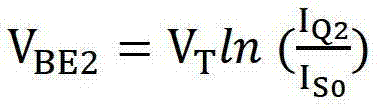Low-static-power current-mode band-gap reference voltage circuit
A low static power consumption, reference voltage technology, applied in the direction of adjusting electrical variables, control/regulation systems, instruments, etc., can solve problems such as large static power consumption, and achieve the effect of reducing static power consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0033] The principles and features of the present invention will be described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings, and the examples given are only used to explain the present invention, and are not intended to limit the scope of the present invention.
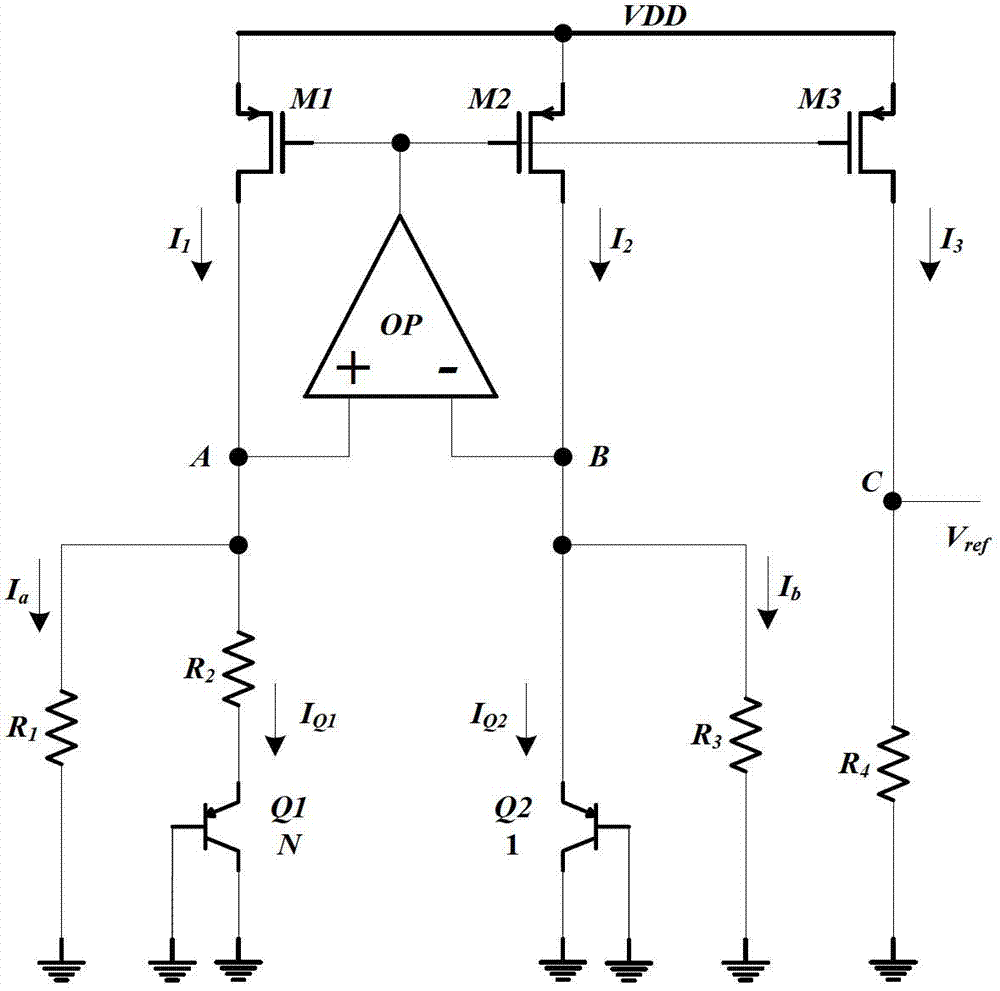
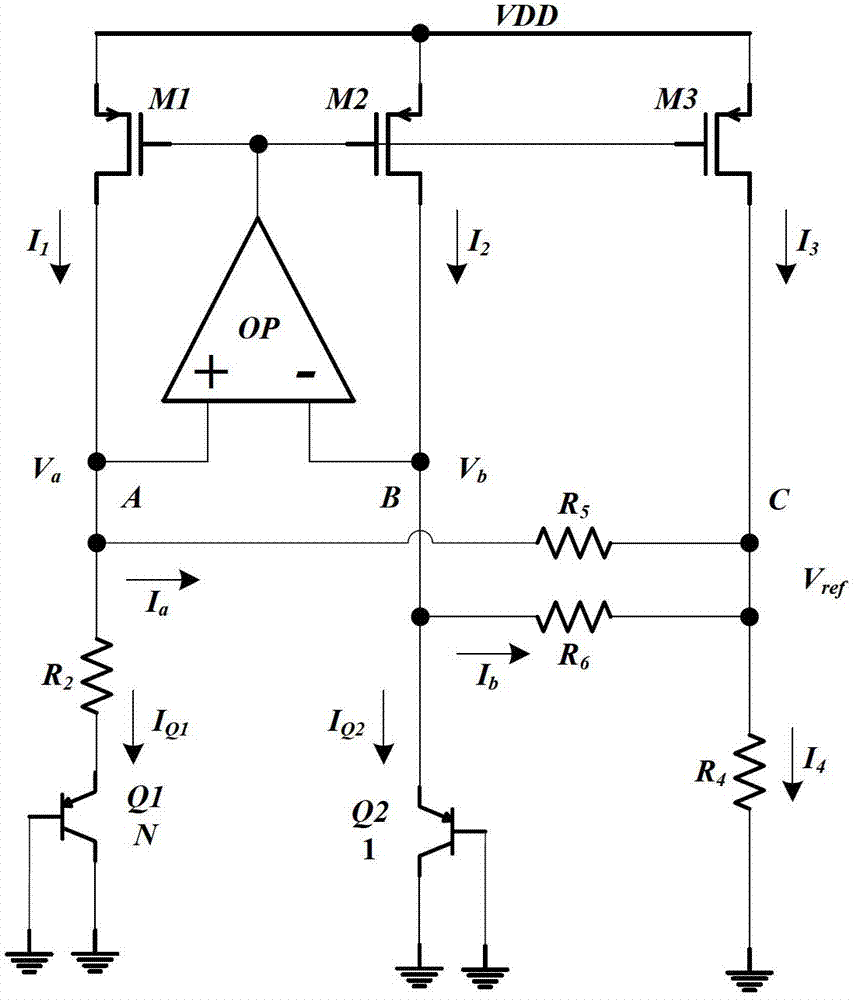
[0034] see figure 2 , the current mode bandgap reference voltage circuit with low static power consumption of the present invention is based on the traditional bandgap reference voltage circuit, comprising PNP transistors Q1 and Q2, PMOS transistors M1, M2 and M3, operational amplifier OP, resistor R 1 , R 2 , R 3 , R 4 ; The bases and collectors of the PNP transistors Q1 and Q2 are grounded, and the emitter of the PNP transistor Q1 passes through the resistor R 2 With the non-inverting input terminal of the operational amplifier OP and the drain of the PMOS transistor M1, the resistor R 1 Connected at one end, the resistor R 1 The other end is grounded, the emitter of the PNP transistor Q2 is connected to...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com