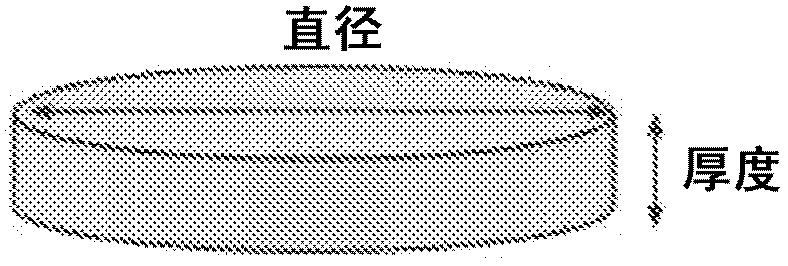
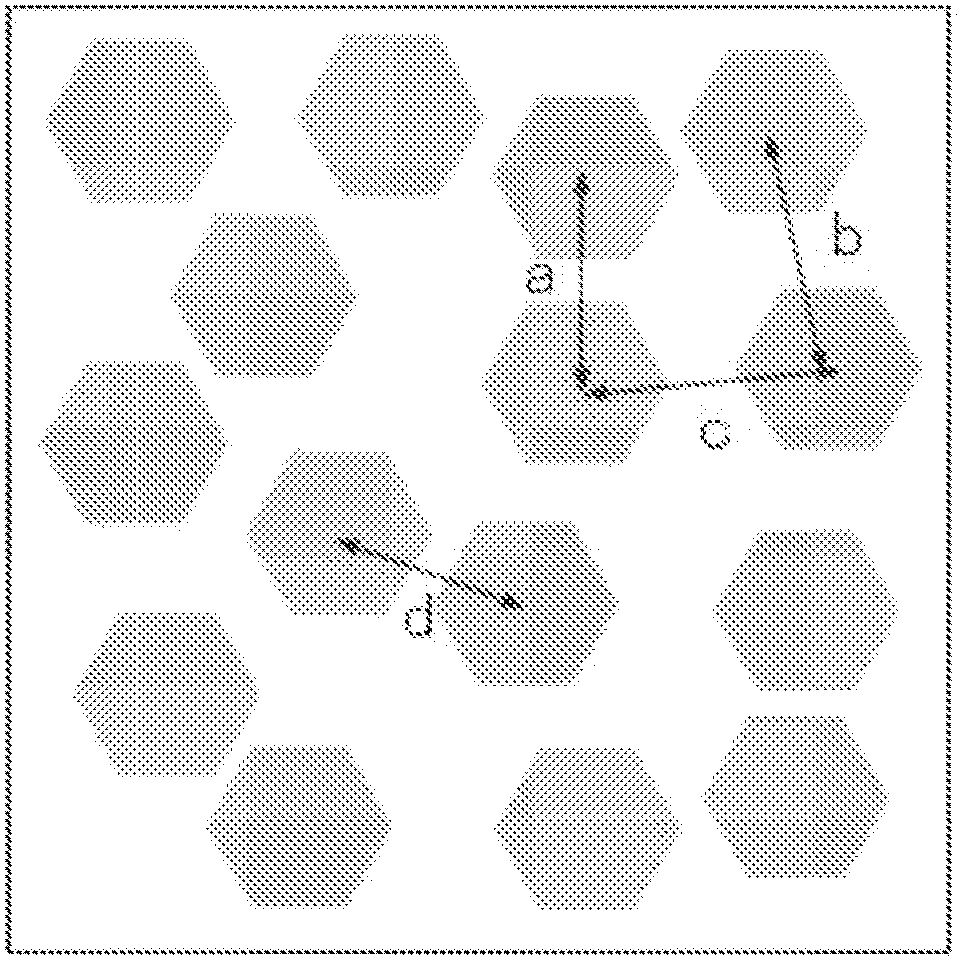
Heat-ray shielding material
A technology of heat ray shielding and light, applied in thin material processing, biochemical instruments, biochemical equipment and methods, etc., can solve problems such as increased haze and impossible control of silver particles
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0188]
[0189] -Synthesis of Flat Metal Particles-
[0190] A 0.5 g / L polystyrenesulfonic acid aqueous solution (2.5 mL) was added to a 2.5 mM sodium citrate aqueous solution (50 mL), followed by heating to 35°C. Next, 10 mM sodium borohydride solution (3 mL) was added to the resulting solution. Next, 0.5 mM silver nitrate aqueous solution (50 mL) was added thereto at 20 mL / min with stirring. This solution was stirred for 30 min to prepare a seed particle solution.
[0191] Next, ion-exchanged water (87.1 mL) was added to a 2.5 mM sodium citrate aqueous solution (132.7 mL), followed by heating to 35°C. Subsequently, a 10 mM ascorbic acid aqueous solution (2 mL) was added to the resulting solution, followed by adding thereto 42.4 mL of the seed particle solution prepared above. Further, 0.5 mM silver nitrate aqueous solution (79.6 mL) was added thereto at 10 mL / min with stirring. Next, the solution obtained above was stirred for 30 min, and then 0.35M aqueous potassium h...
Embodiment 2 to 29 and comparative example 1 to 6
[0198]
[0199] Except changing the amount of 1M NaOH and water, and the number of rotations and the rotation time of the centrifuge (product of KOKUSAN Co., Ltd., H-200N, ANGLE ROTOR BN) to those shown in Tables 1-1 and 1-2 Except that, the flat metal particles and heat ray shielding materials of Examples 2 to 29 and Comparative Examples 1 to 6 were prepared in the same manner as in Example 1.
Embodiment 30 to 47
[0201]
[0202] In addition to changing the amount of 2.5mM sodium citrate aqueous solution from 132.7mL to 255.2mL, changing the amount of ion-exchanged water from 87.1mL to 127.6mL, changing 72mL of 0.17M NaOH aqueous solution to 72mL of 0.08M NaOH aqueous solution, and changing The amount of 1M NaOH and water, and the number of revolutions and the rotation time of the centrifuge (the product of KOKUSAN Co., Ltd., H-200N, ANGLE ROTOR BN) are changed to those shown in Table 1-2, with embodiment 1 Flat metal particles and heat ray shielding materials of Examples 30 to 47 were prepared in the same manner as in Examples 30 to 47.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com