Time slot scheduling method and device
A time slot scheduling and time slot technology, applied in electrical components, wireless communication and other directions, can solve the problem of high frequency of time slot resource occupation, and achieve the effect of improving service quality, small impact, and avoiding the possibility of impact
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
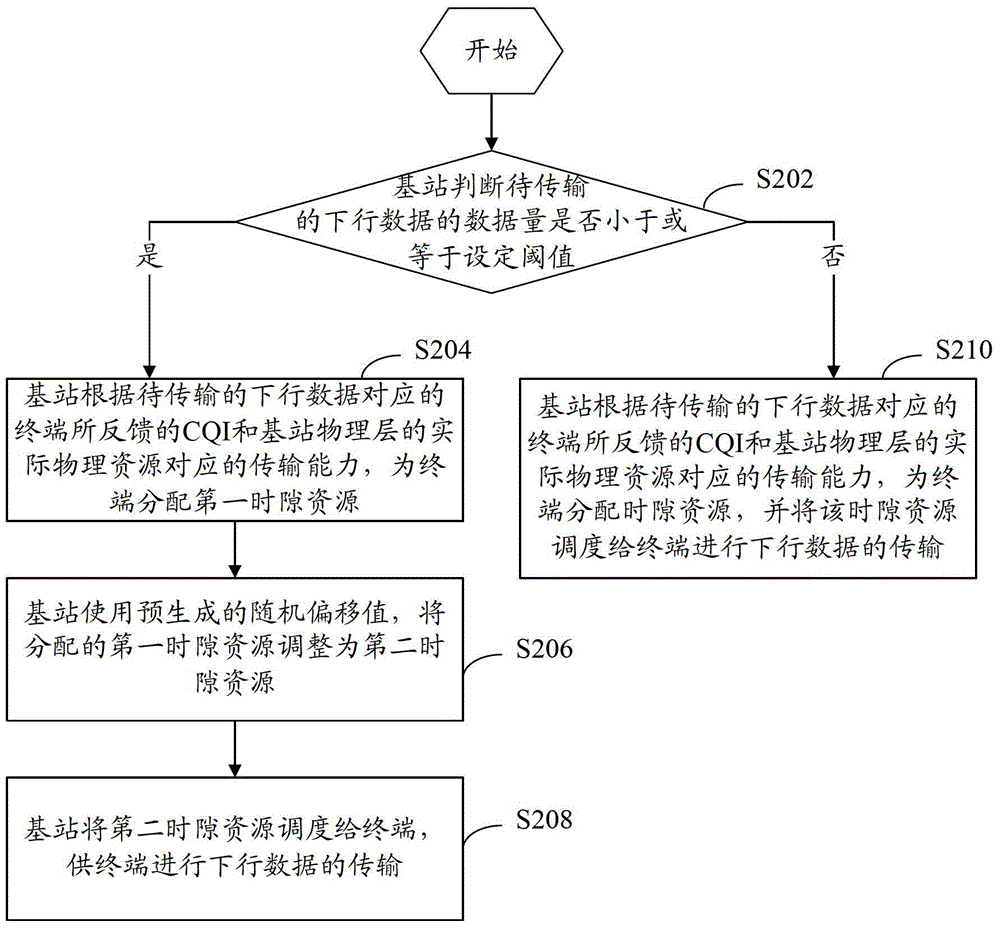
[0026] refer to figure 2 , shows a flow chart of steps of a time slot scheduling method according to Embodiment 1 of the present invention.
[0027] The time slot scheduling method of the present embodiment includes the following steps:
[0028] Step S202: the base station judges whether the amount of downlink data to be transmitted is less than or equal to a set threshold, if yes, execute step S204; if not, execute step S210.
[0029] In this step, the base station judges whether the amount of downlink data of the HSDPA service to be transmitted in the TD-SCDMA system is small, that is, whether it is less than or equal to a set threshold. Wherein, the setting threshold can be appropriately set by those skilled in the art according to the actual situation, and the data transmission volume of not more than one time slot resource is a principle.
[0030] Step S204: If the amount of downlink data to be transmitted is less than or equal to the set threshold, the base station wi...
