TLS (Transport Layer Security) scanning method and device
A network device and algorithm technology, applied in the field of TLS scanning, can solve problems such as low efficiency, unsupported client authentication, and unsupported certain algorithm, etc., to achieve the effect of improving processing performance, efficient algorithm and/or client authentication
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
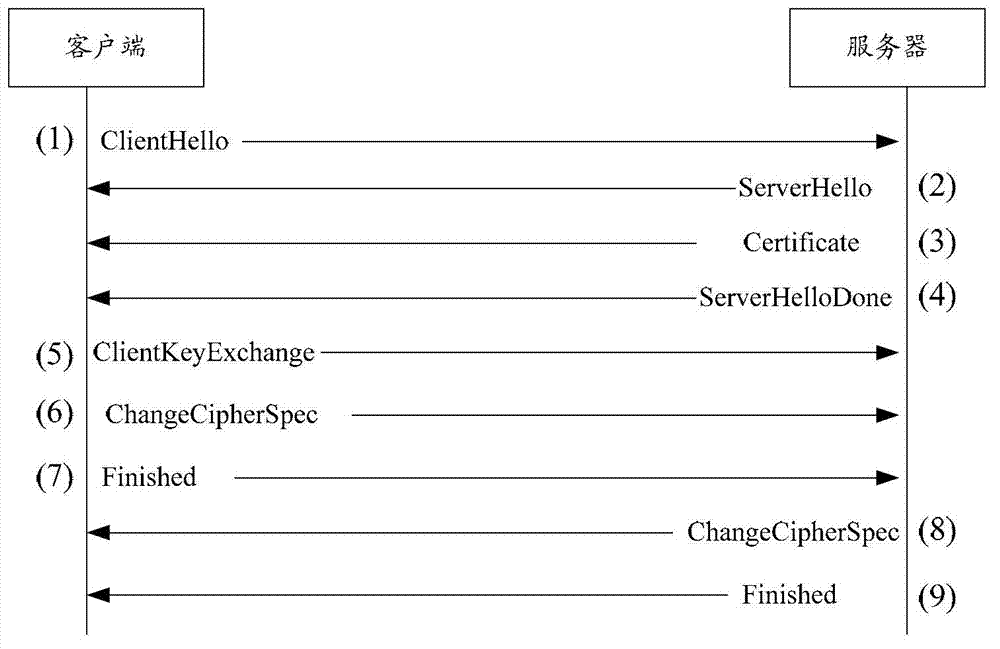
[0048] Figure 4 It is a schematic diagram of the interaction between the client, the agent, and the server when the export RSA algorithm without ServerKeyExchange or the standard RSA algorithm without ServerKeyExchange is supported. refer to Figure 4 , the TLS scanning method provided in this embodiment may include:
[0049] The certificate of the deployment server on the proxy.
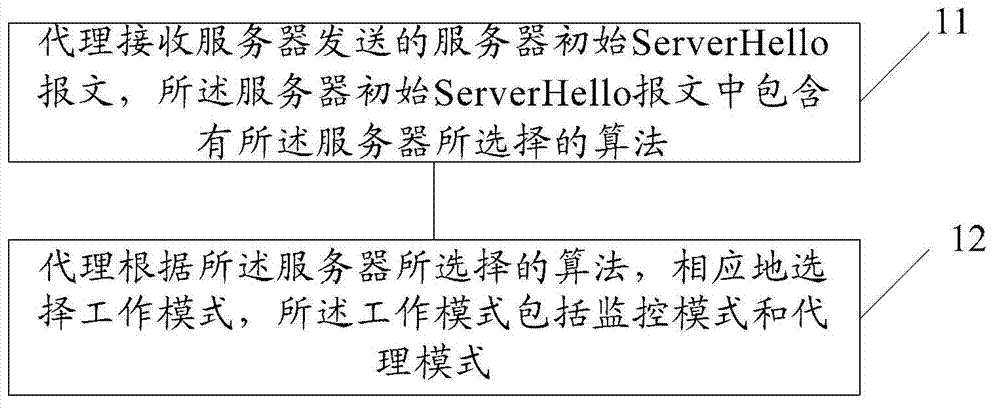
[0050] When the agent receives the ServerHello message, it checks the cipher_suite (algorithm suite) field in the ServerHello to determine whether the key exchange algorithm is RSA or RSA export (RSA_Export) algorithm.
[0051] If the agent determines that the key exchange algorithm is the RSA algorithm or the egress RSA algorithm, and no ServerKeyExchange message is received, the agent works in monitoring mode and does not modify any message. At this time, the specific process of the interaction between the client, the agent and the server is as follows: Figure 4 shown.
