Method for online separation and purification of butanol, acetone and ethanol in fermentation solution by using active carbon in-situ adsorption
A technology of activated carbon and fermentation broth, which is applied in the biological field to achieve the effects of low product purity, strong adsorption capacity and energy saving
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0047] A method for on-line separation and purification of butanol, acetone and ethanol in fermentation broth by using activated carbon in-situ adsorption;
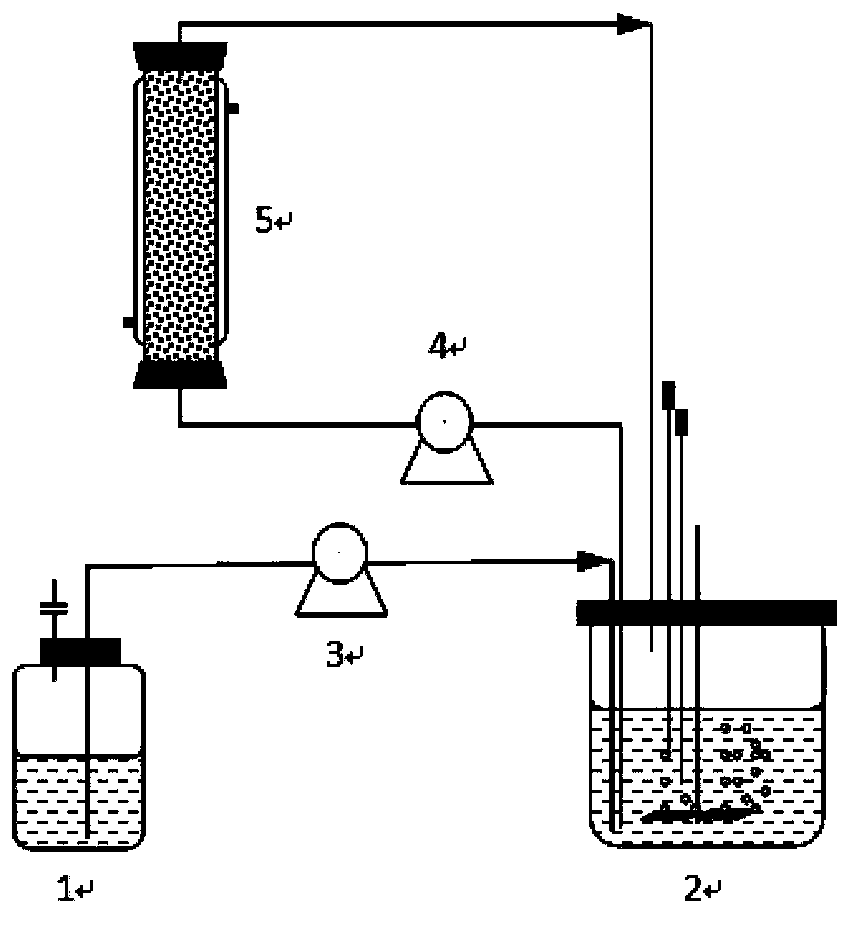
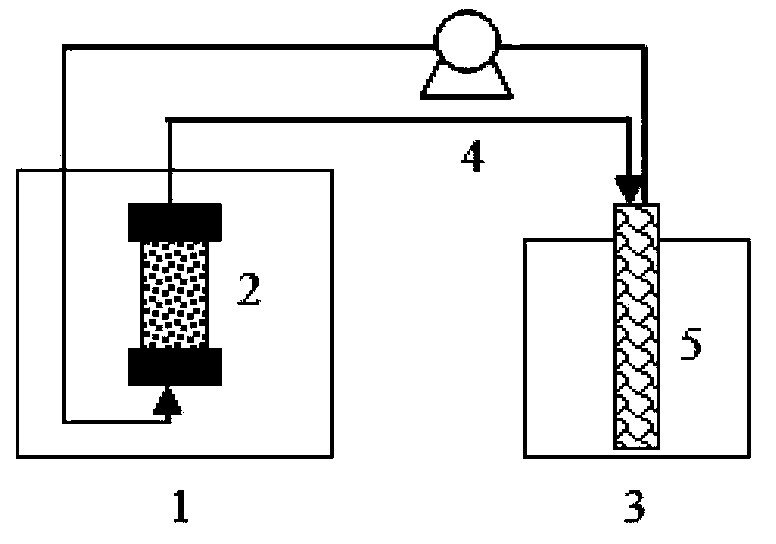
[0048] ① if figure 1 As shown, the seed medium was first passed nitrogen in the seed tank for 10 minutes to deoxygenate, then sterilized at 121°C for 30 minutes, cooled to room temperature, inserted into the acetone butanol ethanol production bacteria, and the production bacteria were cultivated to the most active logarithm of growth growth period. The cultivation time until the logarithmic growth phase is 12-18 hours, preferably 15 hours; the cultivation temperature is 30-40°C, preferably 37°C. After the seed culture is completed, it is ready to be inserted into the fermenter.
[0049] ② if figure 1 As shown, first sterilize the fermentation medium at 121°C for 30 minutes, then pass nitrogen gas for 2 hours to deoxygenate, cool to room temperature, turn on the pump I, and put the seed liquid containing acetone, buta...
