Special vehicle signal priority control method based on global position system (GPS)
A signal priority, special vehicle technology, applied in the traffic control system of road vehicles, traffic control systems, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of priority control, priority signal signal priority control effect, etc., to improve efficiency and simplify equipment maintenance in the later stage , The effect of reducing construction costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0060] Below in conjunction with specific embodiment, further illustrate the present invention, should be understood that these embodiments are only used to illustrate the present invention and are not intended to limit the scope of the present invention, after having read the present invention, those skilled in the art will understand various equivalent forms of the present invention All modifications fall within the scope defined by the appended claims of the present application.
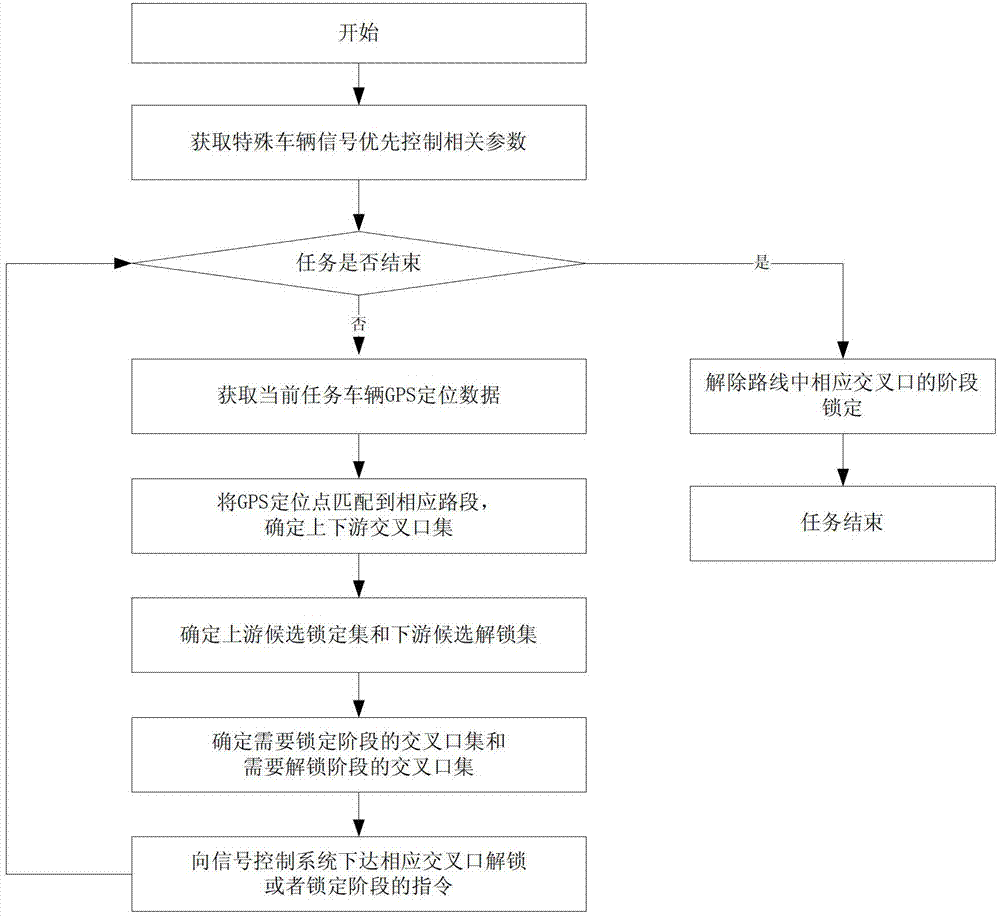
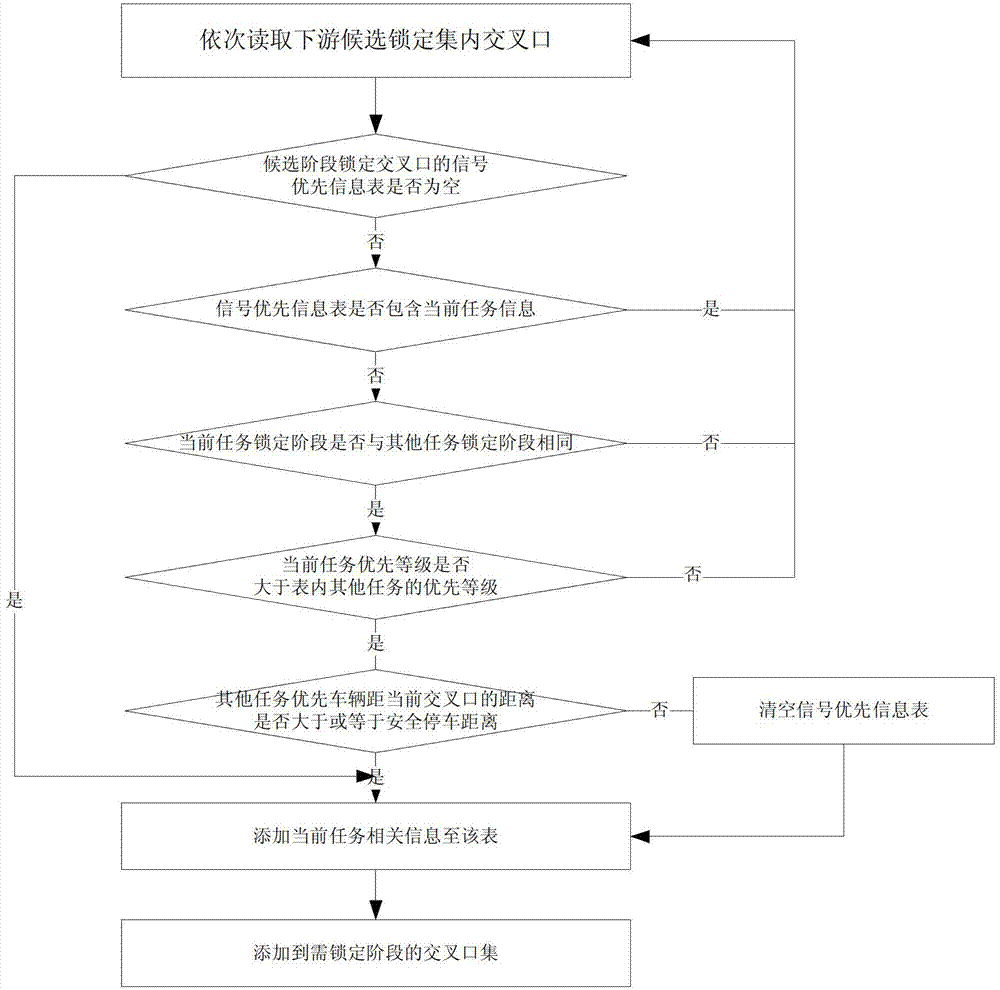
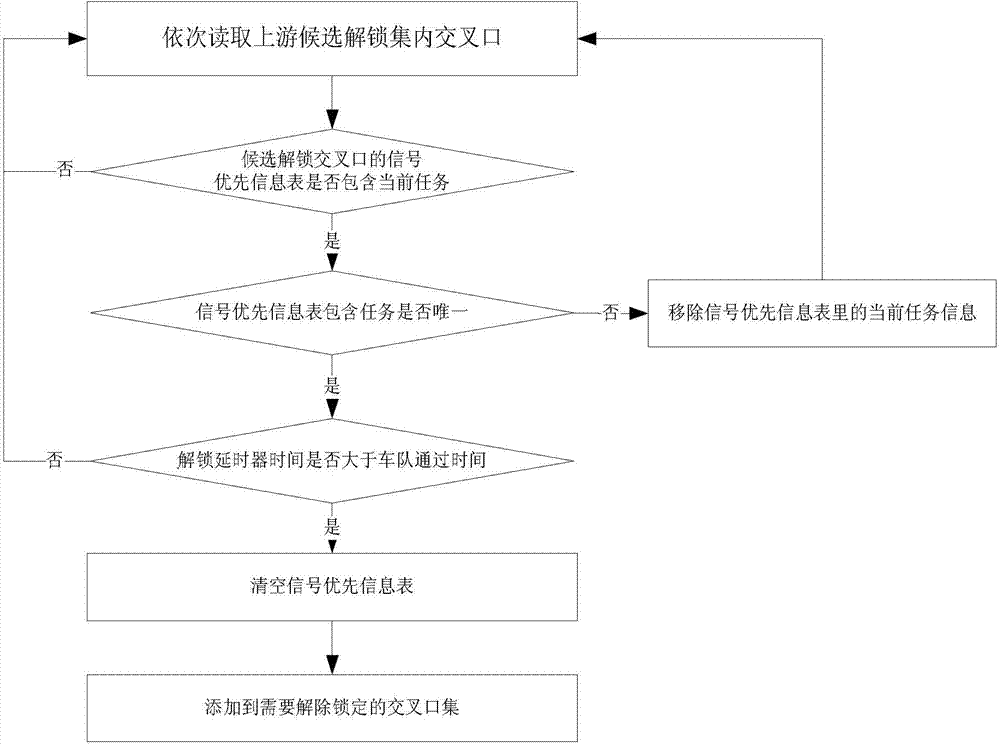
[0061] Such as figure 1 Shown is the flow chart of the special vehicle signal priority control method based on GPS, and the specific implementation steps are as follows:
[0062] 1) Obtain the configuration parameters of special vehicle signal priority control tasks in real time, and build a signal priority information table for priority route intersections;
[0063] Special vehicle signal priority control task configuration parameters, mainly including priority route, priority level, number of v...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com