Patents
Literature
141 results about "Dynamic memory management" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
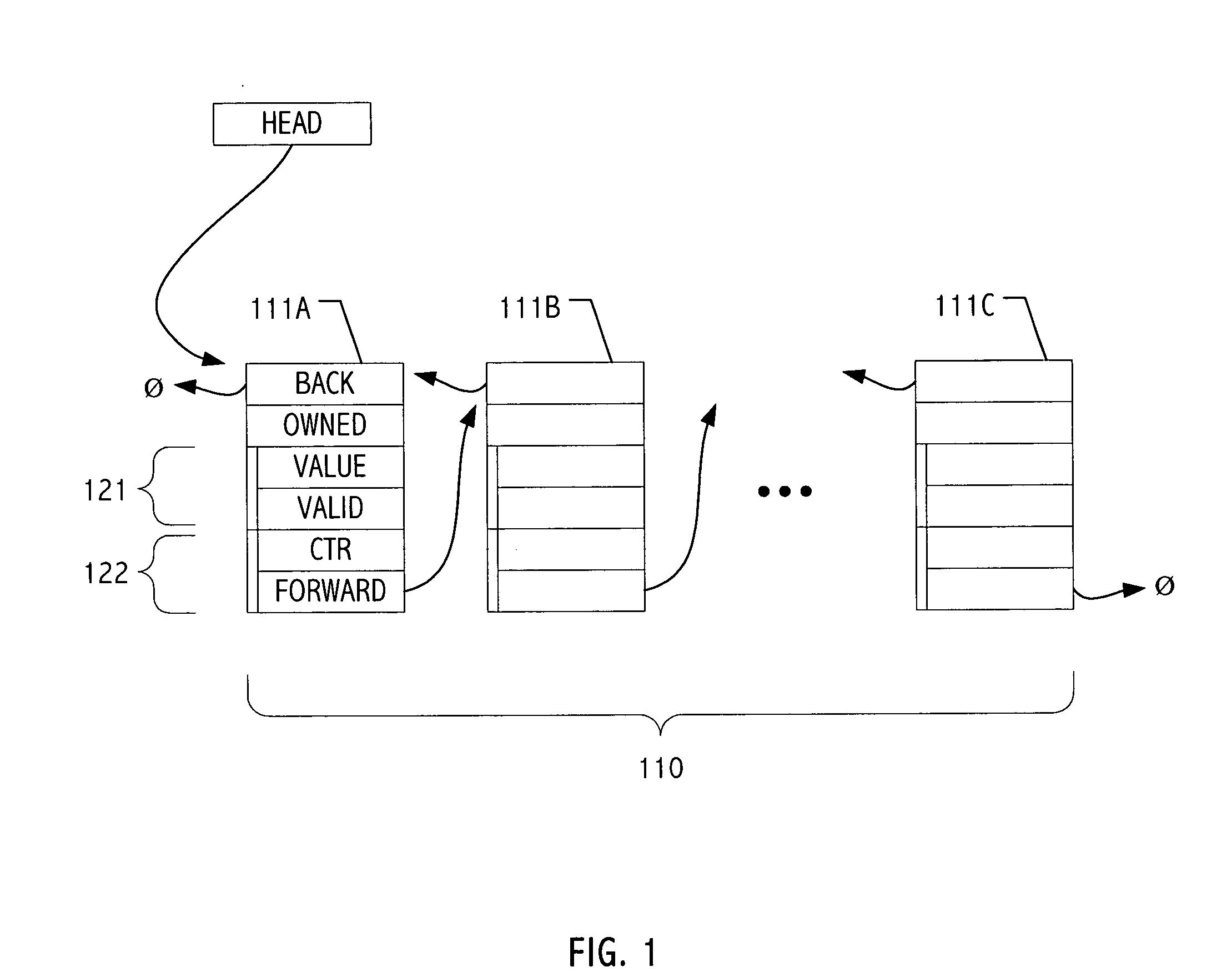
Dynamic memory management involves the use of pointers and four standard library functions, namely, malloc, calloc, realloc and free. The first three functions are used to allocate memory, whereas the last function is used to return memory to the system (also called freeing/deallocating memory).
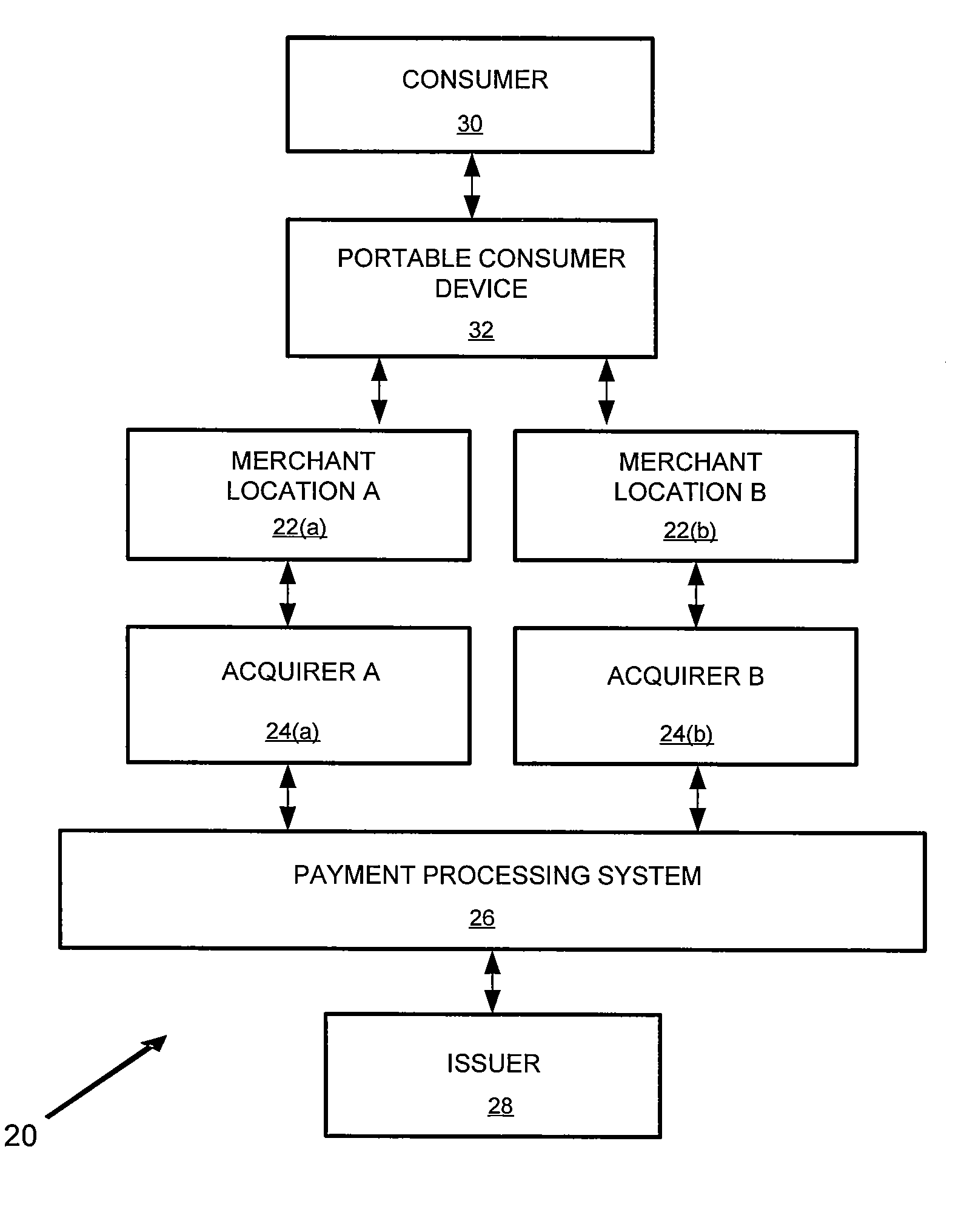
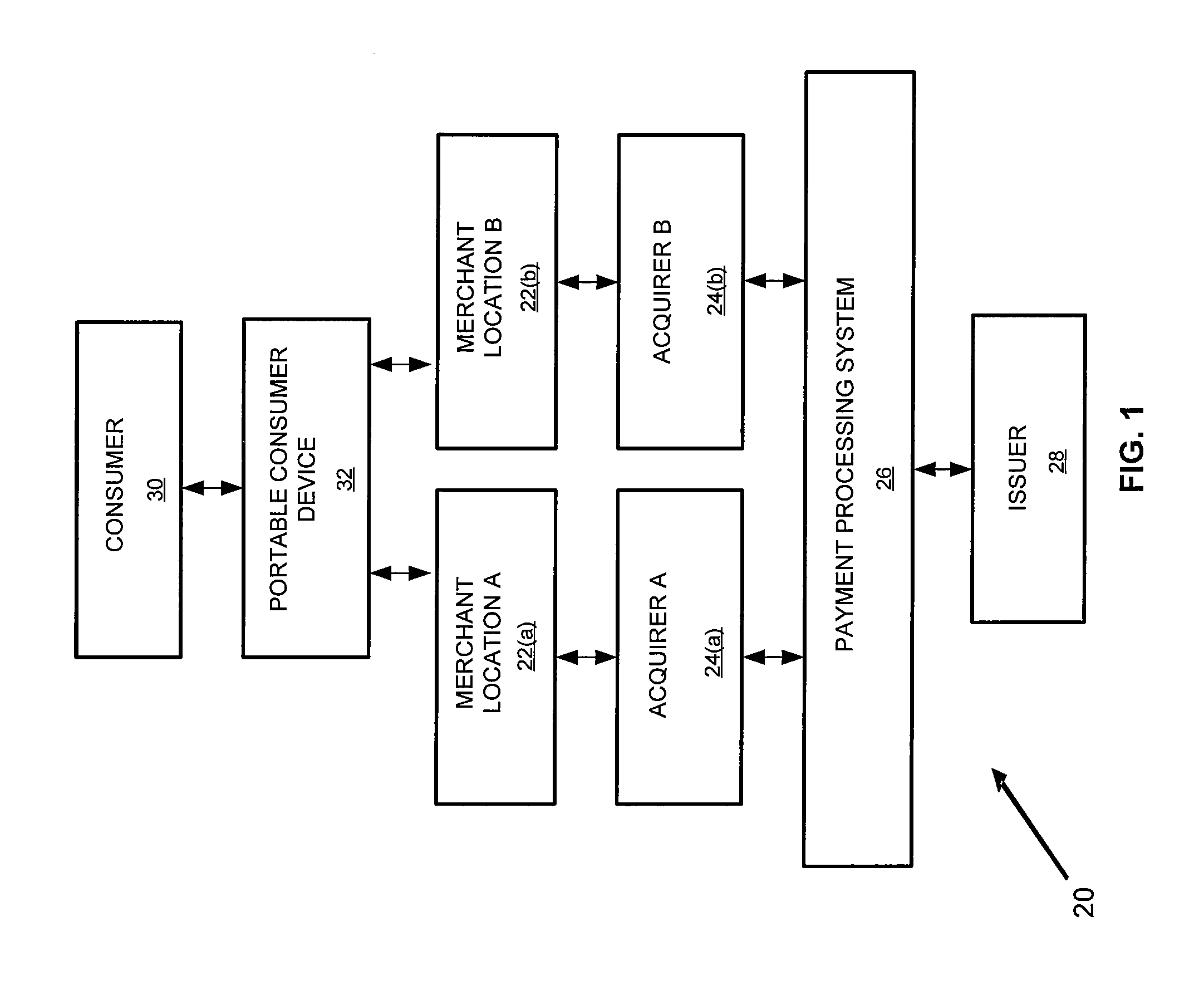
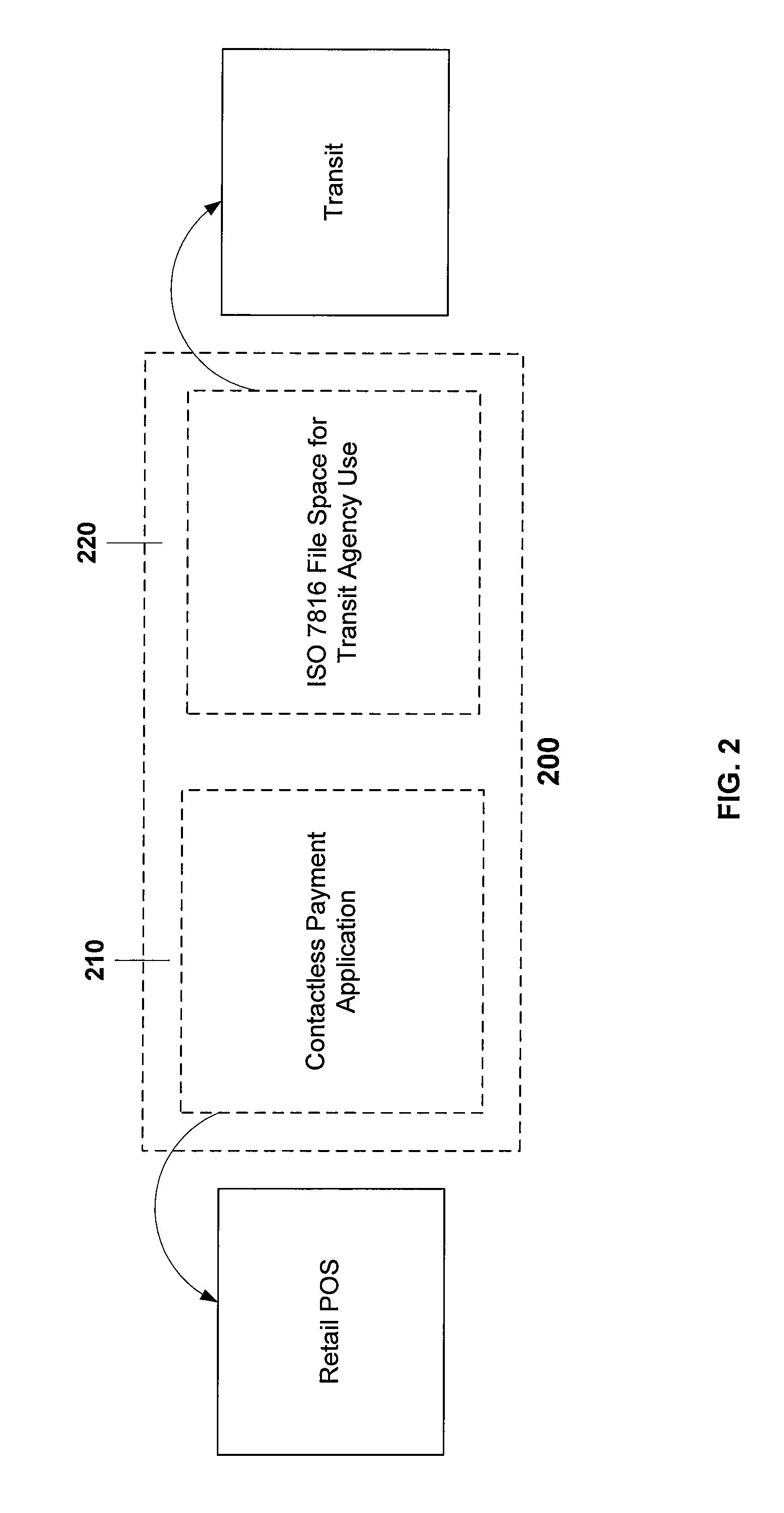
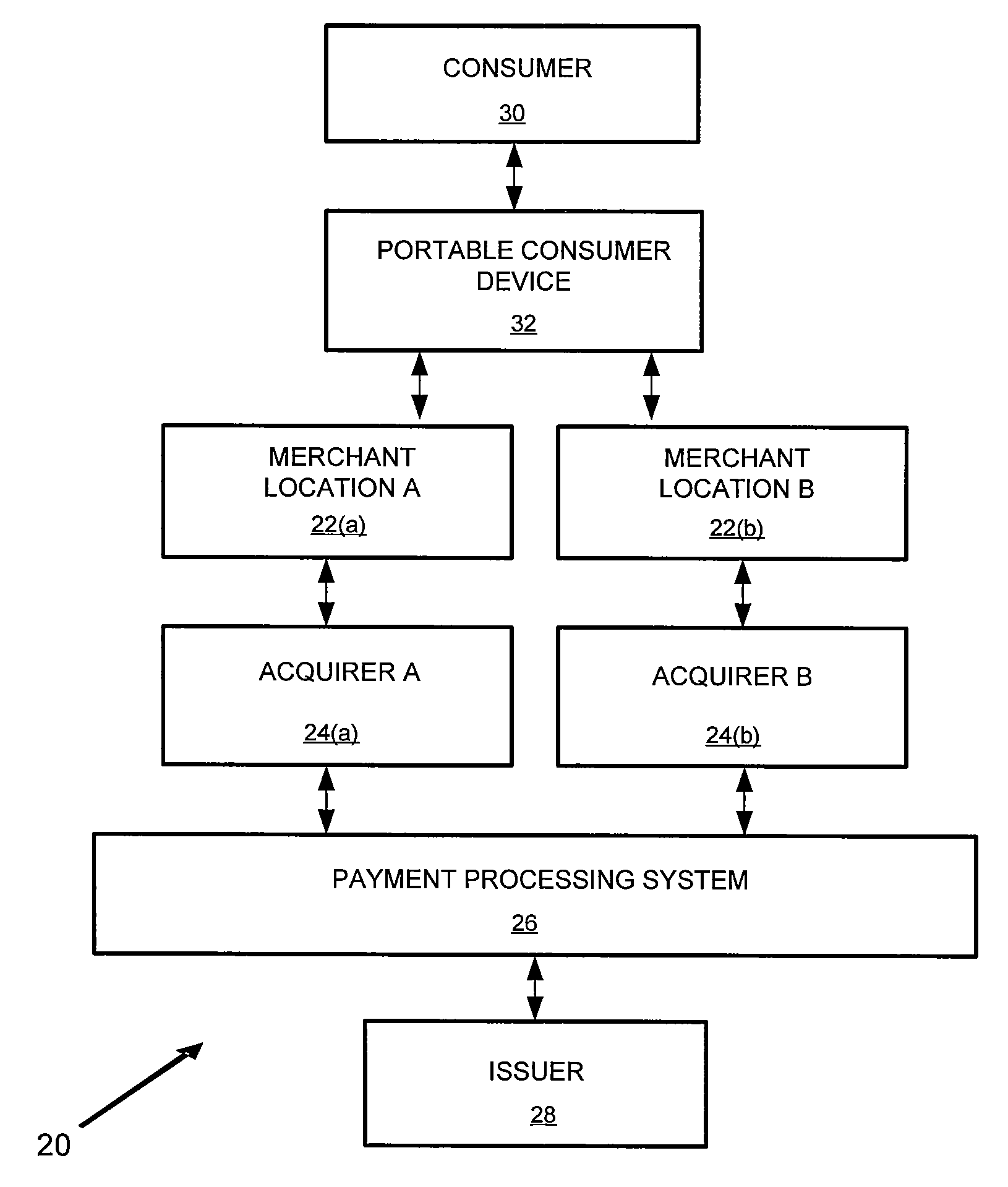
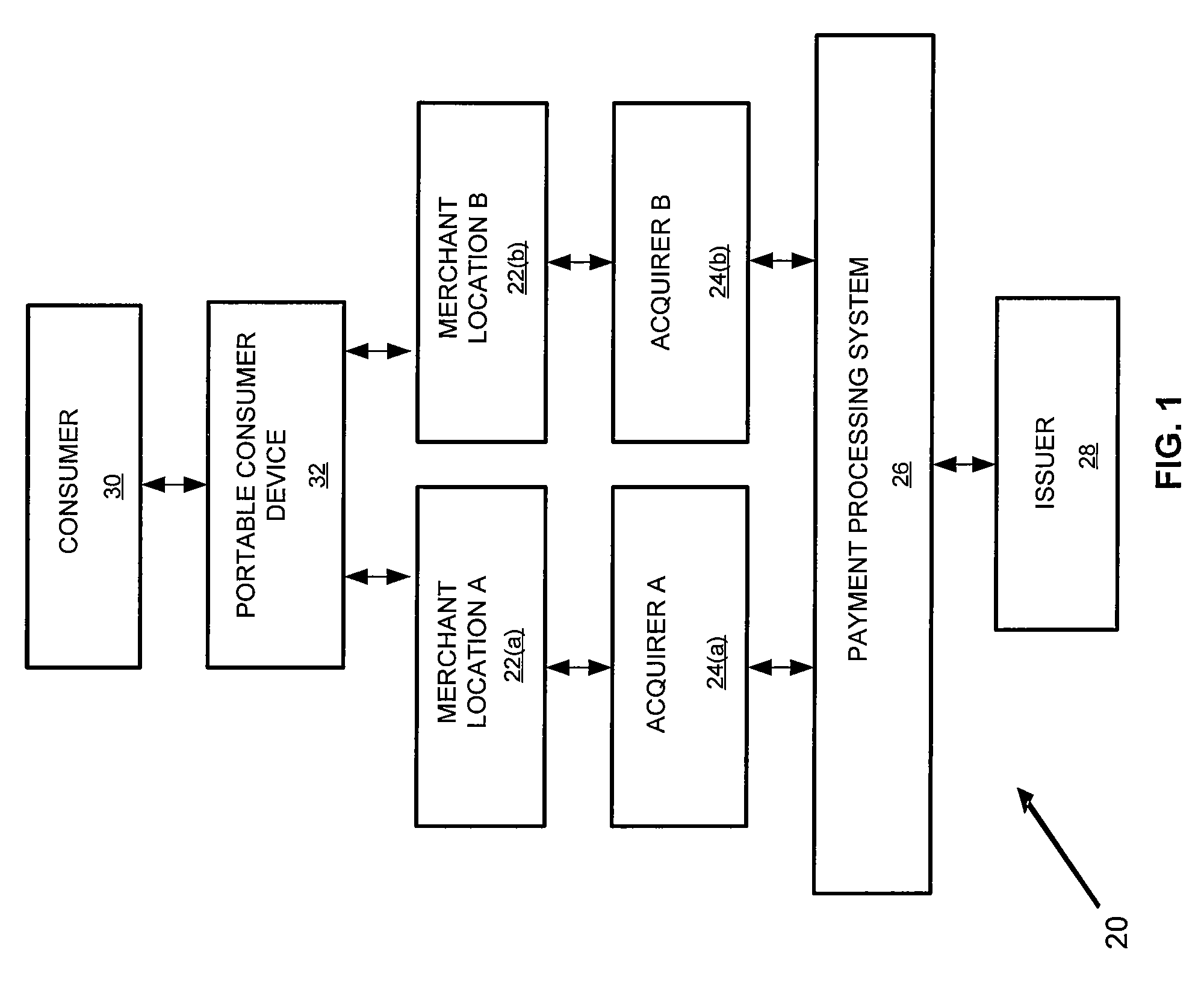
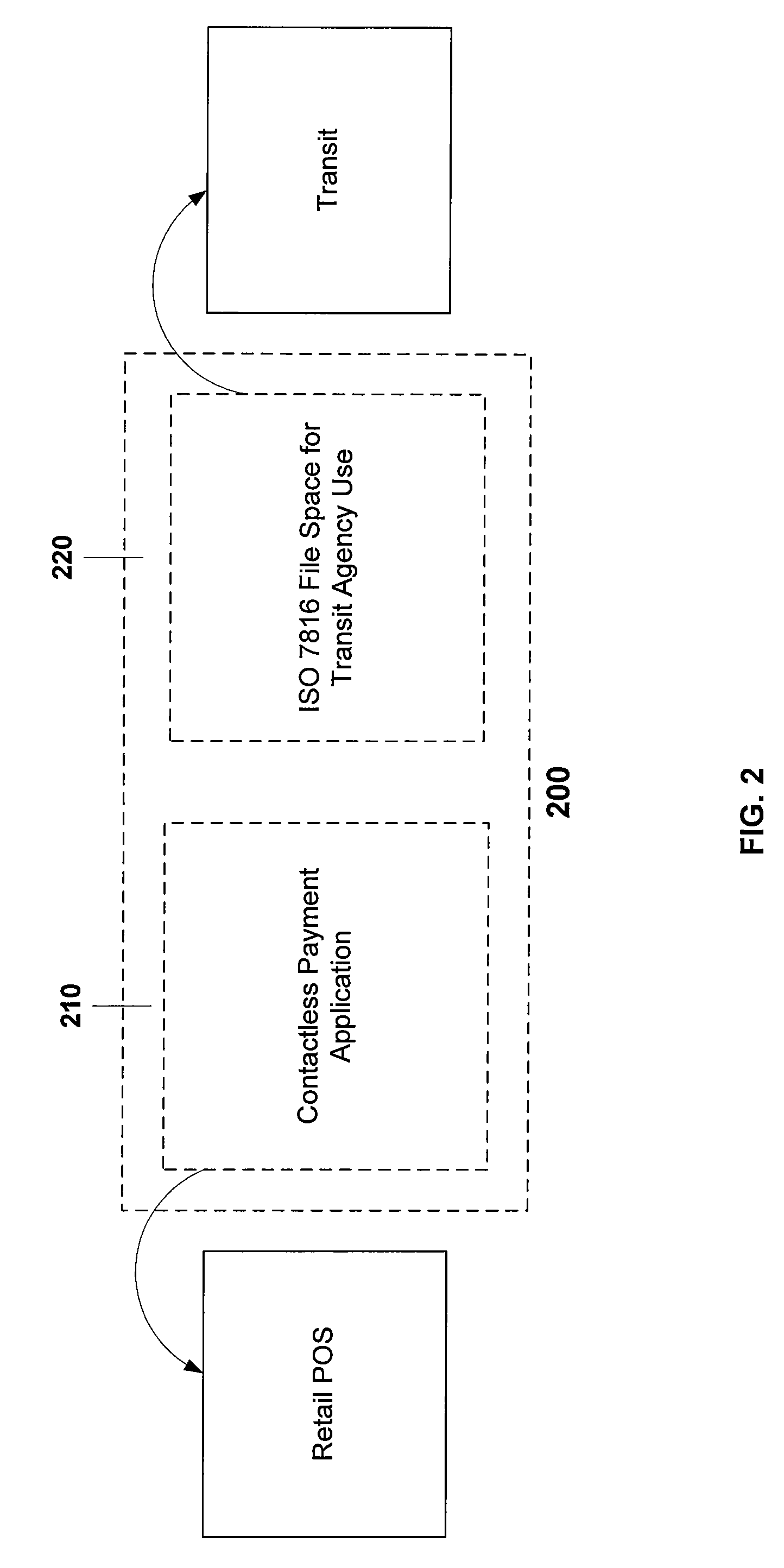
Bank issued contactless payment card used in transit fare collection
An architecture for a contactless smart card or payment device, where the smart card is intended for use in both commerce transaction payment and transit fare payment (or other venue access) environments. The payment device may function as both an electronic wallet