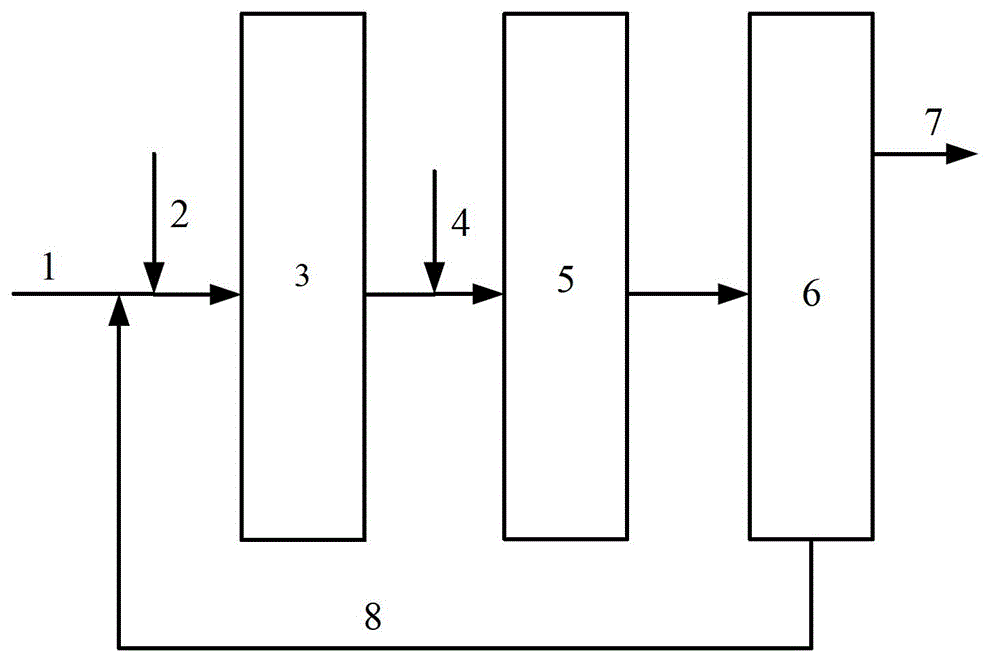
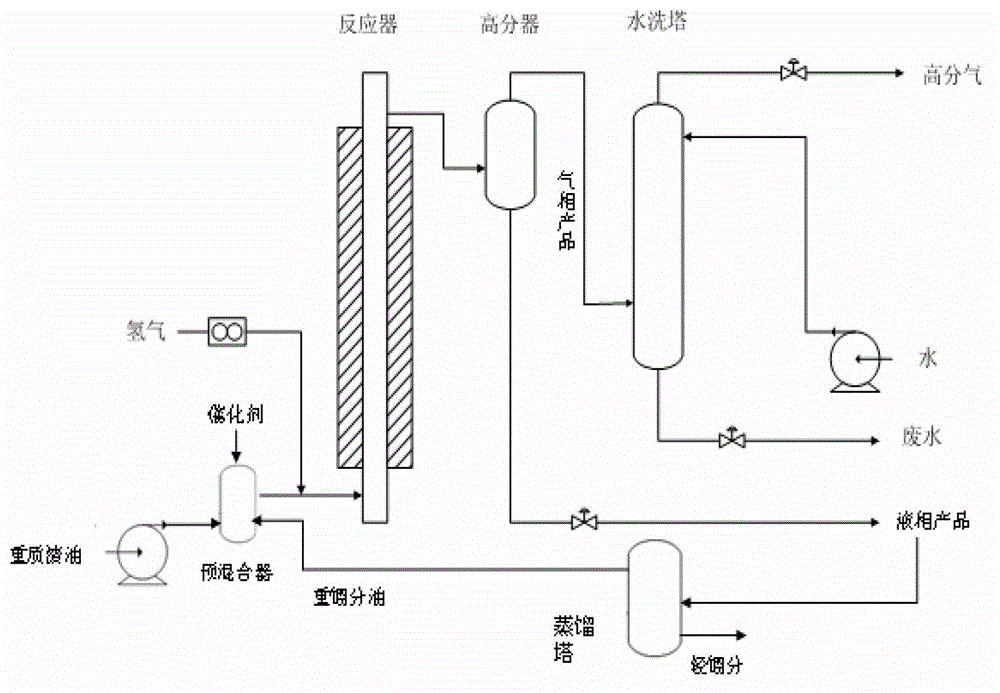
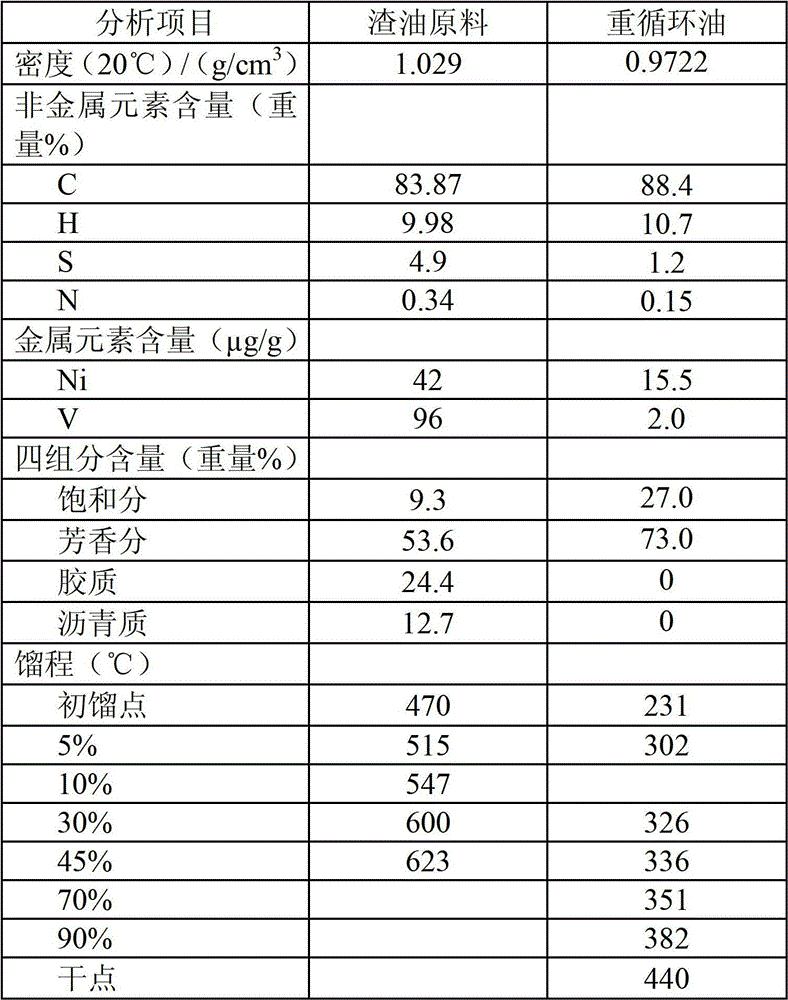
Modifying method for heavy oil hydrogenating
A heavy oil hydrogenation and heavy oil technology, which is applied in the fields of hydrogenation treatment process, petroleum industry, and hydrocarbon oil treatment, can solve the problems of easy deactivation of catalyst, low catalyst concentration, and expensive catalyst cost, so as to promote rapid mixing and uniformity, promote Hydrocracking reaction, effect of increasing reserves
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example 1
[0040] 5.7g ammonium tungstate (H 18 N 2 o 9 W), 3.6g nickel carbonate (NiCO 3 ), 2.9g vanadyl sulfate (VOSO 4 ), 300mL of water, 5.4g of vulcanizing agent (sublimed sulfur) and 90g of carbon black were sequentially added into a 500mL autoclave, and vulcanized at 320°C, 6.0MPa (hydrogen initial pressure), and high-speed stirring (500rpm) for 120min. Catalyst A was obtained after filtration and vacuum drying. The elemental composition of catalyst A is listed in Table 1.
[0041] Observed under an electron microscope, the average particle diameter of the catalyst A is 100 μm, and the average particle diameter of the metal element sulfide is 30 nm.
preparation example 2
[0043] 30.4g tungsten naphthenate (W content is 8.78% by weight), 30.4g nickel tetracarbonyl (Ni content is 33.73% by weight), 6.5g vanadium hexacarbonyl (V content is 23.29% by weight), 4.5g vulcanizing agent (sublimation sulfur), 200mL solvent