A single-phase grounding protection method for distribution network based on the straight line fitting direction of zero-sequence current mutation
A zero-sequence current and straight line fitting technology, which is applied in the direction of current indication, emergency protection circuit devices, electrical components, etc., can solve problems such as prominent interference signals, misoperation or refusal of protection devices, and eliminate high-frequency interference signals Effect of improving reliability, effect of high protection reliability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
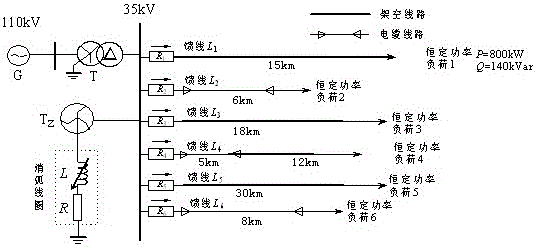
[0041] Embodiment 1: as figure 1 Shown is a 35kV distribution network composed of 6 feeder lines whose neutral point is grounded through an arc suppression coil. G in this network is an infinite power supply; T is the main transformer with a transformation ratio of 110 kV / 35kV, and the connection group is YN / d11; the distribution voltage side of the main transformer in my country's distribution network is generally connected in a triangle, and there is no neutral point in the system. When the system adopts the resonance grounding method, it is necessary to obtain a neutral point that can be grounded by the arc suppression coil. Adding a grounding transformer is The best way, here T Z It is a zigzag transformer specially used for grounding of the compensation grid; L is the arc suppression coil, and R is the damping resistance of the arc suppression coil. The line adopts three types of lines: overhead line, overhead line-cable hybrid line and cable line, and the numbers of the ...
Embodiment 2
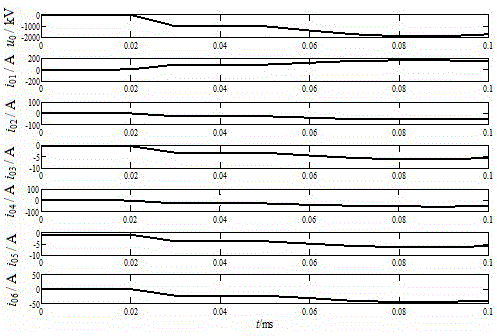
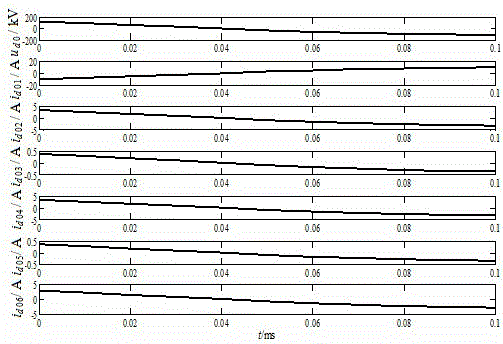
[0047] Embodiment 2: as figure 1 In the distribution network system shown in which the neutral point is grounded through the arc suppression coil, the system parameters are the same as those in Embodiment 1. Now suppose the feeder L 2 A single-phase ground fault occurs in phase A at a distance of 4km from the busbar. The initial phase angle of the fault is 90°, the fault transition resistance is 20Ω, and the sampling frequency is 100kHz. The waveforms of bus zero-sequence voltage and feeder zero-sequence current in the 0.1ms time window after the fault are as follows: Figure 4 shown. Using the db4 wavelet to decompose the zero-sequence voltage of the bus and the zero-sequence current of each feeder with 6 layers of wavelets, the wavelet coefficients of the zero-sequence voltage wave of the bus and the zero-sequence current of each feeder in the frequency band of the power frequency in the 0.1ms time window after the fault are obtained. Figure 5 shown. The least square me...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com