Embodiment 2
[0054] A method for on-line separation and purification of butanol, acetone and ethanol in fermentation broth by using activated carbon in-situ adsorption;
[0055] The difference with embodiment 1 is:
[0056] When the pH of the fermentation broth is lower than 5.0, ammonia water is automatically added to adjust the pH to above 5.0.
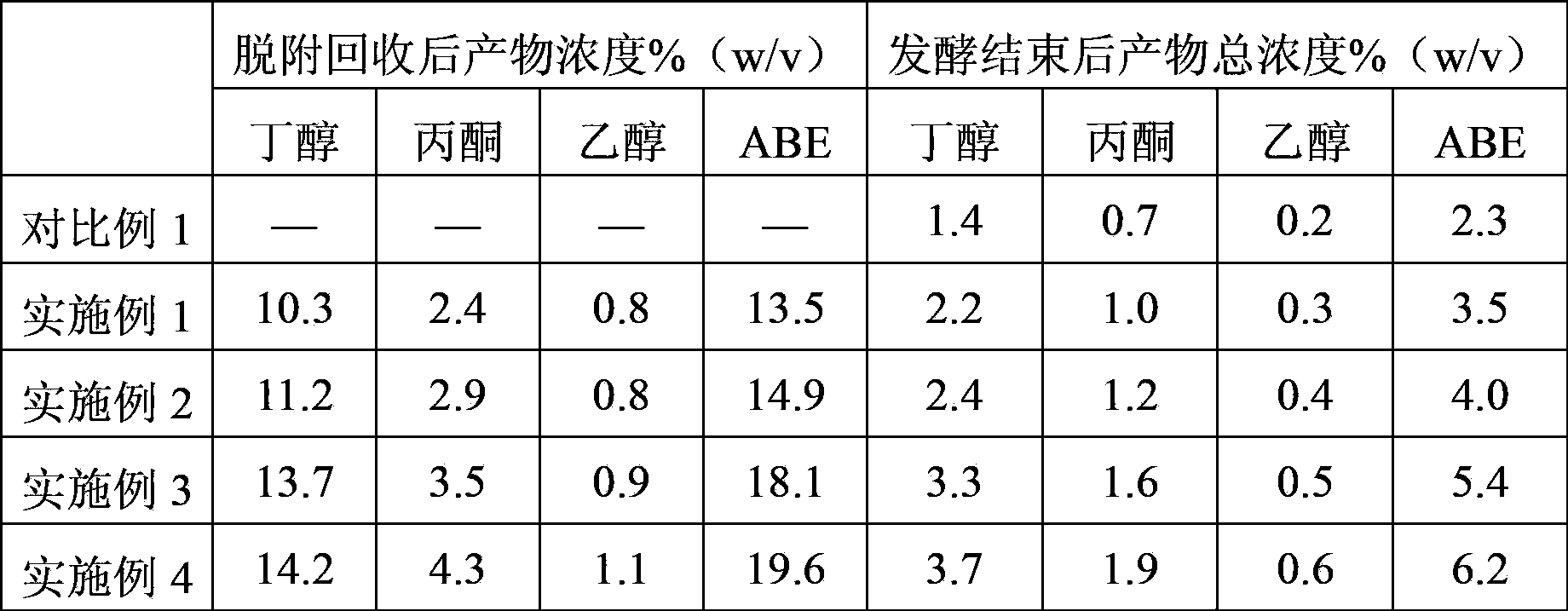
[0057] The experimental data are shown in Table 1 and Table 2.
[0058] Summary: After the fermentation, the concentrations of butanol and ABE total solvent were 2.4% (w / v) and 4.0% (w / v), respectively, which were 71.4% and 73.9% higher than those in Comparative Example 1. Glucose consumption was 12.0%, an increase of 71.4% compared with Comparative Example 1. The concentrations of butanol and ABE total solvent recovered after desorption were 11.2% (w / v) and 14.9% (w / v), which were 8.0 times and 6.5 times higher than those in Comparative Example 1, respectively. The production intensity of butanol and ABE total solvent is 0.26g / L / h and 0.43g / ...
Embodiment 3
[0060] A method for on-line separation and purification of butanol, acetone and ethanol in fermentation broth by using activated carbon in-situ adsorption;
[0061] The difference with embodiment 1 is:
[0062] When the pH of the fermentation broth is lower than 5.0, ammonia water is automatically added to adjust the pH to above 5.0. The fermentation method is feed-fed fermentation. When the glucose concentration in the fermentation broth drops below 10g / L, glucose is added to continue to provide carbon sources for the fermentation until the fermentation is terminated.
[0063] The experimental data are shown in Table 1 and Table 2.
[0064] Summary: After the fermentation, the concentrations of butanol and ABE total solvent were 3.3% (w / v) and 5.4% (w / v), respectively, which were 36.4% and 33.3% higher than those in Comparative Example 1. Glucose consumption was 16.5%, which was 2.4 times higher than that of Comparative Example 1. The concentrations of butanol and ABE tota...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| boiling point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com