oil (hydrogenated diesel oil) and 60g heavy oil asphaltene (Qingchuan 3# natural asphalt, C content 88.9 wt%, H content 7.2 wt%, S content 5.8 wt%, N content 1.1 wt%) in order Put it into a 500mL autoclave, and vulcanize for 210min under the conditions of 350°C, 8.0MPa (hydrogen initial pressure), and high-speed stirring (500rpm). The product is centrifuged, extracted with toluene, and vacuum-dried to obtain catalyst B. in Table 1.
[0044] Observed under the electron microscope, the average particle diameter of the catalyst B is 1 μm, and the average particle diameter of the metal element sulfide is 12 nm.
preparation example 3
[0046] Preparation of Fe-based catalysts conventionally used in heavy oil hydro-upgrading process.
[0047] Add 100g of diesel oil, 50g of iron naphthenate (Fe content is 12% by weight), and 8.2g of sulfur into a 500mL autoclave in sequence, and vulcanize for 60min under the conditions of 350°C, 8.0MPa (hydrogen initial pressure), and 500rpm stirring speed , the product was filtered and vacuum-dried to obtain catalyst C, the active component of the catalyst was Fe-containing sulfide, and the elemental composition of the catalyst was listed in Table 1.
[0048] The element composition of the catalyst that each preparation example of table 1 makes
[0049]
Catalyst preparation example 1
Catalyst preparation example 2
Catalyst preparation example 3
Element content / %
Catalyst A
Catalyst B
Catalyst C
Fe
-
-
20.5
W
2.8
3.2
0
Ni
1.8
2.4
0
V
0.9
1.8...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com