A Low Bounce Vacuum Interrupter Structure
A vacuum interrupter and cup holder technology, which is applied to high-voltage air circuit breakers, electrical components, electric switches, etc., can solve the problems of large bounce range, long bounce time, and hot contacts, so as to shorten the bounce time and prolong the use life, reducing the effect of heating
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
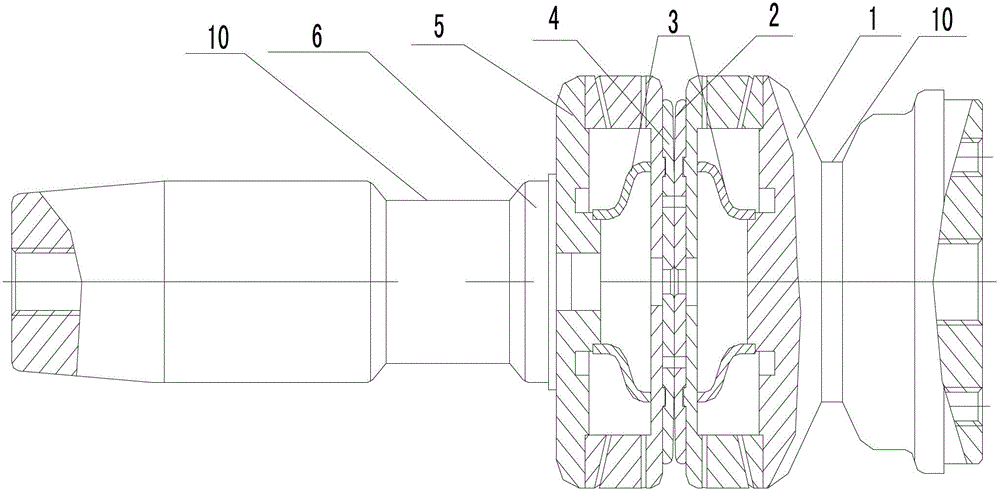
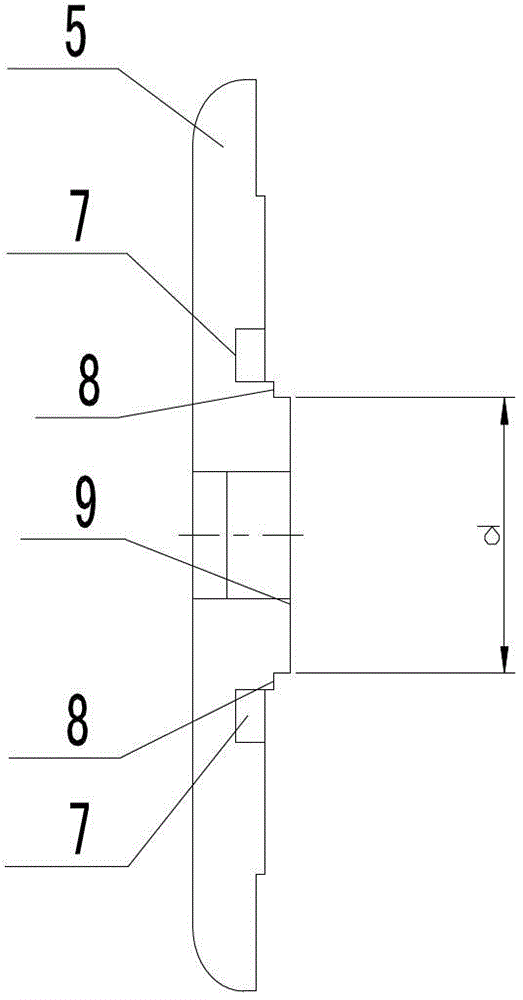
[0016] Embodiment 1 of the present invention: as attached figure 1 And attached figure 2 As shown, it includes a cup holder 5, the outer surface of the cup holder 5 is connected with the static conductive rod 1 and the movable conductive rod 6, the inner surface of the contact seat 5 is connected with the static contact 2 and the movable contact 4, and the inner surface of the cup holder 5 is connected. There is an annular groove 7 on the side, and the inner ring surrounded by the annular groove 7 is the middle stress part 9, and the middle stress part 9 surrounded by the annular groove 7 is provided with a positioning groove 8, and one end of the reinforcing rib 3 is snapped into the middle stress part 9 At the positioning groove on the top, the other end is connected with the static contact 2 and the movable contact 4, and a groove 10 is respectively provided on the static conductive rod 1 and the movable conductive rod 6.
