Diode and power conversion system
A diode and electrode technology, applied in the field of power conversion systems and diodes, can solve the problems of small recovery loss, disappearance of electrons and holes, etc., and achieve the effect of reducing recovery loss
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 approach
[0061] [Structure of Diode]
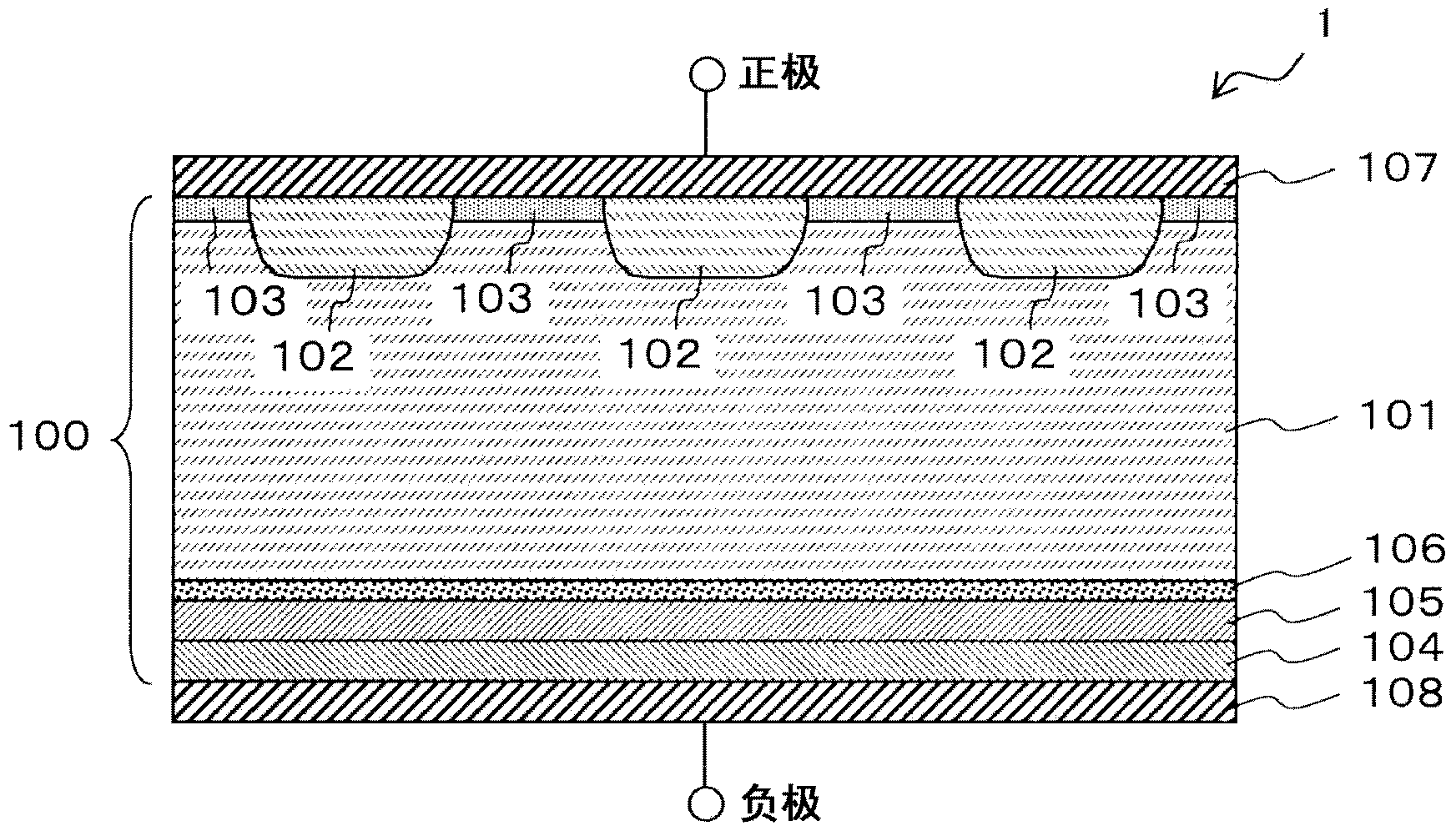
[0062] First, refer to figure 1 The structure of the diode according to the first embodiment of the present invention will be described. in addition, figure 1 is a schematic cross-sectional view of the active region of the diode 1 of the first embodiment. The description of the termination region is omitted, and a conventional termination structure such as an FLR (Field Limiting Ring) type in which p-type recesses and electrodes are arranged in a ring shape is used for the termination region.
[0063] Such as figure 1 As shown, the diode 1 of the first embodiment includes an n-drift layer 101, an anode p-layer 102, an anode p-layer 103, an anode n-layer 104, an anode buffer n-layer 105, a low lifetime region layer 106, an anode electrode 107 and an anode electrode 107. electrode 108 .
