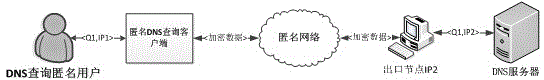DNS query method based on anonymous network
A DNS query and anonymous network technology, applied in the field of computer software security testing, can solve problems such as large-scale network paralysis and inability to provide normal services, so as to improve security, resist DNS domain name hijacking attacks, and ensure user experience.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0087] Proxy-based anonymous network DNS query, the network architecture diagram is as follows figure 2 shown.
[0088] At the beginning, the user initiates a normal DNS query request, through the firewall rules: all data packets with the destination port 53 and the protocol as UDP are redirected to the DNS anonymous query client port.
[0089] Step 1: After the anonymous query client receives the user query request, it first checks whether the result already exists in the DNS cache, and if it exists, go to step 8. If not, go to step 2.
[0090] Step 2: To query the client anonymously through DNS, first change the initial destination IP address of the data packet to the IP address of the third-party trusted agent. Then, the public key of the third-party trusted agent is used to encrypt the DNS query message and send it to the third-party trusted agent.
[0091] Step 3: The third-party trusted agent uses the private key to decrypt and restore the received query.
[0092] S...
Embodiment 2
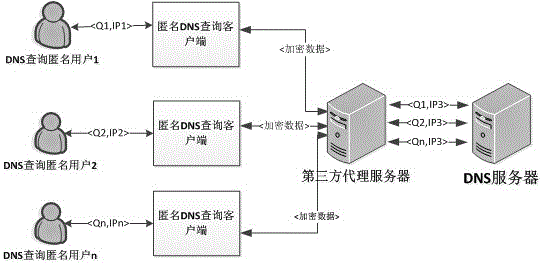
[0098] Anonymous network DNS query based on anonymous chain, the network architecture diagram is as follows Figure 4 shown.
[0099]At the beginning, the user initiates a normal DNS query request, through the firewall rules: all data packets with the destination port 53 and the protocol as UDP are redirected to the DNS anonymous query client port. Then, set the maximum number of forwarding times N.
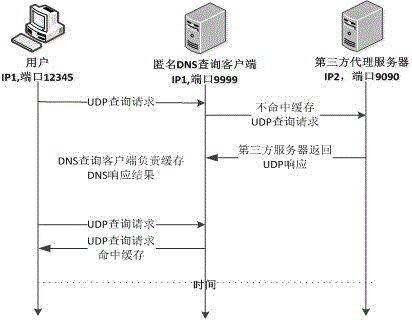
[0100] Step 1: After the anonymous query client receives the user query request, it first checks whether the result already exists in the DNS cache, and if it exists, go to step 9. If not present, initialize the structure as Figure 5 shown in the anonymous DNS query packet, and then go to step 2.
[0101] Step 2: The node performs next-hop relay route selection according to the node information received from the relay directory node in advance (the route selection algorithm can be performed according to the delay to the next-hop relay), and then changes the destination IP add...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com