for commerce transactions and as a transit system card, for access to and fare payment of transit services. Implementation of both functions may be achieved by use of a dynamic memory management system that permits data for both the payment and transit applications to be stored on the card, with the transit data and storage locations isolated from those used to store data intended for use in paying for commerce transactions. The transit application specific data may include access control data (keys, passwords, identification data) or data required for fare calculations (rates, historical data on system use), for example.
Owner:VISA USA INC (US)
Bank issued contactless payment card used in transit fare collection
An architecture for a contactless smart card or payment device, where the smart card is intended for use in both commerce transaction payment and transit fare payment (or other venue access) environments. The payment device may function as both an electronic wallet for commerce transactions and as a transit system card, for access to and fare payment of transit services. Implementation of both functions may be achieved by use of a dynamic memory management system that permits data for both the payment and transit applications to be stored on the card, with the transit data and storage locations isolated from those used to store data intended for use in paying for commerce transactions. The transit application specific data may include access control data (keys, passwords, identification data) or data required for fare calculations (rates, historical data on system use), for example.
Owner:VISA USA INC (US)
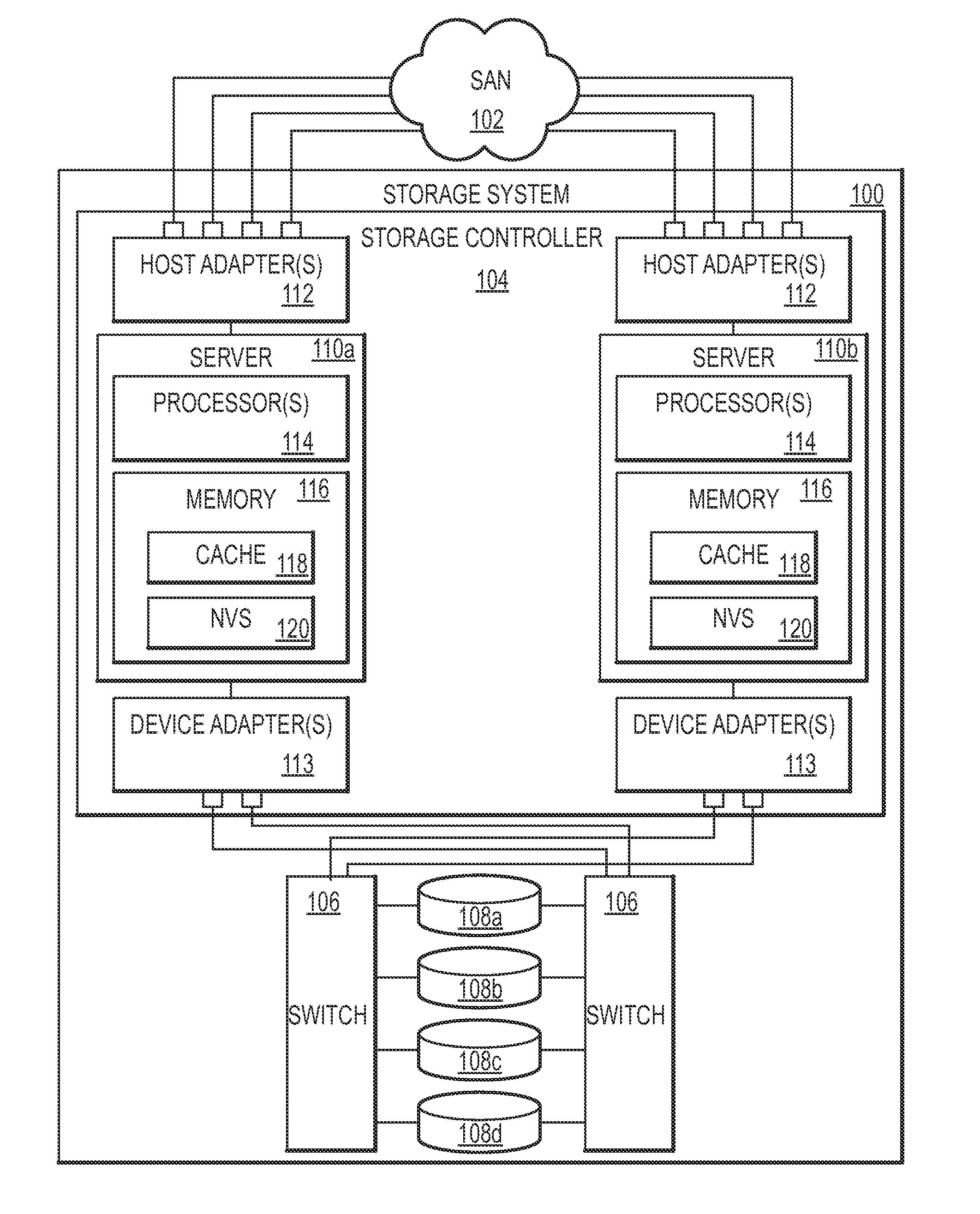
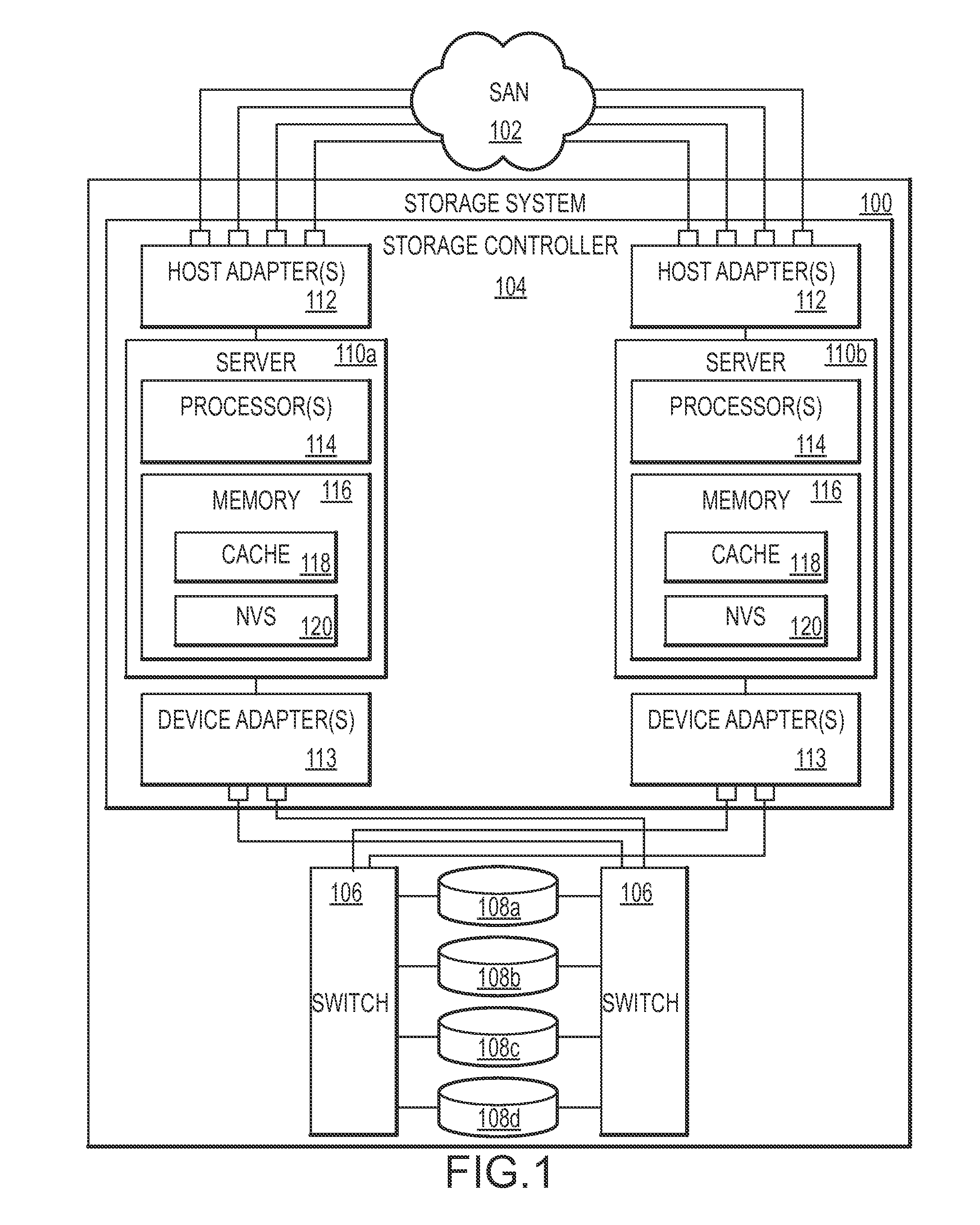
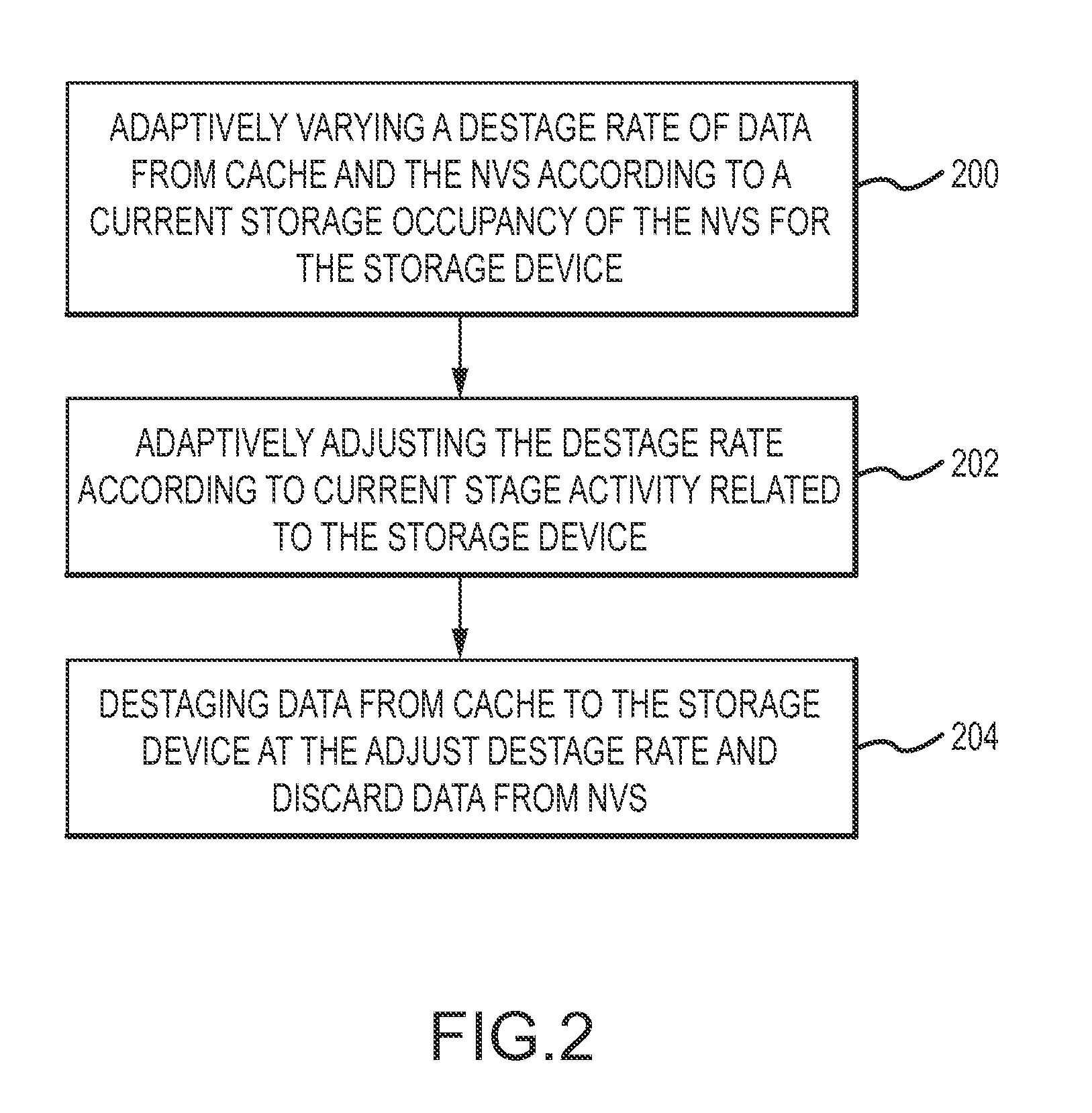
Dynamic management of destage tasks in a storage controller
ActiveUS20110191534A1Desired overall occupancy of the NVSExtension of timeMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationOccupancy rateDynamic management
