Step of automatic escalator
A step and elevator technology, applied in escalators, transportation and packaging, etc., can solve the problems of fatigue damage, spending a lot of time and cost, easy to attach dirt and dirt, etc., and achieve the effect of preventing serious injuries
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0049] currently in use Figure 1 to Figure 9 The structure of Embodiment 1 will be described.
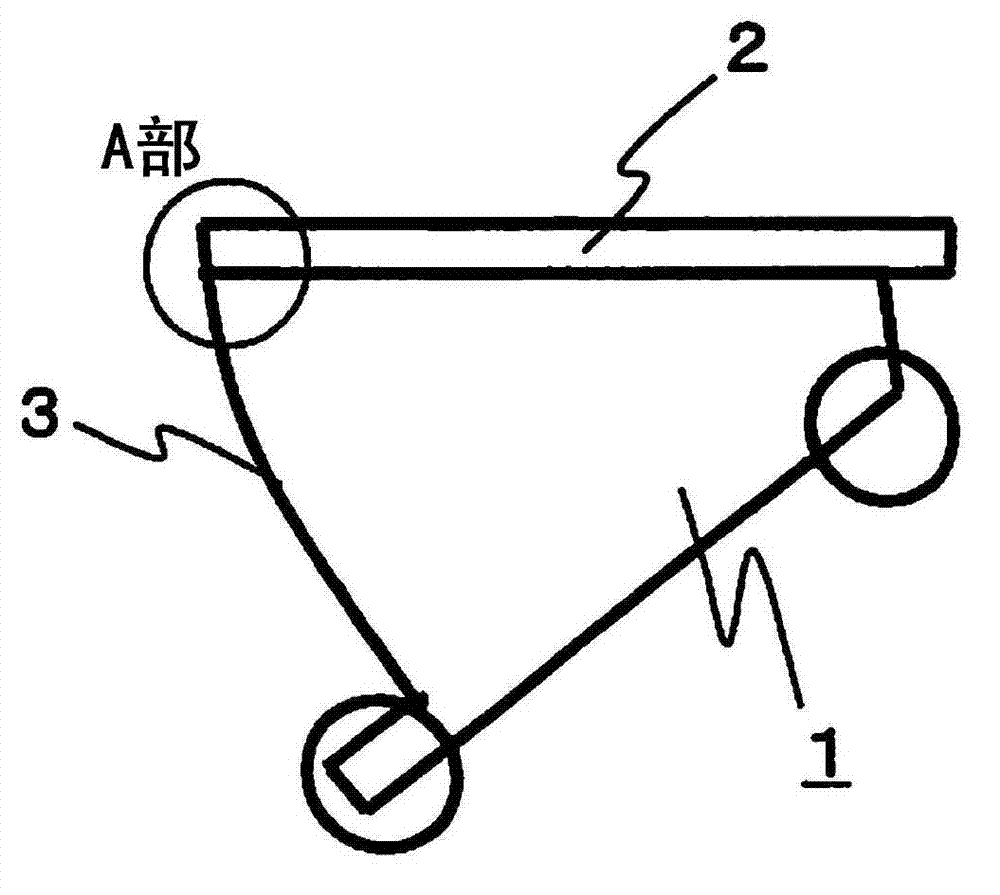
[0050] figure 1 It is a side view of step 1 of the escalator. The upper part of the step 1 has a tread 2 on which passengers ride, ascending or descending. In the description below, the figure 1 The direction of travel when rung 1 ascends ( figure 1 The middle is the right side) is defined as the front side, its opposite direction ( figure 1 The left side in the middle) is defined as the rear side for illustration. A step riser portion 3 is provided at the rear end of the step 1, and a corner portion (part A in the figure) is formed by intersecting the rear end of the tread 2 at its upper portion.
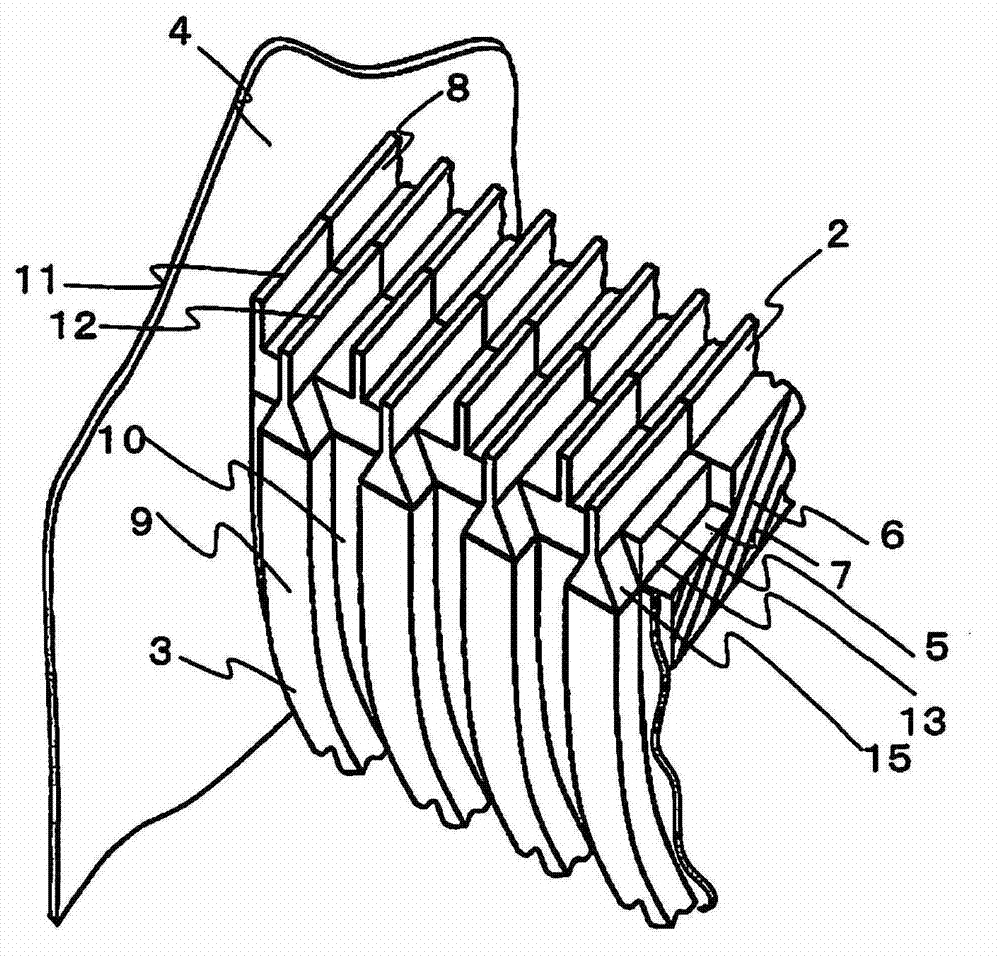
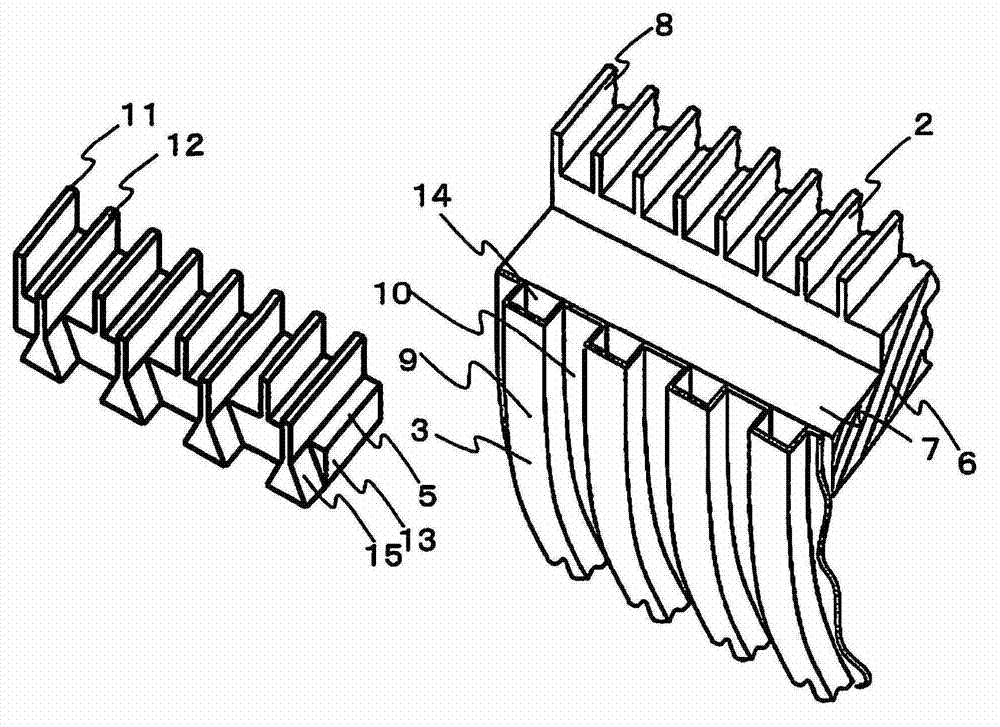
[0051] figure 2 and image 3 It means that the corner is seen from the center of the step 1 along the step baffle 4 ( figure 1 A partial perspective view of the state of Part A). figure 2 It shows the state after attaching the impact-absorbing splint 5 to the main body porti...
Embodiment 2
[0075] currently in use Figure 10 to Figure 12 Embodiment 2 will be described.
[0076] The difference between Embodiment 2 and Embodiment 1 is that the materials of each part constituting the impact-absorbing splint 20 are different, and their shapes are the same. Therefore, different parts will be described below, and descriptions of other parts will be omitted.
