Fine partition method of soil pollutant content spatial distribution
A technology of spatial distribution and pollutants, applied in image analysis, image data processing, instruments, etc., can solve the problem of high interpolation results, achieve the effect of wide application, guarantee objectivity and accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] A fine zoning method for the spatial distribution of soil pollutant content, comprising the following steps:
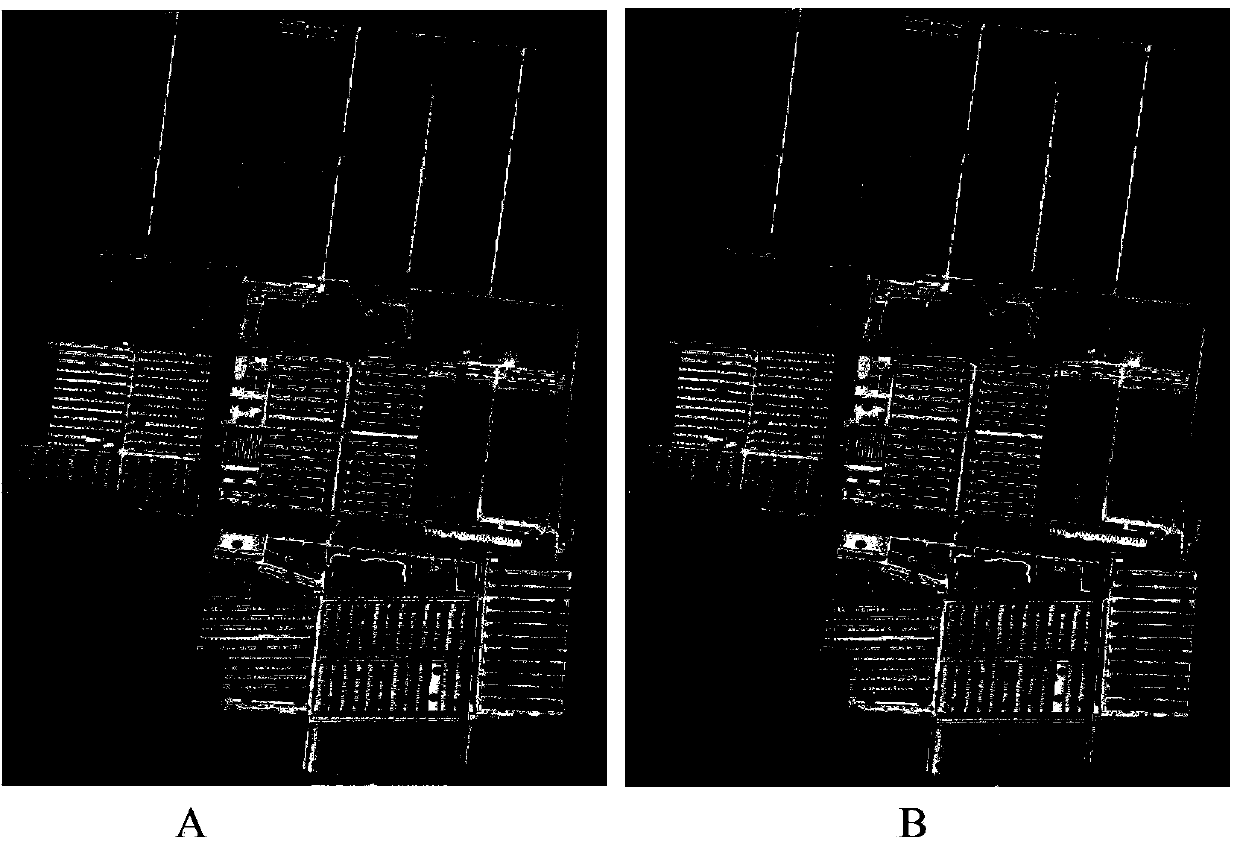
[0028] Step 1. By classifying remote sensing images or aerial photographs, extract the restricted area BArea of the research area;
[0029] The constraint area BArea is the spatial range covered by the spatial interpolation operation. The extraction of the restricted area includes extracting two parts, the non-monitoring target area NMArea and the monitoring target area MArea. Non-target monitoring areas refer to monitoring areas that are not usually involved in soil pollutant monitoring, such as water areas, construction areas, forest land, etc. The monitoring target area refers to the actual monitoring area in soil pollution sampling monitoring, usually referring to agricultural land. The three of the restricted area, the non-target monitoring area and the monitoring target area obey the following spatial relationship:
[0030]
[0031] ...
