Fault isolation and service restoration in an electric grid
A fault isolation, power fault technology, applied in the fault location, detection of faults by conductor type, electrical components, etc., can solve problems provided by power suppliers, unable to respond to power faults and control, monitor power grids, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
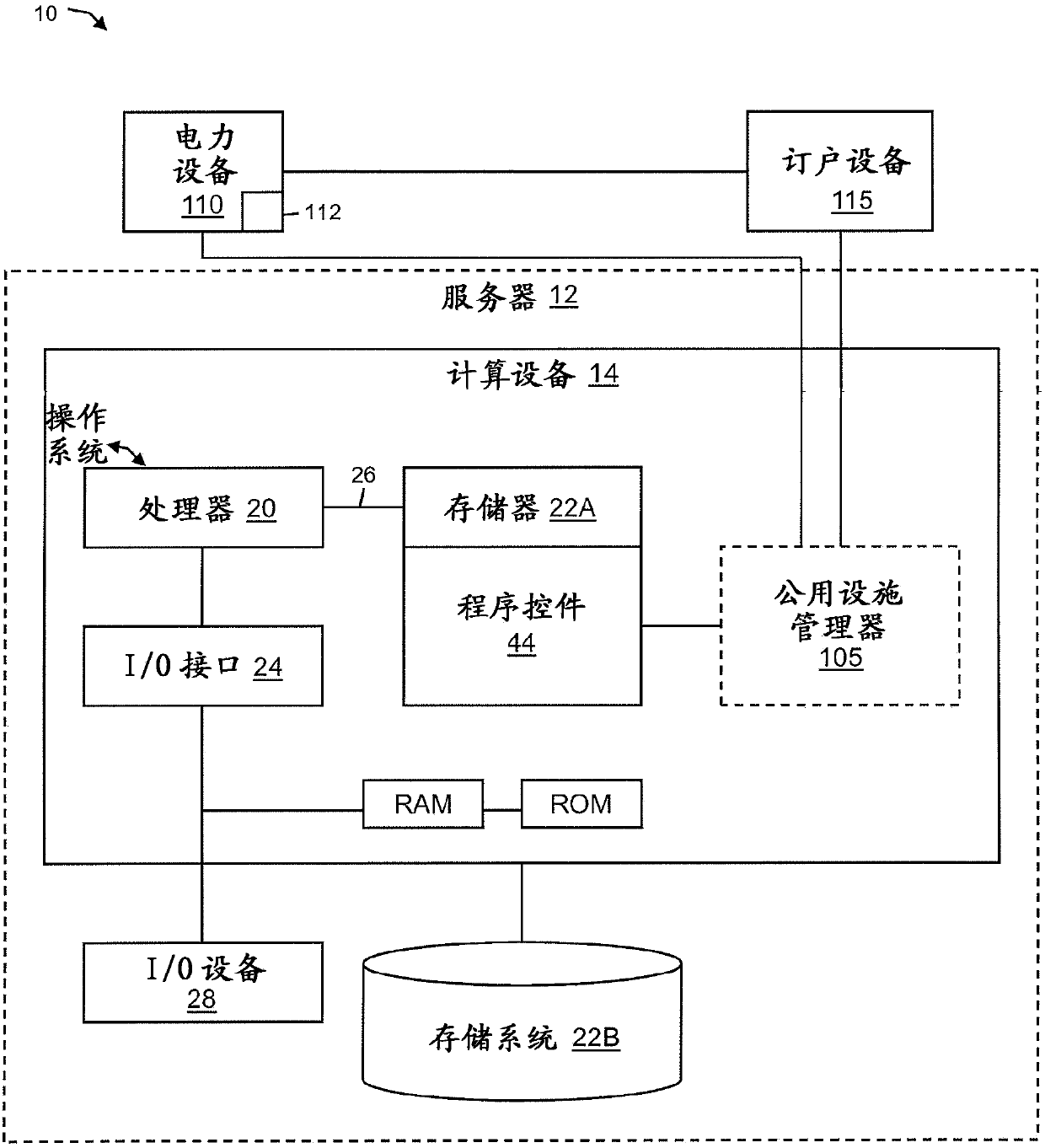
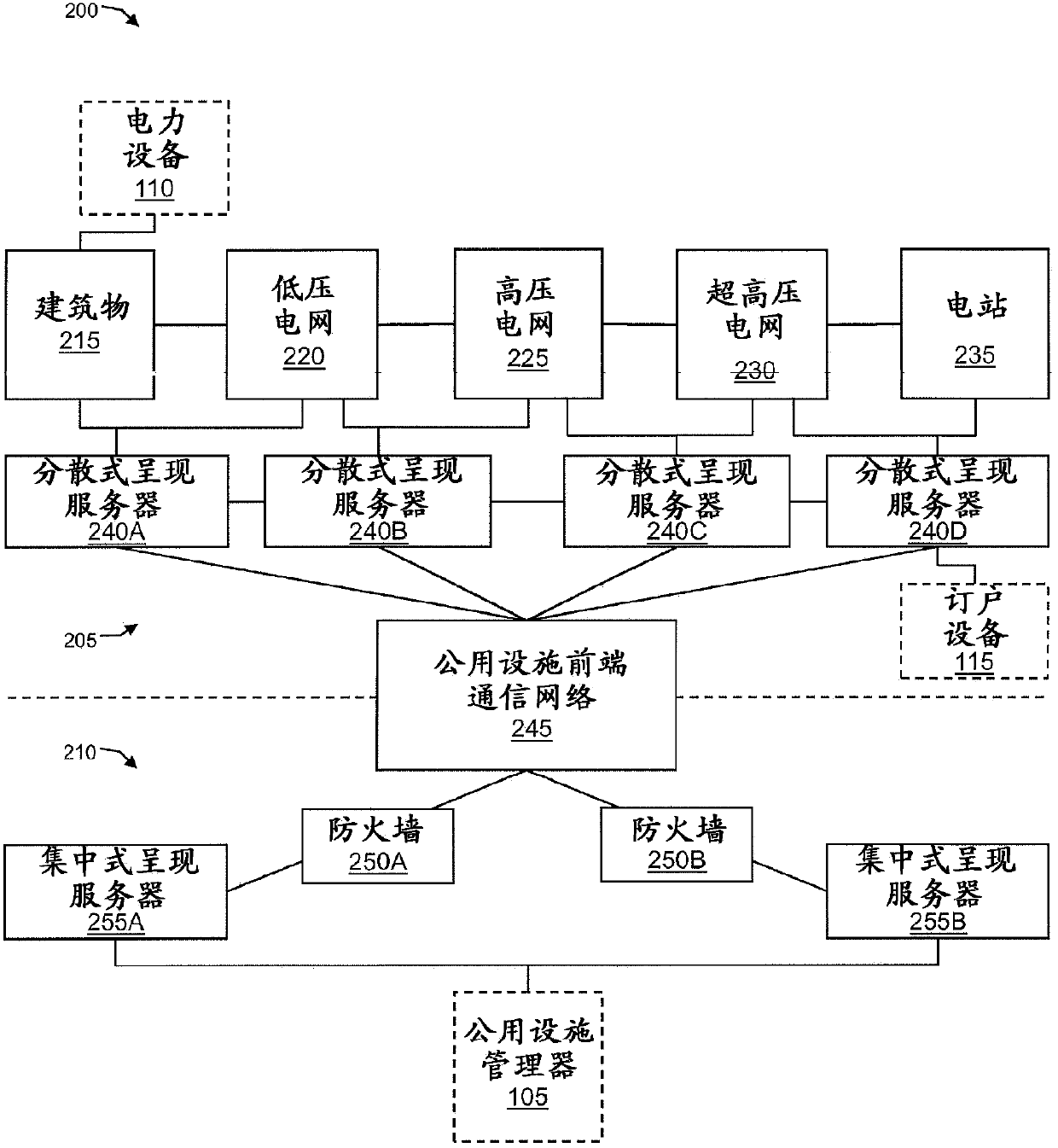
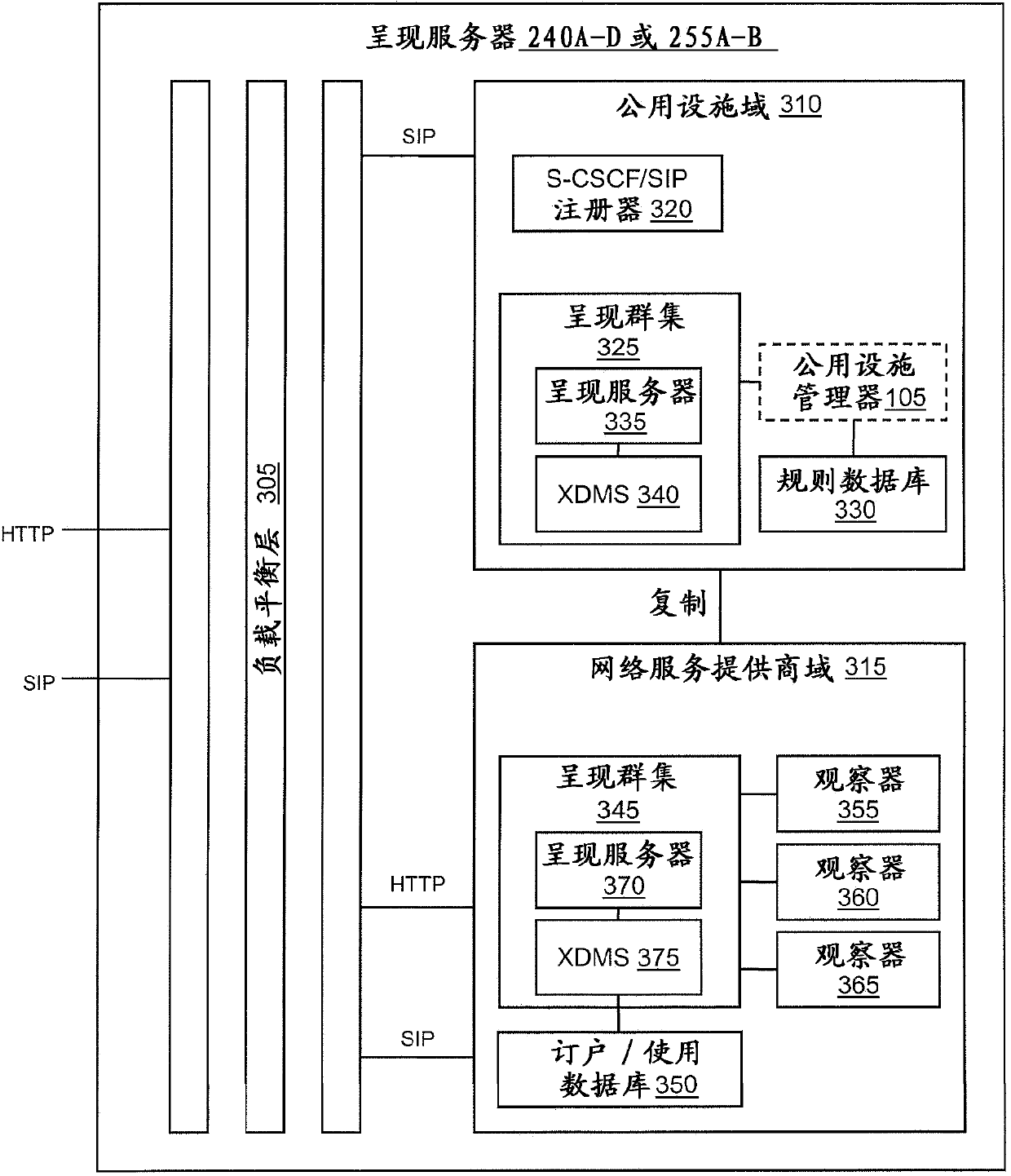
[0019] The present invention relates generally to fault isolation in electrical grids, and more particularly to systems and methods for decentralized and centralized fault isolation and service restoration in electrical grids. In various embodiments, the present invention provides communication and monitoring capabilities of the grid to more effectively manage the grid as it becomes more complex and difficult to manage. For example, in order to manage the many different needs of the grid and to ensure that the grid works most efficiently, the invention provides an Internet Protocol (IP) backplane for the traditional grid to allow utilities (e.g., service providers, power suppliers, etc.) and electricity Efficient communication between electrical devices on the Internet.
[0020] More specifically, the present invention provides Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) as a low-latency, scalable communication protocol for use between electrical grids, especially between electrical equ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com