Pathogenic factor production-inhibiting fiber and method for producing same
A technology of pathogenic factors and manufacturing methods, applied in the directions of biochemical fiber treatment, plant fiber, fiber treatment, etc., can solve application problems and achieve the effect of high washing durability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1)
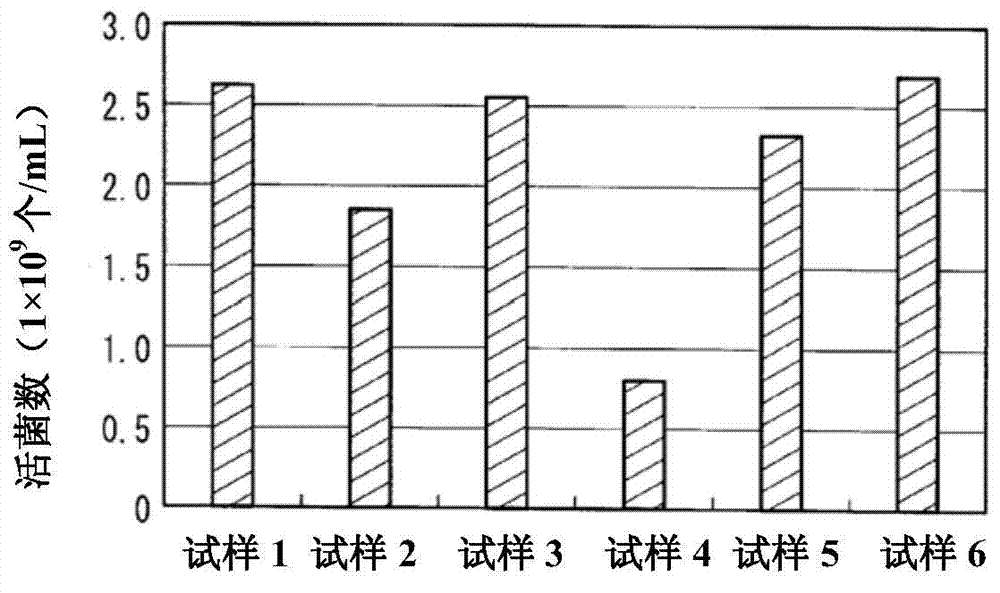
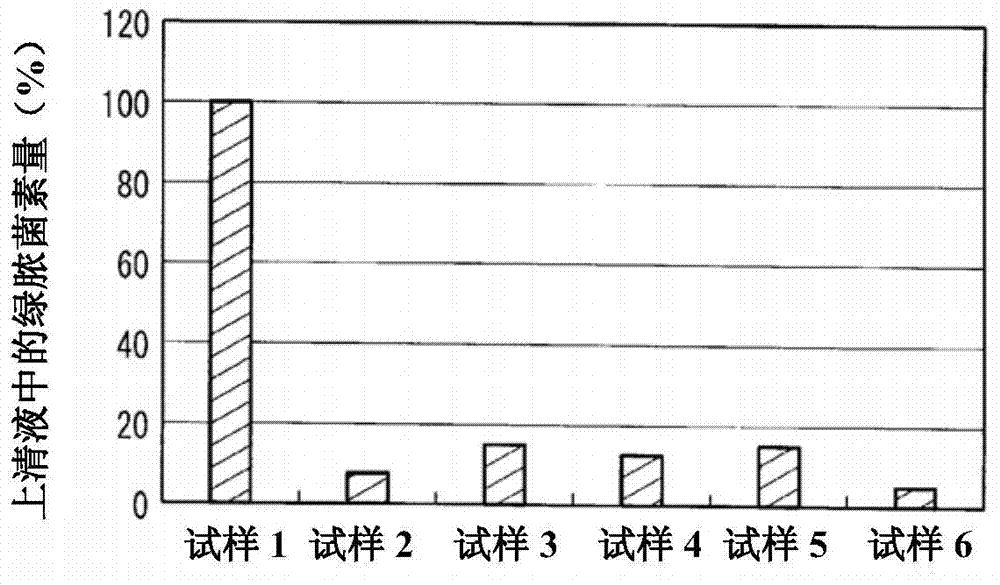
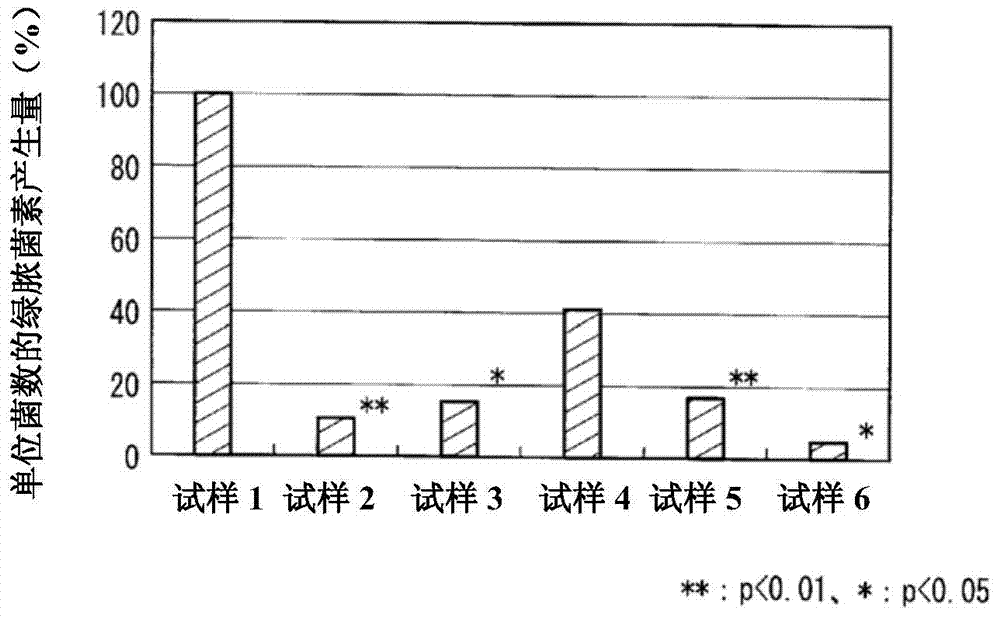
[0065] This example is an example in which a compound containing a phosphoric acid group (hereinafter also referred to as a phosphorus compound) is bonded to cellulose fibers of cloth by the Pad method. Among the above, they correspond to the cases represented by the formulas (1) to (5). Using an electron curtain (electrocurtain) type electron beam irradiation device (EC250 / 30 / 90L; manufactured by EYE ELECTRON BEAM Co., Ltd.), under the conditions of a nitrogen atmosphere, an accelerating voltage of 200kV, and an irradiation dose of 40kGy, the caustic soda mercerizing treatment was performed. 100% cotton fabric of medium thickness (weight per unit area 300g / m 2 ) is irradiated with an electron beam. The cloth irradiated with electron beams was dipped in 10% by mass of P1M {mono(2-methacryloyloxyethyl) phosphate; manufactured by Kyoeisha Chemical Co., Ltd.} aqueous solution, and squeezed to The liquid rate was about 70 mass %, and it left to stand overnight at 35 degreeC afte...
Embodiment 2)
[0069] This example is an example in which the Pad method of Example 1 is replaced by the dipping method. Nitrogen bubbling treatment was performed on the 10% by mass P1M aqueous solution in advance so that the dissolved oxygen concentration was 0.1 ppm or less. Using an electron curtain type electron