[0064] In addition, in the following description, including the intermediate stage of a manufacturing process, the whole of a semiconductor layer part is call...
no. 2 approach
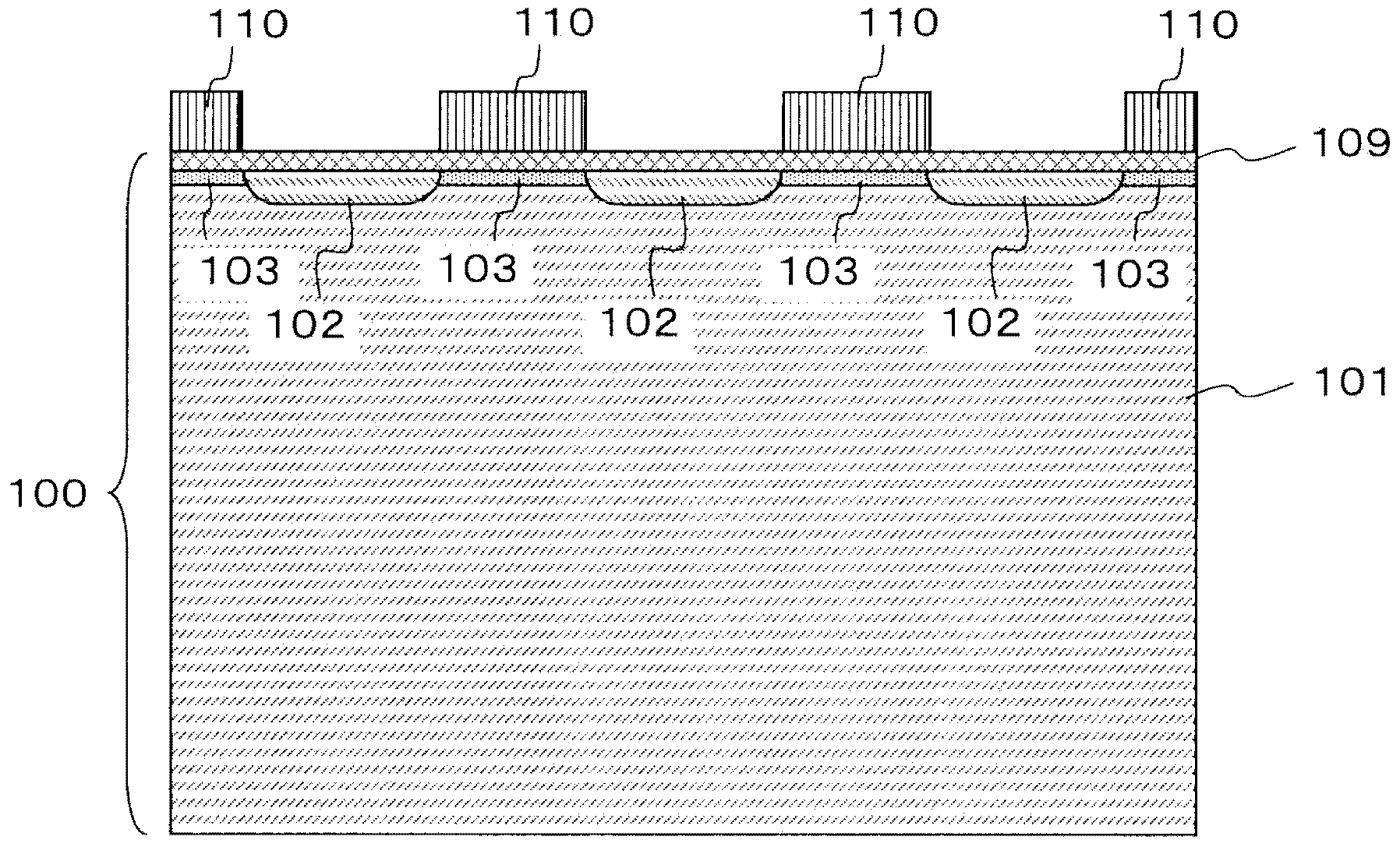
[0136] Next, refer to Figure 7 Now, the structure of a diode according to a second embodiment of the present invention will be described. in addition, Figure 7 It is a schematic sectional view of the active region of the diode 1A of the second embodiment. The description of the termination region is omitted, but similar to the first embodiment, a conventional termination structure such as an FLR type in which a p-type recess and electrodes are arranged in a ring shape is used.
[0137] Such as Figure 7 As shown, the diode 1A of the second embodiment is relative to figure 1 The diode 1 of the first embodiment shown differs in that the anode p layer 102 does not have a recess structure and the anode p - layer 103, a positive electrode p-layer (second semiconductor layer) 102 is formed on the entire surface of the active region on the positive electrode side. The other structures are the same as those of the first embodiment, and description thereof will be omitted.
[0...
no. 3 approach
[0140] Next, refer to Figure 8 Now, the structure of a diode according to a third embodiment of the present invention will be described. It should be noted, Figure 8 It is a schematic sectional view of the active region of the diode 1B of the third embodiment. The description of the termination region is omitted, but similar to the first embodiment or the second embodiment, an existing termination structure such as the FLR type in which p-type recesses and electrodes are arranged in a ring shape can be used.
[0141] Such as Figure 8 As shown, the diode 1B of the third embodiment is relative to Figure 7 The diode 1A of the second embodiment shown is different in that the negative electrode buffer n layer 105 is not provided and the low lifetime region layer (fourth semiconductor layer) 106 is provided on the nth side of the negative electrode n layer (third semiconductor layer) 104. - The position where the surface on the side of the drift layer (first semiconductor la...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com