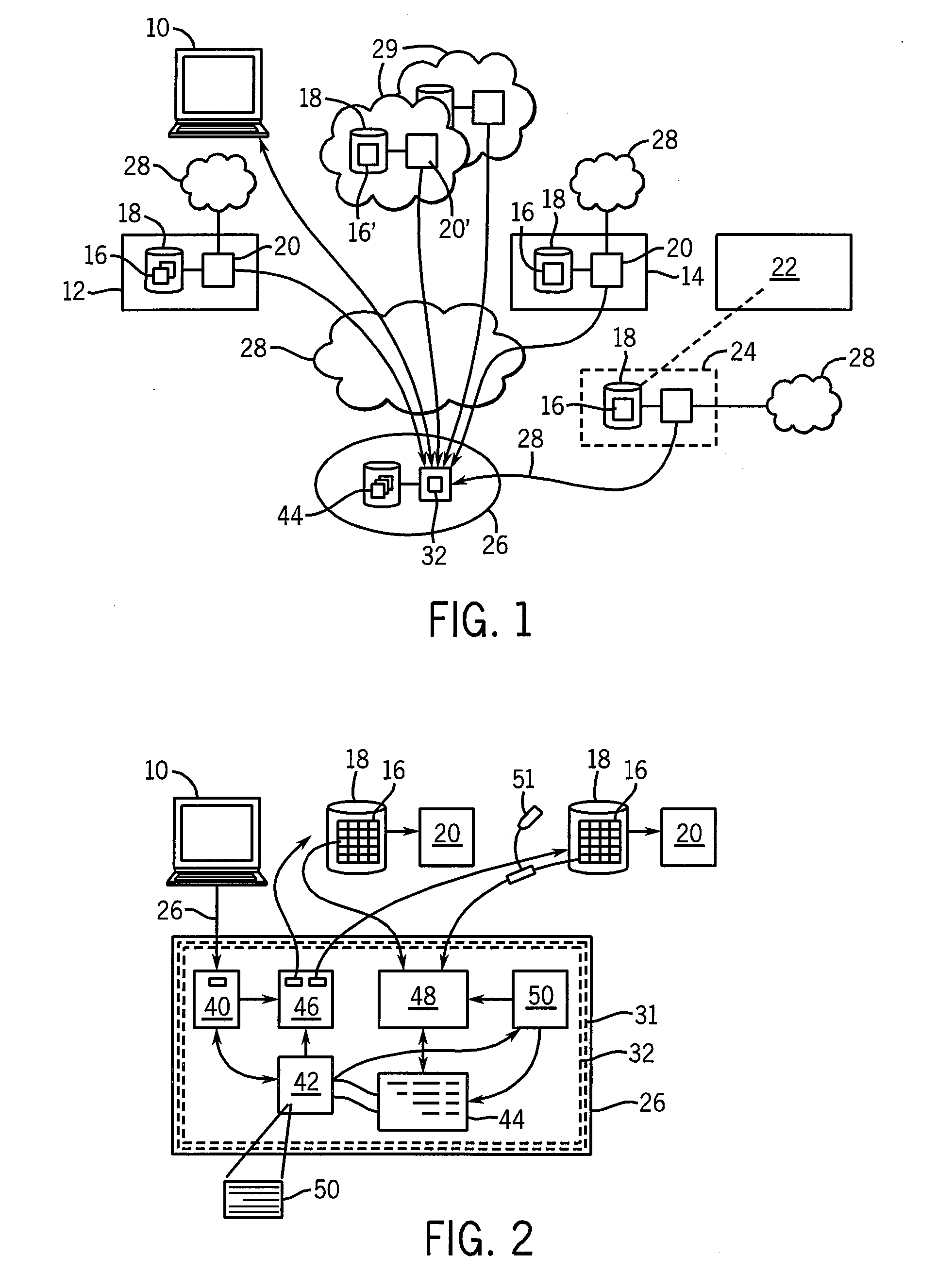
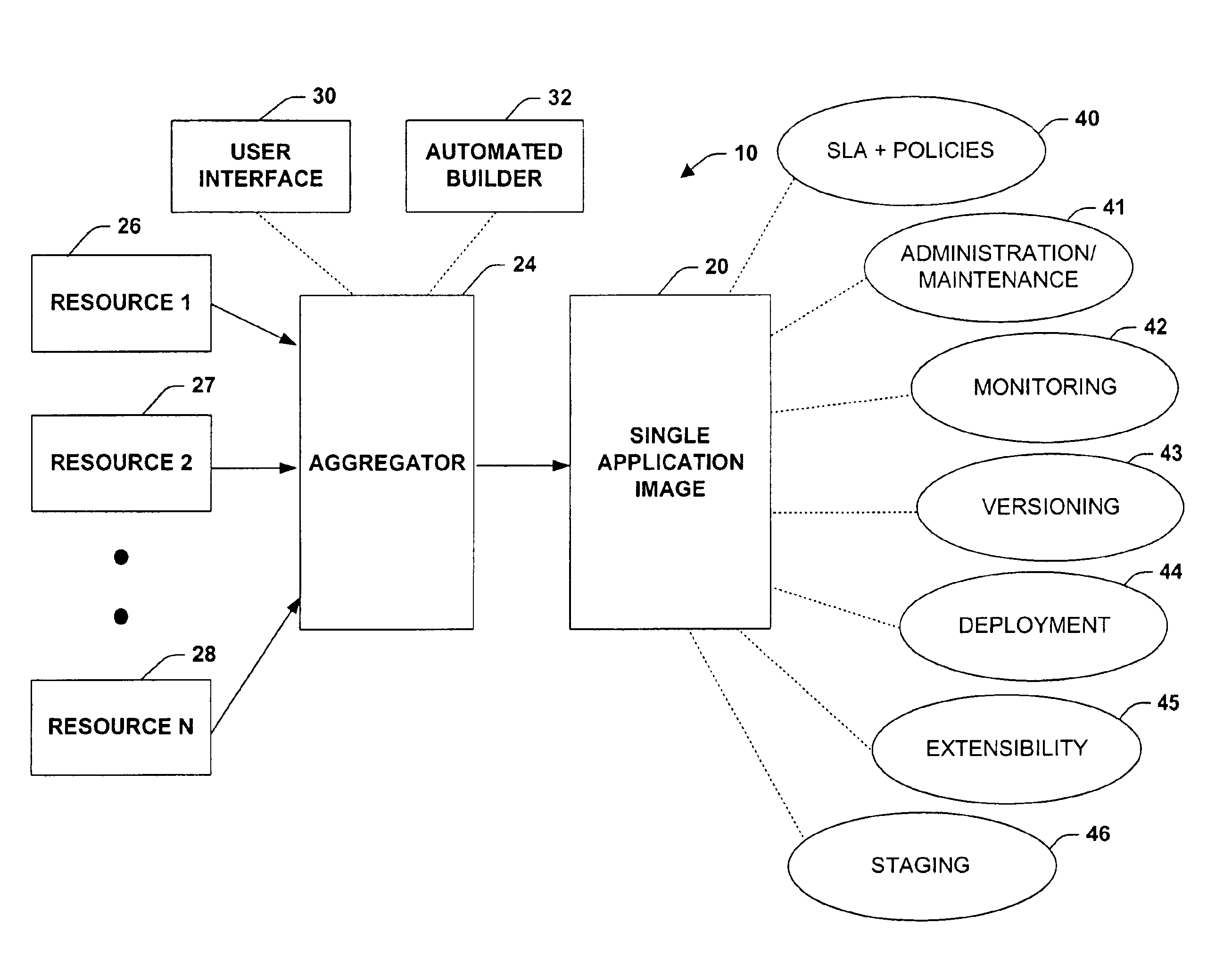
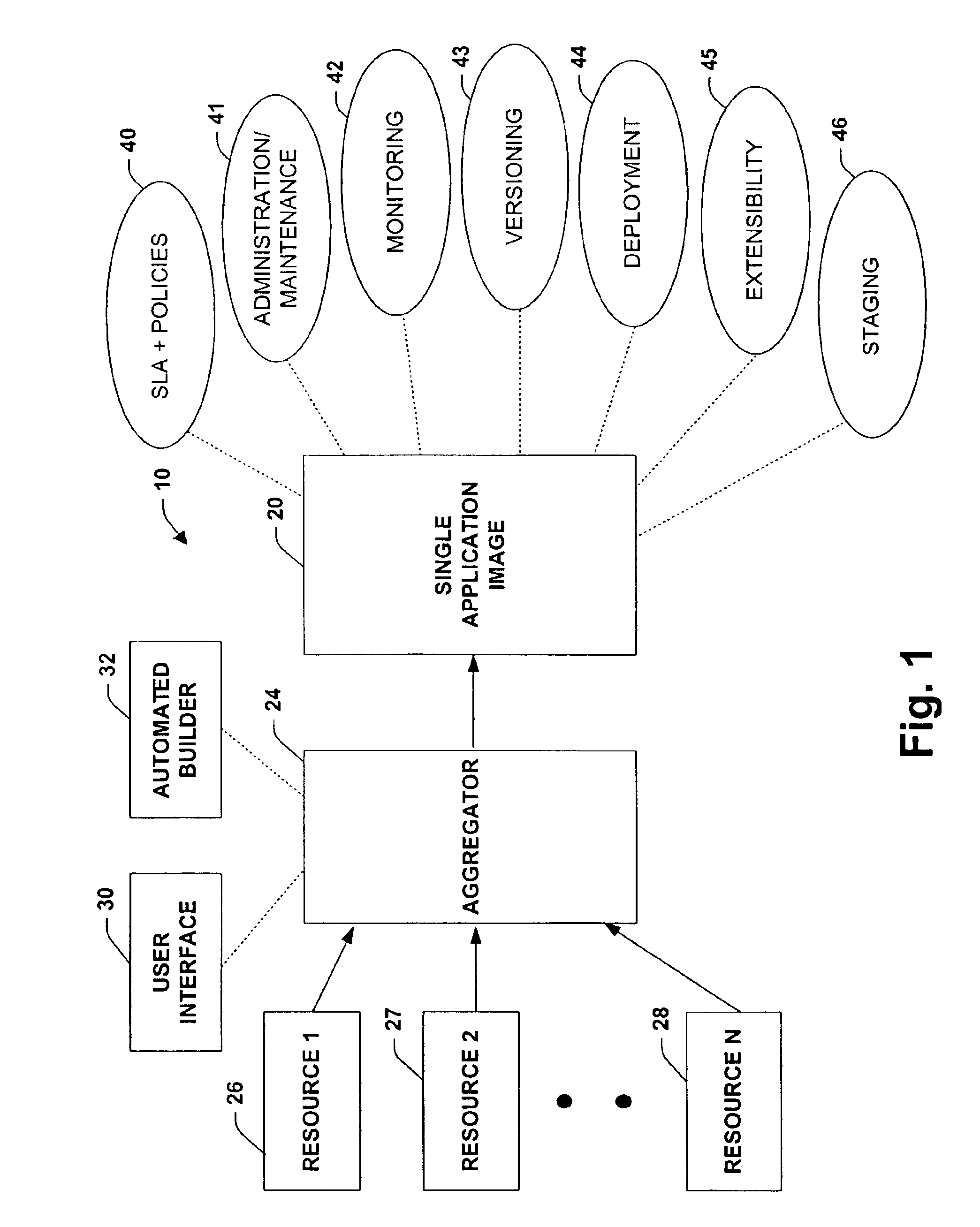
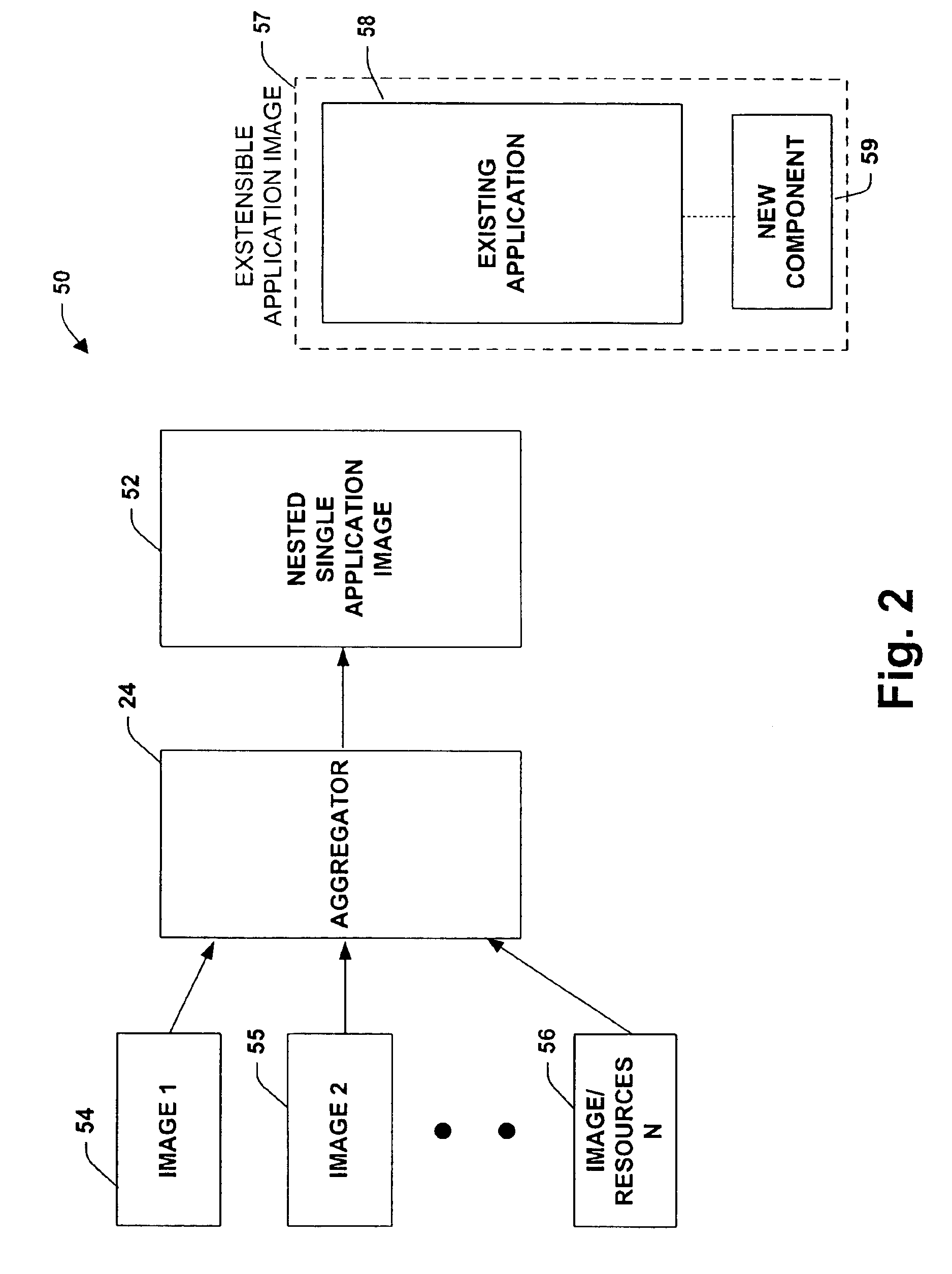
System and method providing single application image
InactiveUS6868539B1Shorten the timeReduce complexitySoftware designProgram loading/initiatingGraphicsGraphical user interface
A system and method is provided that facilitates the administration of an application in accordance with the present invention. The system includes a resource identifier that identifies resources associated with the application and a manifest that logs the resources. An aggregator is provided that aggregates a subset of the resources into the manifest to facilitate administration of the application. The aggregator can be provided by a user interface and / or an automated builder. A graphical user interface is also provided to facilitate deployment, creation and enumeration of the application.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
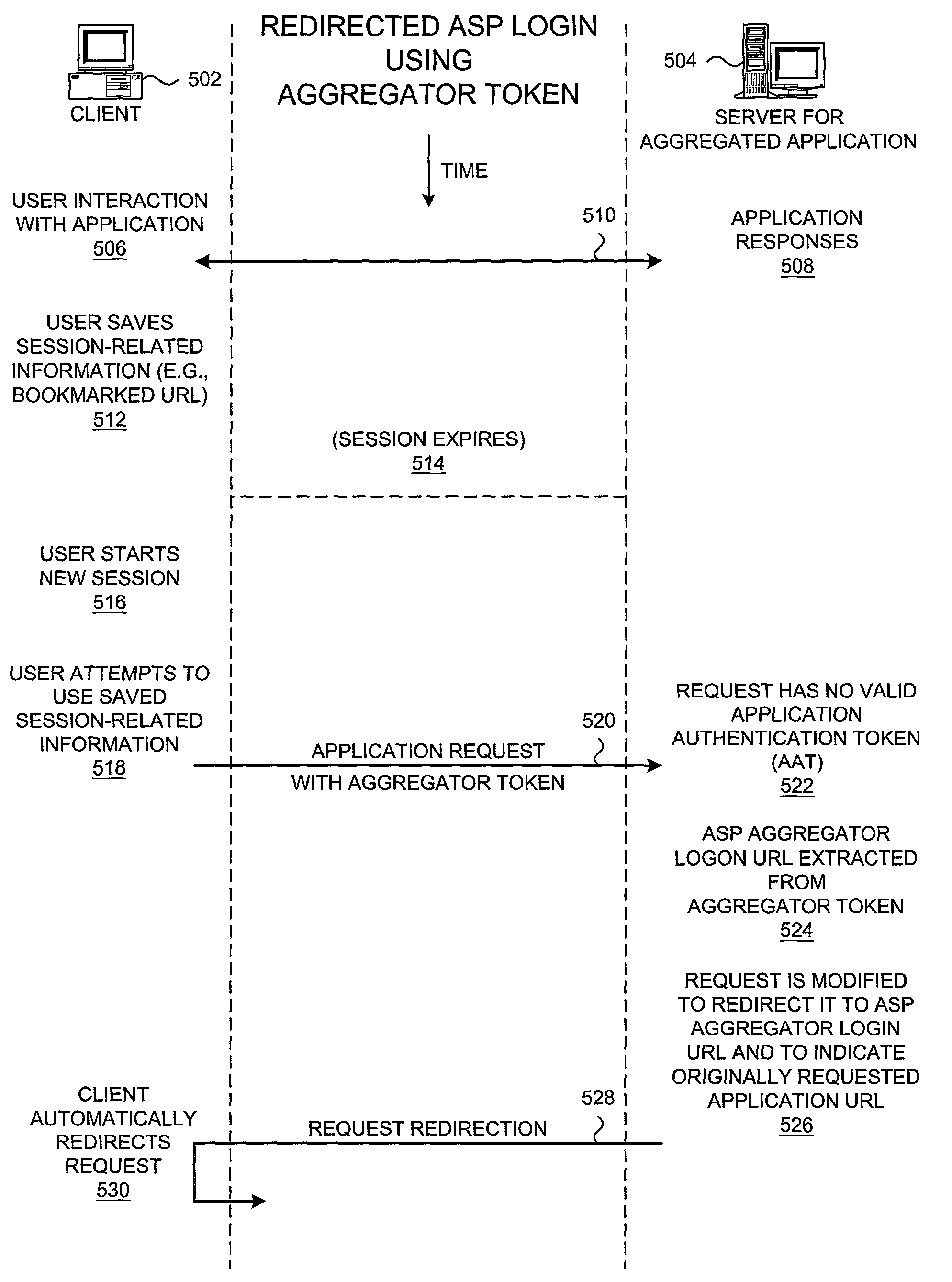
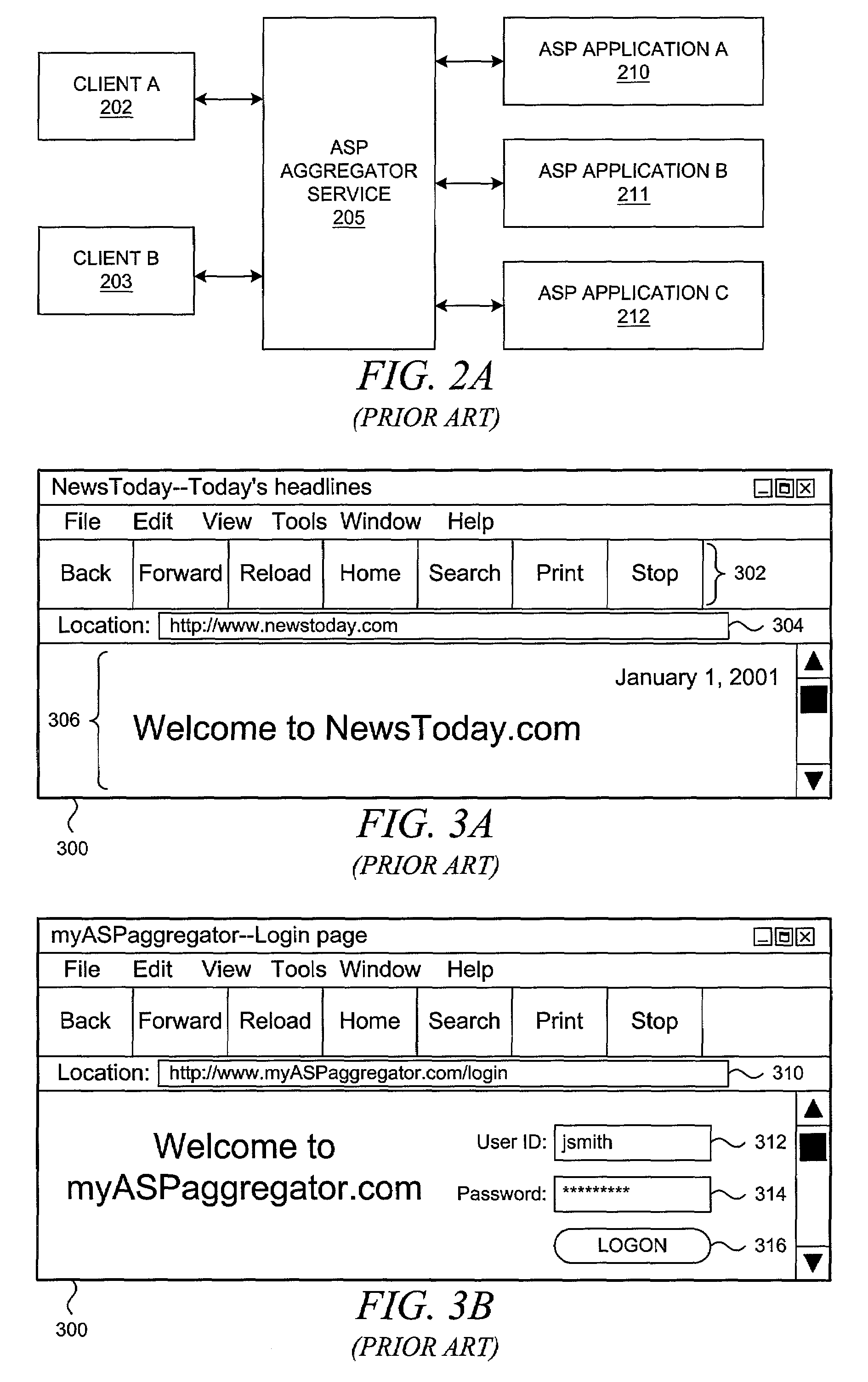
Method and system for a single-sign-on mechanism within application service provider (ASP) aggregation
InactiveUS7530099B2Digital data processing detailsMultiple digital computer combinationsUser needsApplication service provider
A methodology for providing a single-sign-on mechanism within an ASP aggregator service is presented. An aggregator token is generated by an ASP aggregator service and sent to a client device after its user has been successfully authenticated during a single-sign-on operation that is provided by the ASP aggregator service. The aggregator token then accompanies any request from the client to aggregated applications within the ASP aggregator service's infrastructure. The aggregator token comprises an indication of an address or resource identifier within the ASP aggregator service to which a client / user can be redirected when the client / user needs to be authenticated by the ASP aggregator service. In other words, the address / identifier is associated with a logon resource; when a request from a client is sent to this address, the ASP aggregator service responds with an authentication challenge to force the user to complete a single-sign-on operation.