Method, system, and computer program product embodiments for facilitating data transfer from a write cache and NVS via a device adapter to a pool of storage devices by a processor or processors are provided. The processor(s) adaptively varies the destage rate based on the current occupancy of the NVS for a particular storage device and stage activity related to that storage device. The stage activity includes one or more of the storage device stage activity, device adapter stage activity, device adapter utilized bandwidth and the read / write speed of the storage device. These factors are generally associated with read response time in the event of a cache miss and not ordinarily associated with dynamic management of the destage rate. This combination maintains the desired overall occupancy of the NVS while improving response time performance.
Owner:IBM CORP
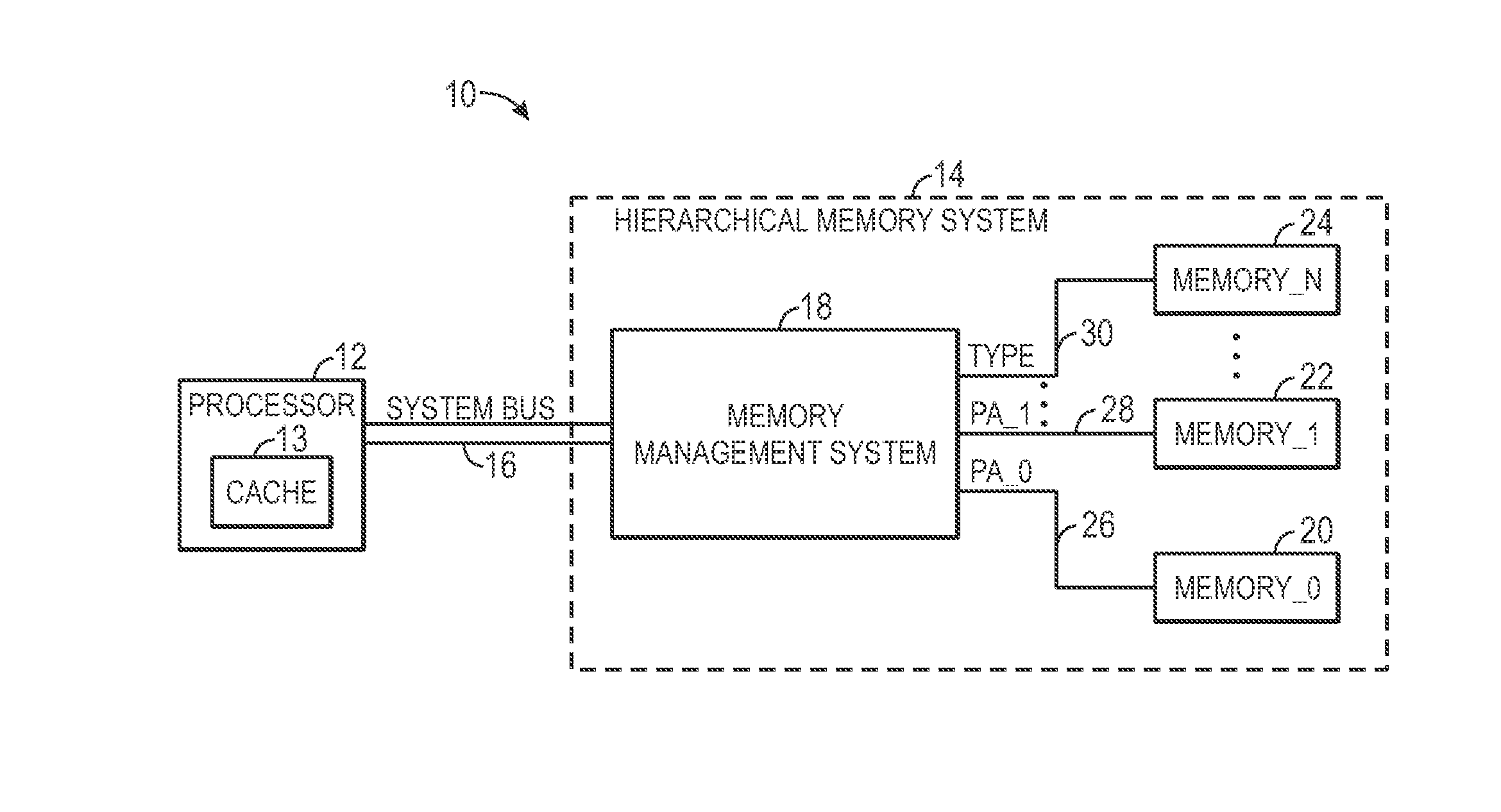
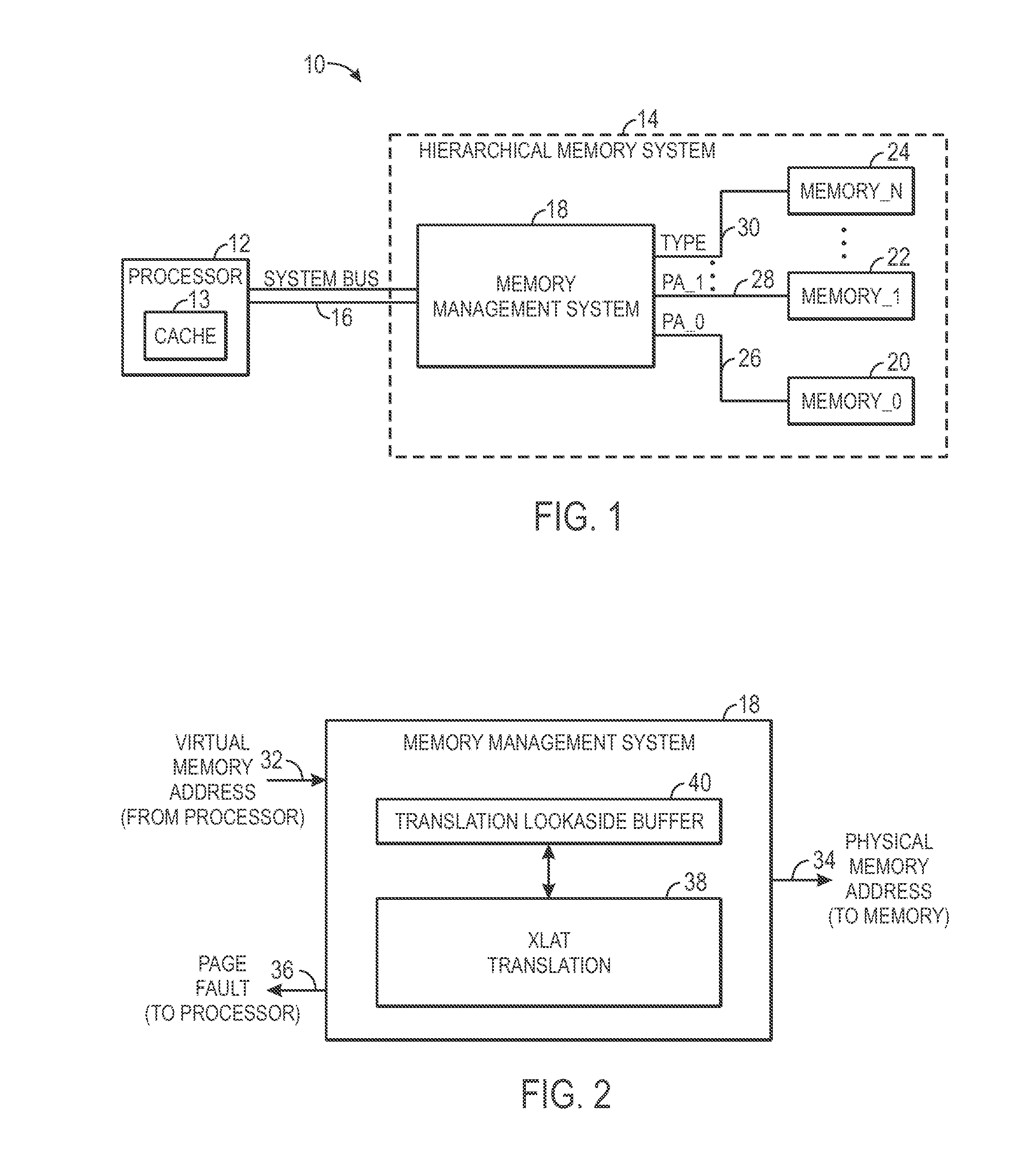
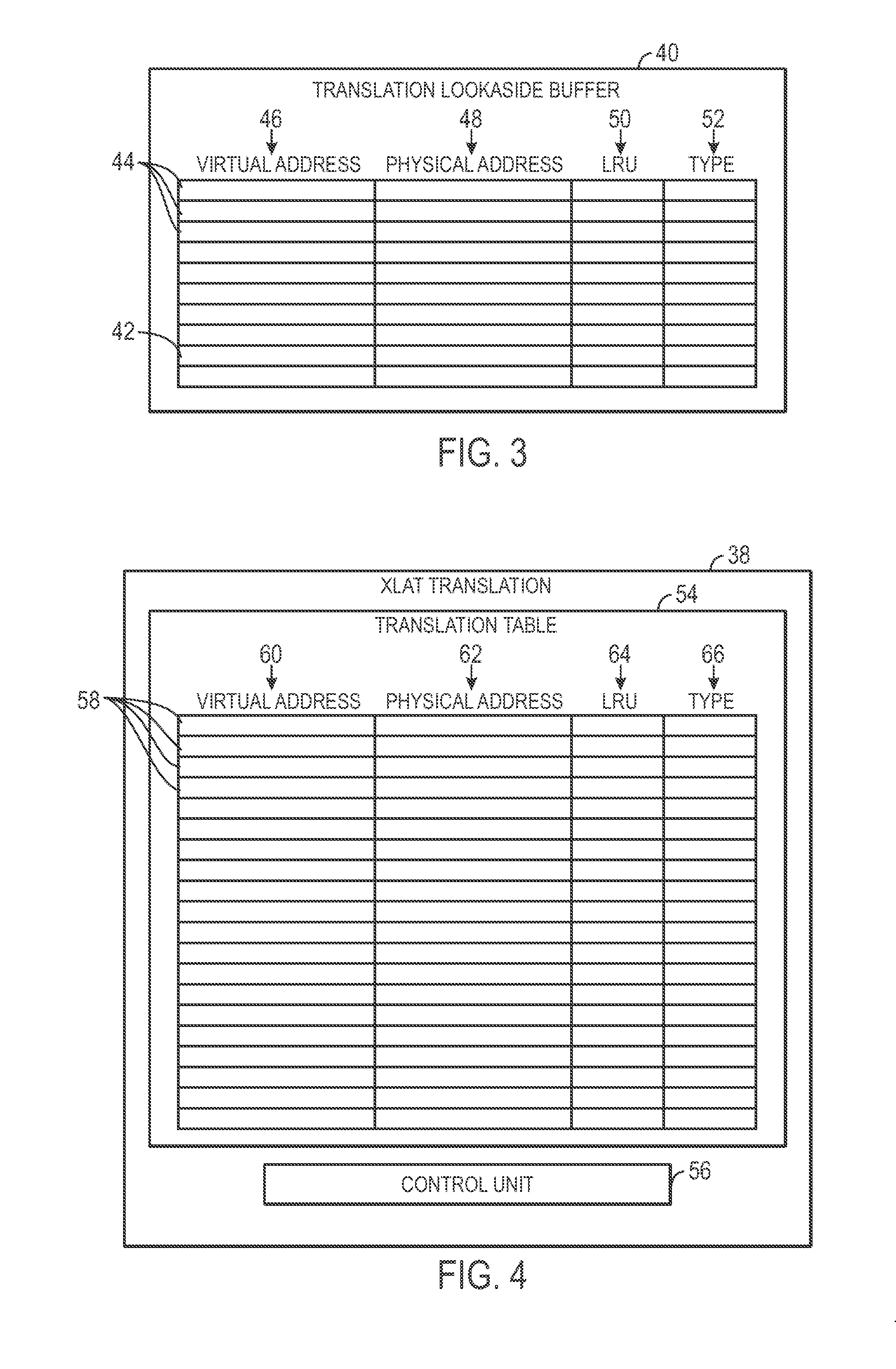
Memory management for a hierarchical memory system
ActiveUS20140025923A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationMemory addressTerm memory
