Voice-endpoint-detection based artificial cochlea automatic gain control method and system
An automatic gain control, cochlear implant technology, applied in speech analysis, speech recognition, medical science, etc., can solve the problem of loud and small voice, and achieve the effect of improving listening ability and speech recognition effect.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0055] In order to make the object, technical solution and advantages of the present invention clearer, the present invention will be described in further detail below in conjunction with specific embodiments and with reference to the accompanying drawings.
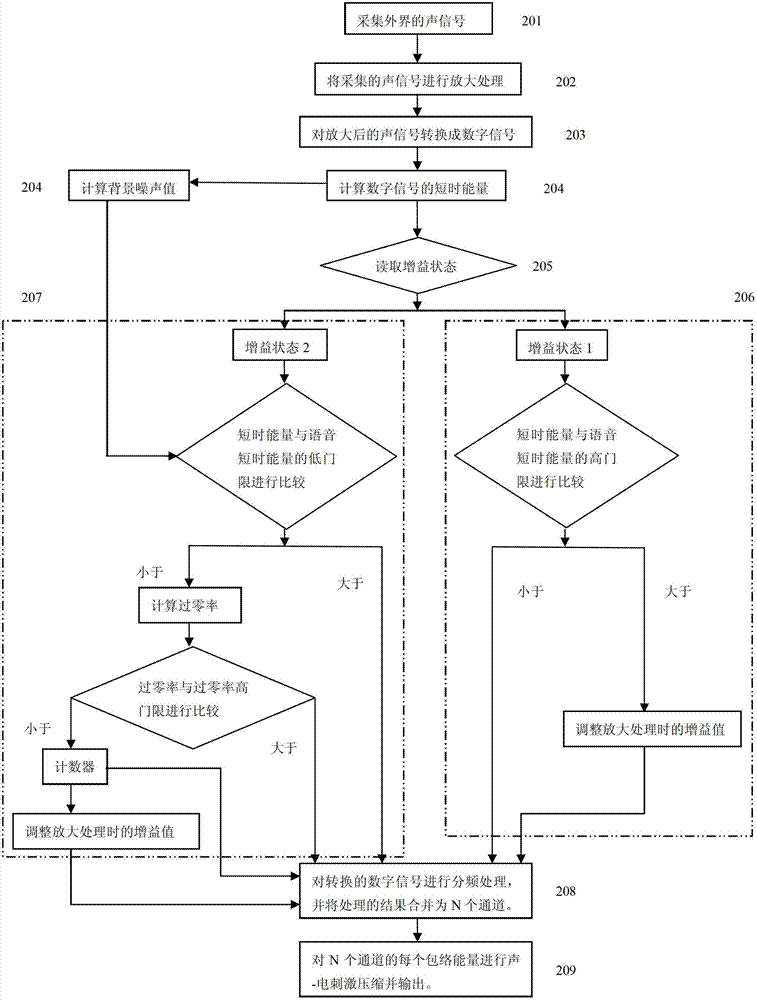
[0056] refer to figure 2 As shown, it is a schematic flow chart of an embodiment of the cochlear implant automatic gain control method based on voice endpoint detection in the present invention, wherein:
[0057] Step 201, collecting external acoustic signals.
[0058] Step 202, amplify the collected acoustic signal: pass the collected acoustic signal through an amplifier whose gain value can be adjusted, that is, the gain value of the amplifier can be set as required, and amplify the collected acoustic signal according to the set gain value.
[0059] In one embodiment of the present invention, the amplifier is set with two gain values, namely the default gain Gain_Default and the default gain Gain_Loud for noisy enviro...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com