Owner:AIRBNB
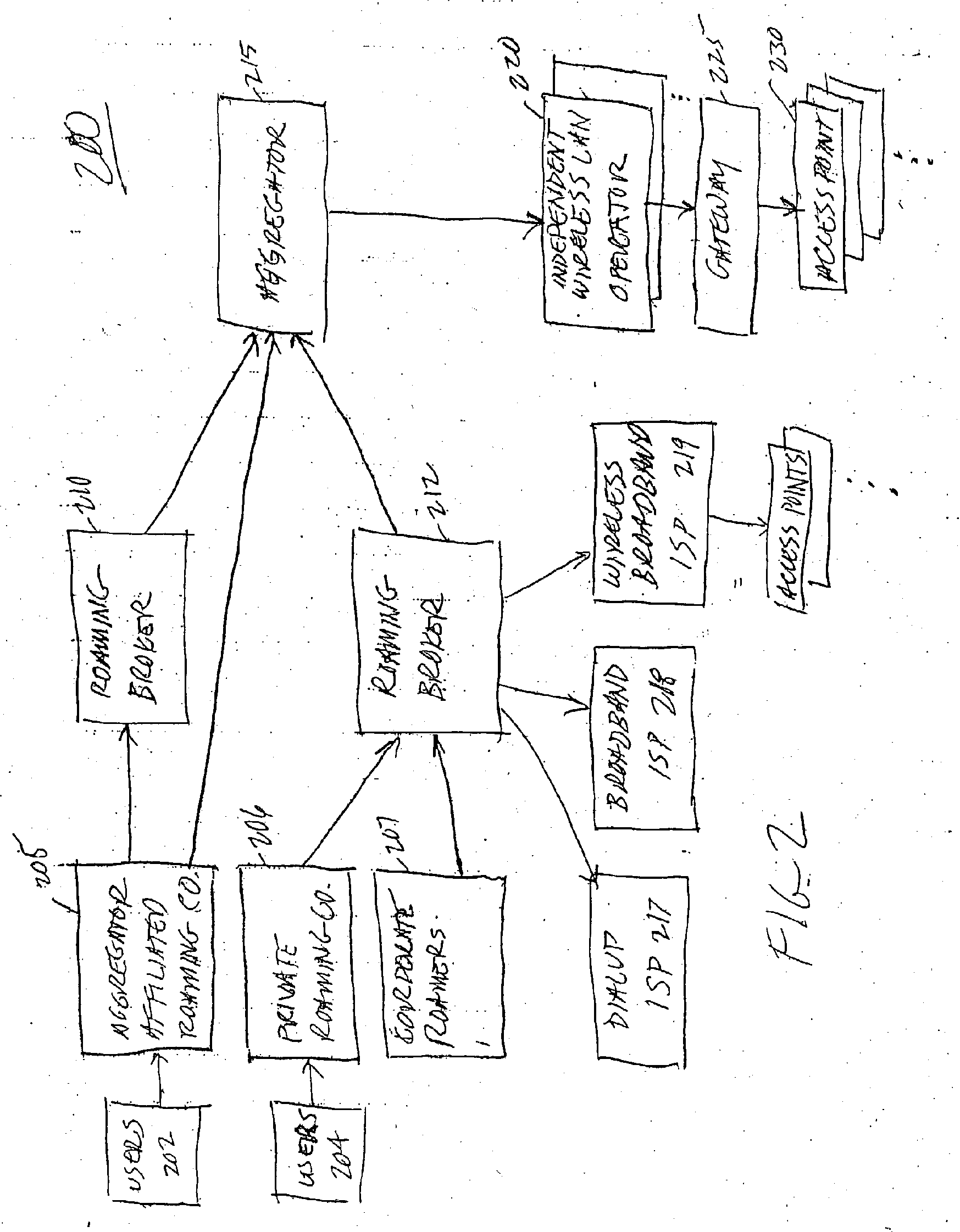
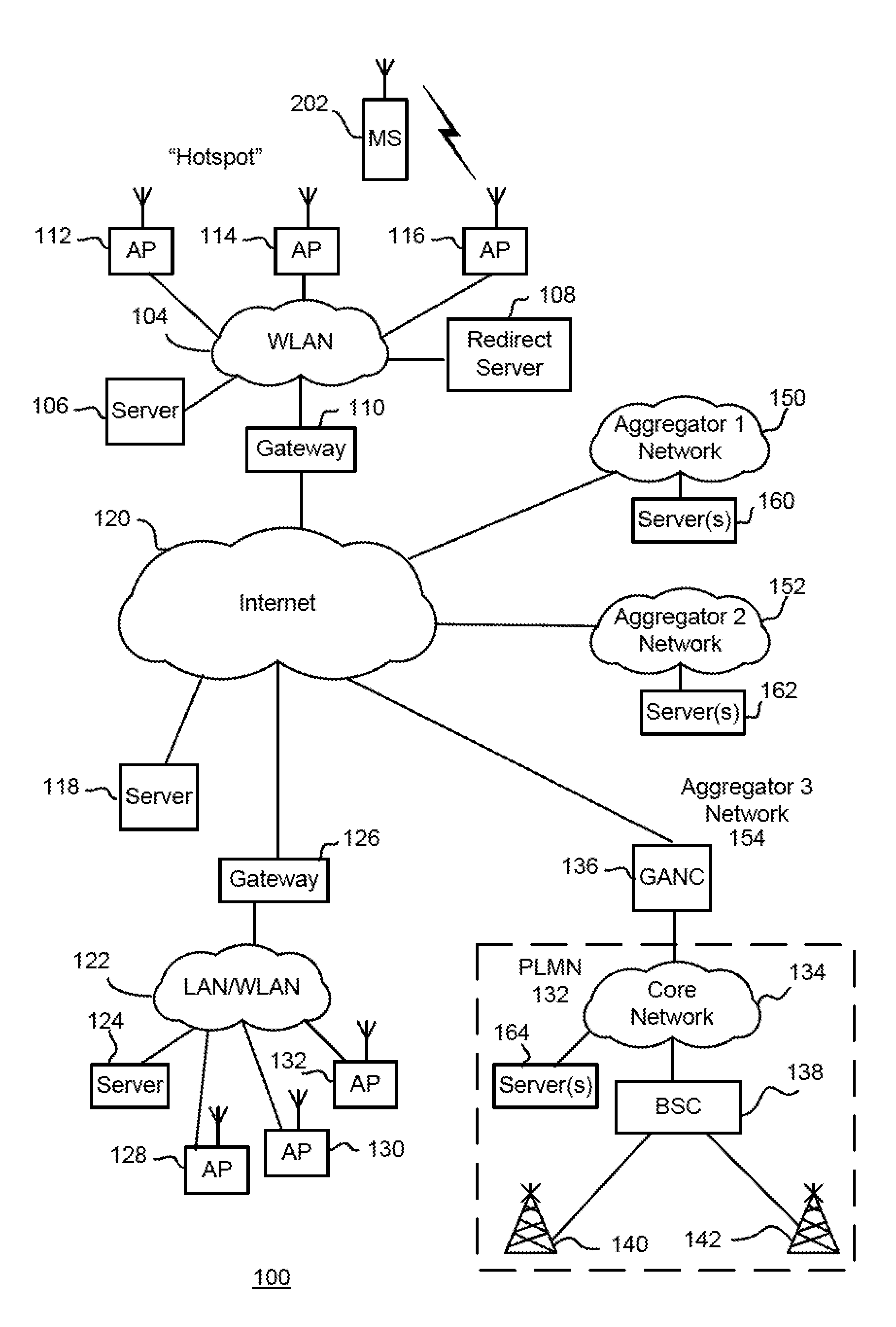
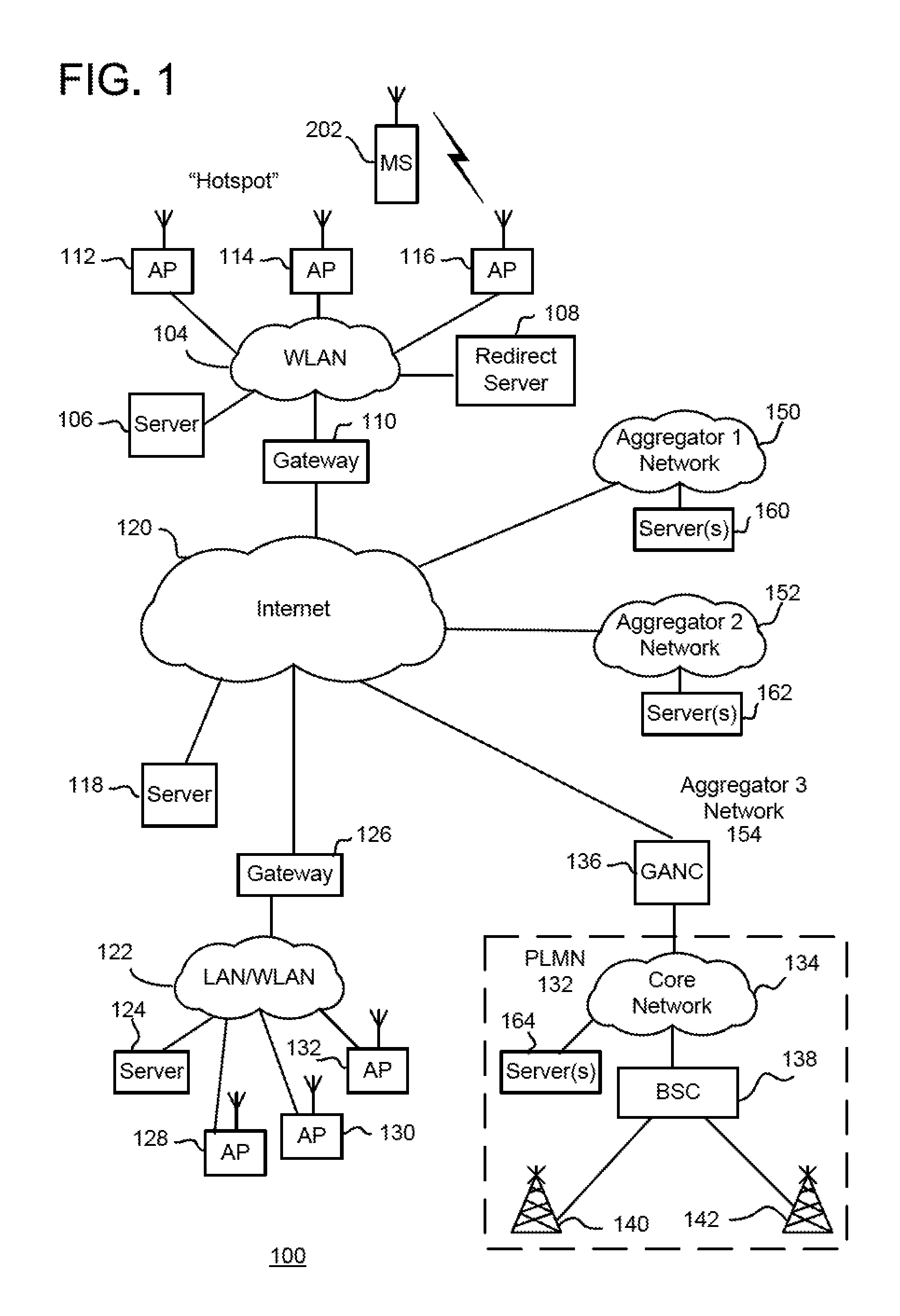
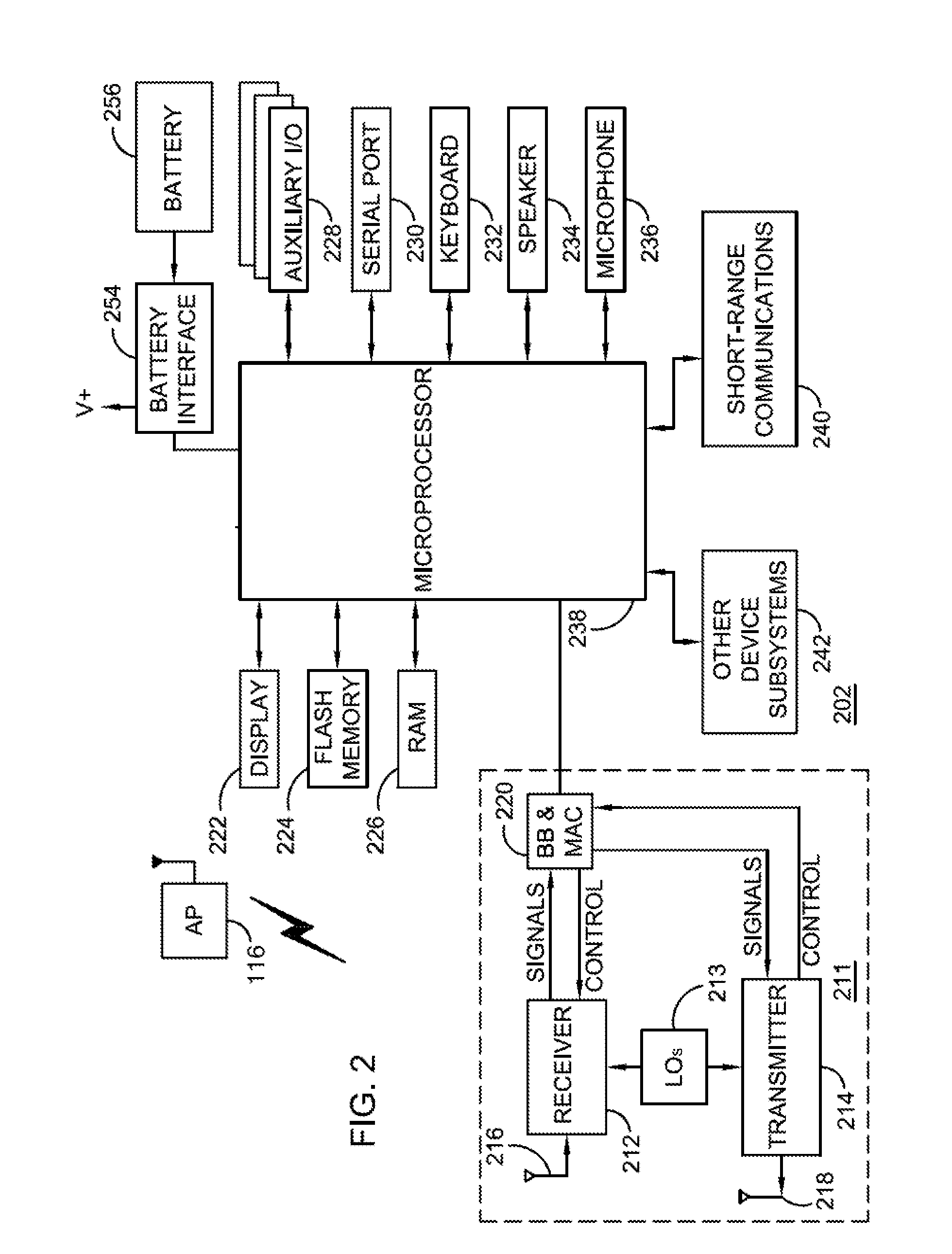
Methods And Apparatus For Use In Facilitating Access To Aggregator Services For Mobile Communication Devices Via Wireless Communication Networks
ActiveUS20110149874A1Accounting/billing servicesAssess restrictionUniform resource locatorService information
In one illustrative example, a wireless local area network (WLAN) regularly broadcasts or otherwise communicates one or more aggregator service identifiers which identify one or more aggregator services made available via the WLAN. In addition, a mobile communication device has a memory for storing aggregator service information. During operation, the mobile device performs a scanning operation and receives, from the scanning operation, the one or more aggregator service identifiers from the WLAN. The mobile device compares a received aggregator service identifier with one or more stored aggregator service identifiers of the aggregator service information. When there is a match between the received and the stored aggregator service identifiers, the mobile device may connect with and receive the aggregator service via the WLAN. For newly-encountered WLANs, the mobile device may also automatically create and store a wireless network profile associated with the WLAN that provides the aggregator service. For each aggregator or aggregator service, the aggregator service information may include a service name of the aggregator or aggregator service, a security type for authentication, a first URL for obtaining service information for the aggregator service, and a second URL for subscribing to the aggregator service, all of which may be displayed or otherwise utilized for obtaining service.
