A non-rigid registration method for 3D CT images of mice
A non-rigid registration, CT image technology, applied in the field of medical image processing, can solve the problems of difficult to achieve manual segmentation of mouse atlas bones, long registration time, and complicated registration process, and achieve registration of three-dimensional images. Fast, reduced registration time, easy to achieve results
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0057] Combine below figure 1 The specific implementation steps of the present invention are further described in detail.
[0058] Step 1. Rigid calibration of the source image
[0059] During rigid calibration, first correct the direction of the head and tail of the mouse in the image, then correct the supine posture of the mouse, and finally align the central axis of the mouse.
[0060] Step 2. Extract feature points of source image and target image
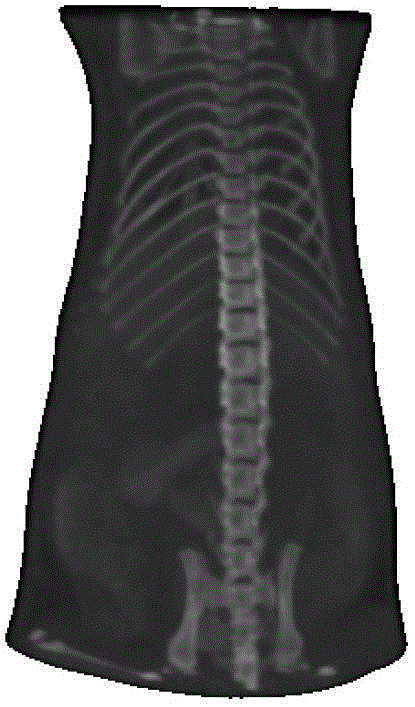
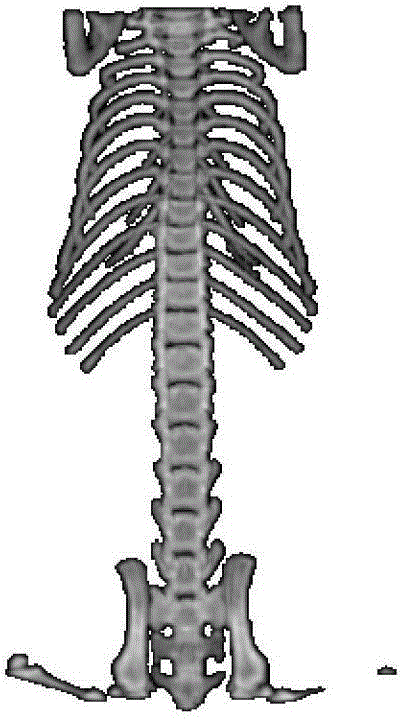
[0061] (1) Select the threshold, and use the threshold segmentation method to extract the bone of the mouse in the source image and the target image to obtain the source bone image and the target bone image. In this embodiment, the threshold value is 105;
[0062] (2) Calculate the area of each connected region in the target bone image perpendicular to the main axis of the mouse, calculate the centroid of the connected region with an area greater than 10, and obtain the feature points of the target image;
[0063] (3) Calc...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com