Maximum likelihood phase estimation method based on X-ray pulsar
A technique of maximum likelihood estimation and phase estimation, which is applied in the field of navigation and can solve the problems such as the decrease of signal phase measurement accuracy, the reduction of signal information utilization rate, and the loss of useful information.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0061] The present invention will be described in further detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings:
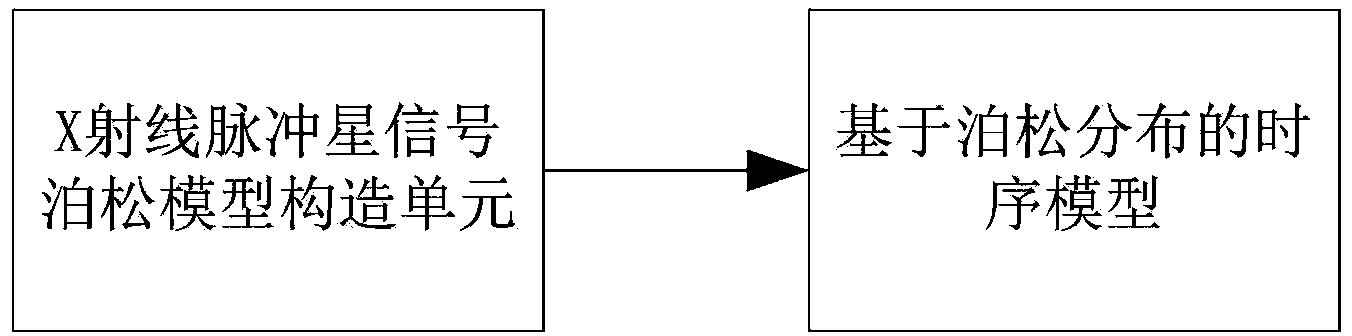
[0062] Reference figure 1 In this invention, the Poisson distribution-based time series model in the X-ray pulsar signal Poisson model construction unit is constructed as follows: Due to the high stability of the radiation period, X-ray pulsar radiation can be regarded as a kind of periodic stationary process. The stability of the pulsar allows us to accurately predict the phase of the pulsar signal in the solar system center (SSB) reference coordinates at any moment. In this coordinate system, the phase of the pulsar signal can be expressed by the following expression:
[0063] Φ n SSB ( t ) = Φ n SSB ( t 0 ) + f n · ( t - t 0 ) + O ( m ) - - - ( 1 )
[0064] among them Is the phase of the nth star at universal time t, f n Is the pulse frequency of the nth pulsar, O(m) ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com