Owner:MALIKIE INNOVATIONS LTD
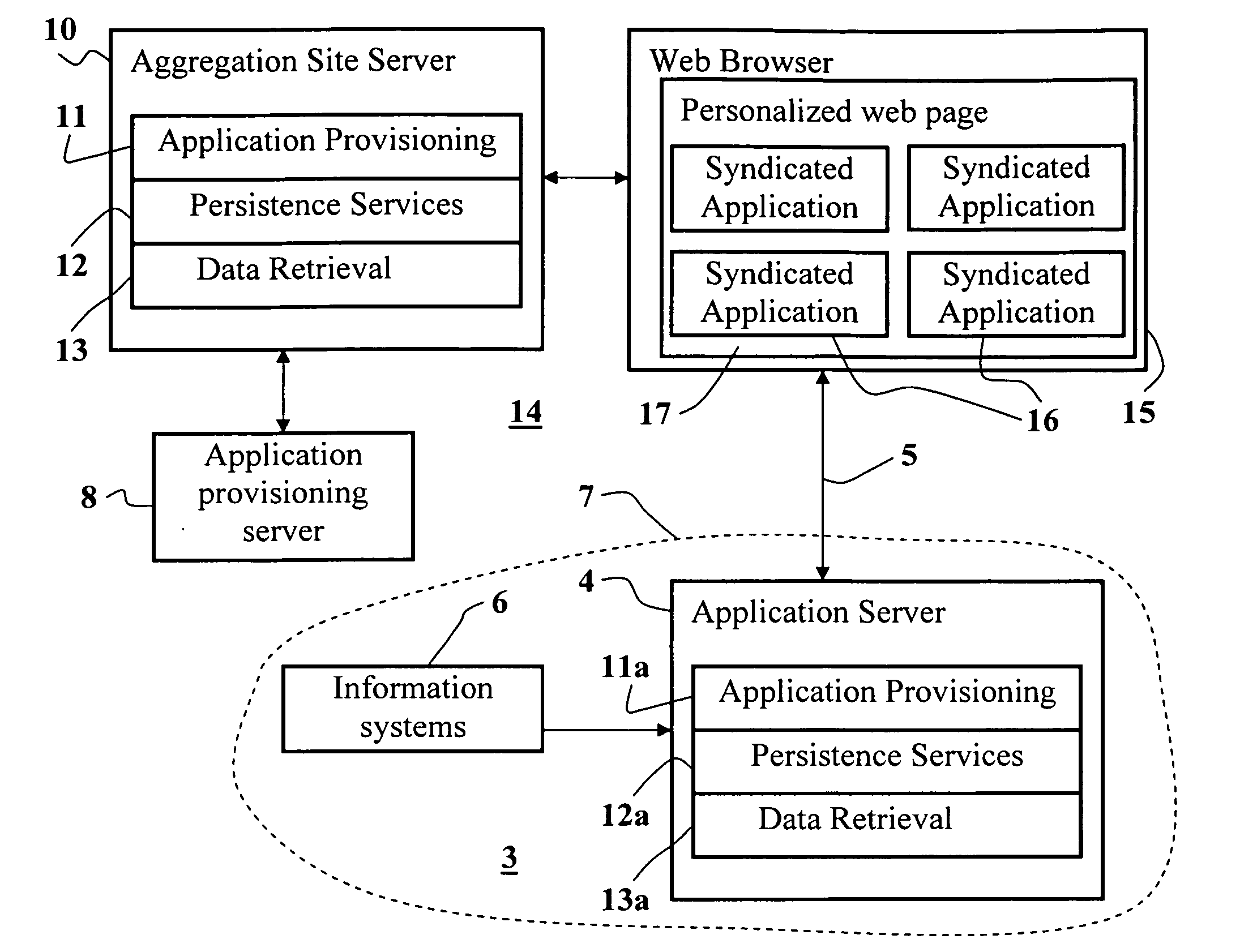
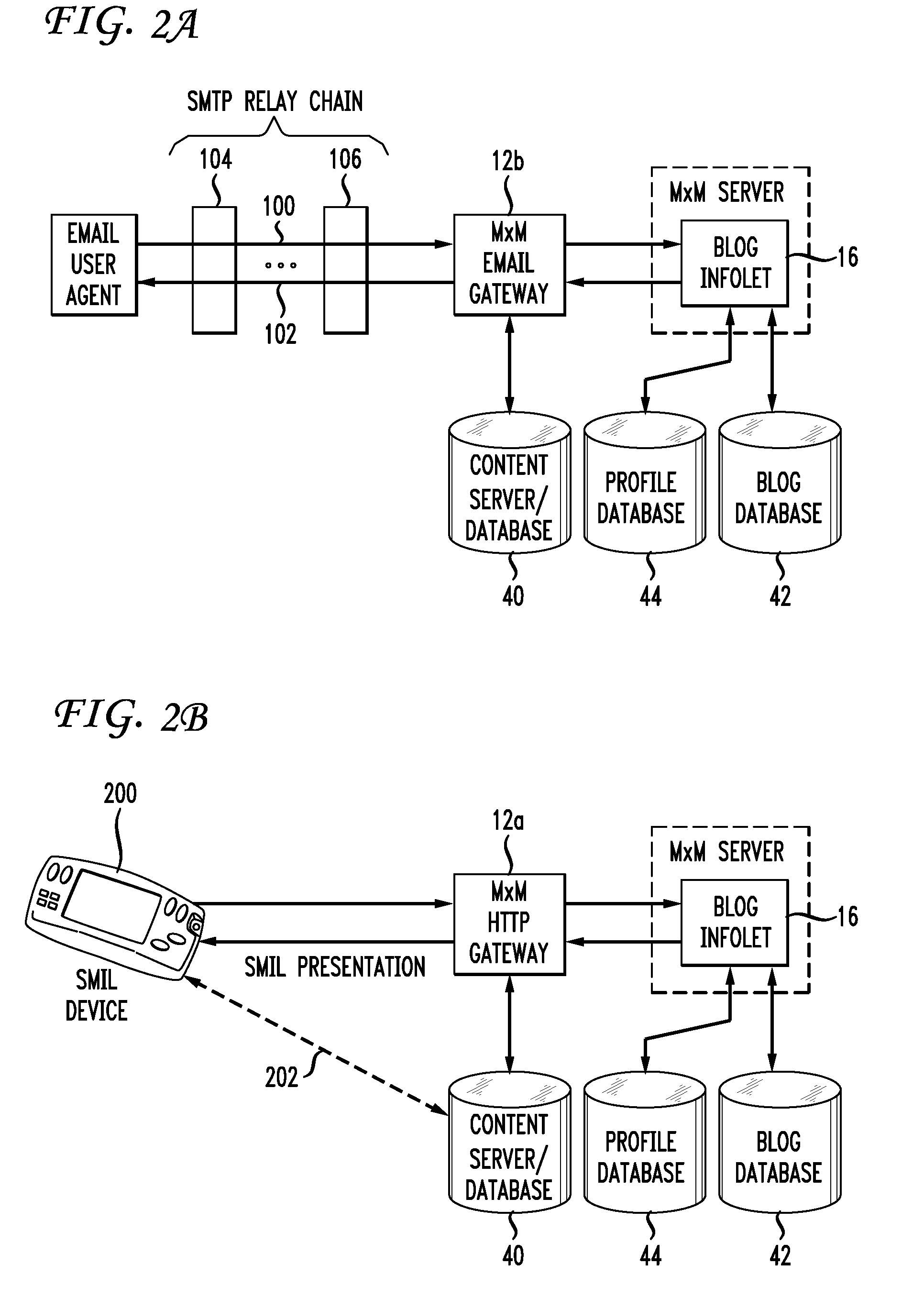
Method and system for secured syndication of applications and applications' data
InactiveUS20080215675A1Advantageously employedMultiple digital computer combinationsDigital data authenticationApplication softwareWeb page
The present invention provides a new syndication system allowing secure syndication of applications in conventional web aggregators of authorized users, and allowing secured and controlled access to privileged content by means of the syndicated applications. The system of the invention advantageously employs conventional web syndication servers and aggregators thereby allowing authorized users to securely add applications and access privileged content via their favorable web aggregation sites (e.g., personalized web pages) along with other non-privileged content syndicated therein.
Owner:WORKLIGHT
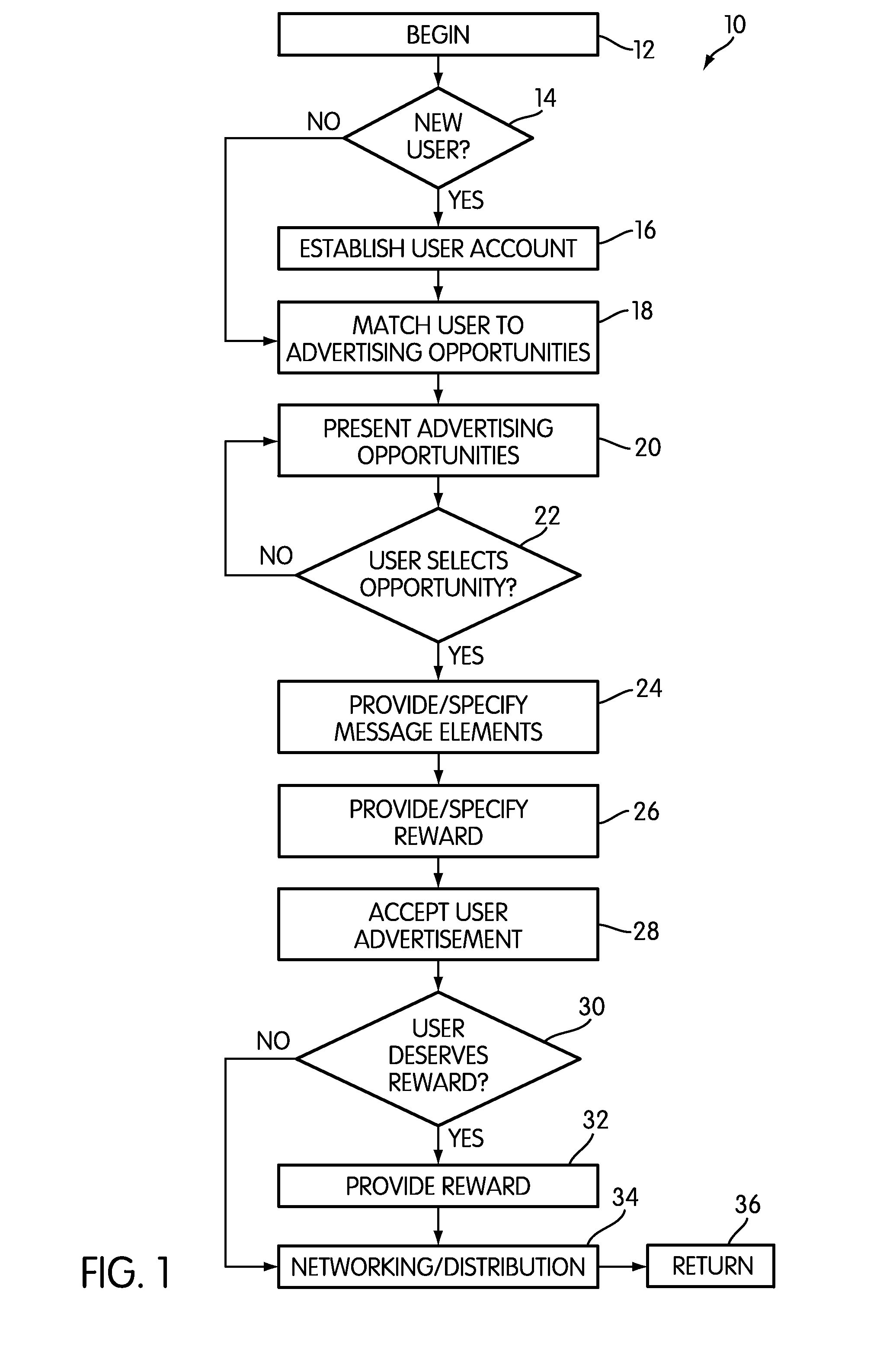
Methods and systems for user-produced advertising content
Owner:BRANDPORT
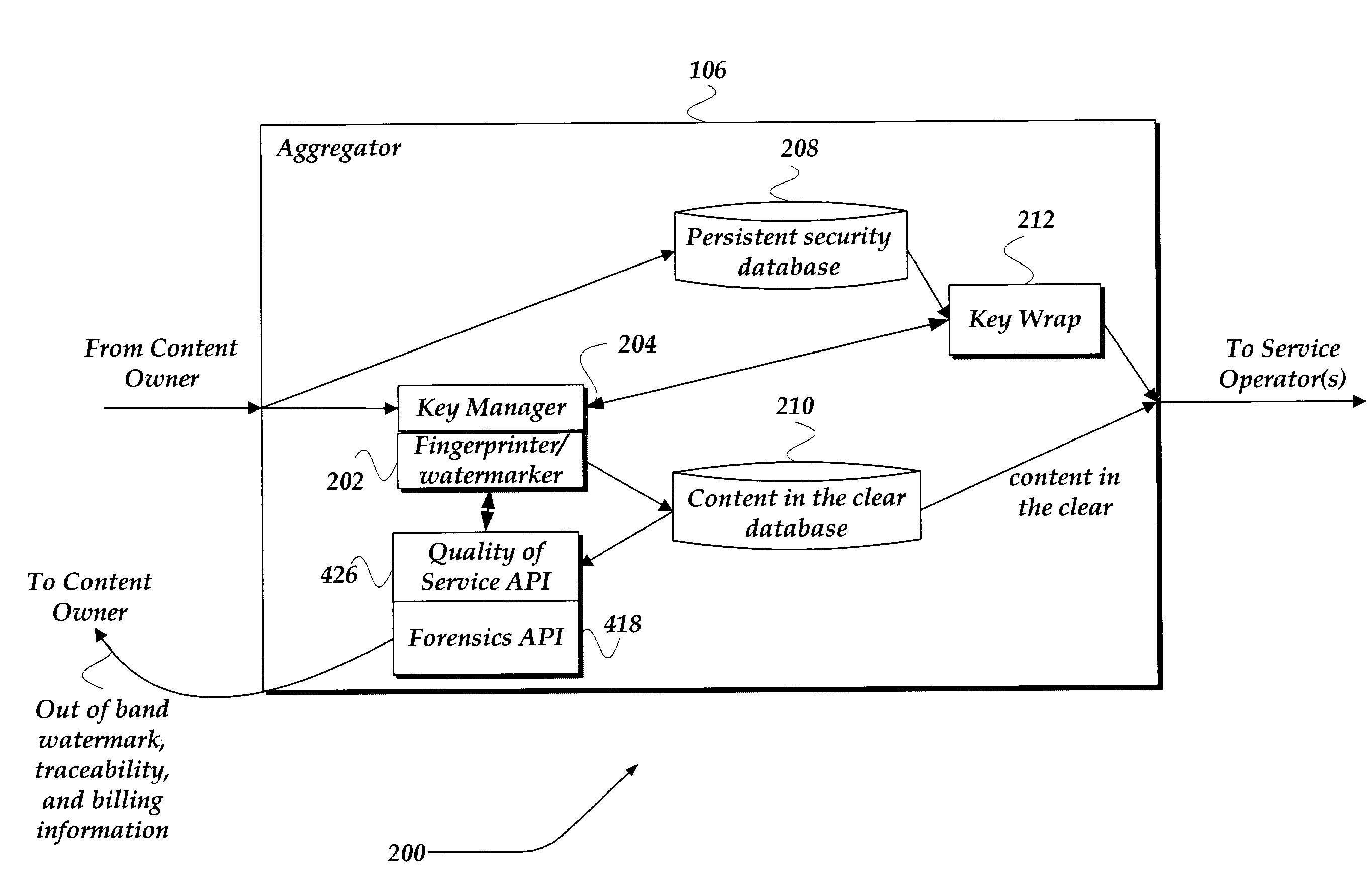
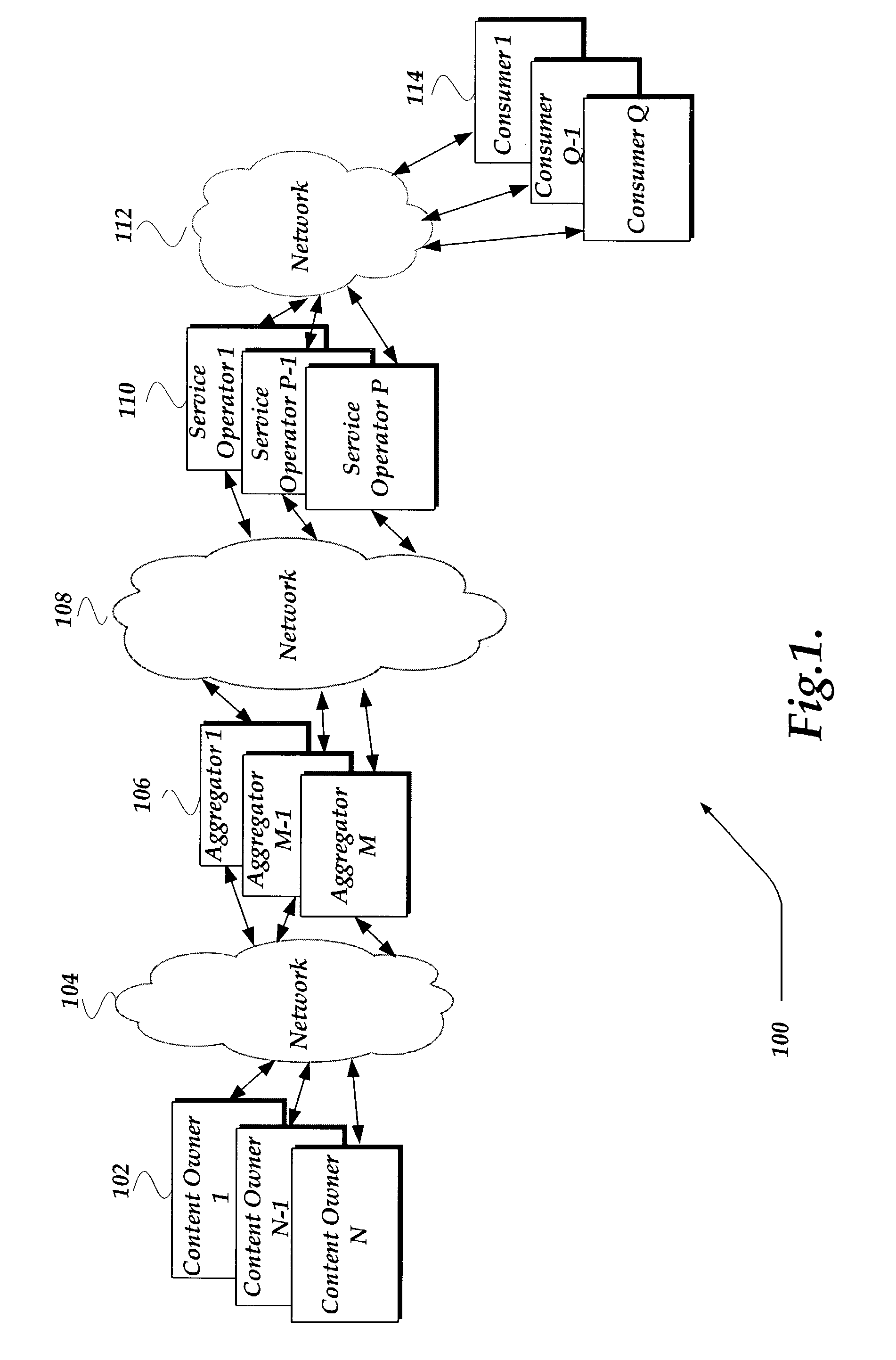
Method and system for end to end securing of content for video on demand
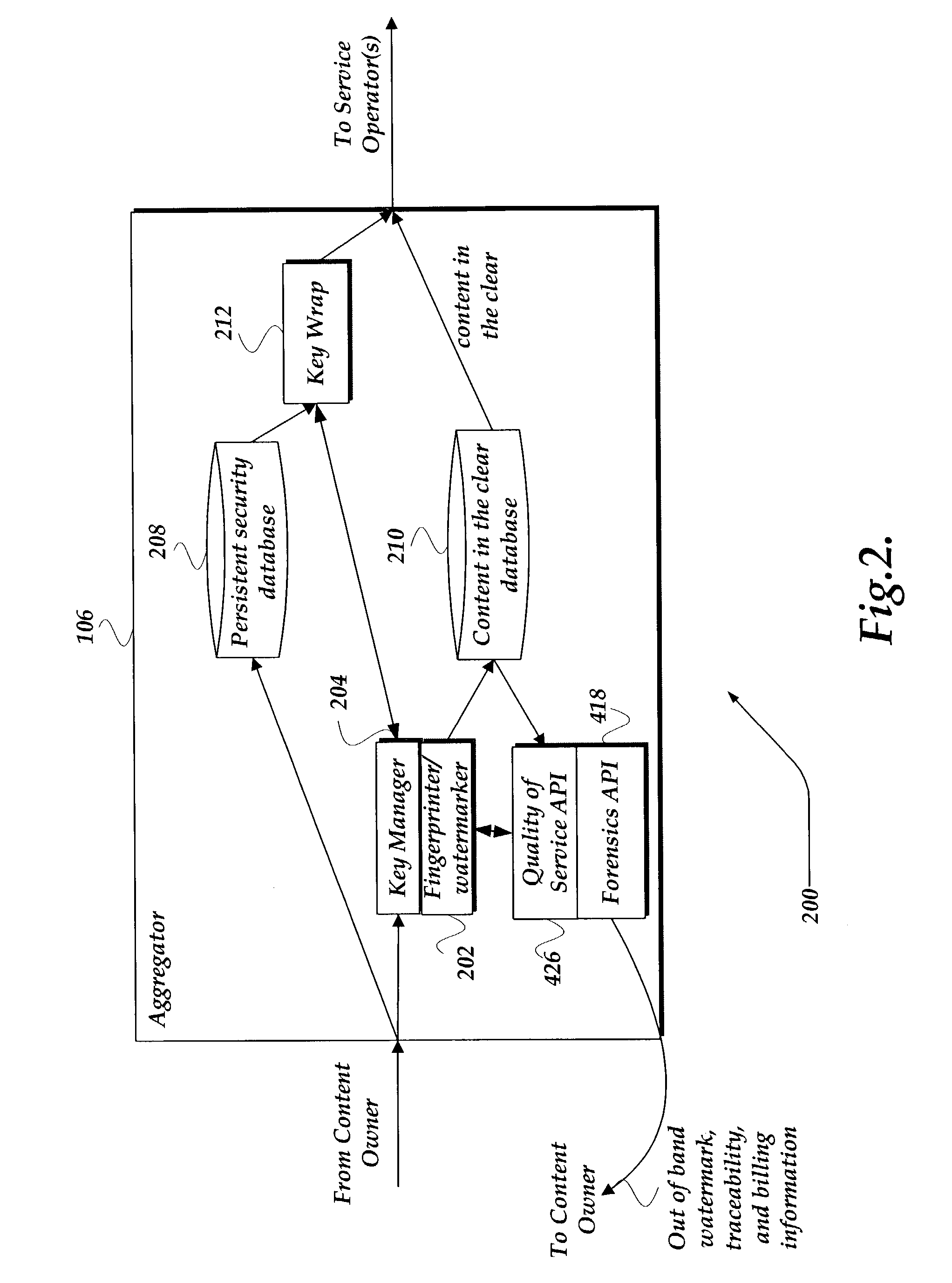
ActiveUS7328345B2Provide securityKey distribution for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationEnd to end securityMedia transparency
A system and method for providing end-to-end security of content over a heterogeneous distribution chain is provided. A content owner provides content to an aggregator that receives the content and processes the content. The processing may involve decrypting the content and associating at least one of a unique fingerprint and a watermark to the decrypted content. The unique fingerprint and a watermark to the decrypted content provide identifying characteristics to the content. Additional content-based fingerprints may be used to monitor quality