[0052] When the age...
Embodiment 2
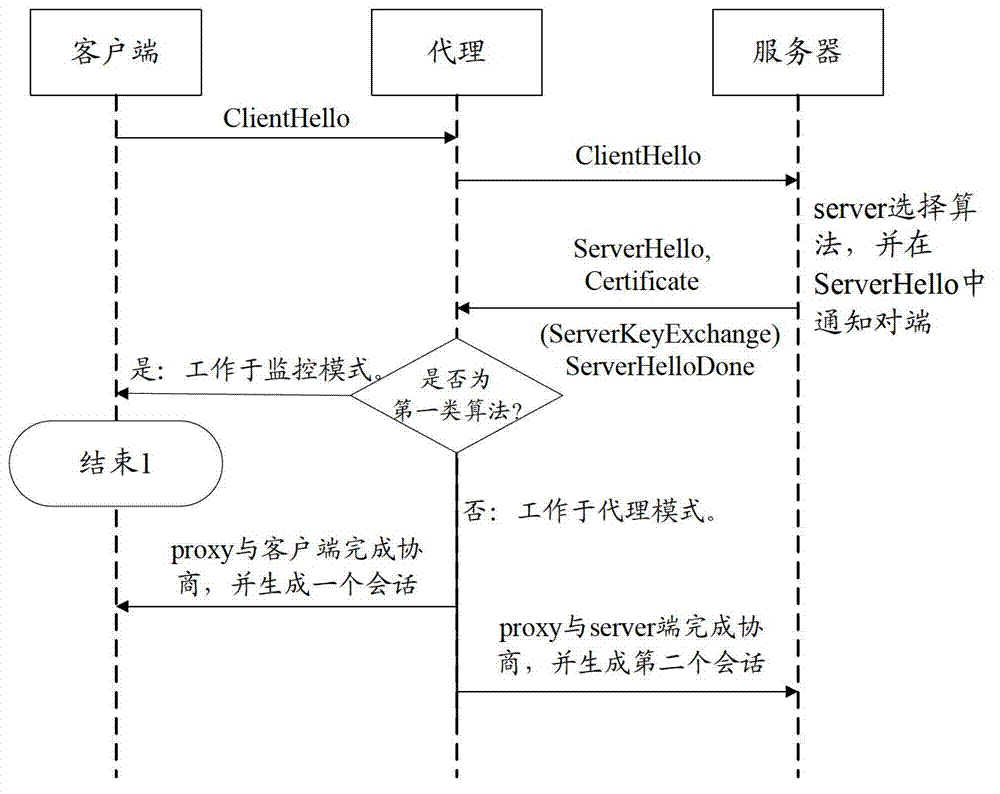
[0056] Figure 5 and Figure 6 It is a schematic diagram of the interaction between the client, the agent, and the server when the DH algorithm is supported. The TLS scanning method provided in this embodiment may include:
[0057] The certificate of the deployment server on the proxy.
[0058] When the agent receives the ServerHello, it confirms whether it is an RSA algorithm or an egress RSA algorithm.
[0059] If it is an RSA algorithm or an egress RSA algorithm, and no ServerKeyExchange message is received, the agent works in monitoring mode and does not modify any message. The proxy obtains the pre-master key by decrypting the ClientKeyExchange message, and derives the session key according to the TLS standard, and decrypts the subsequent TLS record message. The process ends.
[0060] If it is a DH algorithm, the agent works in an agent mode to regenerate a new ServerHello or ServerKeyExchange message. The proxy can make this selection according to local policy.
...
Embodiment 3
[0096] Figure 7 It is a schematic diagram of the interaction between the client, agent and server when supporting the export RSA algorithm with ServerKeyExchange or the non-standard RSA algorithm with ServerKeyExchange. refer to Figure 7 , the TLS scanning method provided in this embodiment may include:
[0097] The certificate of the deployment server on the proxy.
[0098] When the agent receives the ServerHello, it confirms whether it is an RSA algorithm or an egress RSA algorithm.
[0099] If it is the RSA algorithm or the export RSA algorithm, and the ServerKeyExchange message is not received, the agent works in the monitoring mode and does not modify any message. The proxy obtains the pre-master key by decrypting the ClientKeyExchange message, and derives the session key according to the TLS standard, and decrypts the subsequent TLS record message. The process ends.
[0100] If the agent receives the export RSA algorithm or RSA algorithm in the ServerHello, and re...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com