An asynchronous underwater full-rate cooperative communication method
A cooperative communication and full-rate technology, applied in the direction of sustainable communication technology, preventing/detecting errors through diversity reception, advanced technology, etc., can solve the problems of low transmission efficiency and slow speed, and achieve the effect of increasing the transmission rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
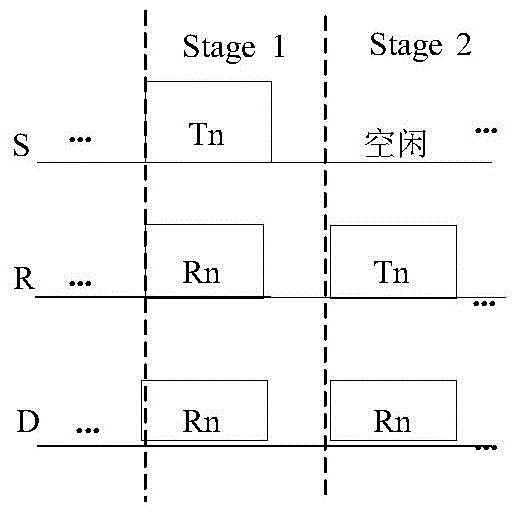
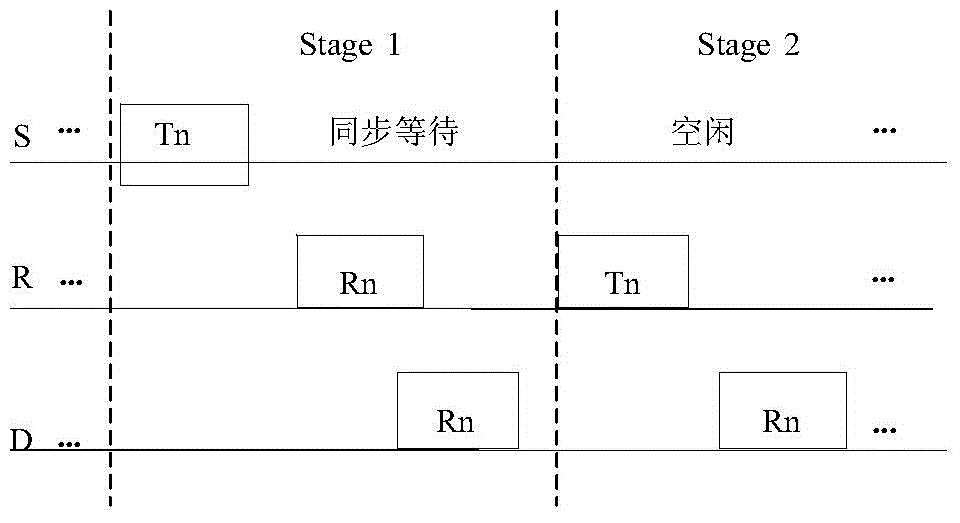
[0037] This embodiment is an underwater acoustic communication network comprising M+2 nodes, such as Figure 4 As shown, where S is the source node that needs to send data, D is the destination node, R i (0i , S → D, R i →D The maximum distance of these three links is 2km, and the size of the data packet is 240 bytes. If synchronous full-rate cooperative communication is used, the cooperative transmission needs two time slots to complete, and each time slot requires at least Such a long time slot will seriously reduce the channel capacity. Therefore, in the above embodiments, the asynchronous full-rate cooperative communication method is adopted between nodes, which can effectively increase the sending rate of source node information and reduce the waiting time for synchronization, thereby significantly improving the efficiency and speed of transmission.
[0038] This embodiment adopts the following steps to realize asynchronous underwater full-rate cooperative communicati...
Embodiment 2
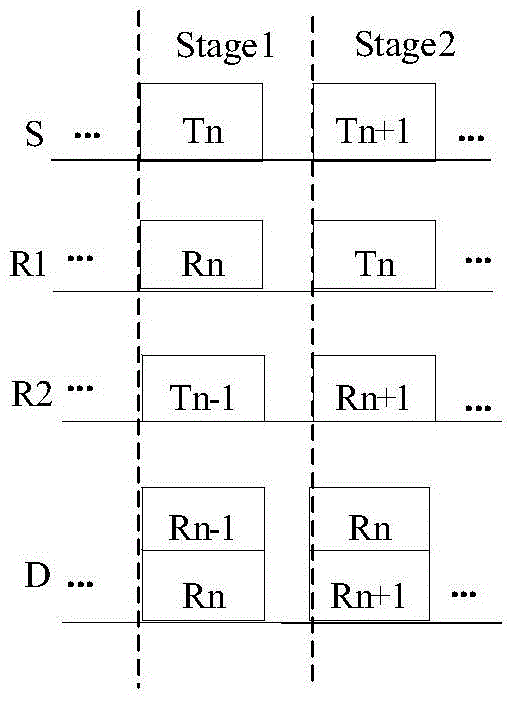
[0084] This embodiment is the same as Embodiment 1 except for the following:
[0085] Such as Image 6 As shown, it is a structural diagram of the dual-relay full-rate cooperative communication system in this embodiment, the source node S sends information omnidirectionally by broadcasting, and the H SR1 、H SR2 、H SD is the channel impulse response from the source node to the relay nodes R1, R2 and from the source node to the destination node D. After receiving the information of the source node, the relay nodes R1 and R2 also use the same channel as the source node to amplify and forward the information of the source node in a broadcast manner, H R1R2 、H R1D is the channel impulse response from relay node R1 to relay node R2 and the destination node, H R2R1 、H R2D is the channel impulse response from the relay node R2 to the relay node R1 and the destination node. The information received by the destination node includes the information sent by the source node and the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com