of consumer experience for Video and Audio. The content may be sent in a decrypted state to a client or in an encrypted state. When the content is encrypted the aggregator wraps and encrypts the content with a signature such that an end-to-end flow of the content may be determined. Application Level encryption is used to provide network / distribution medium transparency as well as persistent encryption. When the content is transmitted from a consumer to another consumer the transmitting consumer loses rights to the content.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
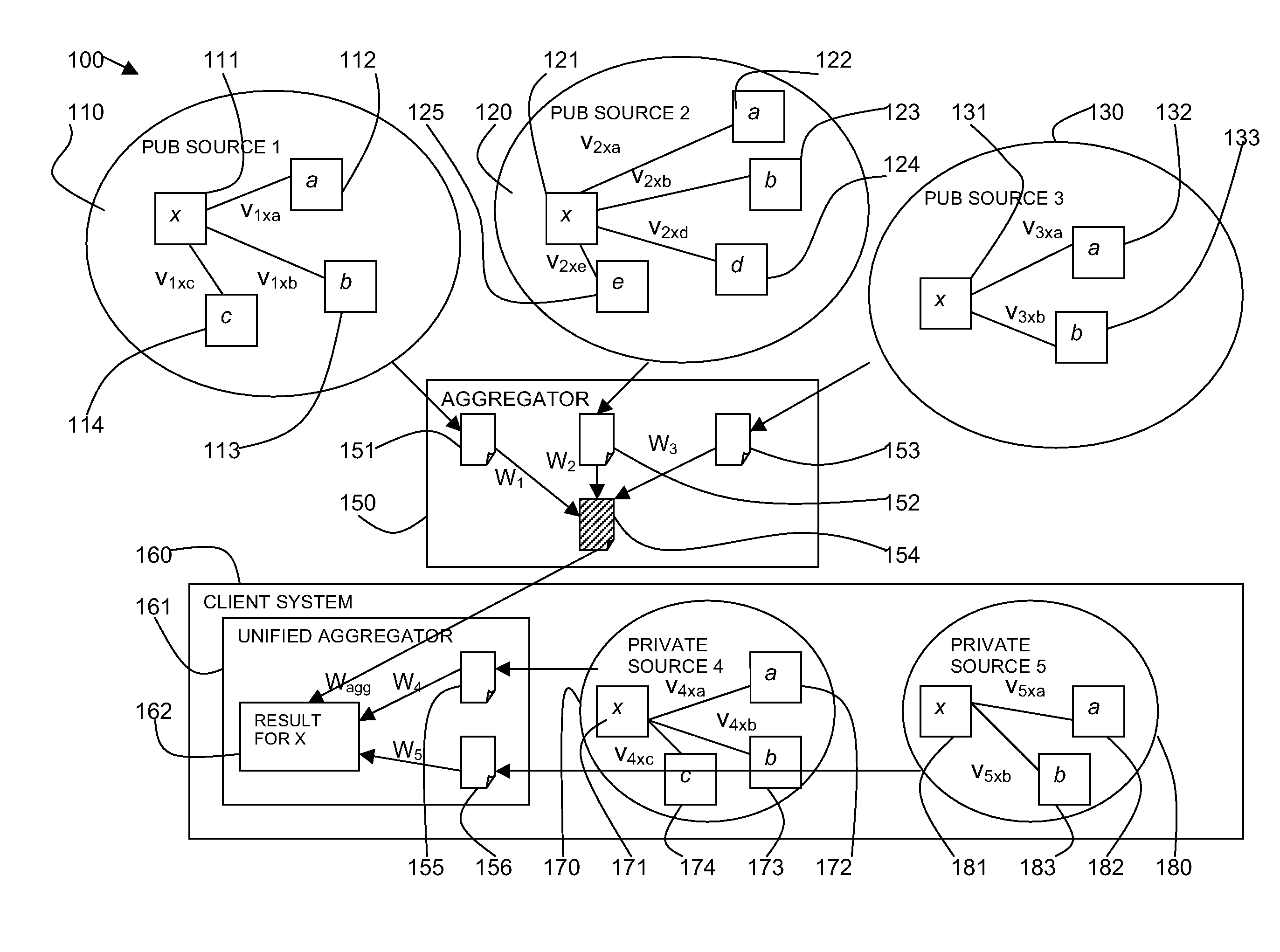
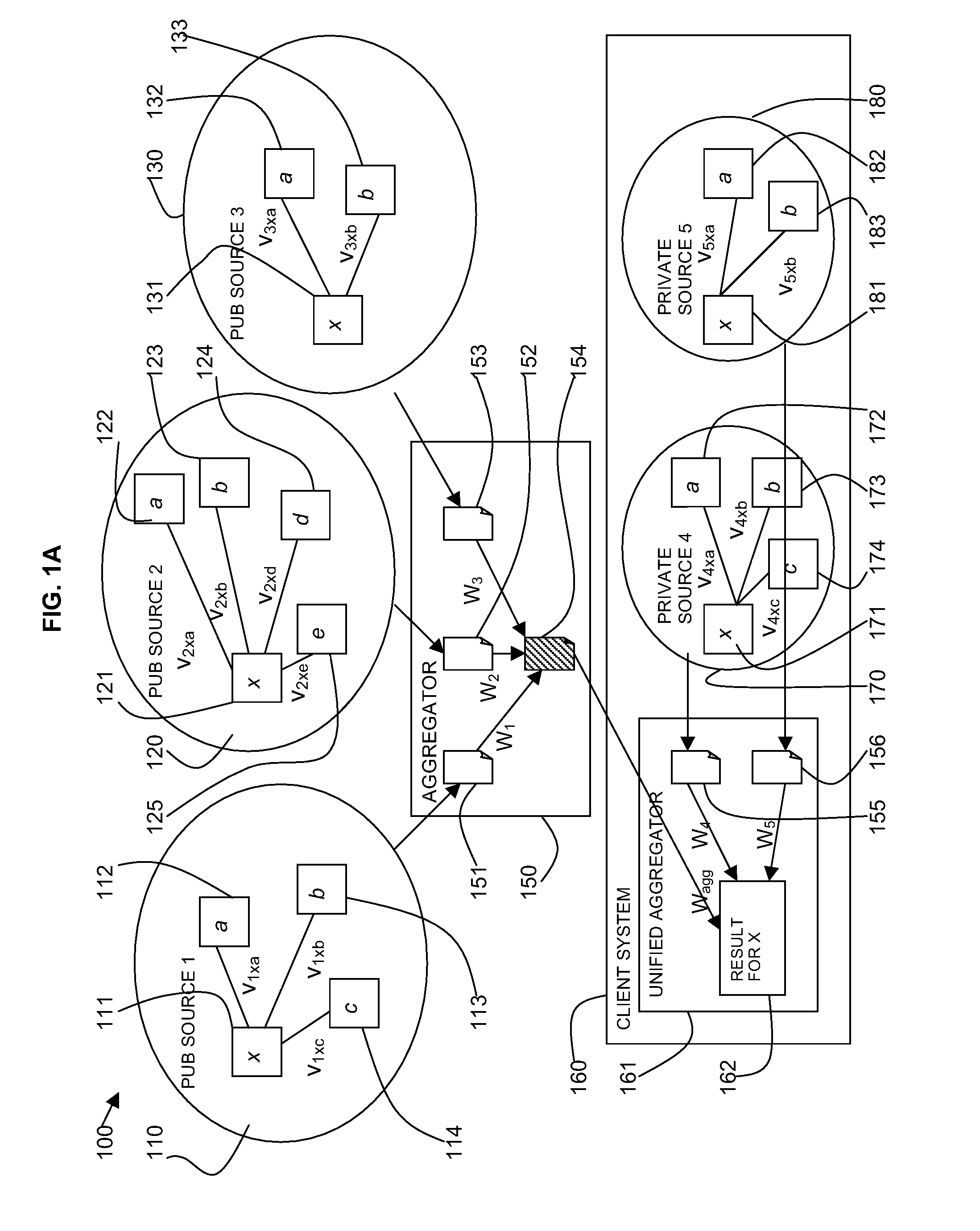
Structured and Social Data Aggregator
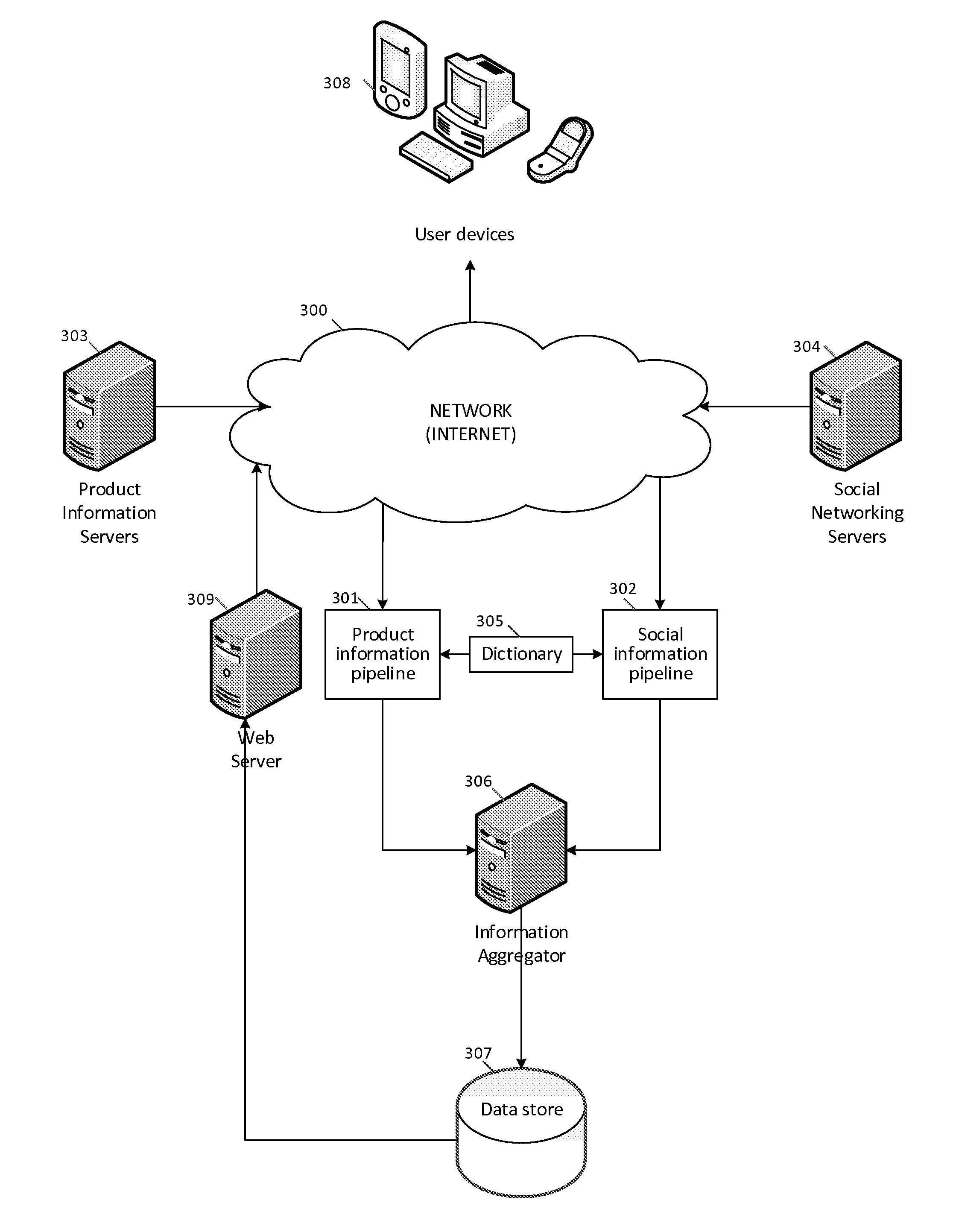
ActiveUS20130332460A1Quality improvementEfficient extractionWeb data indexingDigital data processing detailsThe InternetData aggregator
Information is obtained from the Internet is combined with processed and rated information from social networking services by a structured and social data aggregator providing highly relevant search results. In accordance with an embodiment of the present invention, there is provided a product information crawler, which crawls the Internet in search of web pages relevant to a requested subject or product. The product information crawler conveys captured web pages to a structured data extractor, which extracts product information. A social networking crawler crawls social networking services in search of social network information to the requested subject or product. The processed product information and processed social network information is conveyed to an information aggregator, which merges the information and stores it in a data store that can be queried by a user. A user would then be able conduct a single search about a subject or product, and retrieve highly relevant structured product information enhanced by social networking information.