[0017] During the closing process of the vacuum ...
Embodiment 2
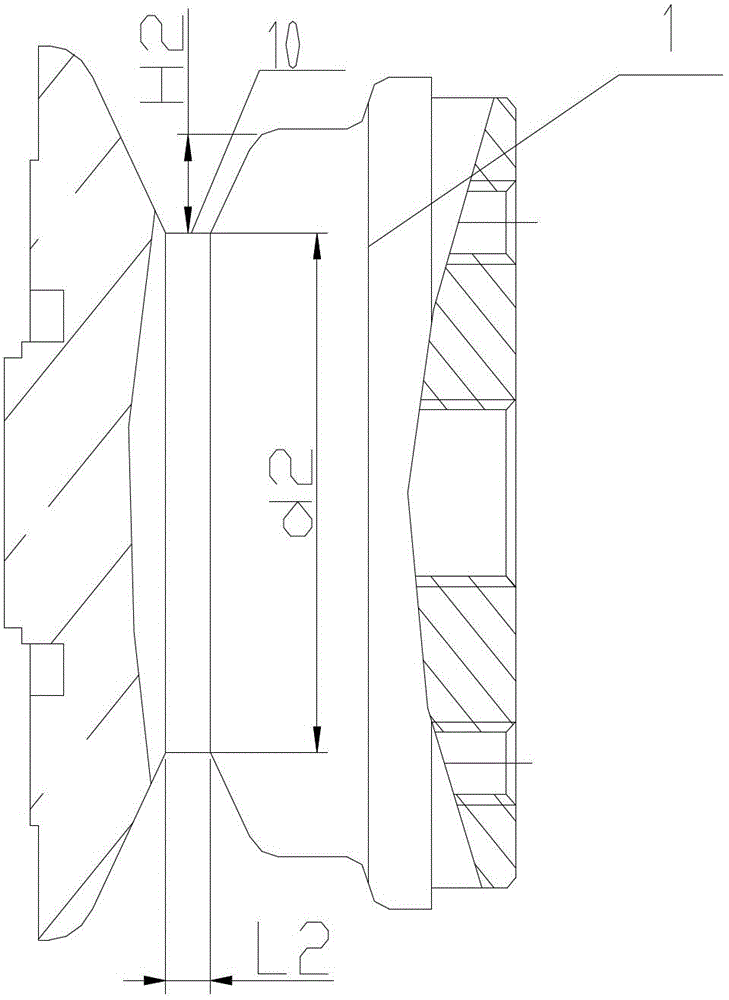
[0019] Embodiment 2 of the present invention: The structural position and working principle of the low-bounce vacuum interrupter are as described in Embodiment 1. In order to ensure that the middle stress-bearing part 9 can undergo a small amount of plastic deformation and can Ensure that its deformation will not be too large, so as to change the performance of the entire mechanism. Therefore, when opening the annular groove 7, the diameter d of the middle force-bearing part 9 can be 30mm, and the depth of the annular groove 7 is 10mm. When the groove 10 is opened, the width corresponding to the groove 10 on the moving conductive rod 6 is L1, the width corresponding to the groove 10 on the static conductive rod 1 is L2, the range of L1 and L2 is 2-50mm, and the moving conductive rod 6 The depth H1 of the groove 10 on the top is 1 / 2 to 1 / 4 times of the diameter d1 of the moving conductive rod at the corresponding slot, and the depth H2 of the groove 10 on the static conductive r...
Embodiment 3
[0020] Embodiment 3 of the present invention: when opening the annular groove 7, the size of the diameter d of the middle stressed part 9 can be: 45mm, and the depth of the annular groove 7 can be: 15mm. When the groove 10 is opened, the width corresponding to the groove 10 on the moving conductive rod 6 is L1, the width corresponding to the groove 10 on the static conductive rod 1 is L2, the range of L1 and L2 is 2-50mm, and the moving conductive rod 6 The depth H1 of the groove 10 on the top is 1 / 3 times of the diameter d1 of the moving conductive rod at the corresponding slot, and the depth H2 of the groove 10 on the static conductive rod 1 is 1 / 3 of the diameter d2 of the static conductive rod at the corresponding slot. / 3 times.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com