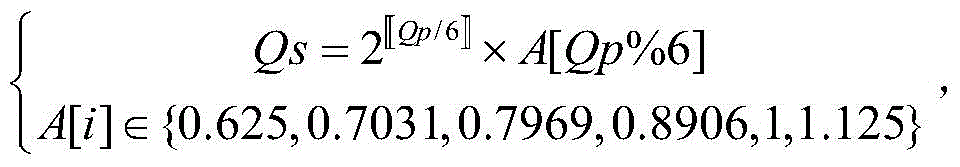A method and system for intra-frame coding optimization based on mode preprocessing
A technology of intra-frame encoding and optimization method, applied in the field of video processing, can solve the problems of low encoding speed, unstable complexity, and inability to fundamentally guarantee the real-time encoding function.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
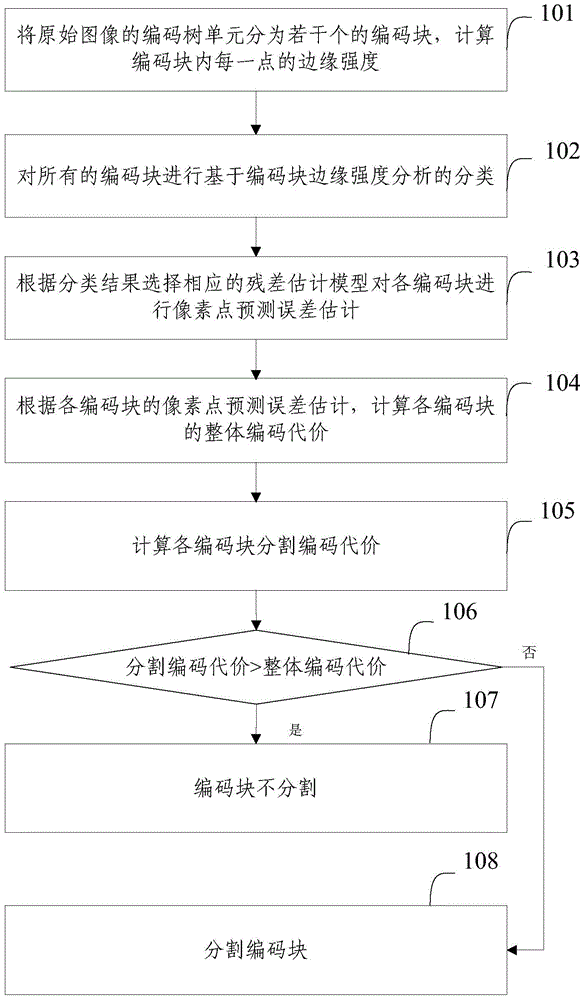
[0087] Embodiment 1 of the present invention proposes an intra-frame coding optimization method based on mode preprocessing. This method is applied to the coding tree unit CTU before coding the pixel lattice of the coding tree unit CTU. Specifically, from 32 / 16 Select one of the two coding blocks CU, the selection result is called LCB (Large Code Block), choose one of the 8 / 4 two coding blocks CU, and the selection result is called SCB (Small Code Block), so that the frame The calculation amount of inner encoding is reduced by nearly half, and two sets of pattern search engines can be used to realize parallel encoding, thus stably speeding up the encoding process. see figure 1 , the method comprises the steps of:
[0088] Step 101: Divide the coding tree unit of the original image into several N×N coding blocks, N∈{4,8,16,32}, and calculate the edge strength of each point in the coding block.
[0089] In this step, we assume that the coding tree unit CTU of the original ima...
Embodiment 2
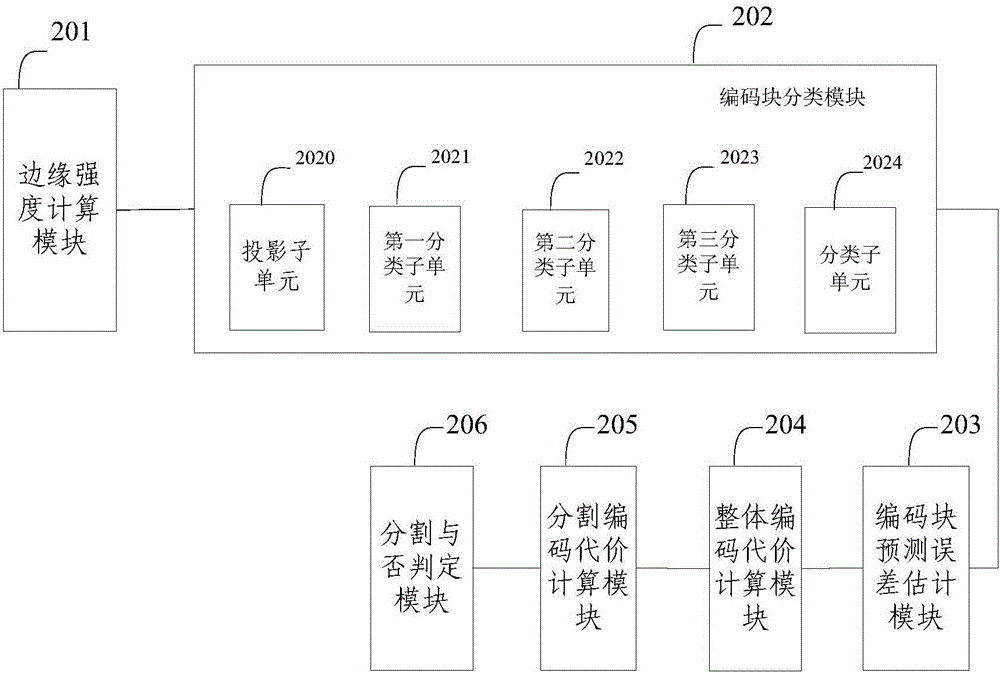
[0130] Embodiment 2 of the present invention also proposes an intra-frame coding optimization system based on mode preprocessing, see figure 2 , the system consists of:
[0131] The edge strength calculation module 201 is used to divide the coding tree unit CTU of the original image into several N×N coding blocks CU, N∈{4,8,16,32}, and calculate the edge strength of each point in the coding block;
[0132] A coding block classification module 202, configured to classify all N×N coding blocks based on the edge strength analysis of coding blocks, N∈{4,8,16,32};
[0133] The coding block prediction error estimation module 203 is used to select a corresponding residual estimation model according to the classification result to perform pixel point prediction error estimation on each N×N coding block, N∈{4,8,16,32};
[0134] The overall encoding cost calculation module 204 is used to calculate the overall encoding cost RD of each N × N encoding block according to the pixel point p...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com