Owner:DATA RECORD SCI INC
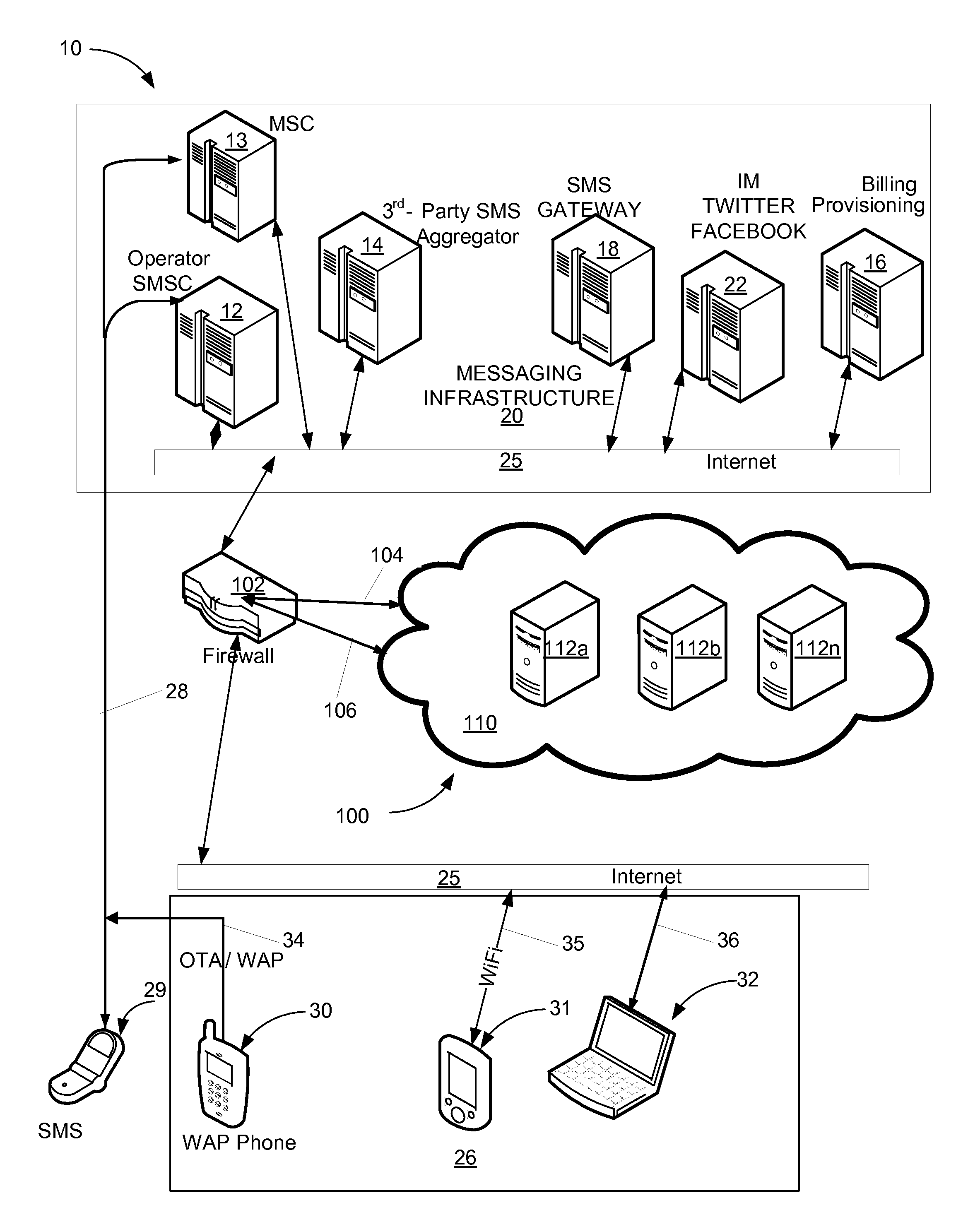
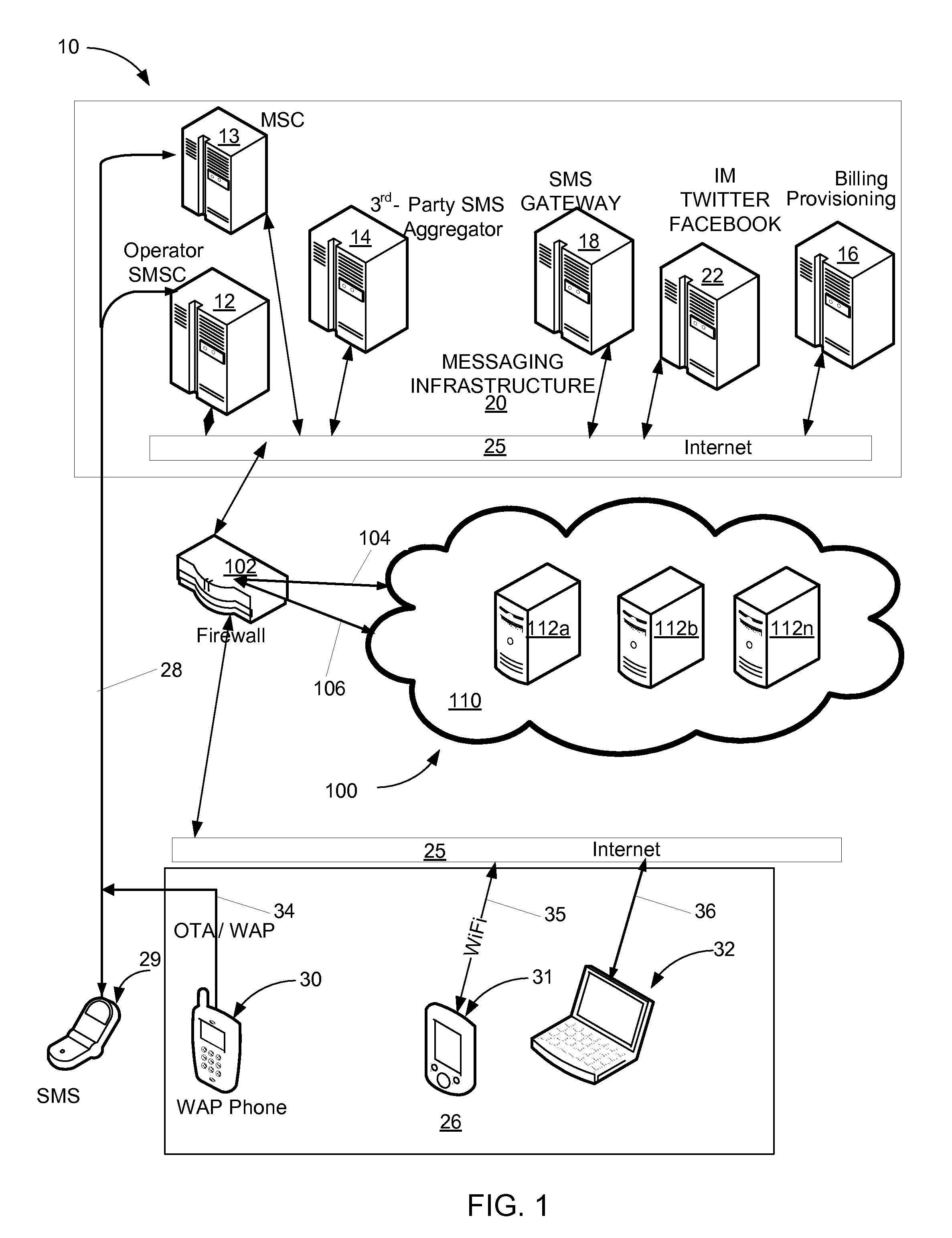
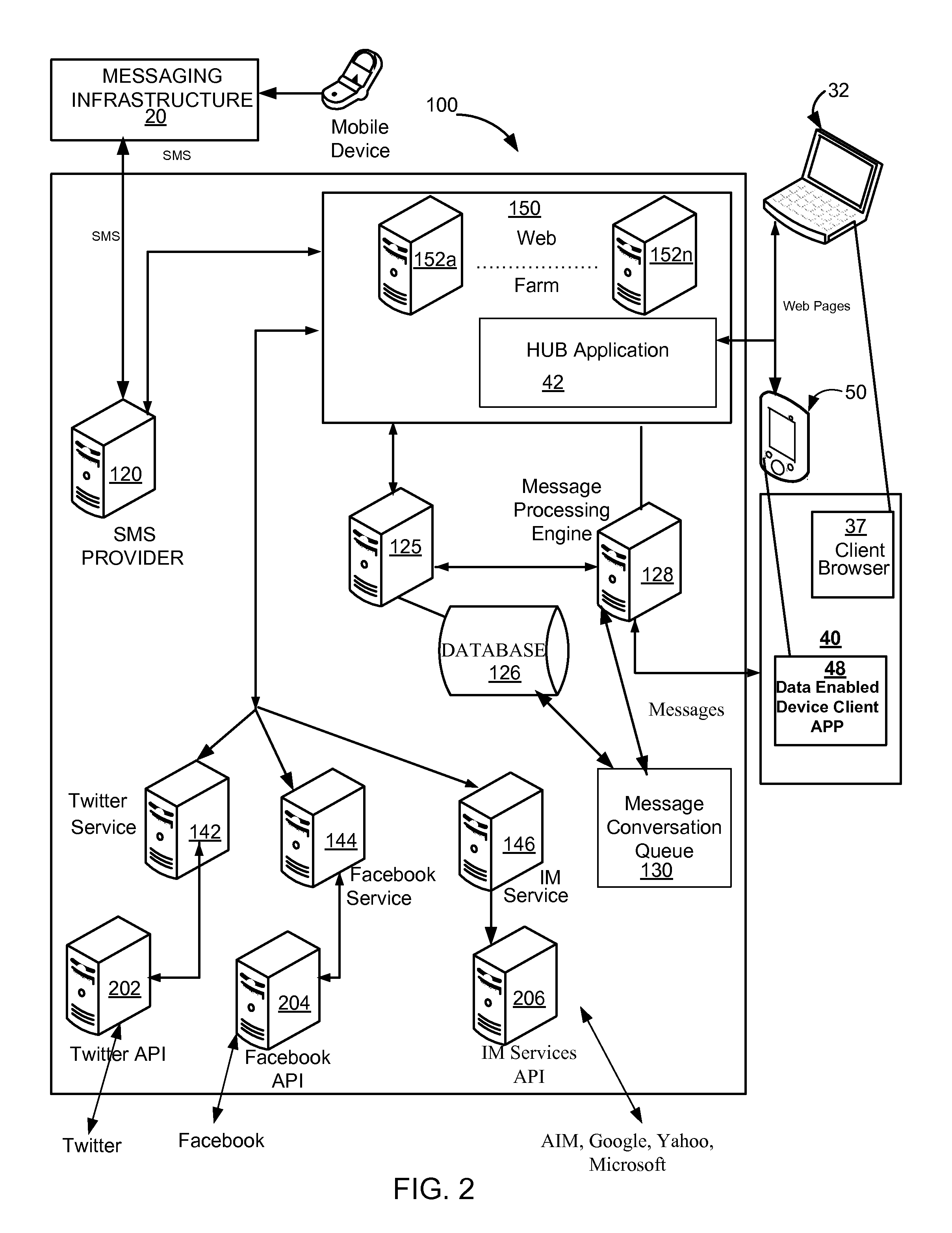
Social messaging hub
ActiveUS20110238766A1Low costAttractive and affordable rateServices signallingConnection managementTablet computerWi-Fi
A social messaging hub provides communication services for a data enabled device having Internet network access capabilities such as a portable media player, personal digital assistant, a Wi-Fi mobile platform, a tablet computer, portable e-Reader, a personal computer, a laptop and a netbook computer. The social messaging hub communicates with the data enabled device over the Internet or cellular data networks, and interfaces with a message infrastructure including mobile carriers, message aggregators, message exchanges and various specialized social messaging services, such as Microsoft Windows Live Messenger, AIM, Yahoo, GoogleTalk, Facebook and Twitter to enable bi-directional messaging communication. The user is given a registered phone number and unique IP addressable identification which serve as a source and destination identifier of the associated data enabled device. Messages may originate in or be delivered to other users' mobile telephones or in similarly equipped and provisioned IP data enabled devices.