Disclosed are systems and methods for managing memory. A memory management system may include a table having multiple virtual memory addresses. Each virtual memory address may correspond to a physical memory address and data that identifies a type of memory device corresponding to the physical memory address. The physical memory device can be used to access the memory device when a table hit occurs.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
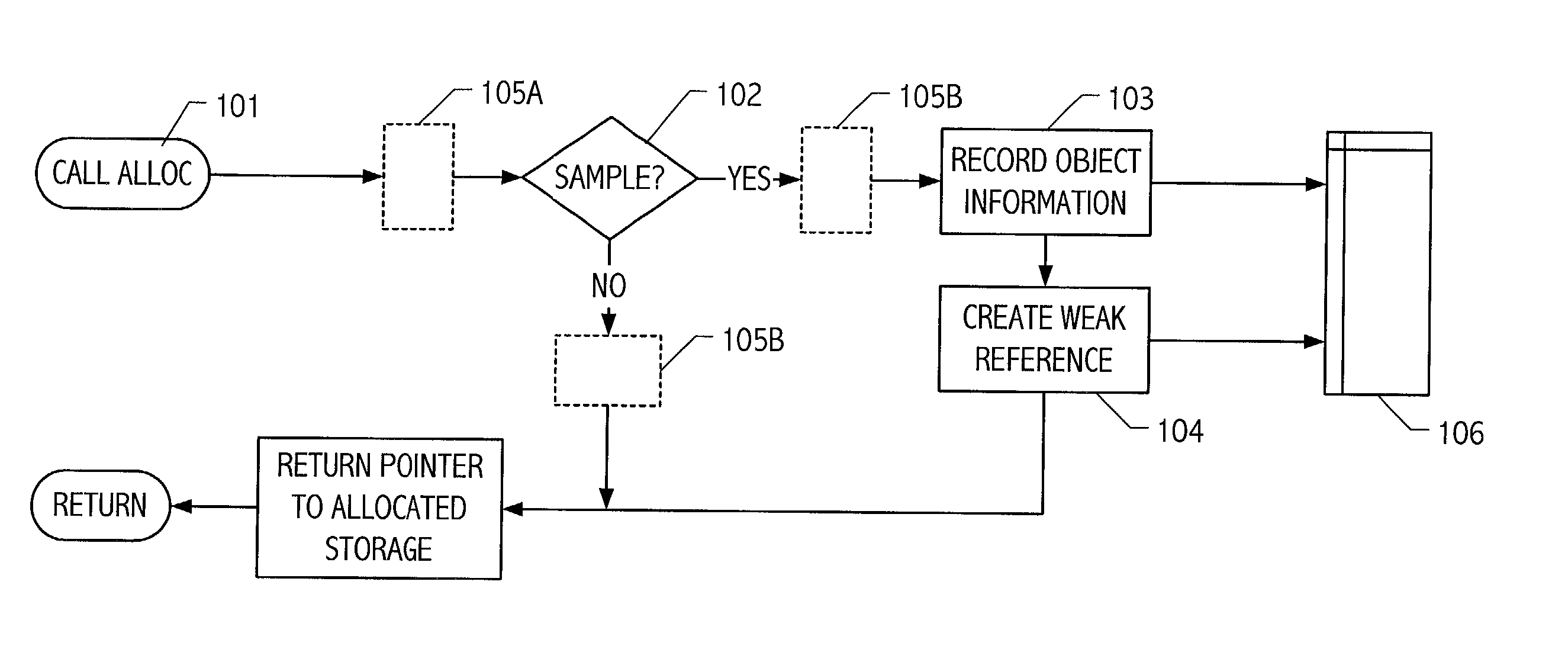
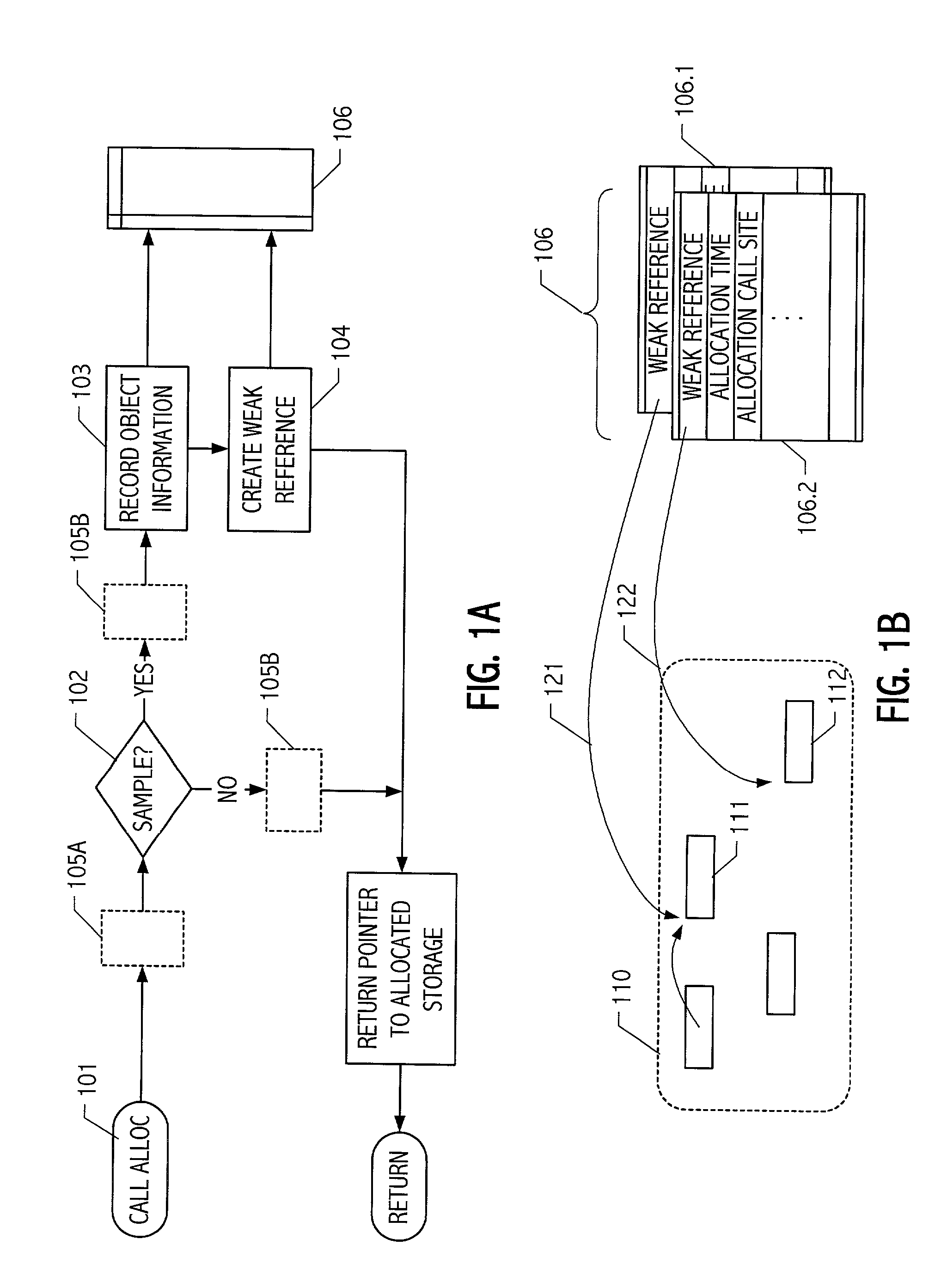
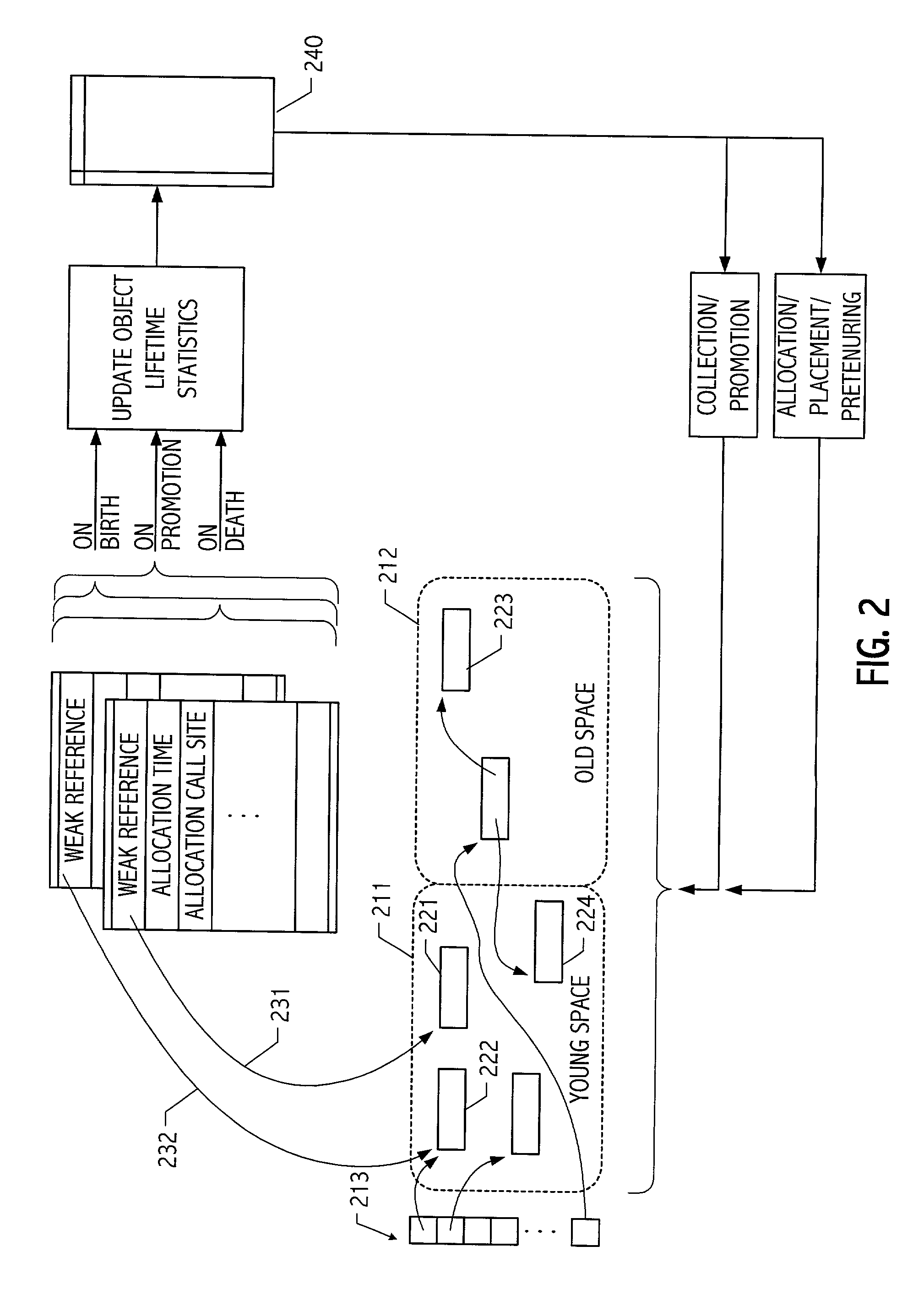
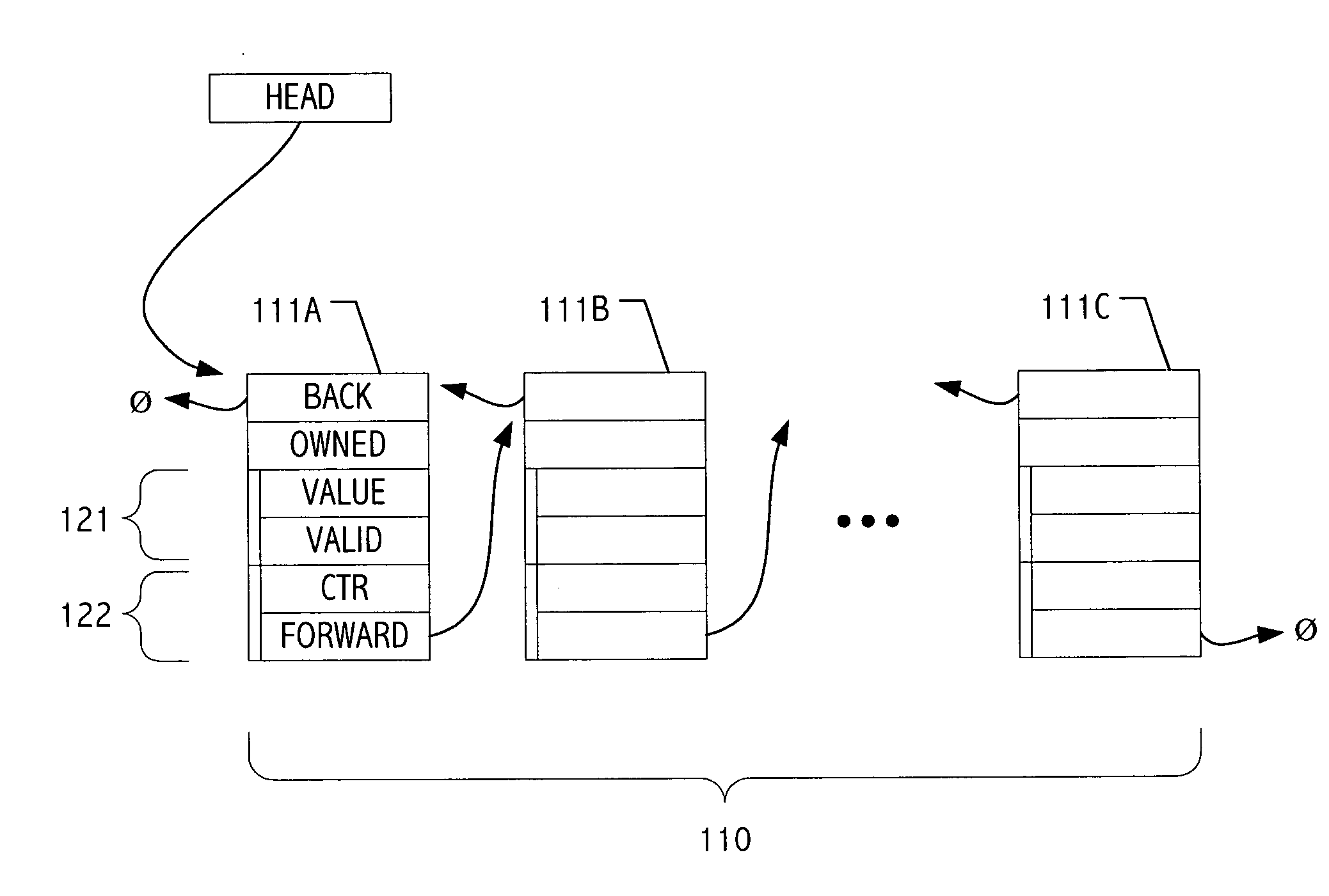
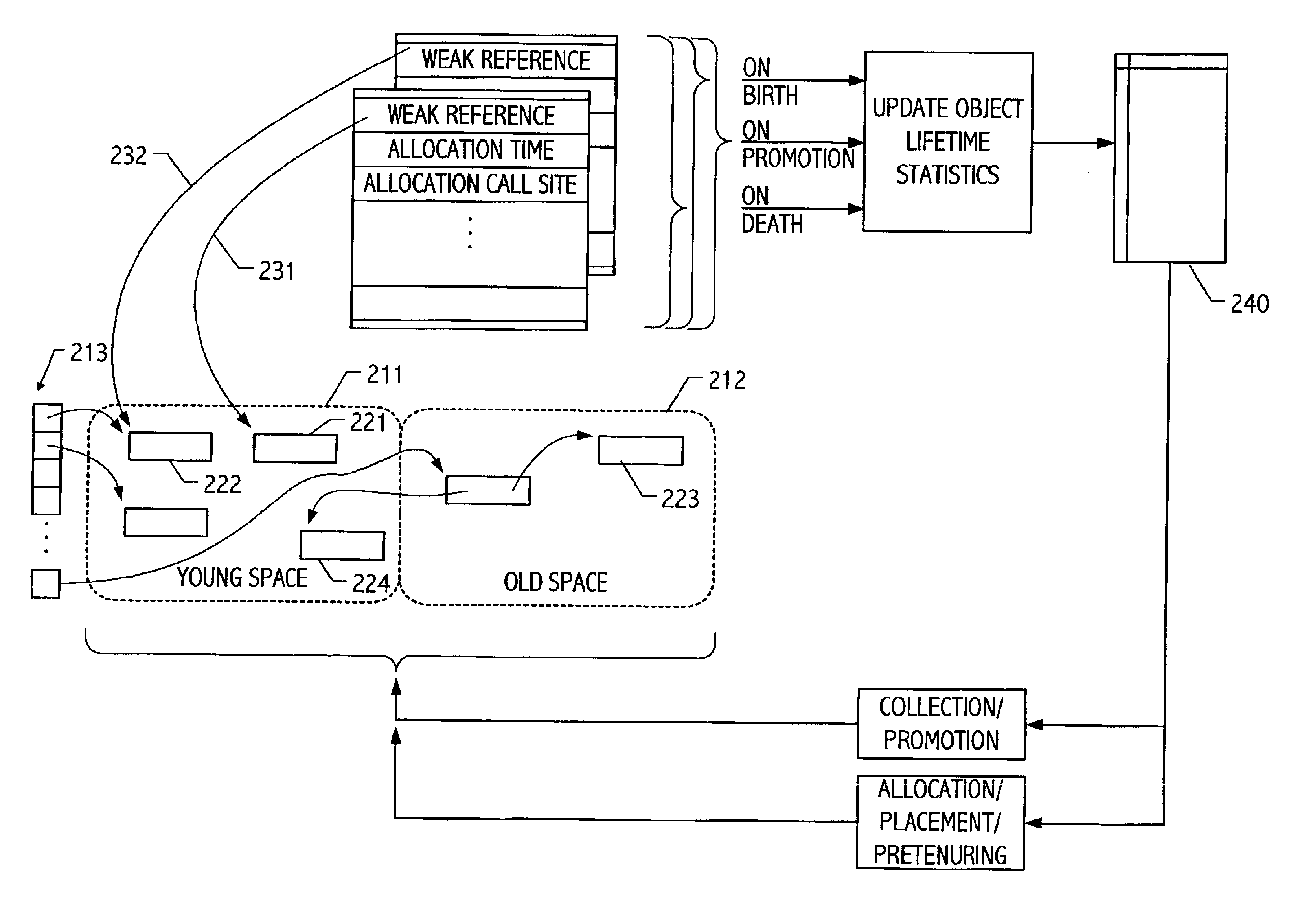
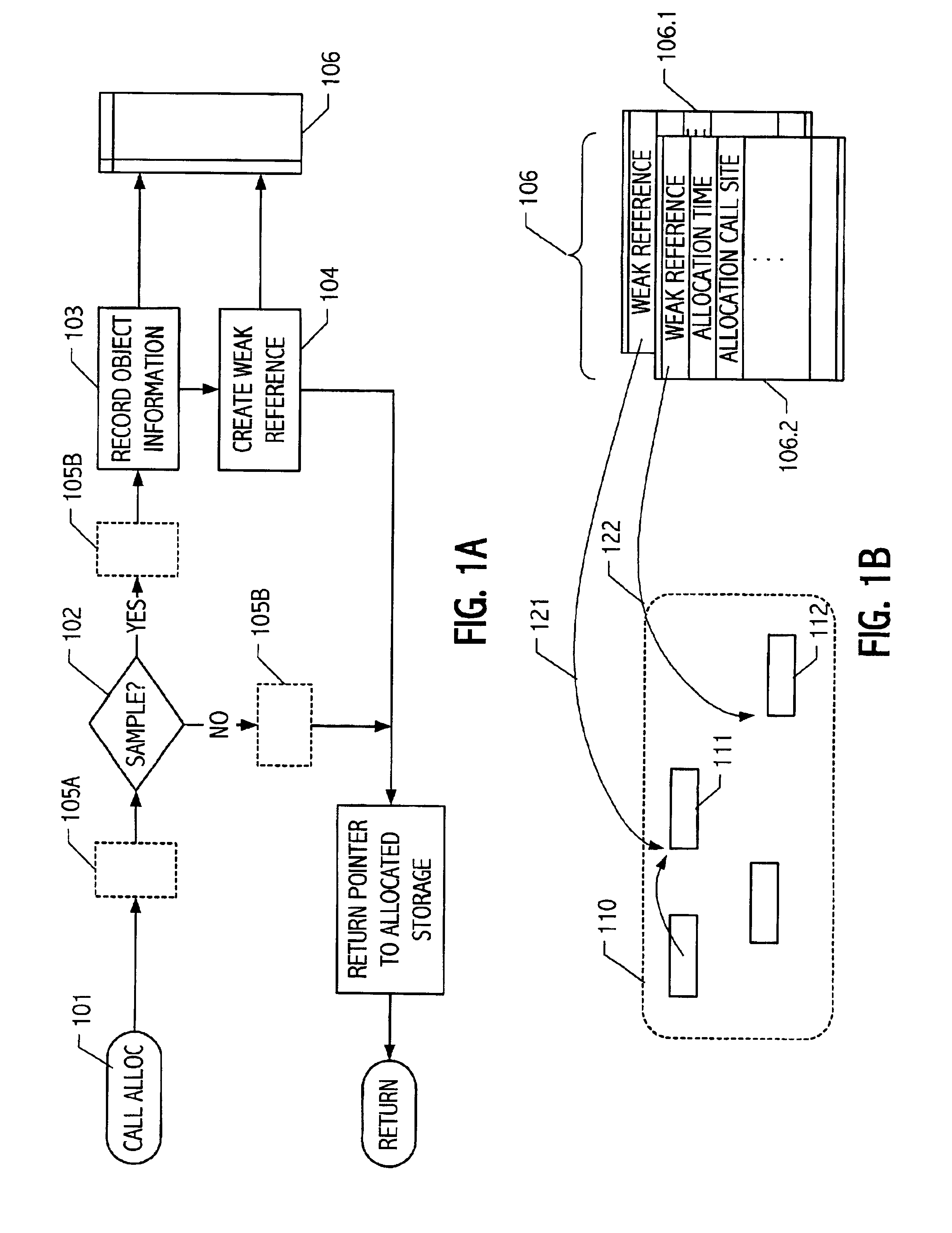
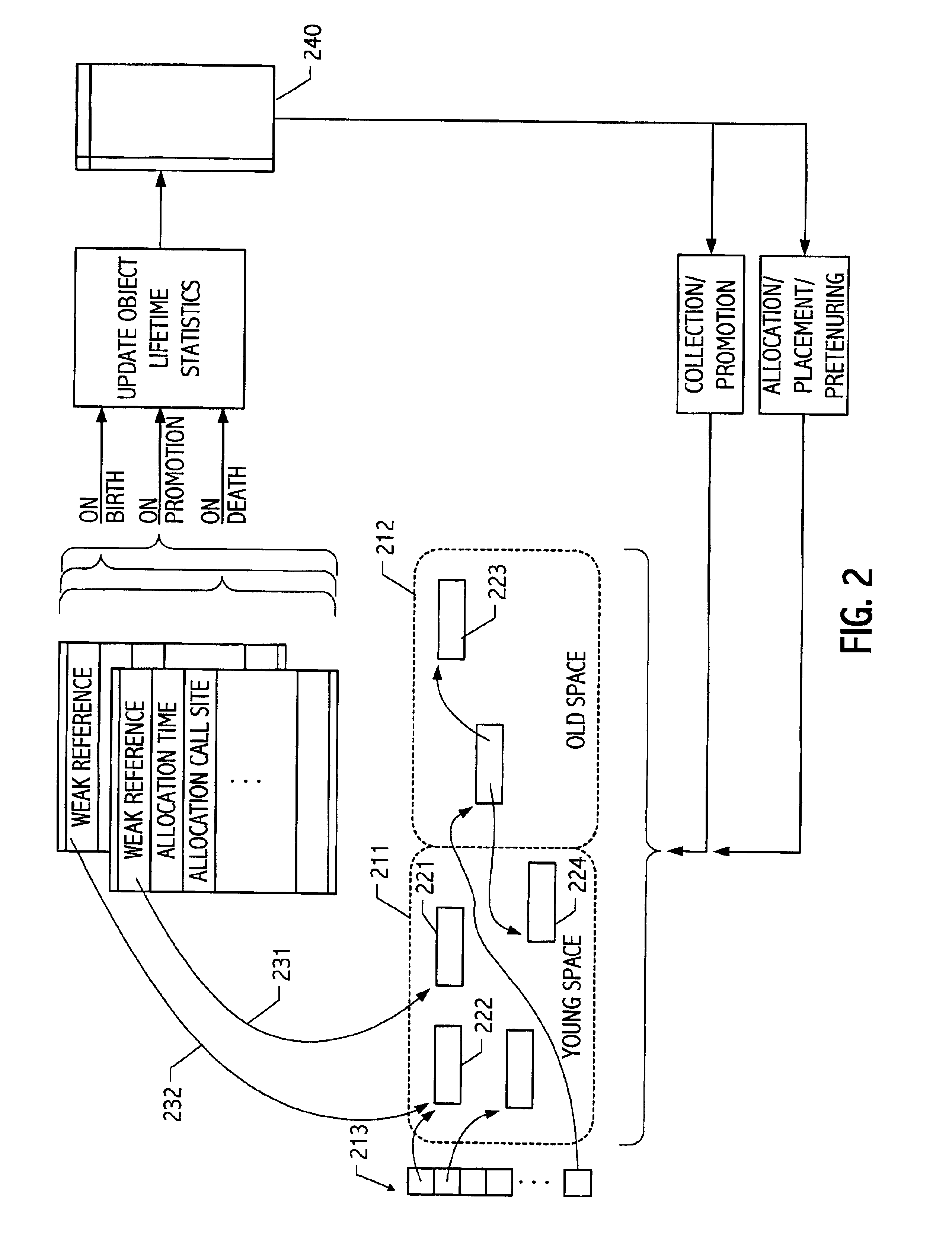
Object sampling technique for runtime observations of representative instances thereof
InactiveUS20020019716A1Data processing applicationsMemory adressing/allocation/relocationObject lifetimeWaste collection
