A Method for Detecting Photochemical Activity of Carbon Nanotubes Using Transient Absorption Spectroscopy
A photochemically active, carbon nanotube technology, applied in the measurement of color/spectral properties, etc., can solve the problem of inability to quickly and accurately judge carbon nanotubes, and achieve the effects of low detection cost, simple condition control, and significant difference.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
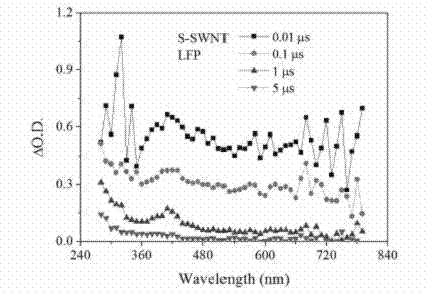
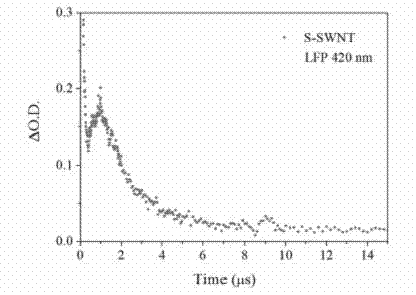
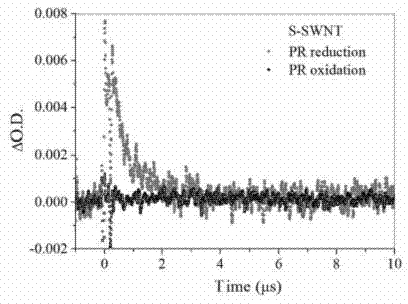
[0034] A method for detecting the photochemical activity of carbon nanotubes using transient absorption spectroscopy, the method comprising the following steps:
[0035]a. To prepare an aqueous solution of carbon nanotubes, weigh 1 mg of single-walled carbon nanotubes (S-SWNTs) and dissolve them in 25 mL of ultrapure water, and sonicate them with an ultrasonic cleaner. The purpose of ultrasonic treatment is to better disperse carbon nanotubes in aqueous solution. Generally speaking, the longer the ultrasonic time, the better the dispersion effect of carbon nanotubes. The carbon nanotubes with hydroxyl, carboxyl and other polar functional groups on the surface need shorter ultrasonic dispersion time than the original carbon nanotubes. Therefore, the time of ultrasonic treatment can be 1-2 h, and the preferred choice of ultrasonic treatment in this embodiment is 2 h. After standing still, the supernatant of the carbon nanotube aqueous solution is taken as the detection object;...
Embodiment 2
[0040] A method for detecting the photochemical activity of carbon nanotubes using transient absorption spectroscopy, the method comprising the following steps:
[0041] a. To prepare an aqueous solution of carbon nanotubes, weigh 1 mg of multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWNT-OH) containing 3.7% hydroxyl groups on the surface and dissolve them in 25 mL of ultrapure water, and then use an ultrasonic cleaner to sonicate for 1 h. Stand still and take the supernatant as the detection object.
[0042] b. Use a laser flash photolysis instrument to analyze the photochemical properties of the carbon nanotube aqueous solution under light conditions; take 2 mL of the supernatant of the carbon nanotube aqueous solution prepared in step a and transfer it into the sample cell of the laser flash photolysis instrument, and then Perform laser photolysis experiments.
[0043] c. Use the pulse radiolysis device to verify and analyze the characteristic peaks of the carbon nanotube transient absor...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com