Owner:HEYWIRE
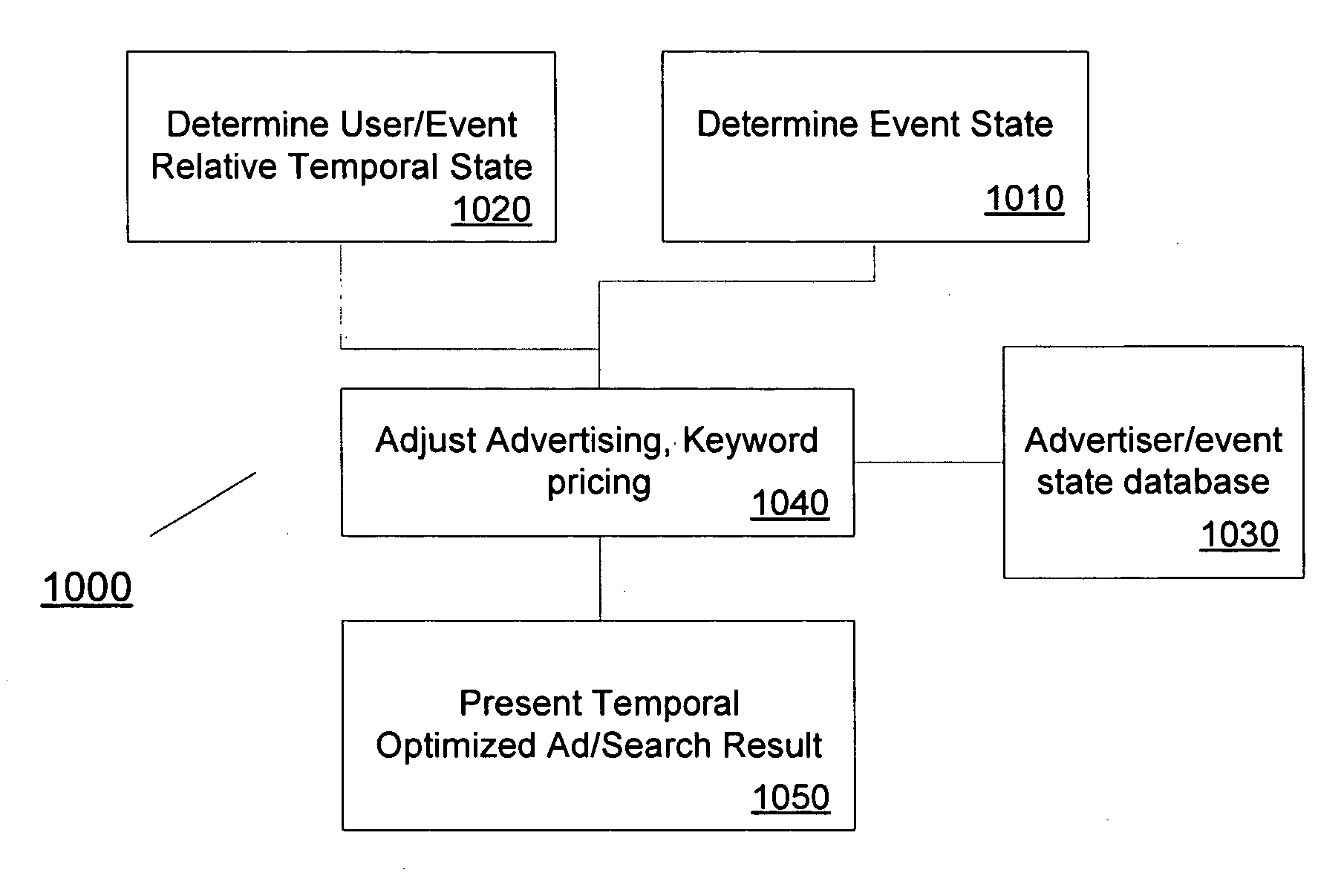
Event Based Document Sorter and Method
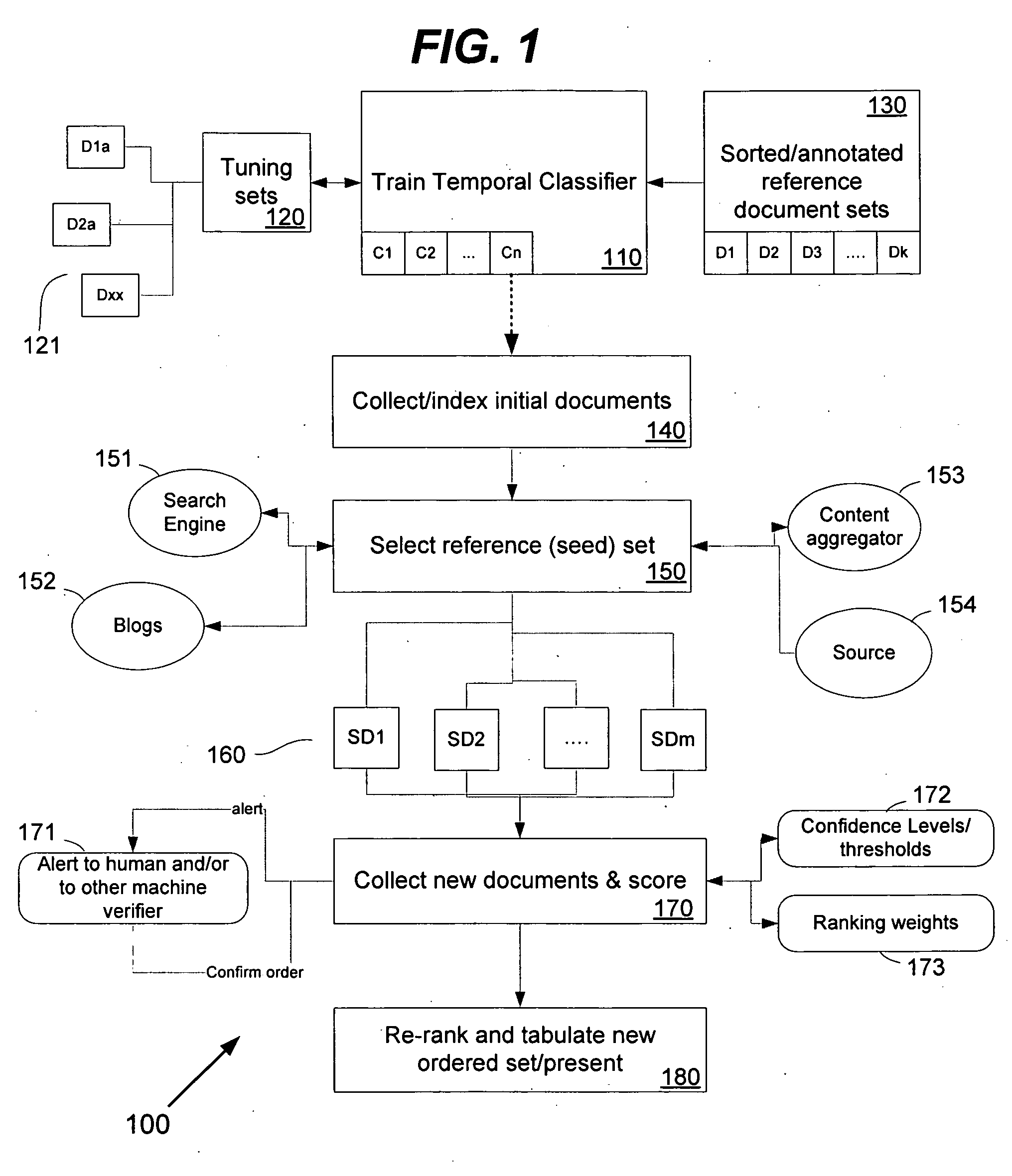
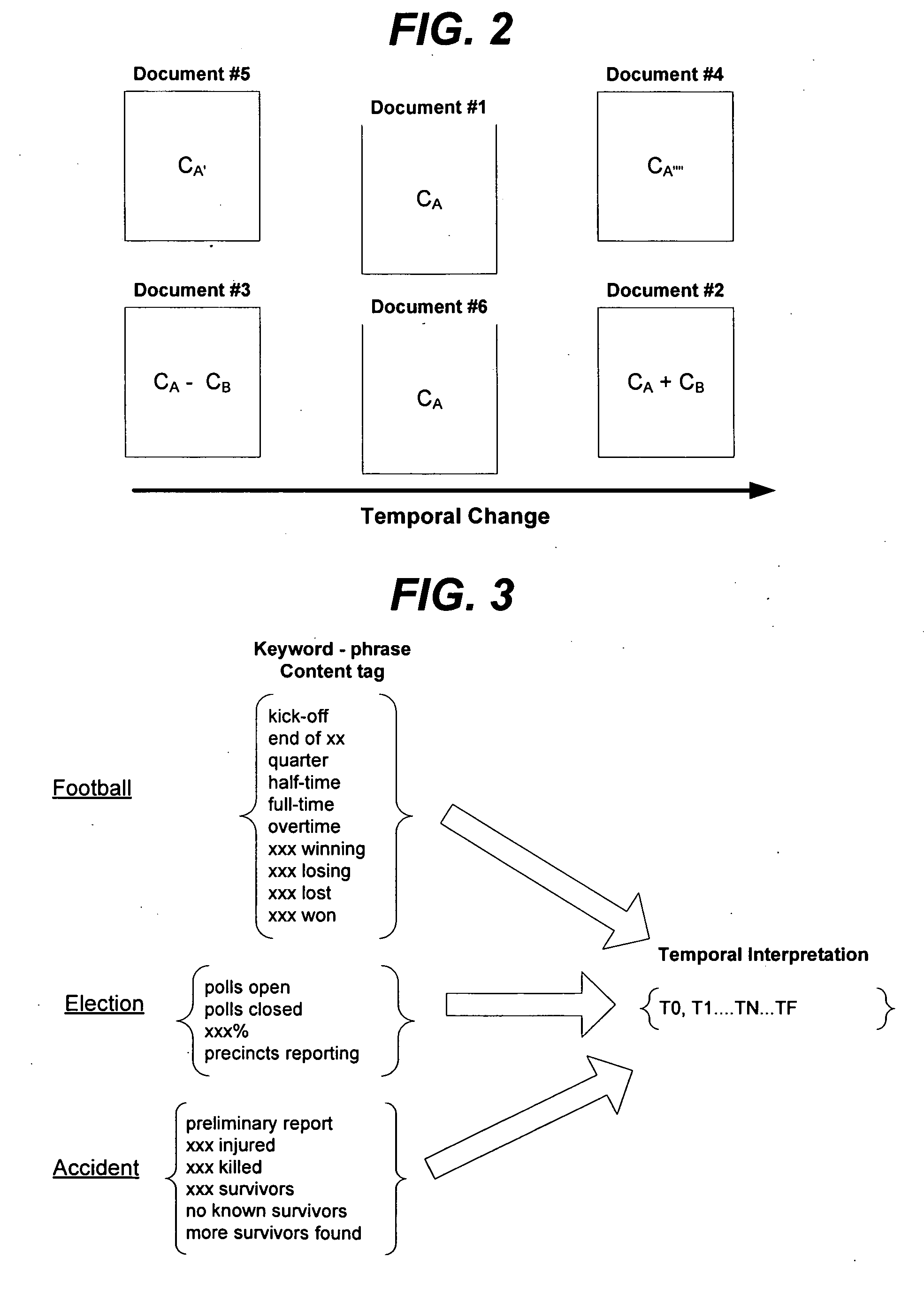
Events and / or topics are studied and classified according to their temporal qualities to determine their relative state. The content of a document relating to such event / topic is analyzed to identify temporal components. These components can be compared with corresponding counterparts in other documents to identify a relative temporal order. The invention can be used in environments such as automated news aggregators, search engines, and other electronic systems which compile information having temporal qualities.
Owner:JOHN NICHOLAS & KRISTIN GROSS
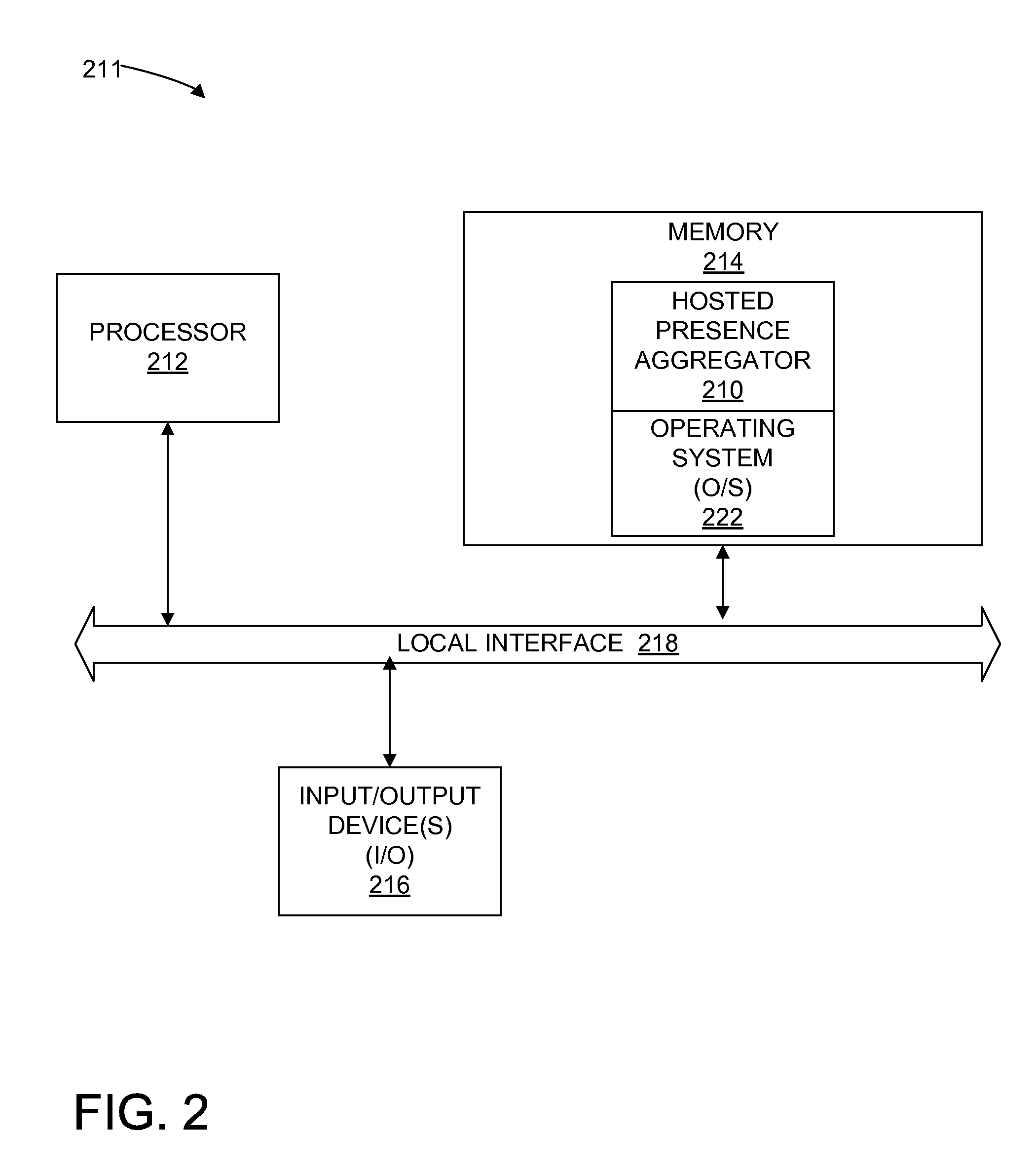
Aggregated Presence Over User Federated Devices
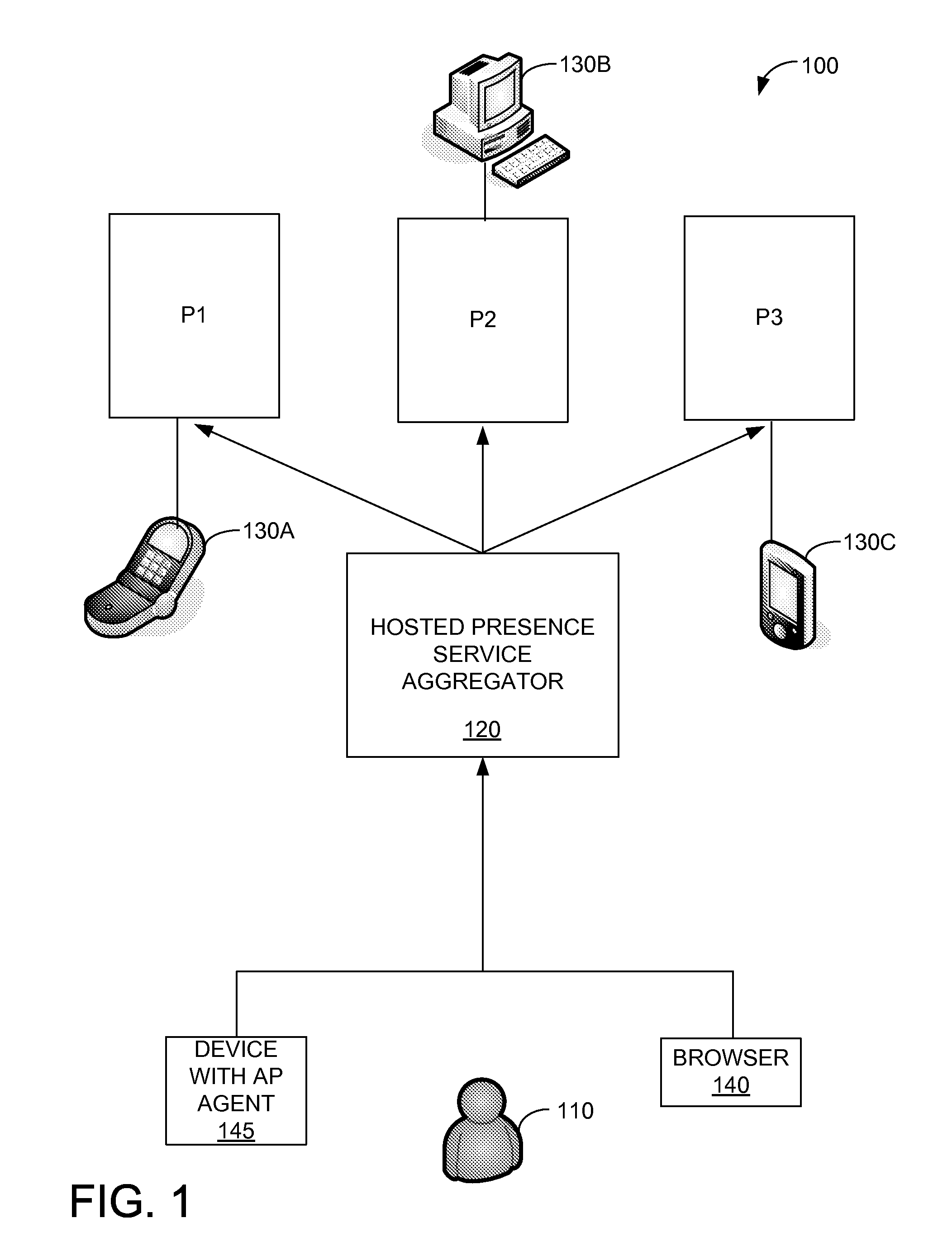
ActiveUS20110035443A1Services signallingMultiple digital computer combinationsUser deviceNews aggregator
One embodiment of a system for aggregating and distributing presence information comprises a hosted presence aggregator server. The hosted presence aggregator server receives an update of presence information from a user device and relays the presence information update to another user device, wherein the user devices are part of a federation of user devices controlled by a single user which relay updates in presence status of the single user to one another via the hosted presence aggregator server.
Owner:AT&T INTPROP I L P
System and method for supply chain aggregation and web services
InactiveUS20040111304A1Increase awarenessLow priceOffice automationResourcesOn demandNews aggregator
An information management system configured to integrate a one-to-many business process interaction using on-demand supply chain management among enterprises who are customers of and suppliers to eachother comprises an entitlement engine, a web service aggregator, and a private exchange network operable to link the entitlement engine with the web service aggregator. The entitlement engine comprises a relational entitlement component, a pass-thru entitlement component, and a resource entitlement component, wherein the relational entitlement component parses data based on a predefined business process among the enterprises, wherein the pass-thru entitlement component parses data from one enterprise up to an n number of enterprises, and wherein the resource entitlement component parses data based on available resources of the enterprises. The web service aggregator comprises rules, which are maintained in the private exchange network.
Owner:IBM CORP
System for on-demand access to local area networks
A roaming company makes payments to an aggregator of independent WLAN operators in exchange for providing Internet access services to subscribers of the roaming company. Independent WLAN operator accounts are maintained at the aggregation company.