With better knowledge of the behavior of objects in a running application, it is possible to improve execution environment decisions that affect management of such objects. For example, if available, object lifetime statistics could be employed in decisions that affect how and where objects are placed, e.g., on allocation or during operation of automatic dynamic memory management facilities such as a garbage collector. Typically, instrumenting all objects to sample lifetimes or other characteristics would impose an impractical level of overhead. We present a technique for dynamic sampling of a subset of allocated objects that incurs low runtime overheads. Coupled with automatic memory management or collection facilities, this technique allows us to improve the efficiency of a collector by segregating objects, sampled and non-sampled alike, based on observed characteristics such as object lifetime. The sampling techniques facilitate tracking of many kinds of object information. For purposes of illustration, an exemplary implementation is described in which such sampling techniques are exploited to improve performance of generational garbage collectors.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Space- and time-adaptive nonblocking algorithms
ActiveUS20040153687A1Data processing applicationsError preventionNon-blocking algorithmTheoretical computer science
We explore techniques for designing nonblocking algorithms that do not require advance knowledge of the number of processes that participate, whose time complexity and space consumption both adapt to various measures, rather than being based on predefined worst-case scenarios, and that cannot be prevented from future memory reclamation by process failures. These techniques can be implemented using widely available hardware synchronization primitives. We present our techniques in the context of solutions to the well-known Collect problem. We also explain how our techniques can be exploited to achieve other results with similar properties; these include long-lived renaming and dynamic memory management for nonblocking data structures.
