Method of securing memory against malicious attack
A technology of memory and dynamic memory, which is applied in the direction of memory system, internal/peripheral computer component protection, instruments, etc., and can solve problems such as not supporting dynamic allocation of memory for higher protection, vulnerable to reverse engineering, performance is not safe, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
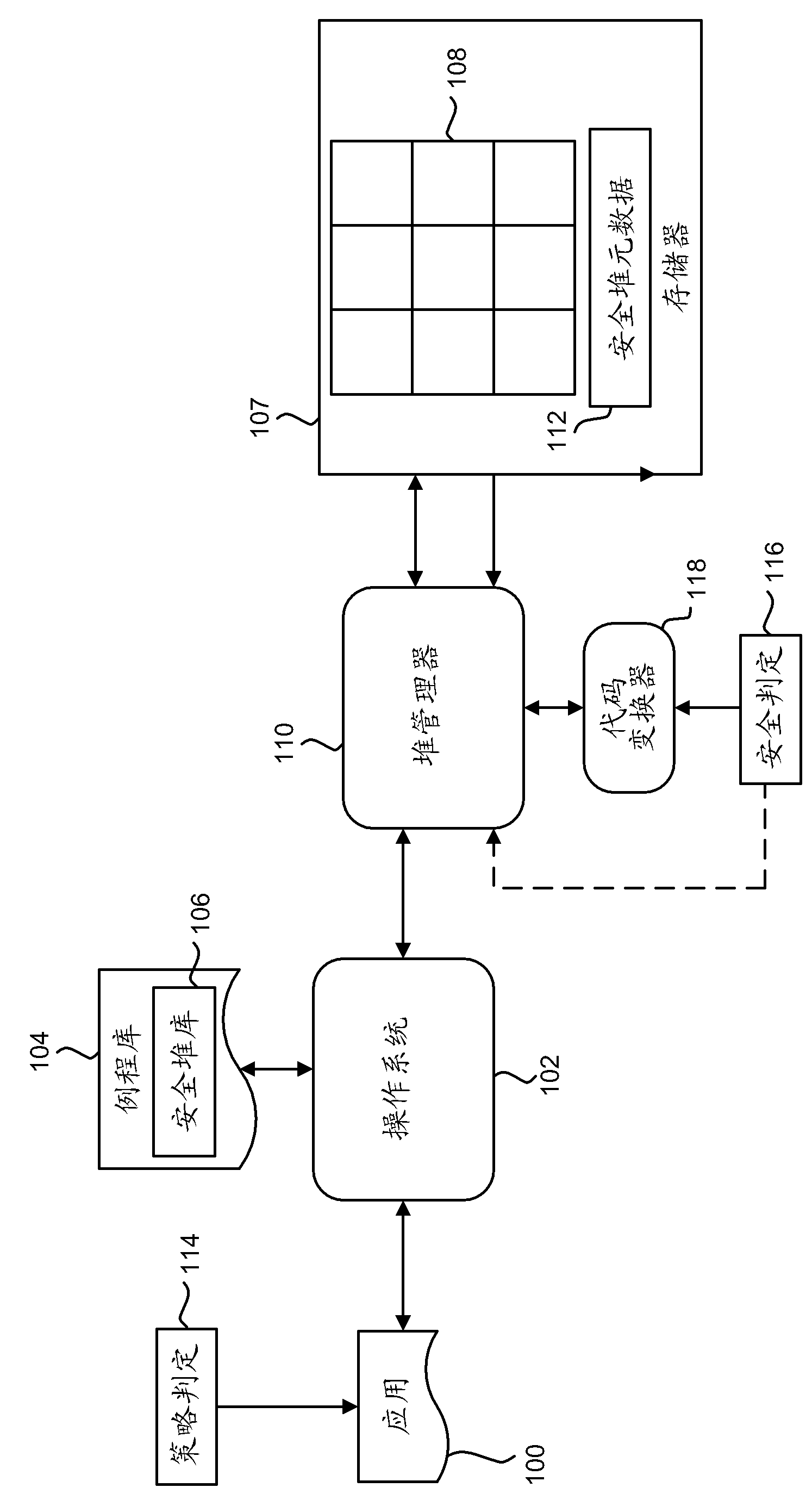
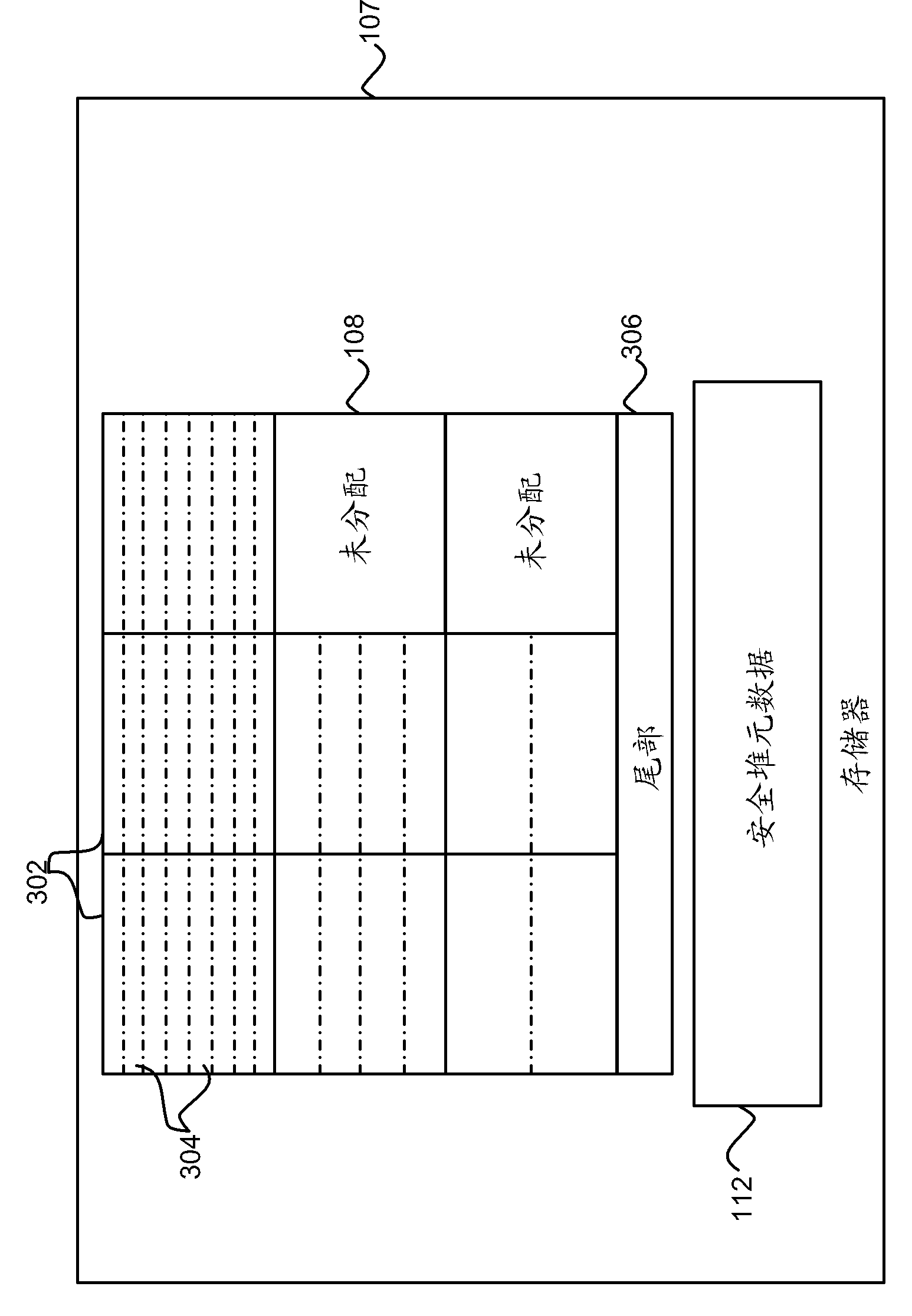
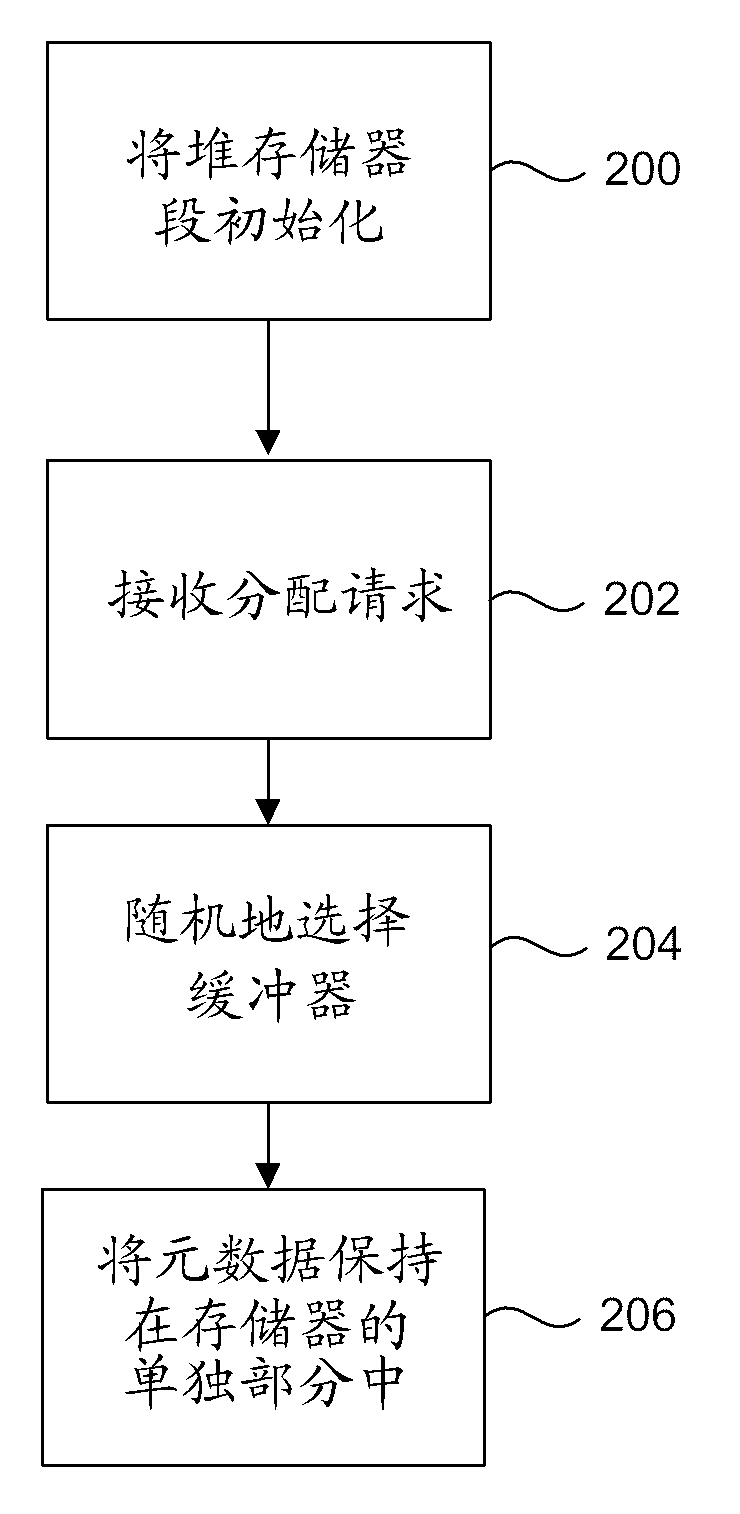
[0017] Generally, this disclosure describes a method and system for secure dynamic memory management. Embodiments are described with respect to a C / C++ implementation, but are not intended to be limited to such implementations, and the methods described herein may be used with respect to any dynamic memory management system that uses heap memory or similar dynamic memory allocation. According to certain embodiments, the secure heap of the present disclosure is capable of safely implementing functions of those parts of the C / C++ stdlib library related to dynamic memory management, specifically malloc(), free(), and variants thereof.
[0018] Broadly speaking, the secure heap implementation supports two types of memory allocation pointers: "smooth" and "handle" pointers. A "smooth" pointer is a standard memory address that points to a piece of memory of the requested size. A "smooth" pointer can be dereferenced directly by the calling application. A "handle" pointer is not a s...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com