Method and device for sending inter-domain fault information
A technology of fault information and sending method, applied in the field of communication, can solve the problems of the client layer being unable to know the protection and recovery of the service layer in time, and prolonging the service interruption time, so as to improve the network survivability and shorten the service interruption time.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
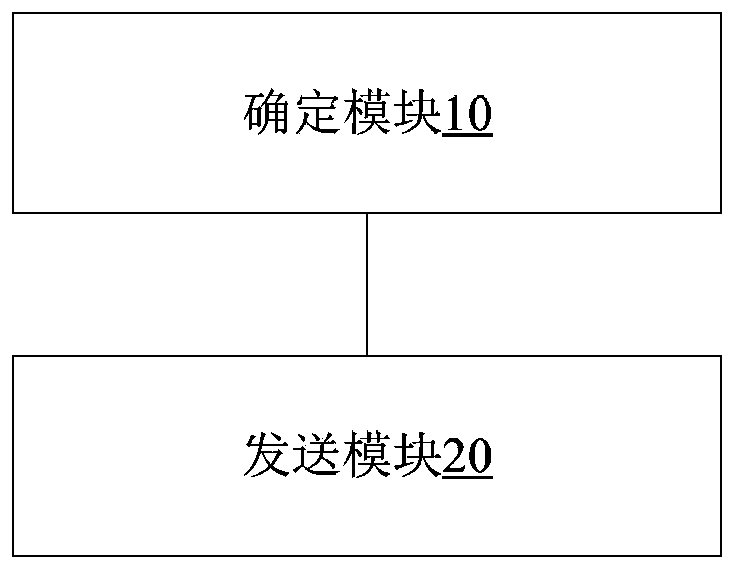
[0031] According to an embodiment of the present invention, a method for sending inter-domain fault information is provided, which realizes sending inter-domain fault information to the upper-layer (client layer) LSP when the protection or recovery of the lower-layer (service layer) LSP fails, so that the upper-layer LSP according to Inter-domain fault information protects or restores service connections.
[0032] figure 1 is a flowchart of a method for sending inter-domain fault information according to an embodiment of the present invention, such as figure 1 As shown, the method may include step S102 to step S104:
[0033] Step S102, the service layer LSP determines that the protection or recovery of the service layer LSP is invalid;
[0034] Step S104, the service layer LSP sends inter-domain fault information to the client layer LSP of the service layer, wherein the inter-domain fault information is used to indicate the failure of protection or recovery of the service la...
Embodiment 2
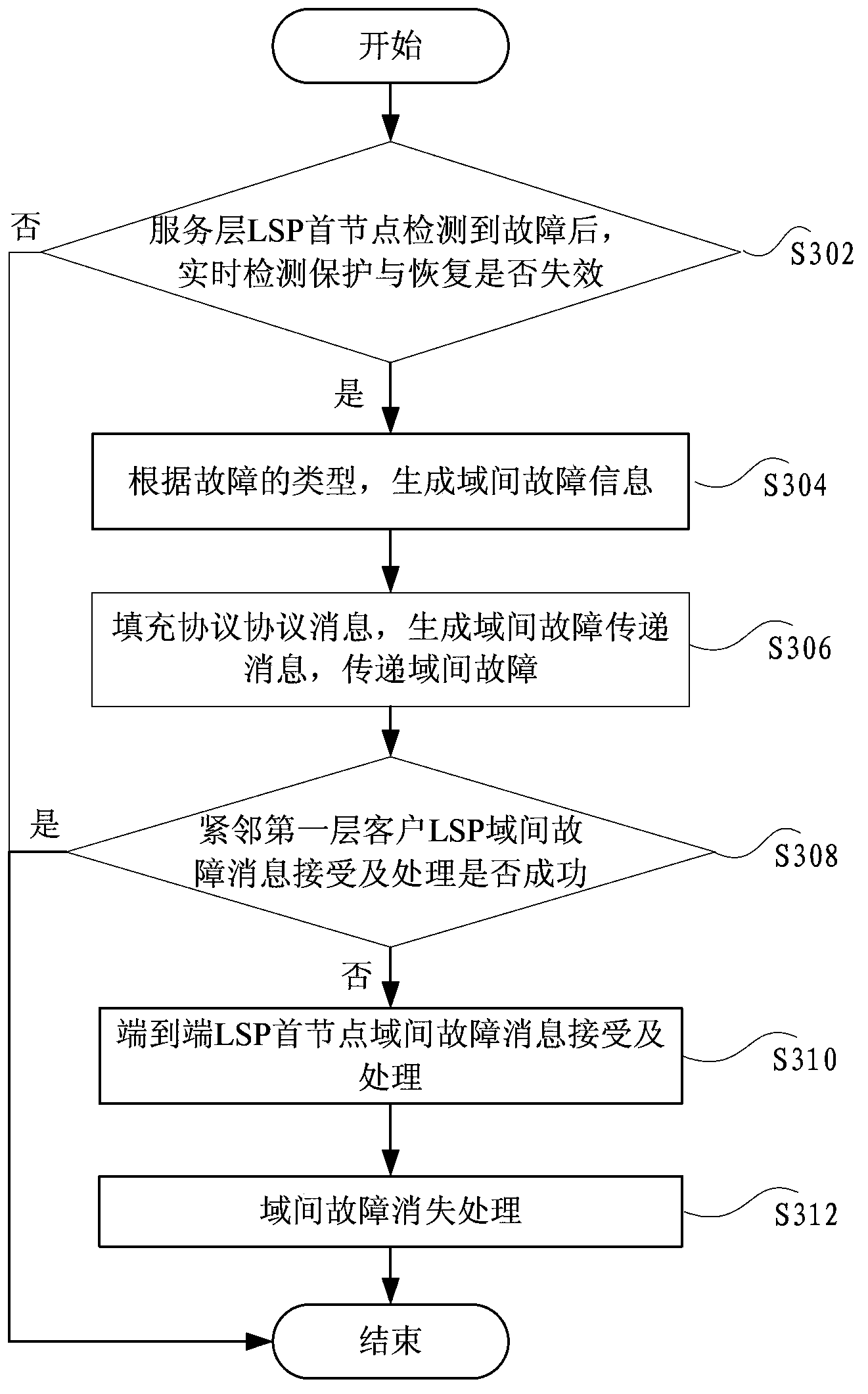
[0047] According to the embodiment of the present invention, a system for dynamic coordination of multi-layer and multi-domain network protection and recovery is provided. Fault information solves the problem that in a multi-layer multi-domain network, the client layer cannot know whether the protection and recovery of the service layer is successful in real time, shortens the end-to-end service interruption time, and improves network survivability.