[0077] The impact-absorbing splint 20 of Example 2 also uses two kinds of urethane rubbers, urethane rubber with relatively high hardness and urethane rubber with relatively low hardness.
[0078] Figure 10 is the cross-section of the base 23 representing the short peak 21 and its lower portion ( Figure 5 A-A section in). The short peak 21 and the base 23 use relatively hard materials.
[0079] Figure 11 is to represent the base 23 section of the long peak 22 and its lower part ( Figure 5 B-B section in). Changfeng 22 using hardness compared to Figure 10 The shown short peak 21 and its lower base 23 ...
Embodiment 3
[0090] currently in use Figure 13 to Figure 15 Embodiment 3 will be described.
[0091] The difference between Embodiment 3 and Embodiment 1 is that, as in Embodiment 2, the materials of each part constituting the impact-absorbing splint 30 are different, and their shapes are completely the same. Therefore, different parts will be described below, and descriptions of other parts will be omitted.
[0092] The impact-absorbing splint 30 of Example 3 also uses two kinds of urethane rubbers, urethane rubber with relatively high hardness and urethane rubber with relatively low hardness.
[0093] Figure 13 is the cross-section of the base 33 representing the short peak 31 and its lower portion ( Figure 5 A-A section in). A relatively hard material is used for the short peak 31 and the base 33 .
[0094] Figure 14 is to represent the base 33 section of the long peak 32 and its lower part ( Figure 5 B-B section in). A material with relatively low hardness is used for the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com