Owner:XYLON LLC
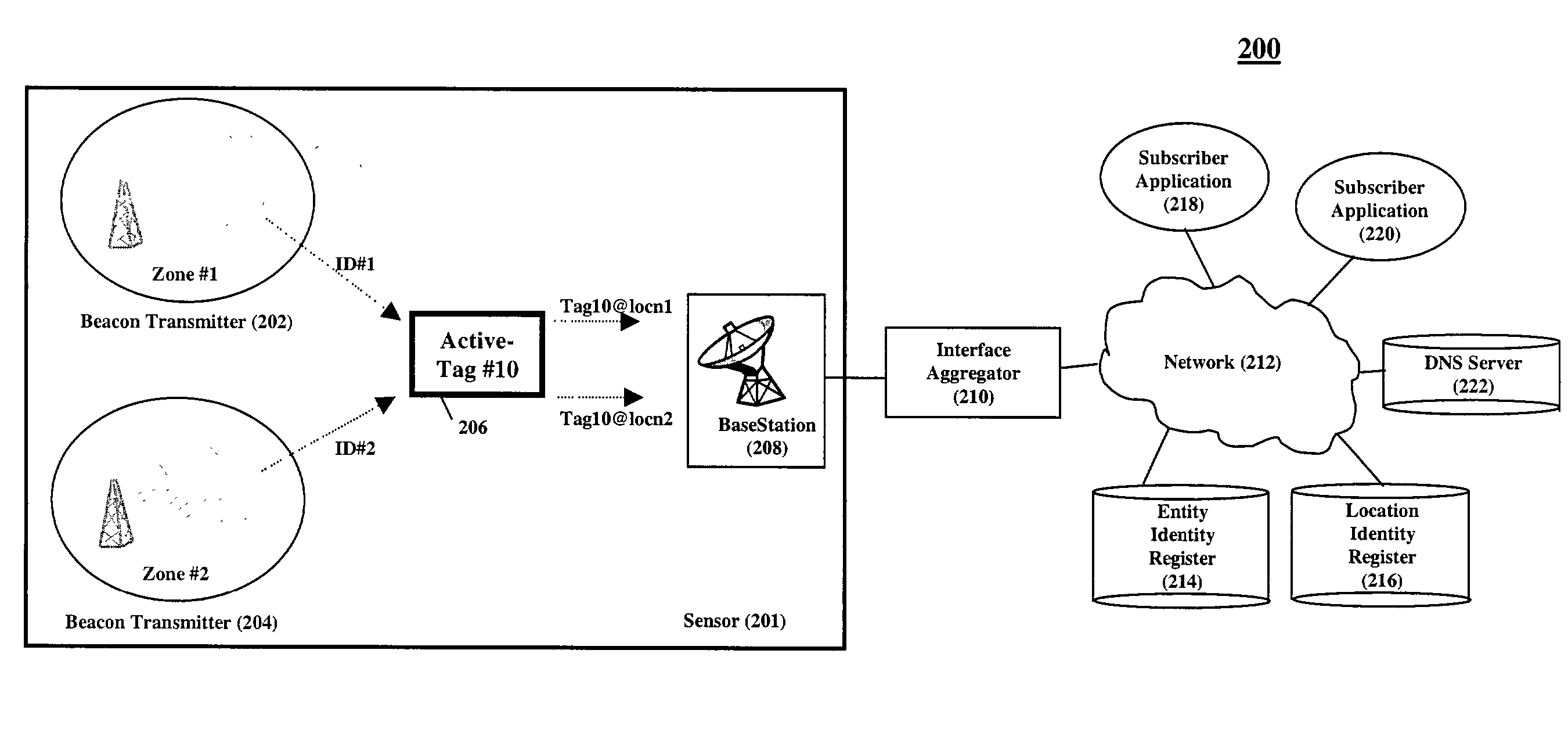
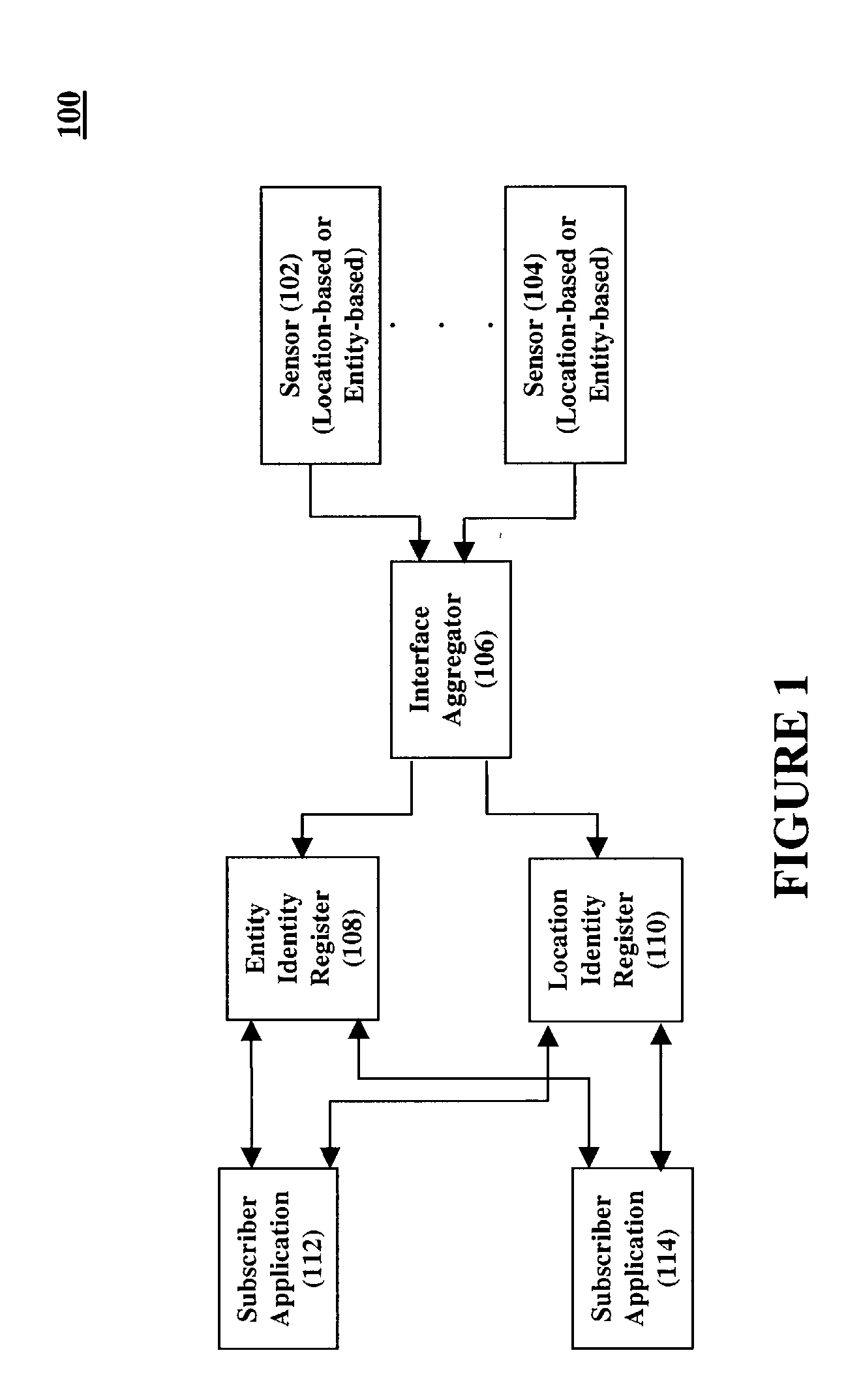
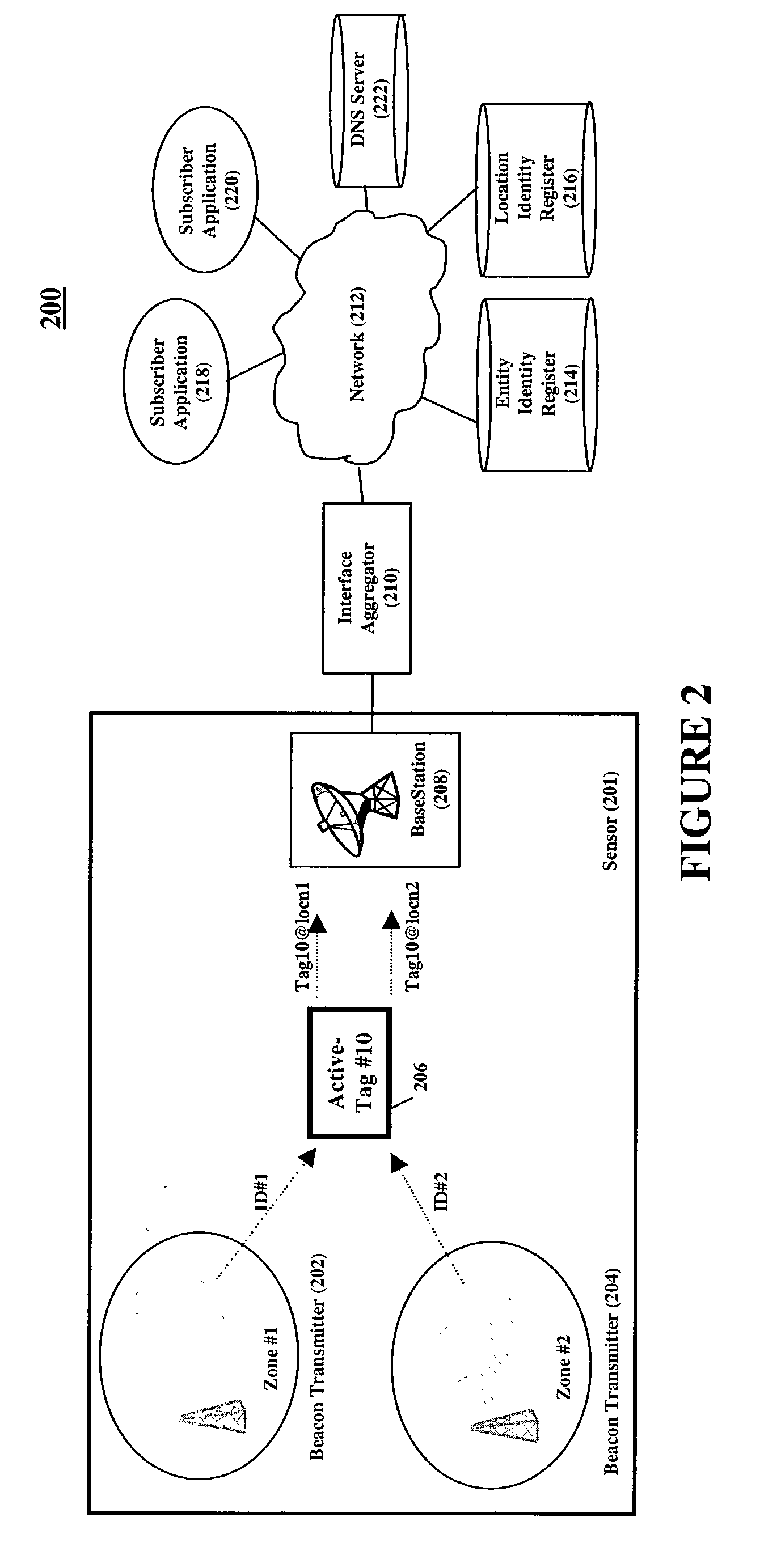
Location aware services infrastructure
InactiveUS20020167919A1Overcome disadvantagesGood serviceElectric signal transmission systemsMultiple keys/algorithms usageProcessor registerGranularity
Entity identity information and location identity information are sensed and made available to subscriber applications through a secure location-aware services infrastructure, thereby allowing for the creation of location-based services. Information detected by a sensor is passed to an interface aggregator for conversion to a standardized format and then forwarded to location registers for the domain of the sensors. Subscriber applications query the registers to determine which entities are in a particular location and to determine the location of entities. By unifying diverse sensing technologies, location information can be simultaneously obtained on varying degrees of granularity. In addition, the system is scalable to large scenarios by using a plurality of sensors, interface aggregators, and registers.
Owner:THINKLOGIX LLC
System for on-demand access to local area networks
InactiveUS7849177B2Metering/charging/biilling arrangementsAssess restrictionPaymentTelecommunications
A roaming company makes payments to an aggregator of independent WLAN operators in exchange for providing Internet access services to subscribers of the roaming company. Independent WLAN operator accounts are maintained at the aggregation company.
Owner:XYLON LLC
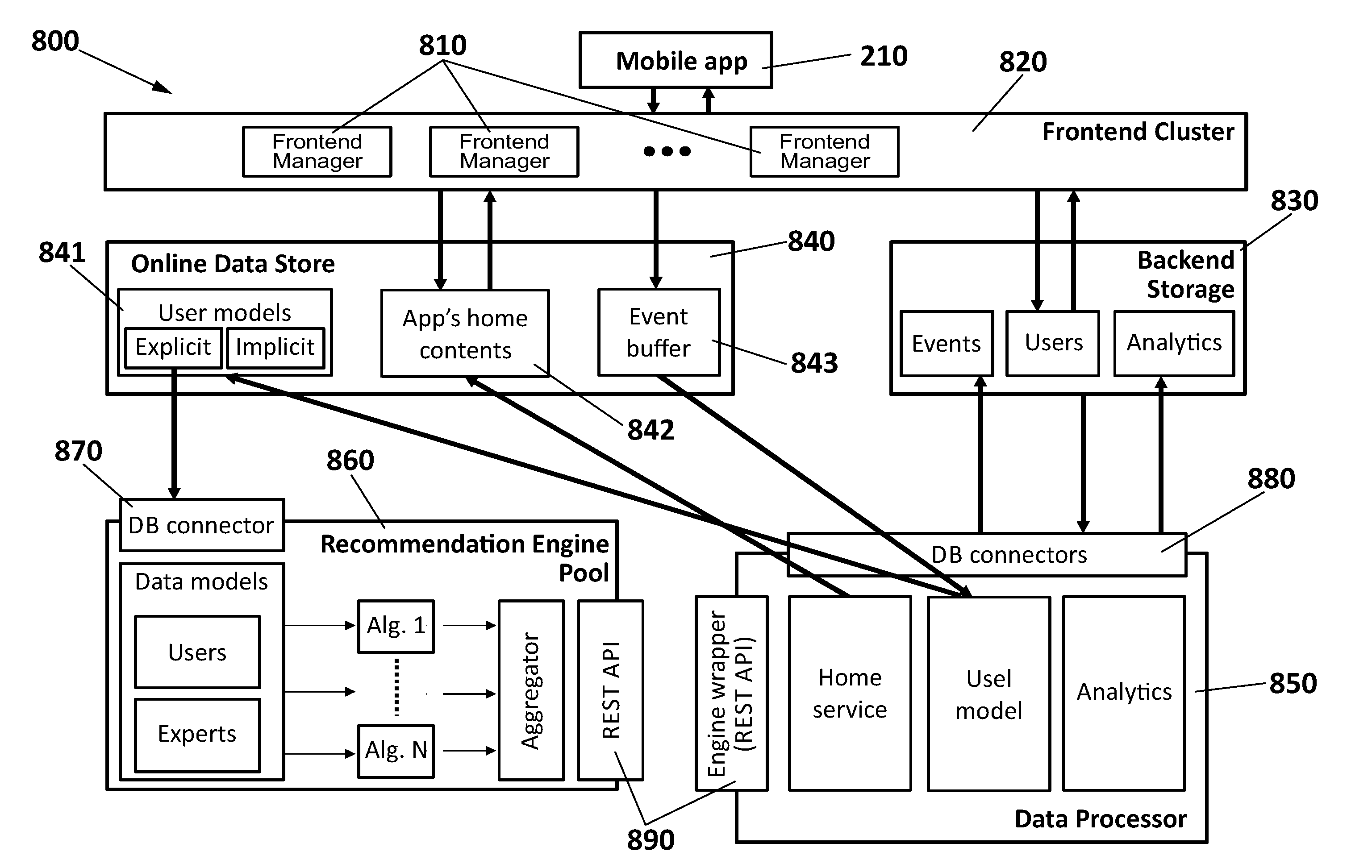
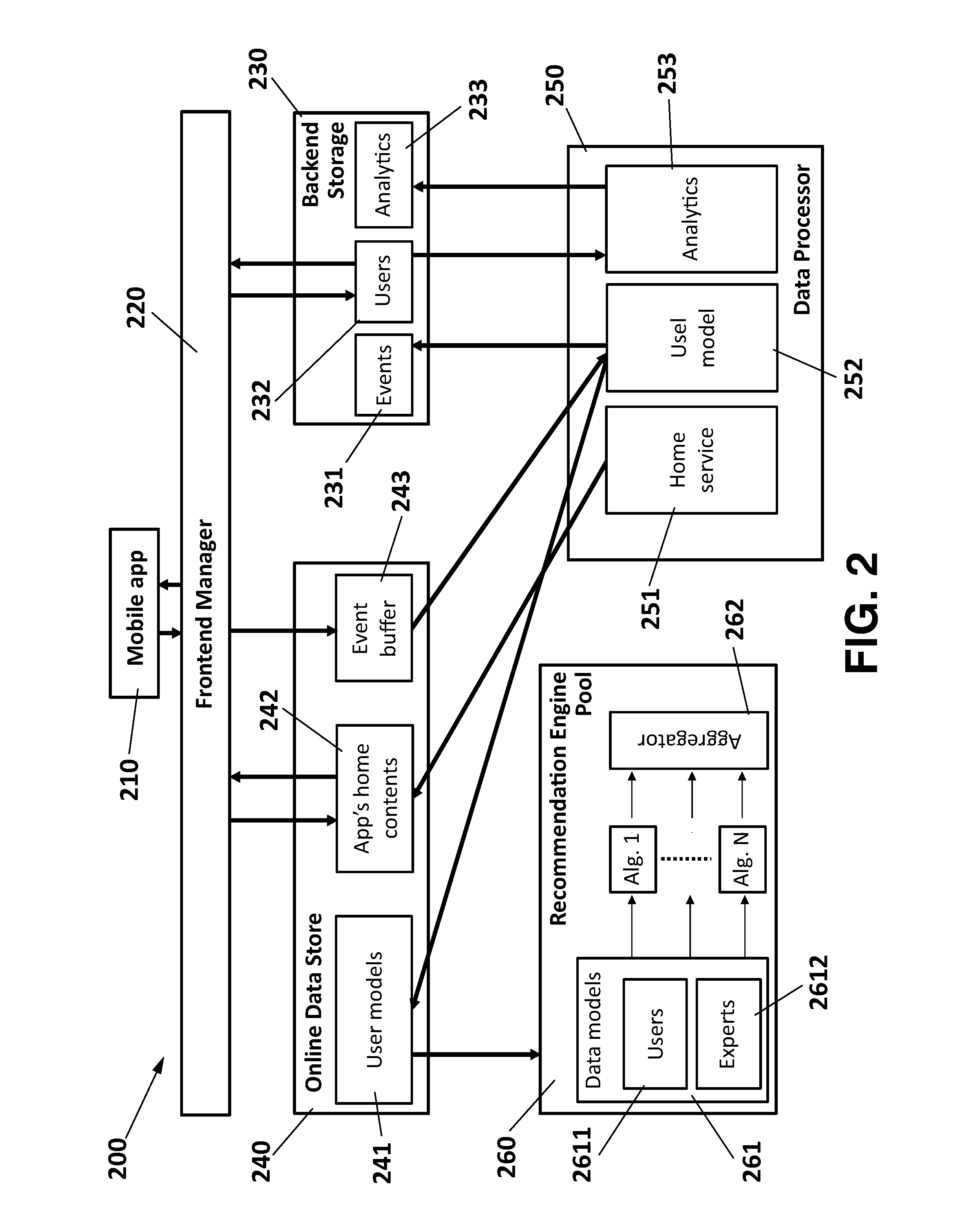
Method and system for providing multimedia content recommendations
InactiveUS20150120722A1Promote assimilationImprove trustDigital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsApplication softwareClient-side
A system for providing content recommendations, including a frontend manager for receiving explicit events from a client application of a user and generating implicit events based upon additional user actions within the client application; a backend storage of data on events and users and an Online Data Store for the explicit events and the implicit events; a Data Processor for creating an explicit user model from the explicit events and an implicit user model from the implicit events; a pool of recommendation engines with one or more recommendation algorithms for receiving the explicit user model and assigning a ranked recommendation list of content items to the user as a result, and further including an aggregator controlled by the Data Processor for aggregating the ranked recommendation lists based on a user-dependent strategy, in order to obtain multiple content recommendation lists of ranked items to be delivered by the frontend server to the client application in a final arrangement, pull from the Online Data Store along with data on the content sources.