beam irradiation device (EC250 / 30 / 90L; manufactured by EYE ELECTRON BEAM Co., Ltd.), under the conditions of a nitrogen atmosphere, an accelerating voltage of 200kV, and an irradiation dose of 40kGy, 100% cotton that has undergone caustic soda mercerizing treatment Medium-thick texture fabric of fiber (mass per unit area 300g / m 2 ) is irradiated with an electron beam. Immerse the cloth irradiated with electron beams in the above-prepared 10% by mass P1M aqueous solution with a dissolved oxygen concentration of 0.1ppm or less (bath ratio: about 1:15), seal it, and leave it at 50°C for 1 hour, then 35°C Leave it overnight. After washing with hot water and water to remove unreact...
Embodiment 3)
[0073] This example is an example in which acrylic acid is used as a compound containing a carboxylic acid group and bonded to cellulose fibers of cloth by the Pad method. This corresponds to the cases shown in the above formulas (6) to (10). Using an electron curtain type electron beam irradiation device (EC250 / 30 / 90L; manufactured by EYE ELECTRONBEAM Co., Ltd.), under the conditions of a nitrogen atmosphere, an accelerating voltage of 200kV, and an irradiation dose of 40kGy, 100% cotton fibers that have undergone caustic soda mercerizing treatment Medium-thick texture fabric (mass per unit area is 300g / m 2 ) is irradiated with an electron beam. The cloth irradiated with electron beams was dipped in a 10% by mass acrylic acid (manufactured by NACALAITESQUE Co., Ltd.) aqueous solution, squeezed with a squeezer until the squeeze rate was about 70% by mass, and then left at 35° C. overnight. After washing with hot water and water to remove unreacted monomers adsorbed on the cl...
PUM
 Login to view more
Login to view more Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap