Fault-tolerance method for high-reliability disk array
A disk array, a reliable technology, applied in the storage field, can solve the problems of unrecognizable read and write errors, the failure to reduce the damage of the disk array, and the inability to continue writing data, etc., to achieve the effect of easy operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0023] This embodiment provides a highly reliable disk array fault-tolerant method, including the following steps:
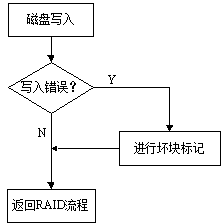
[0024] (1) When a write error occurs in the disk array, the corresponding processing flow can be as follows figure 1 As shown in , determine the storage space of the disk where the write error data is located, and mark the storage space where the write error occurs. The bad block mark here indicates that the data in the storage space has been damaged, and the next read operation , no longer read the storage space marked with bad blocks;
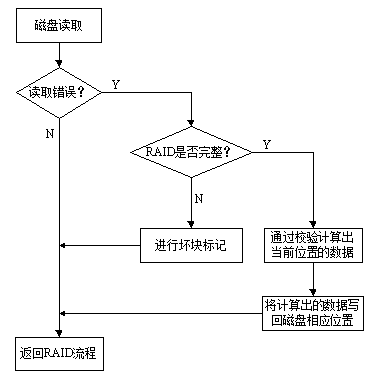
[0025] (2) When a data read error occurs in the disk array, the corresponding processing flow can be as follows figure 2 As shown, first judge whether the disk array system is complete, if it is complete, calculate the data at the current position through verification, and then write the calculated data back to the corresponding position on the disk, otherwise, the disk with data read error will occur The storage space is ma...
Embodiment 2
[0028] This embodiment is based on the Badblock mechanism of Linux kernel version 3.6, and describes in detail the highly reliable disk array fault-tolerant method of the present invention. For Linux kernel version 3.6, in the processing process of RAID5 and RAID6, each time a page is used for processing , a page is 4K, and a sector is the smallest unit of disk data storage, the size is 512 bytes, so 8 sectors are processed at a time, so 8 sectors are marked each time, which is easy to operate. The fault-tolerant method of the highly reliable disk array described in this embodiment includes the following steps:
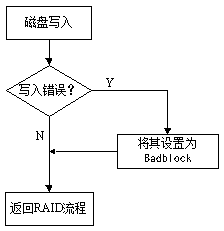
[0029] (1) When a write error occurs in the disk array, the corresponding processing flow can be as follows image 3 As shown in , determine the sector of the disk where the data where the write error occurs. The sectors here are 8 sectors that are simultaneously written. Set the 8 sectors where the write error occurs as Badblock. Here Badblock indicates that the dat...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com