Owner:TELEFONICA DIGITAL ESPANA
System and method of providing a context-aware personalized blogging agent
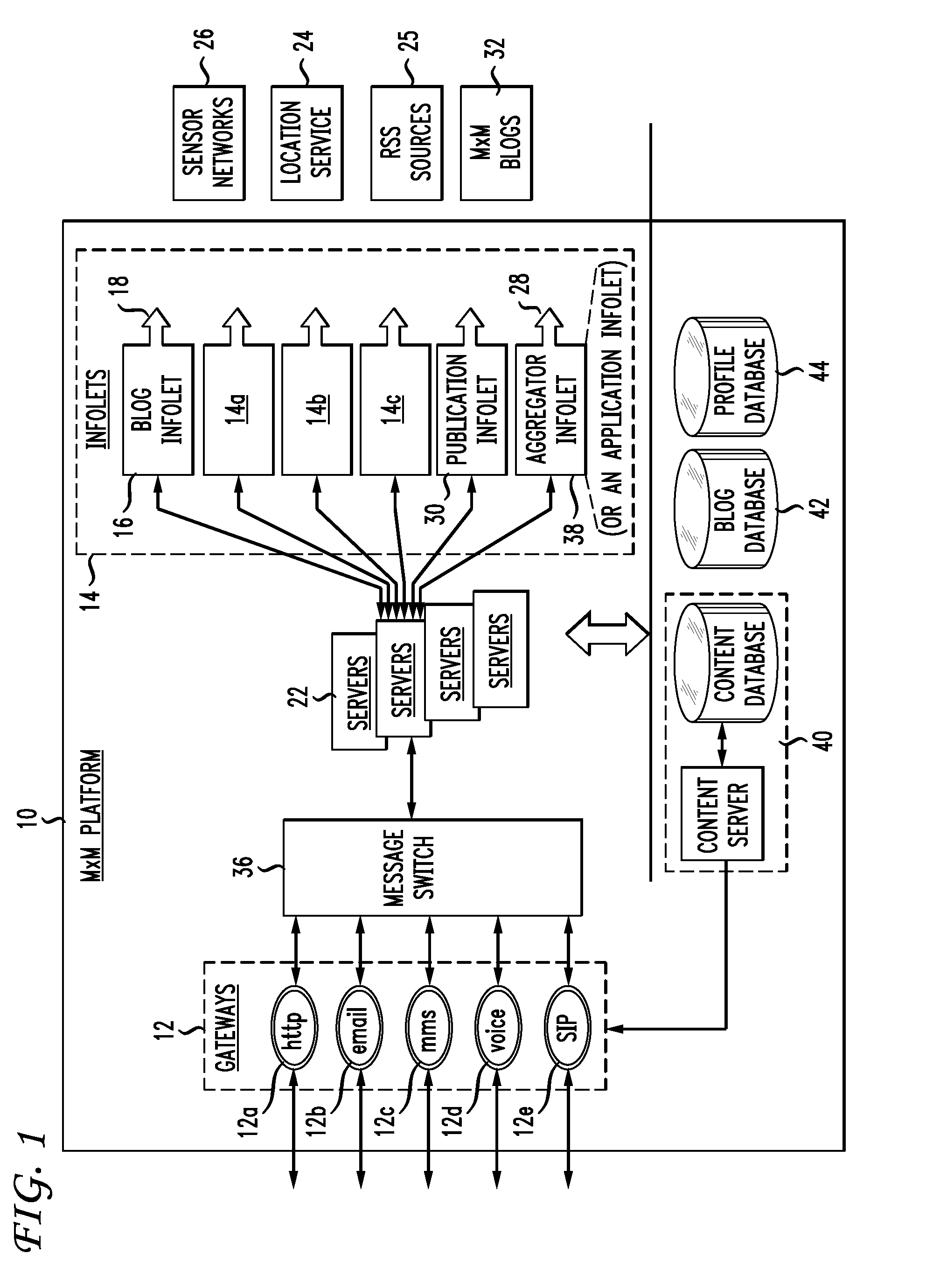
ActiveUS20080021976A1Facilitates of dataPromote productionNatural language data processingMultiple digital computer combinationsPersonalizationNews aggregator
A mobile multimedia content aggregation and dissemination platform is provided that aims to automate the creation, collection, aggregation, and dissemination of RSS and non-RSS information for and to interested parties. This platform may be used for the construction of a personalized blogging agent as well as for a personalized news aggregator.
Owner:AT&T INTPROP I L P
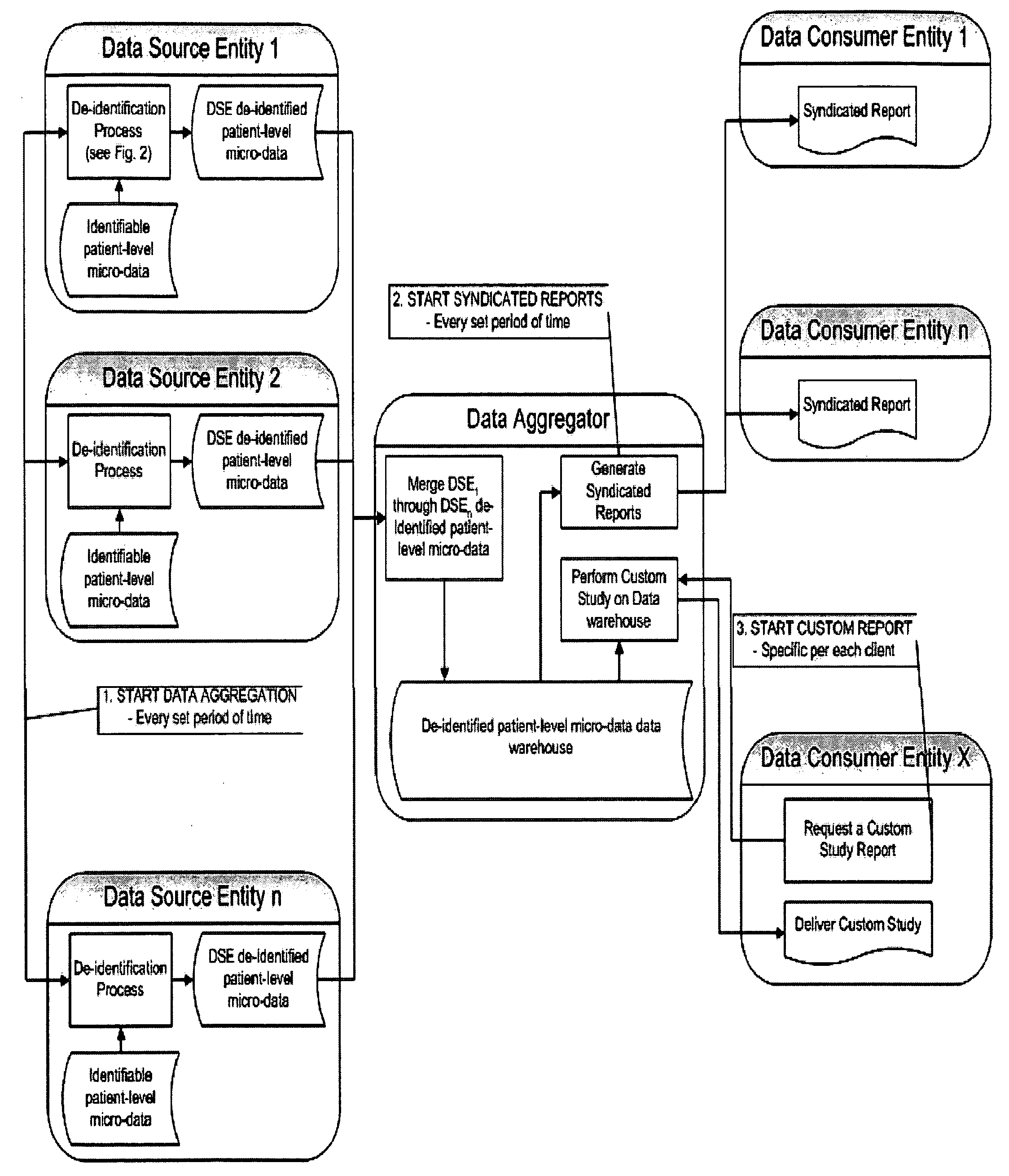
Double Blinded Privacy-Safe Distributed Data Mining Protocol
ActiveUS20090150362A1Easy to analyzeImplementation is particularly straightforwardMedical data miningDigital data processing detailsDouble blindData source
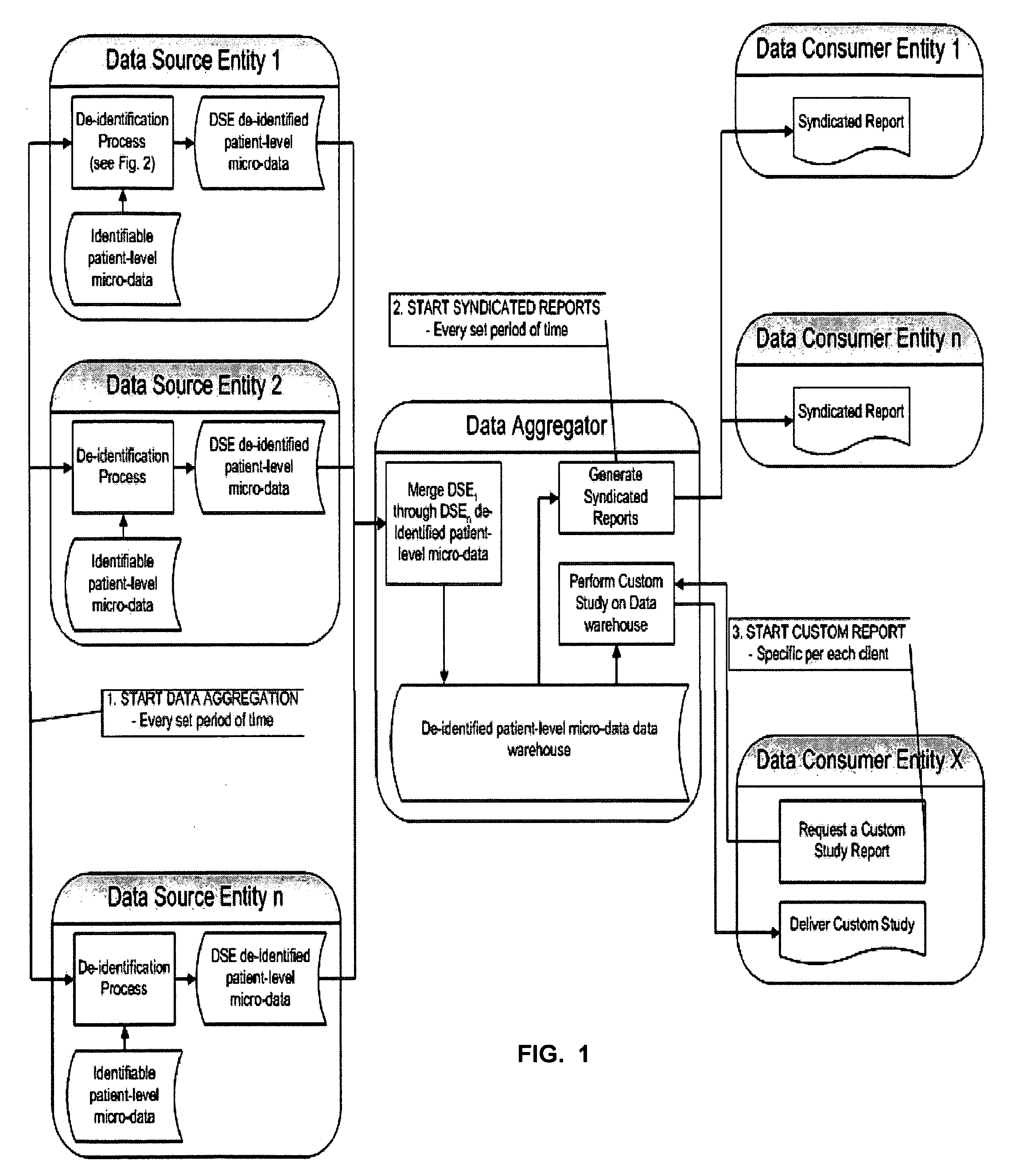
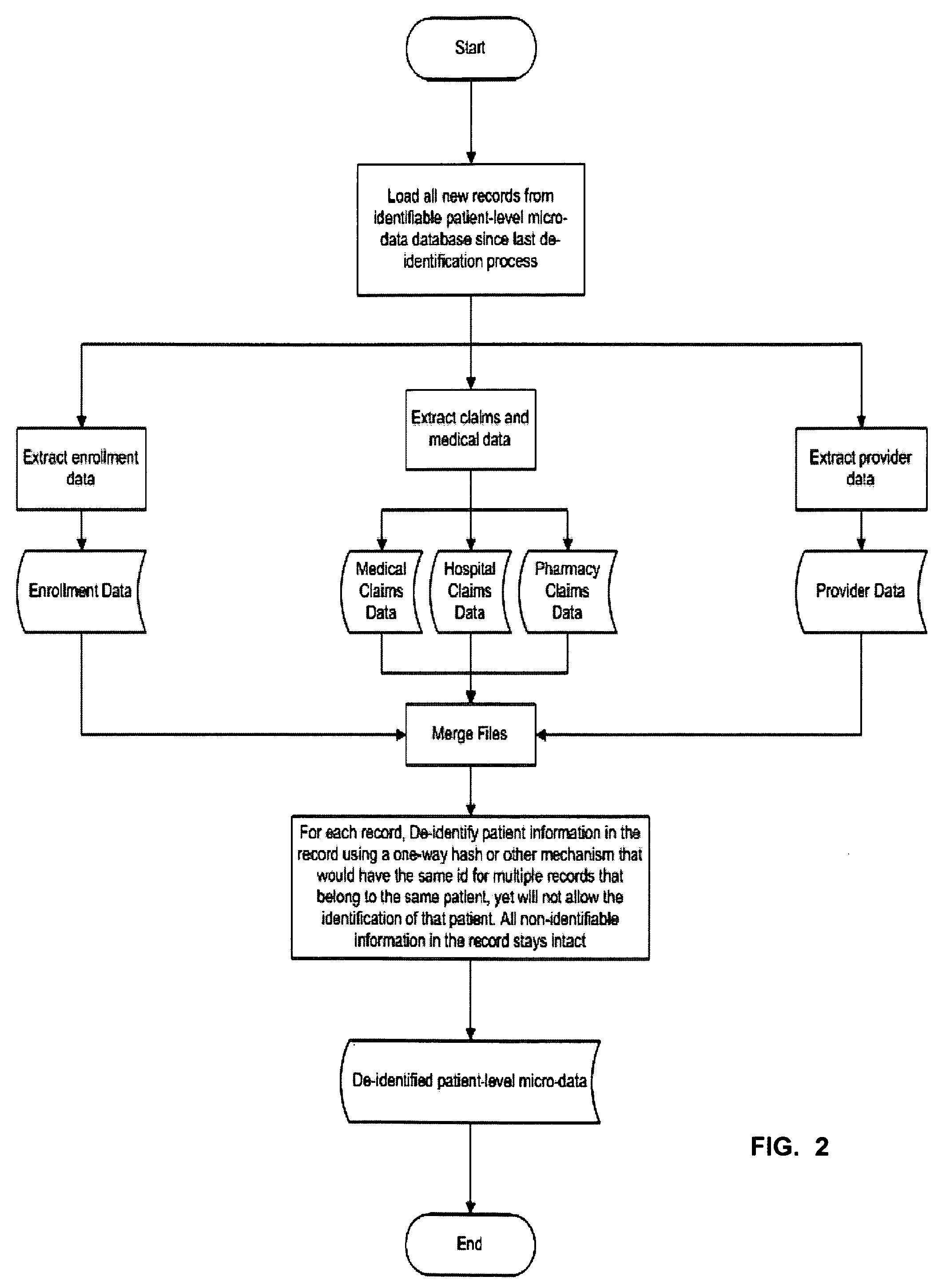
A Double Blinded Privacy-Safe Distributed Data Mining Protocol is disclosed, among an aggregator, a data consumer entity having privacy-sensitive information, and data source entities having privacy-sensitive information. The aggregator does not have access to the privacy-sensitive information at either the data consumer entity or the data source entities. The aggregator formulates a query without using privacy-sensitive information, and sends the query to the data consumer entity. The data consumer entity generates a list of specific instances that meet the conditions of the query and sends the list, encrypted, to the data source entities either directly or through the aggregator. The data source entities match the list against transactional data, de-identify the matched results, and send them to the aggregator. The aggregator combines results from data source entities and sends the combined result to the data consumer entity. This allows for privacy-safe data mining where both the data consumer entity and data source entities have privacy-sensitive information not available for the aggregator to see or use.
Owner:VEEVA SYST
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com