[0048] The method for dynamic coordination of multi-layer multi-domain network protection and restoration in this preferred embodiment includes the following steps (step 1 to step 3):
[0049] Step 1, when the service layer network fails, start inter-domain fault detection on the first node inside the network, detect and determine whether the protection or recovery of the LSP in this layer is invalid;
[0050] Step 2: After the head node of the service layer determines that the protection and recovery of this layer are invalid, i...
Embodiment 3
[0057] There are multiple bearer devices in the communication network, and each device belongs to different layers. And these devices may be located in different regions, so they are distributed in different routing domains. In order to solve the problem of cross-domain end-to-end LSP establishment, IETF has released a series of standards to extend RSVP-TE. There are two solutions, one is hierarchical LSP (Hierarchy-LSP, referred to as H-LSP) , and one is Stitching-LSP (S-LSP for short).
[0058] 1) H-LSP, the LSP created by Hierachy method, that is, H-LSP (RFC4206 defines it as FA-LSP), can form a TE link on its upper layer (client layer); the upper layer LSP can be established using this TE links perform route calculation. As a service layer, H-LSP can be used by multiple client layer LSPs.
[0059] 2) S-LSP, the LSP created by Stiching, that is, S-LSP, can be flooded into one LSP at the same layer, and the stitching technology requires that the interface switching capabi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com