Embodiment 2
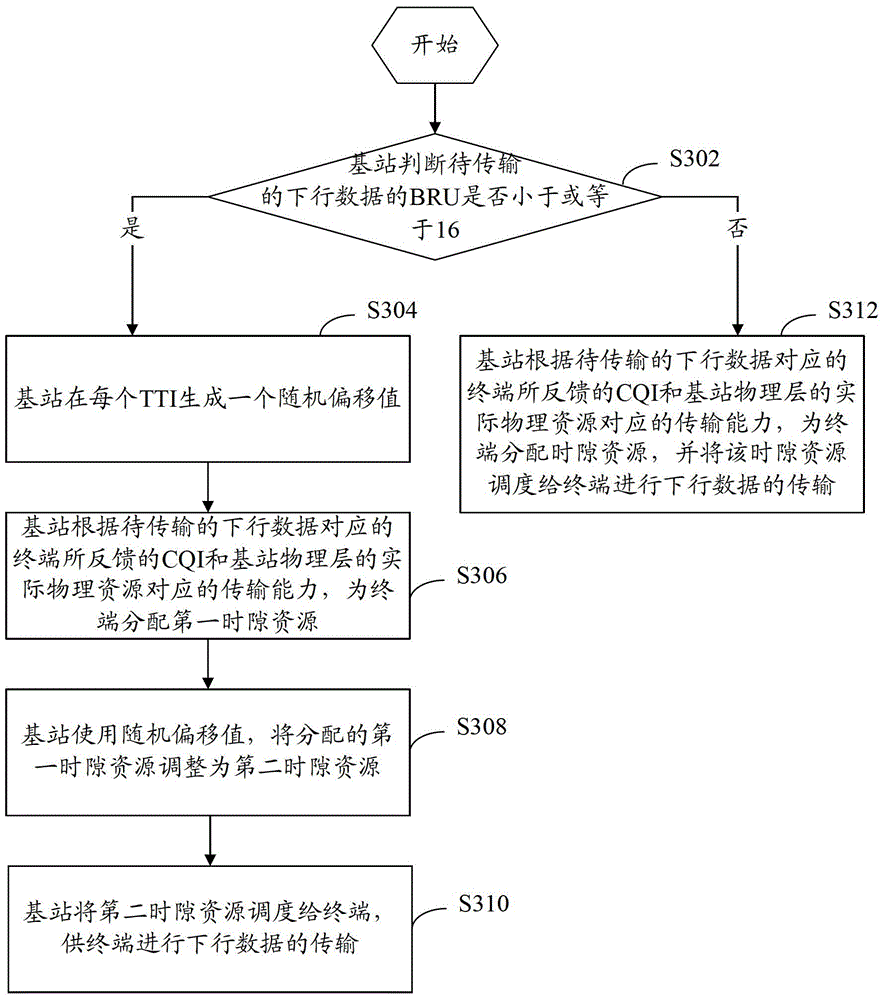
[0039] refer to image 3 , shows a flow chart of steps of a time slot scheduling method according to Embodiment 2 of the present invention.
[0040] The time slot scheduling method of the present embodiment includes the following steps:
[0041] Step S302: the base station judges whether the BRU of the downlink data to be transmitted is less than or equal to 16, if yes, execute step S304; if not, execute step S312.
[0042] In this embodiment, the base station judges whether the downlink data to be transmitted is data with a small data volume by judging the BRU of the downlink data to be transmitted. When the BRU is less than or equal to 16, the downlink data transmission can be completed in one time slot. Therefore, it can be determined that when the BRU is less than or equal to 16, the downlink data to be transmitted is data with a small amount of data. The size of the data to be transmitted is judged by judging the BRU, which is simple to implement, saves the implementati...
Embodiment 3
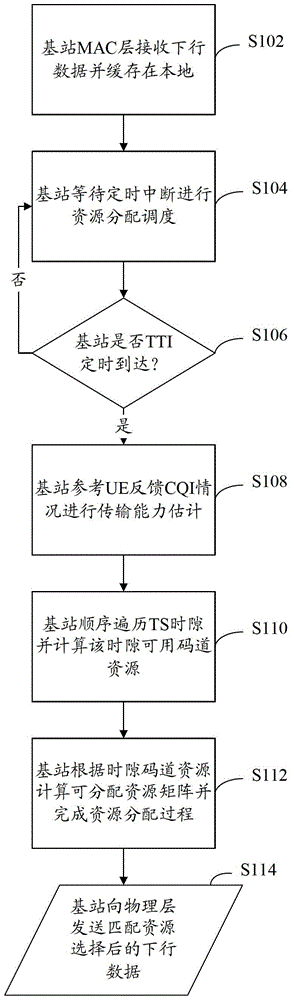
[0057] refer to Figure 4 , shows a flow chart of steps of a time slot scheduling method according to Embodiment 3 of the present invention.
[0058] This embodiment is based on the premise that in the TD-SCDMA system, the downlink data of the HSDPA service to be transmitted is small data volume data, such as the data volume of BRU less than or equal to 16, and the terminal in this embodiment uses UE (User Equipment, user equipment ) as an example.
[0059] The time slot scheduling method of the present embodiment includes the following steps:
[0060] Step S402: After receiving the downlink data from the RNC, the MAC layer of the base station converts the data format through the FP, and caches it in the base station in the form of Mac_hs PDU data.
[0061] Step S404: the base station waits for a timing interrupt to perform time slot resource allocation and scheduling.
[0062] Step S406: the base station judges whether the TTI has arrived, if yes, execute step S408; if not...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com