Method of determining noise measuring point arrangement based on mean deviation
A technology of mean deviation and measuring point layout, which is applied in measuring devices, using electrical devices, and measuring ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic waves, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0045] A method for determining the arrangement of noise measuring points based on mean deviation, comprising the following steps:
[0046] Step 1. Select a noise measurement accuracy level according to the noise measurement national standard, and find out the standard uncertainty limit and the maximum interference standard caused by other interference factors except the measurement point layout factors according to the noise measurement accuracy level Uncertainty, combined with the standard uncertainty limit, the maximum interference standard uncertainty and the maximum standard uncertainty caused by the measurement distance to calculate the standard deviation threshold of the average value of the sound pressure level measured at all microphone positions, referred to as the mean deviation threshold;
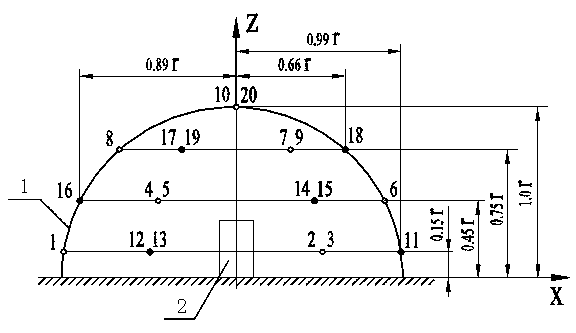
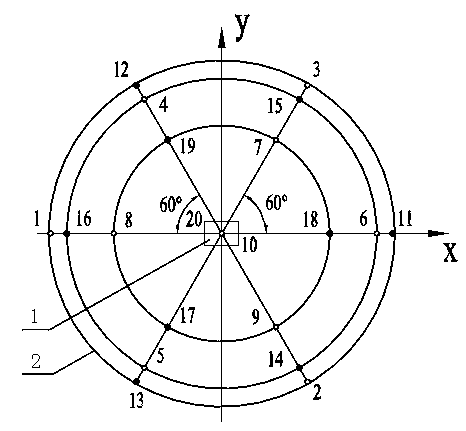
[0047] Step 2. Determine the measurement distance according to the accuracy level of noise measurement, the shape and position of the reference body 2, and the acoustic environm...
Embodiment 2
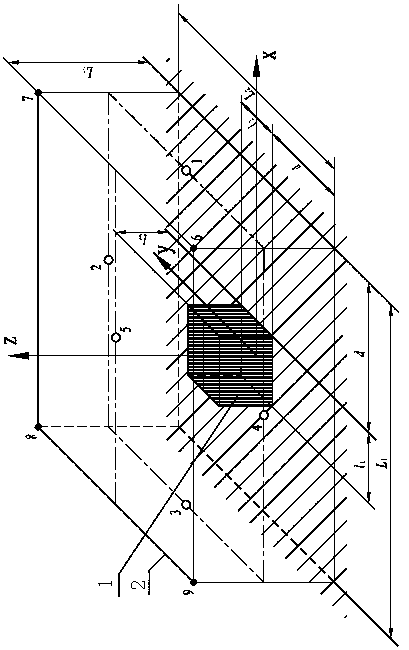
[0074] like image 3 , 4 As shown, in this embodiment, a rectangular hexahedron measuring surface is taken as an example to arrange noise measuring points according to this method.
[0075] Step 1. The noise measurement accuracy grade selected in this embodiment is grade 2, see the description in "Internal Combustion Engine Noise, Vibration and Control" (edited by Wu Yanting and Yuan Weiping, Beijing: Machinery Industry Press, 1999), and the corresponding standard uncertainty limit value 1.5dB. Theoretical analysis and experimental verification show that the maximum interference standard uncertainty caused by other interference factors in addition to the measurement point layout factors during noise measurement for dB, the maximum distance standard uncertainty caused by the measurement distance when the noise measurement points are arranged 0.6dB;
[0076] mean deviation threshold =0.8(dB), ie ≤0.8 (dB).
[0077] Step 2: Determine the measurement distance as 1m ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com