Parallel indexing technology for vector QR trees
A QR tree and vector technology, applied in the field of spatial data management and retrieval, can solve problems such as difficult to solve inter-process load balancing, unable to break through the bottleneck of master node access, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
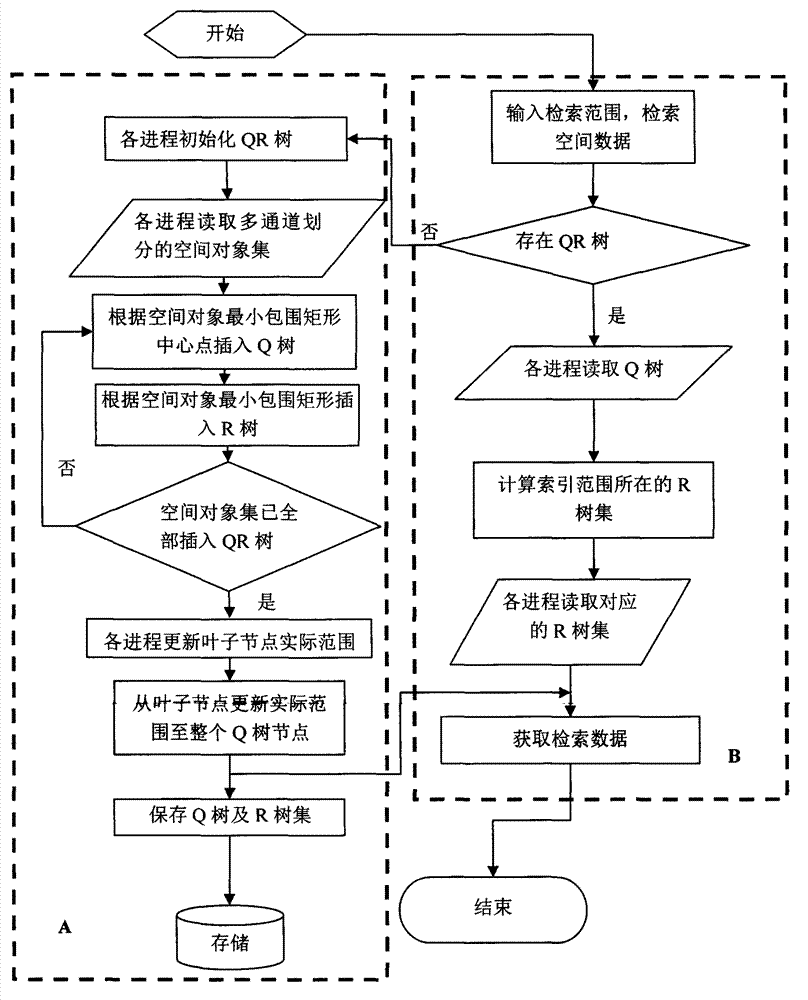
[0073] An example using QR tree parallel indexing. The size of the spatial data range is Rect{(0, 0), (8,000, 8,000)}, and the number of spatial object sets SpatialDataSets=512,000.
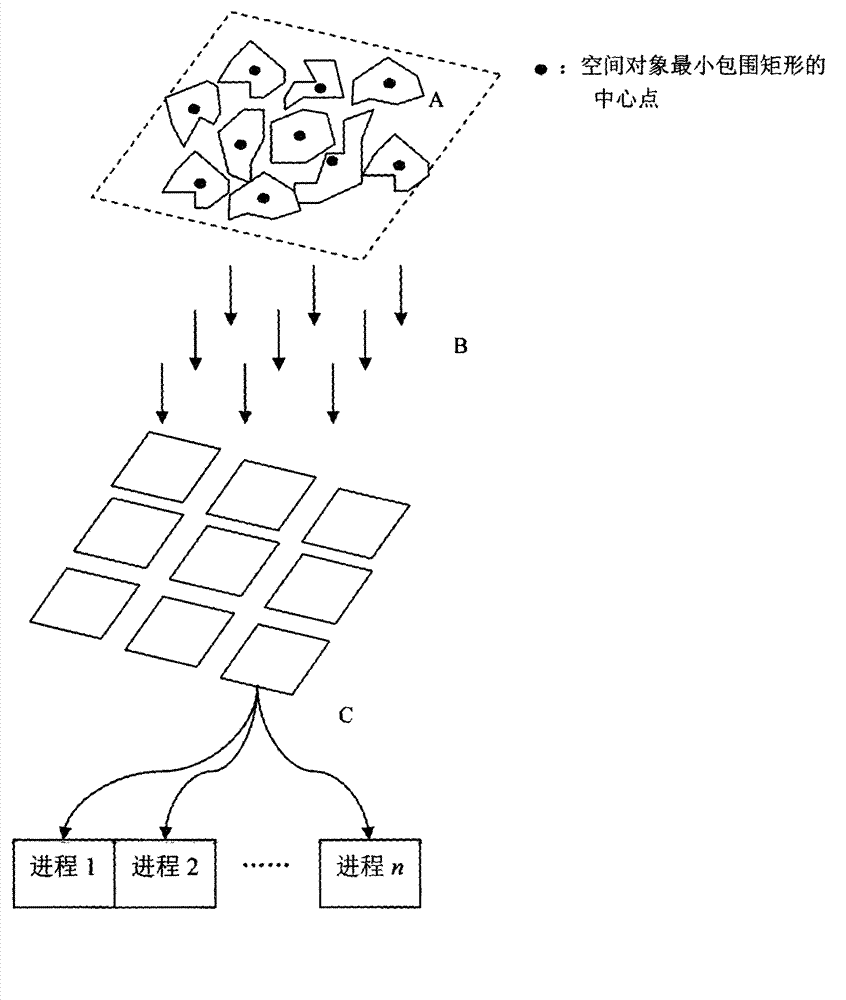
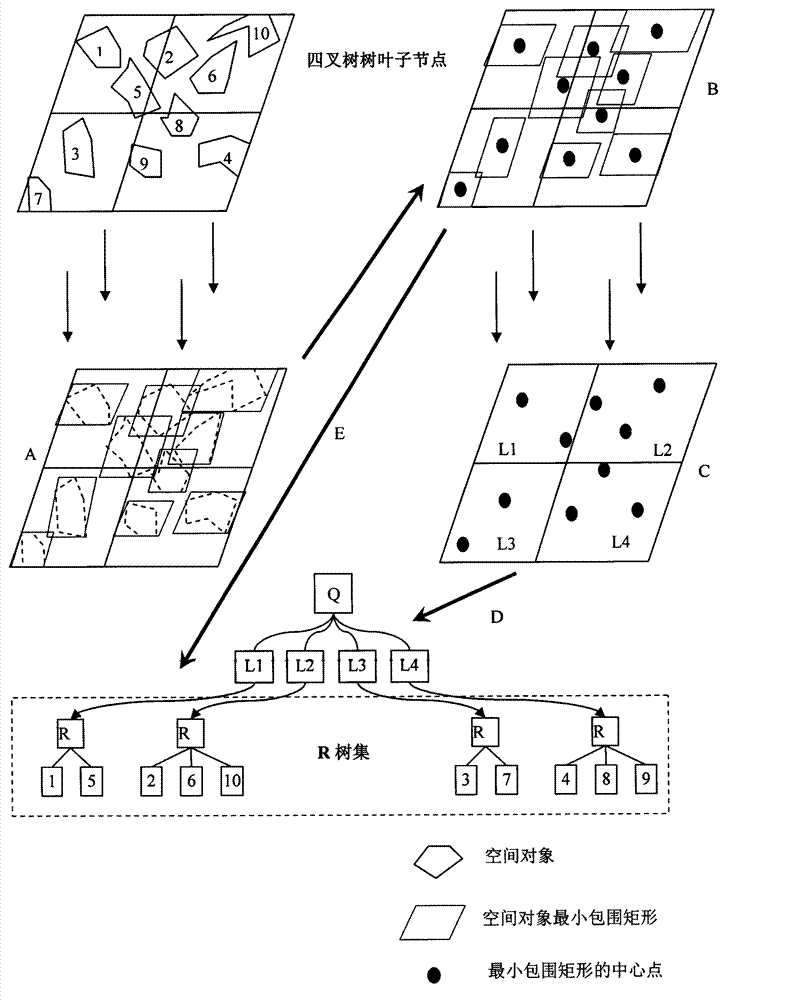
[0074]1. Taking 64 (8×8) multi-channels as an example, the process of dividing the above data set by the matrix MultiChannelArray is as follows Figure 7 Shown:
[0075] 1) Initialize the spatial dataset with a range of Rect{(0, 0), (8,000, 8,000)} to 64 (8×8) channels (such as Figure 7 A), the length of each sub-channel ChannelLength=1,000, the width of ChannelWidth=1,000, each channel is initially assigned data record value NumofObjects=0;
[0076] 2) Traverse the spatial object set to obtain the minimum bounding rectangle (MBR) of each object. Calculate the channel MultiChannelArray[i][j] (0≤i Figure 7 B;
[0077] 3) MultiChannelArray[i][j] of each channel rotates and divides the entered spatial objects into each process in sequence (rotation method) until the spatial data set of the chan...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com