Treatment of Pressure Differences in Low Reynolds Number Incompressible Flows Over Curved Boundaries
A technology with low Reynolds number and curved boundaries, which can be used in electrical digital data processing, special data processing applications, instruments, etc., and can solve problems such as pressure difference
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
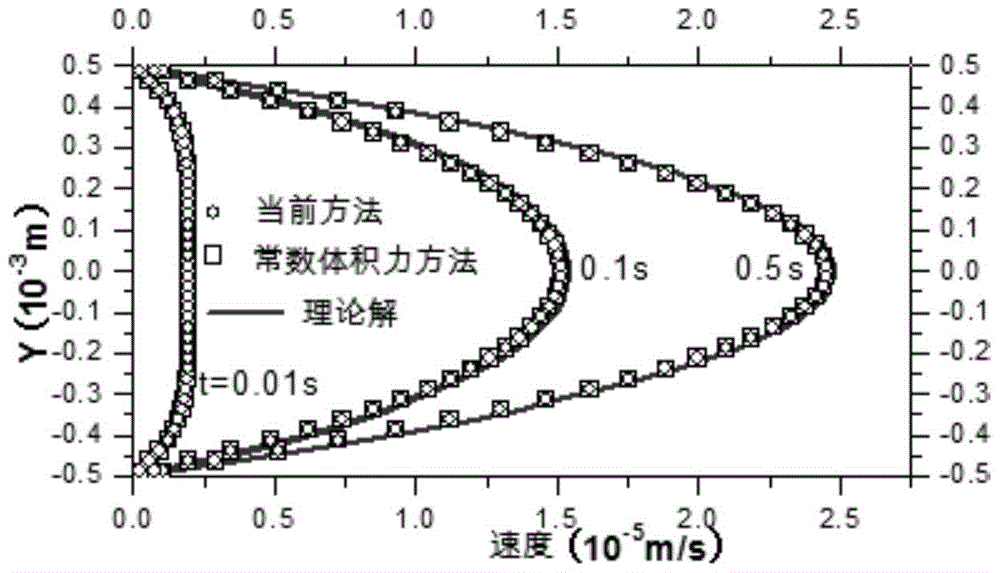
[0046] This embodiment adopts Poiseuille flow, that is, two infinite plates are respectively placed at coordinates y=-0.5YL and y=0.5YL, where YL is the distance between the two plates. Its initially stationary fluid is driven by a body force F (corresponding to the pressure difference between the inlet and outlet) parallel to the X-axis, and will eventually reach a steady state.
[0047] In this embodiment, YL=10-3 m, the flow field length is d=5×10 -4 m, the hydrostatic pressure difference is △p=10 -4 N / m 2 , the simulation results of formula (1), formula (2) and formula (3) are as follows figure 2 shown, and from figure 2 It can be seen that the method of the present invention is consistent with the simulation results using constant body force, and both agree well with the theoretical solution.
Embodiment 2
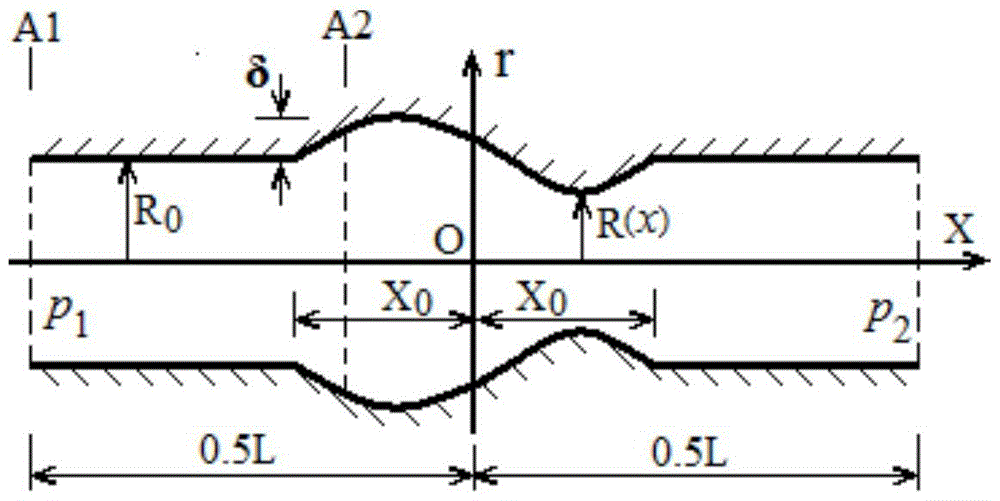
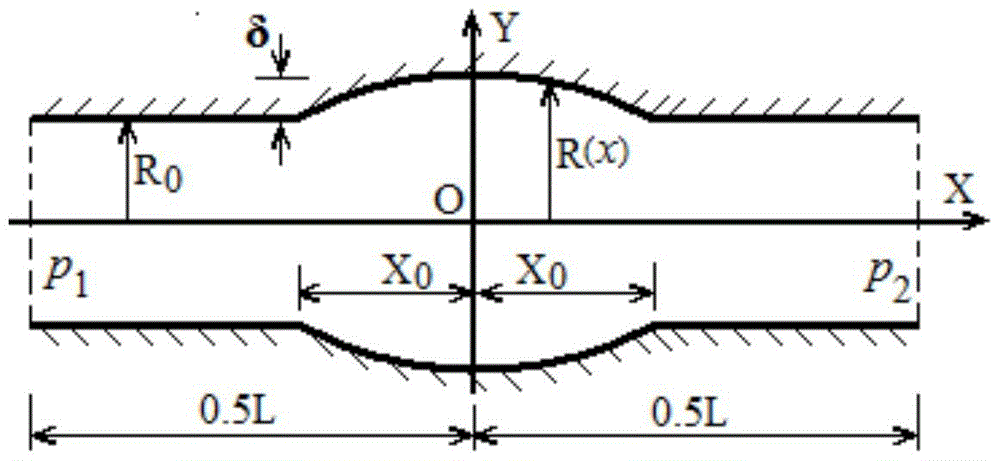
[0049] This embodiment adopts local expansion pipe flow, such as image 3 As shown, an axisymmetric blood vessel can be considered, and its pressure difference drives the fluid to flow in the pipeline, and the pressure difference is △p=p 1 -p 2 =1.939006287×10 -3 N / m 2 , the radius of the pipe is a function of the position x, which can be expressed as (4):
[0050] R R 0 = 1 | x | > X 0 1 + δ 2 R 0 ( 1 ...
Embodiment 3
[0054] The present embodiment adopts inclined plate flow, such as Figure 6 As shown, in this example, d BC =4mm,2l 1 =0.5mm, α=3.503°, and the hydrostatic pressure difference between B and C is △p=1.21665968×10 -3 N / m 2 .
[0055] Using the method of the present invention, the simulation results of the horizontal velocity of the fluid particles along the X axis are as follows: Figure 7 shown; from Figure 7 As can be seen in the figure, the simulation results using the method of the present invention are again in agreement with the theoretical solution, but not in the case of constant body force.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com