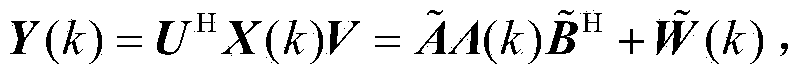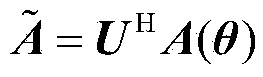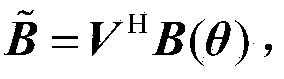Iterative least square method-based MIMO (multiple input multiple output) radar DOA (direction-of-arrival) estimation method
An iterative least squares and least squares technology, applied in the field of radar signal processing technology, can solve problems such as huge amount of calculation, large number of samples, unfavorable engineering implementation, etc., to improve estimation performance, fast convergence speed, and reduce calculation volume effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0022] The implementation process of the method of the present invention will be described below with reference to the accompanying drawings.
[0023] In order to better understand the present invention, the monostatic MIMO radar signal model is introduced first. figure 1 It is the structural diagram of the monostatic MIMO radar system, and the number of transmitting channels and the number of receiving channels are M and N respectively. The far-field target source has the same angle θ with respect to the transmitting and receiving elements. In a coherent processing interval, each transmitting channel simultaneously radiates a burst waveform consisting of K pulses, and the M transmitting waveforms are mutually orthogonal. Suppose the baseband signal of the mth (m=1,2,...,M) transmitted waveform is s m (t), transmit signal vector s(t)=[s 1 (t),s 2 (t),...,s M (t)] T satisfy:
[0024] ∫ T s ( t ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com