Embodiment 2
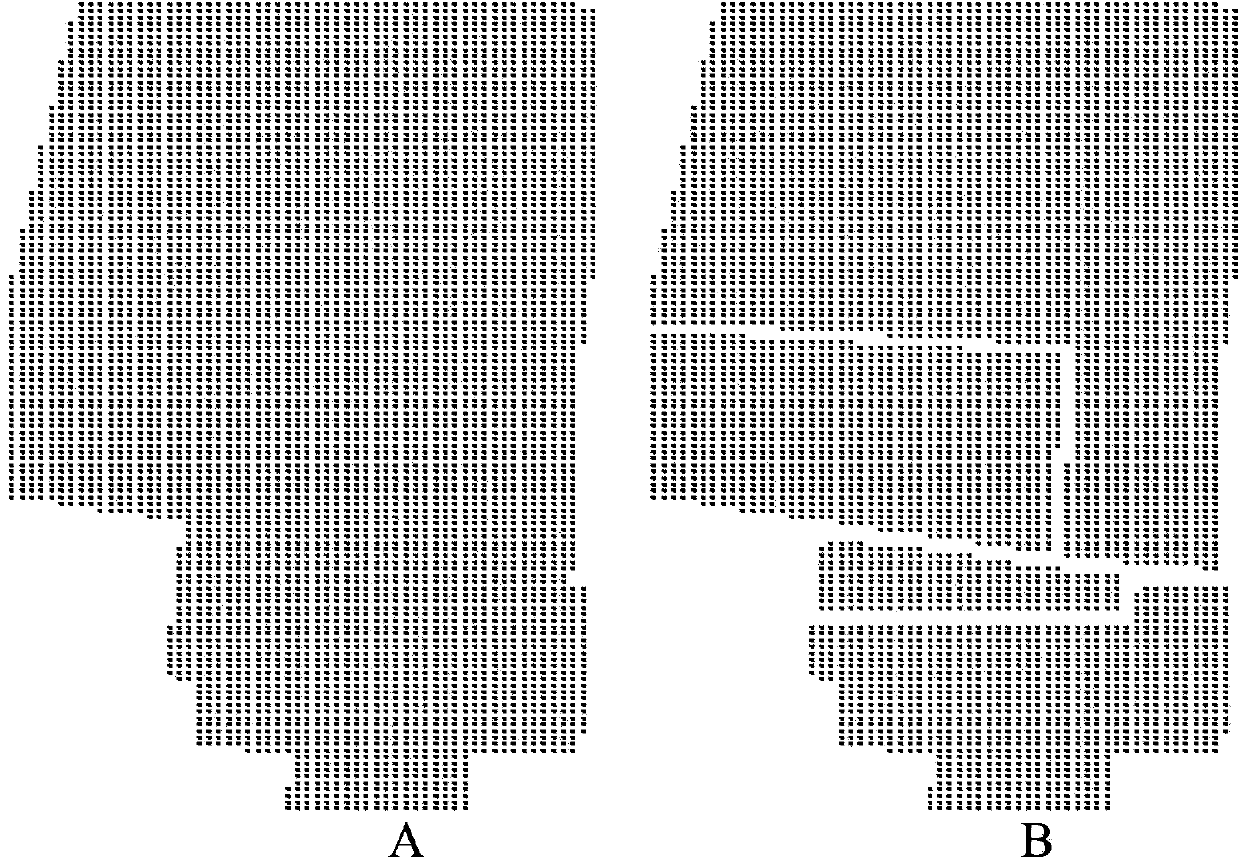
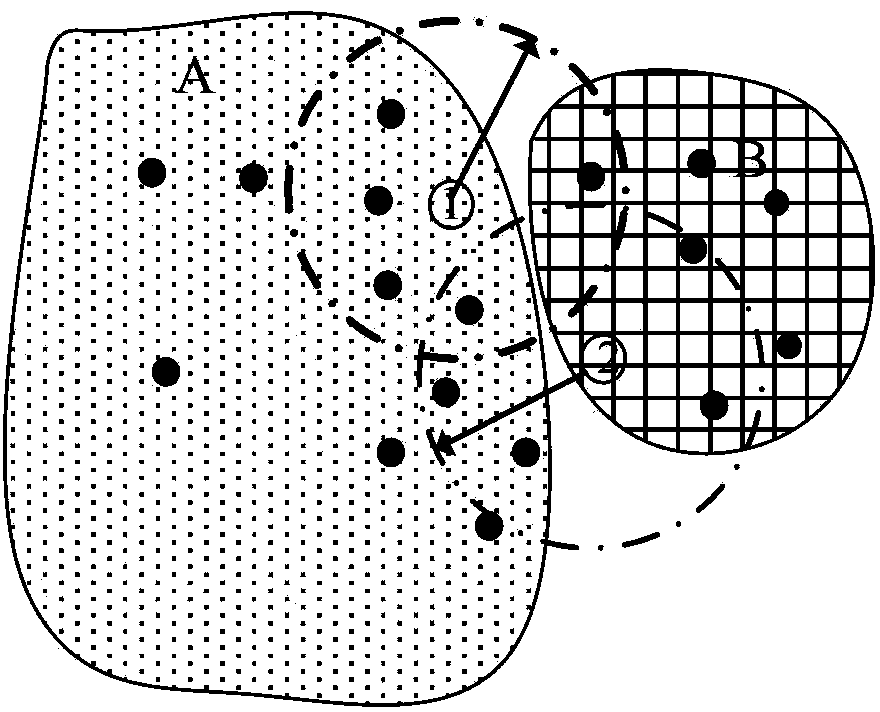
[0053] The following examples are used to illustrate the present invention, but are not intended to limit the scope of application of the present invention. This example comes from an organic agricultural product producing area in Shanghai, which is 1000 meters long from east to west and 600 meters wide from north to south, with a total area of 0.6k square meters. There are two main types of land use in this production area: field and facility vegetable land. In 2010, 193 samples were taken according to the regular grid sampling method to monitor the soil heavy metal Cu content in this production area. The distribution of sample points is shown in ( figure 2 -A). The survey found that the content of heavy metal Cu in the soil of the facility vegetables was significantly higher than that of the field soil. Therefore, the facility vegetable land is considered as the potential pollution area of heavy metal Cu in this production area. Adopt the present invention to make th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com