Device and method for rapidly detecting surviving unicellular organisms in ship ballast water
A ship ballast water, single-cell technology, applied in measurement devices, particle and sedimentation analysis, particle size analysis, etc., can solve the problems of large size, inability to distinguish between life and size of microorganisms, and inconvenient to bring to the site, etc., to achieve small size Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
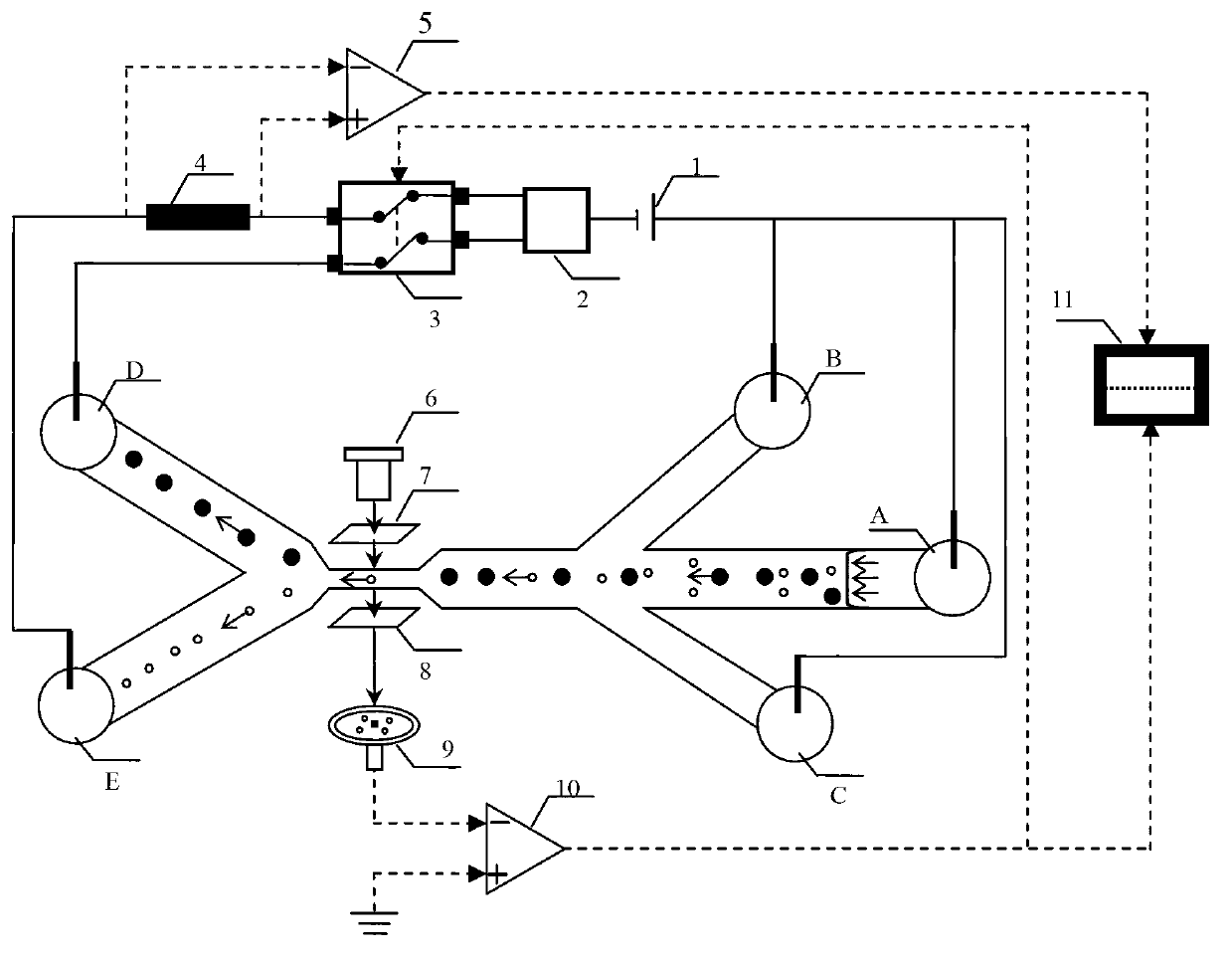
[0020] The invention provides a device and method for rapidly detecting single-celled organisms living in ship's ballast water. The technical solution of the invention will be described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
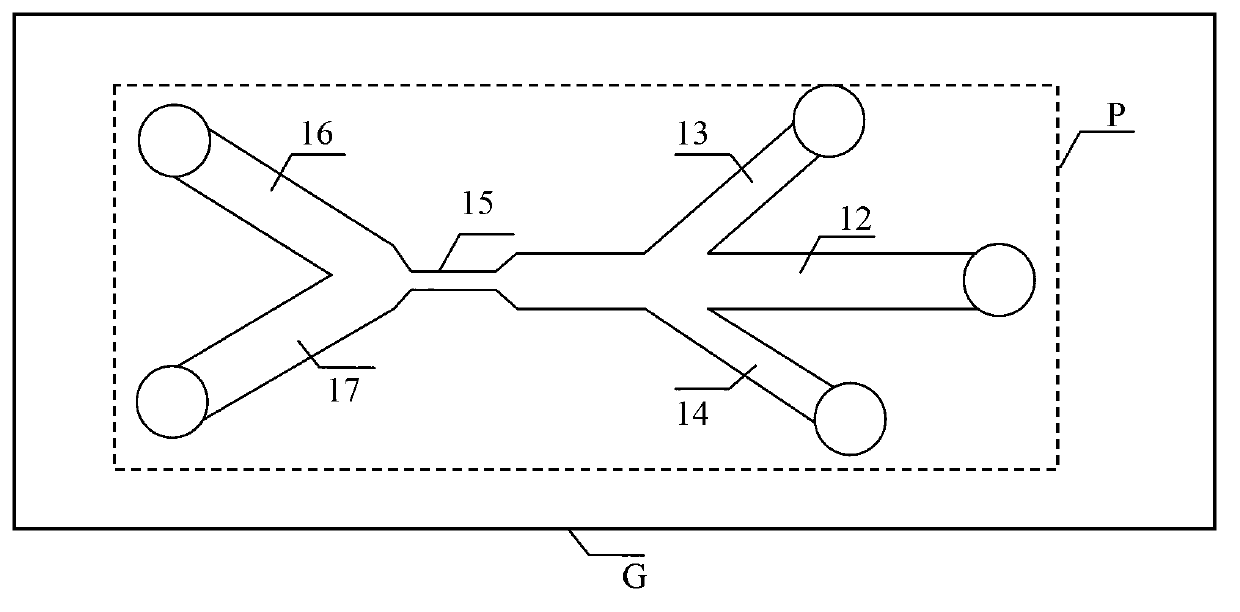
[0021] figure 1 It is a structural schematic diagram of an embodiment of the present invention's device for rapidly detecting surviving single-cell organisms in ship's ballast water; figure 2 It is a schematic structural diagram of an embodiment of the microfluidic chip of the present invention, as shown in the figure.
[0022] PDMS microfluidic chip P includes liquid storage hole A, liquid storage hole B, liquid storage hole C, liquid storage hole D, liquid storage hole E, main channel 12, first focusing channel 13, second focusing channel 14, detection channel 15. The first sorting channel 16, the second sorting channel 17, the liquid storage hole A is connected to the main channel 12, the liquid storage hole B is connected to...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com