Three-dimensional bone tissue model building method and equipment
A bone tissue and three-dimensional bone technology, applied in the field of medical electronics, can solve the problems of inability to simulate stress changes in trabecular bone, complex microstructure of cancellous bone, and poor simulation results
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach
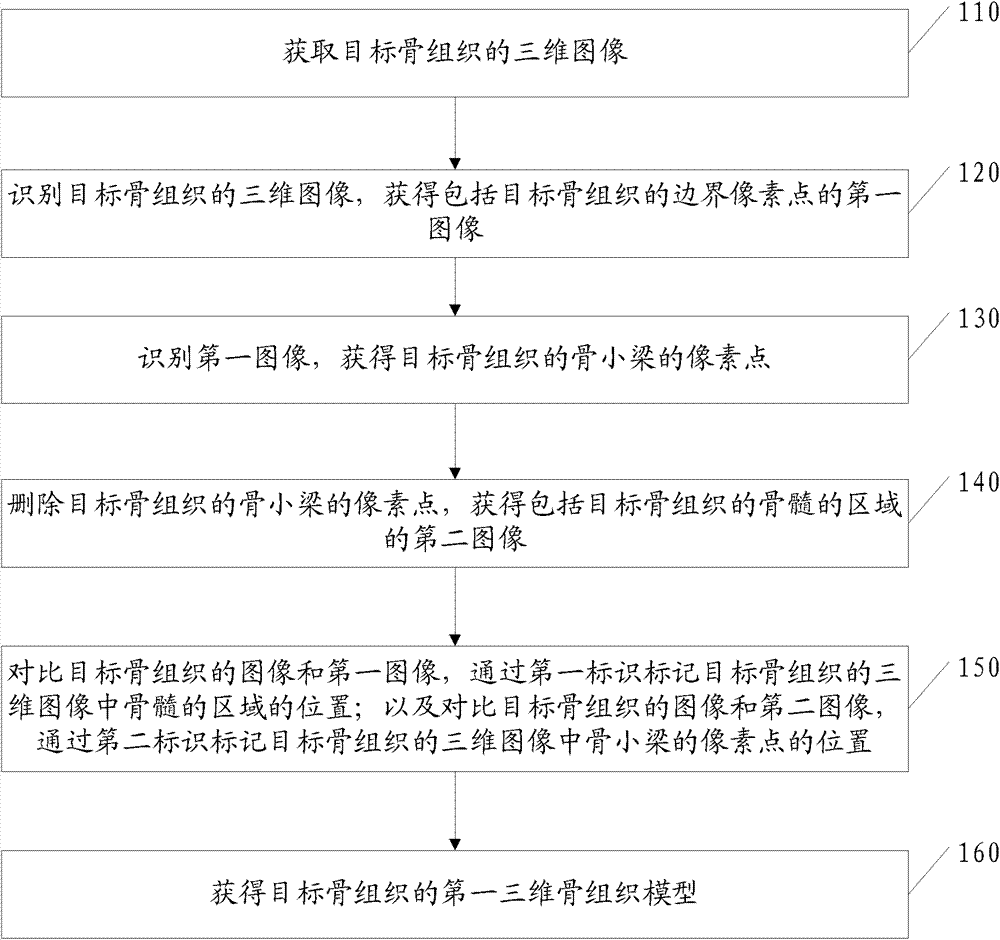
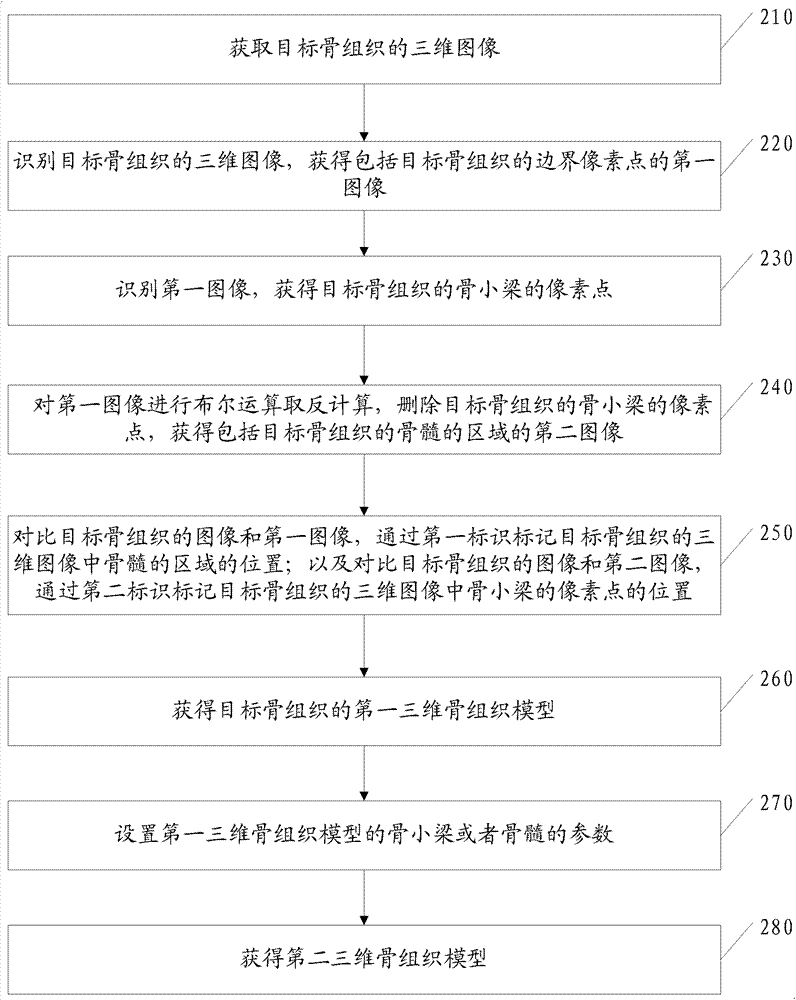
[0094] As an optional implementation, the method also includes:
[0095] A. Setting parameters of trabecular bone and / or bone marrow of the first three-dimensional bone tissue model. Wherein, setting the parameters of the trabecular bone of the first three-dimensional bone tissue model is specifically the following process:
[0096] Invoke the setting process of the porous coupling module to set the trabecular part of the target bone tissue as a linear elastic solid.
[0097] Physical parameters such as Young's modulus, Poisson's ratio, and bone density of the target bone tissue are obtained to set physical parameters such as the Young's modulus, Poisson's ratio, and bone density of the target bone tissue.
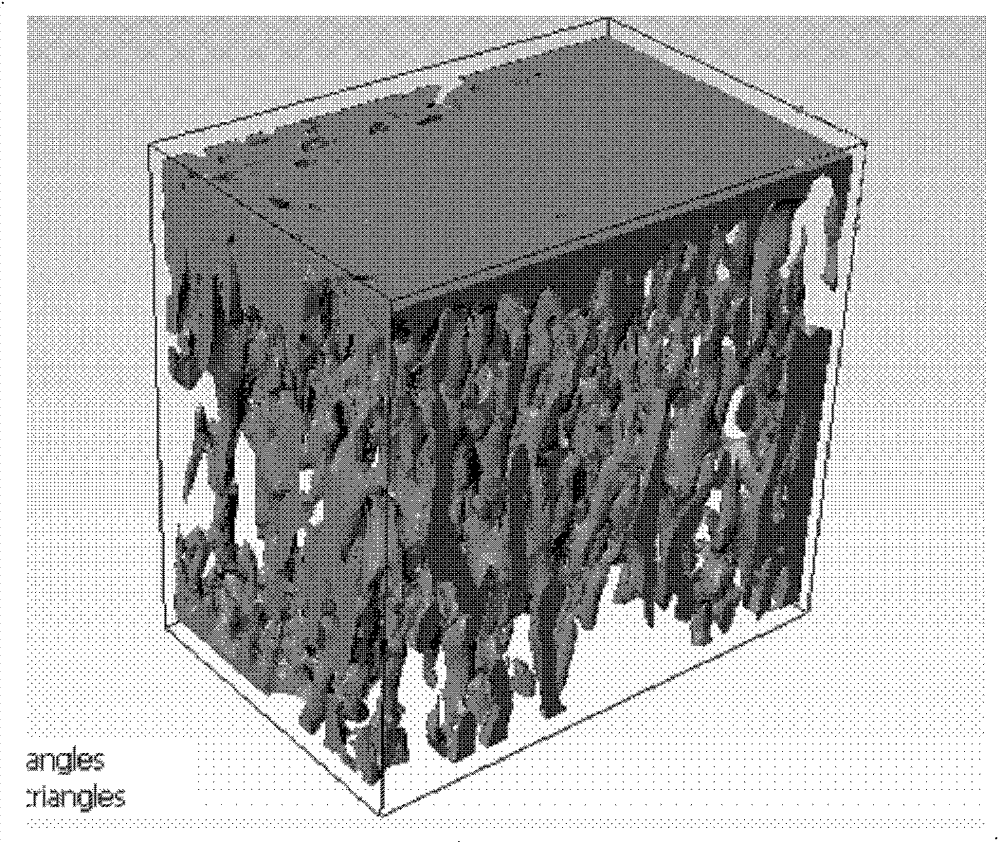
[0098] In this embodiment, setting the parameters of the bone marrow of the first three-dimensional bone tissue model is specifically setting the components of the bone marrow as fluid. Because bone marrow is composed of red bone marrow and yellow bone marrow, the propor...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com