Owner:ORACLE AMERICAN INC
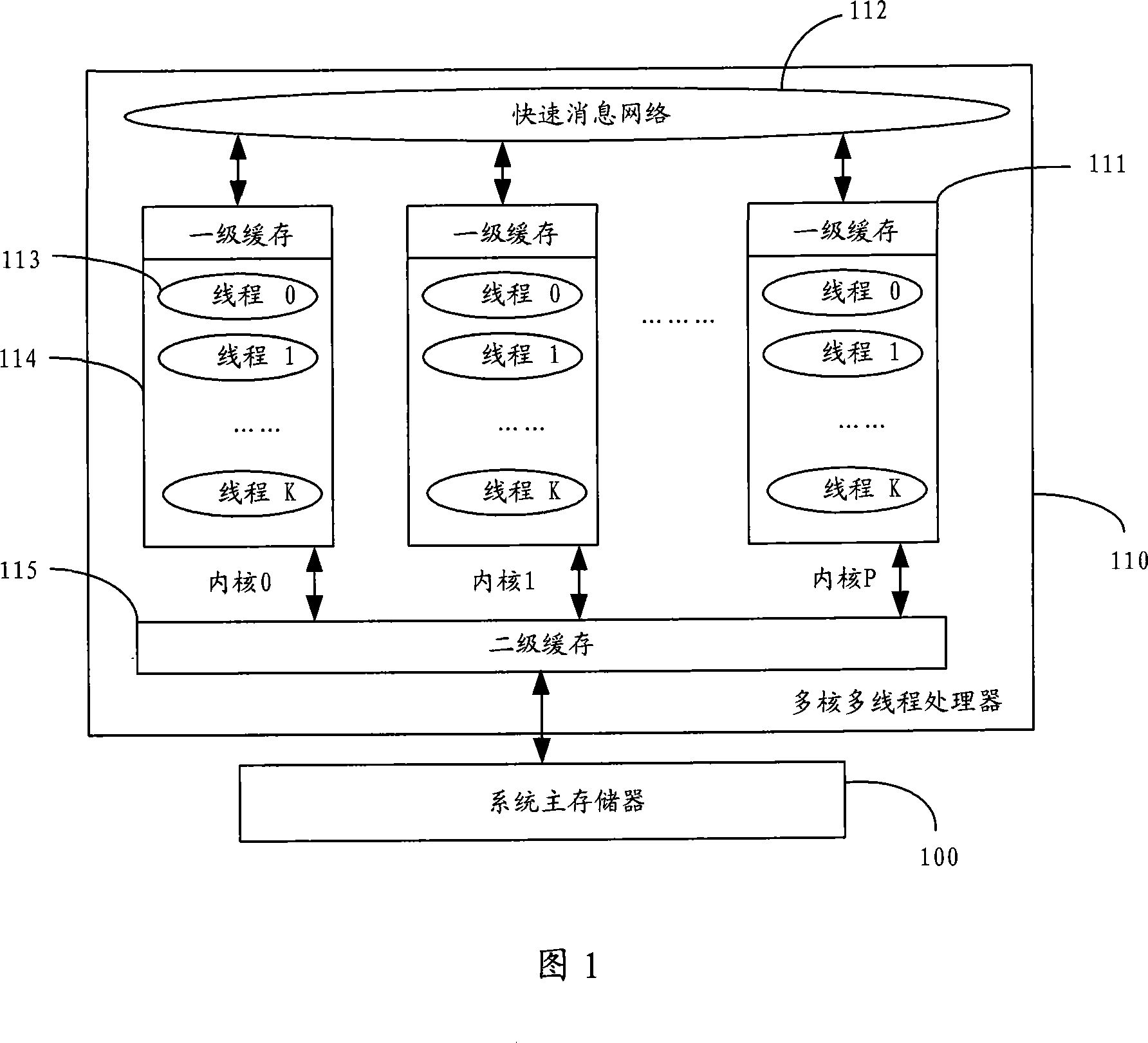
Multithreading processor dynamic EMS memory management system and method
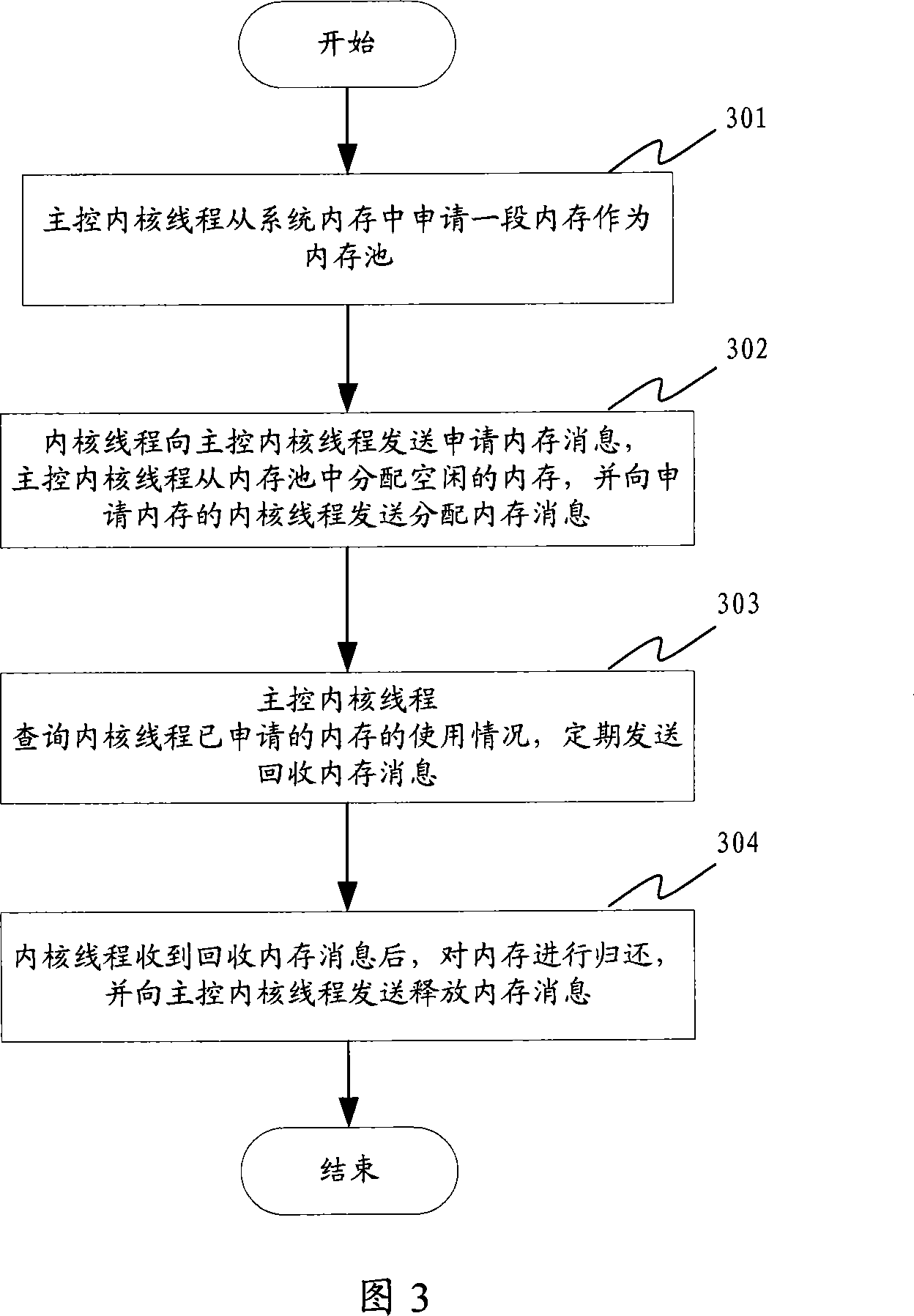
ActiveCN101055533ASolve the problem of static memory allocationImprove efficiencyResource allocationControl memoryDynamic memory management
The invention disclosed a multi-thread processor dynamic memory management system and method. The system includes a message treament module, a main control memory management module and a memory monitoring module. The method includes the steps: a main kernel thread applies to one-stage memory as a memory pool from the memory of system; all kernel threads tranmit the message for applying to the memory for main kernal thread, and main kernel thread distributes free memory in the memory pool to the kernel thread for applying to the memory after receiving the message for applying to the memory, and transmits the message for distributing the memory for the kernel thread for applying to the memory; main control kernel thread inquires the use of memory which has been applied by the kernel thread, and transmits the message of callbacking memory; the kernel thread returns the memory after receiving the medssage of callbacking memory, and transmits the message of releasing the memory for main control thread. The use of memory in the system ia able to be improved using the inventive multi-thread processor dynamic memory management system and method.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Memory management system and algorithm for network processor architecture
InactiveUS7006505B1Low costMaximize memory bandwidthData switching by path configurationMemory systemsLine rateParallel computing
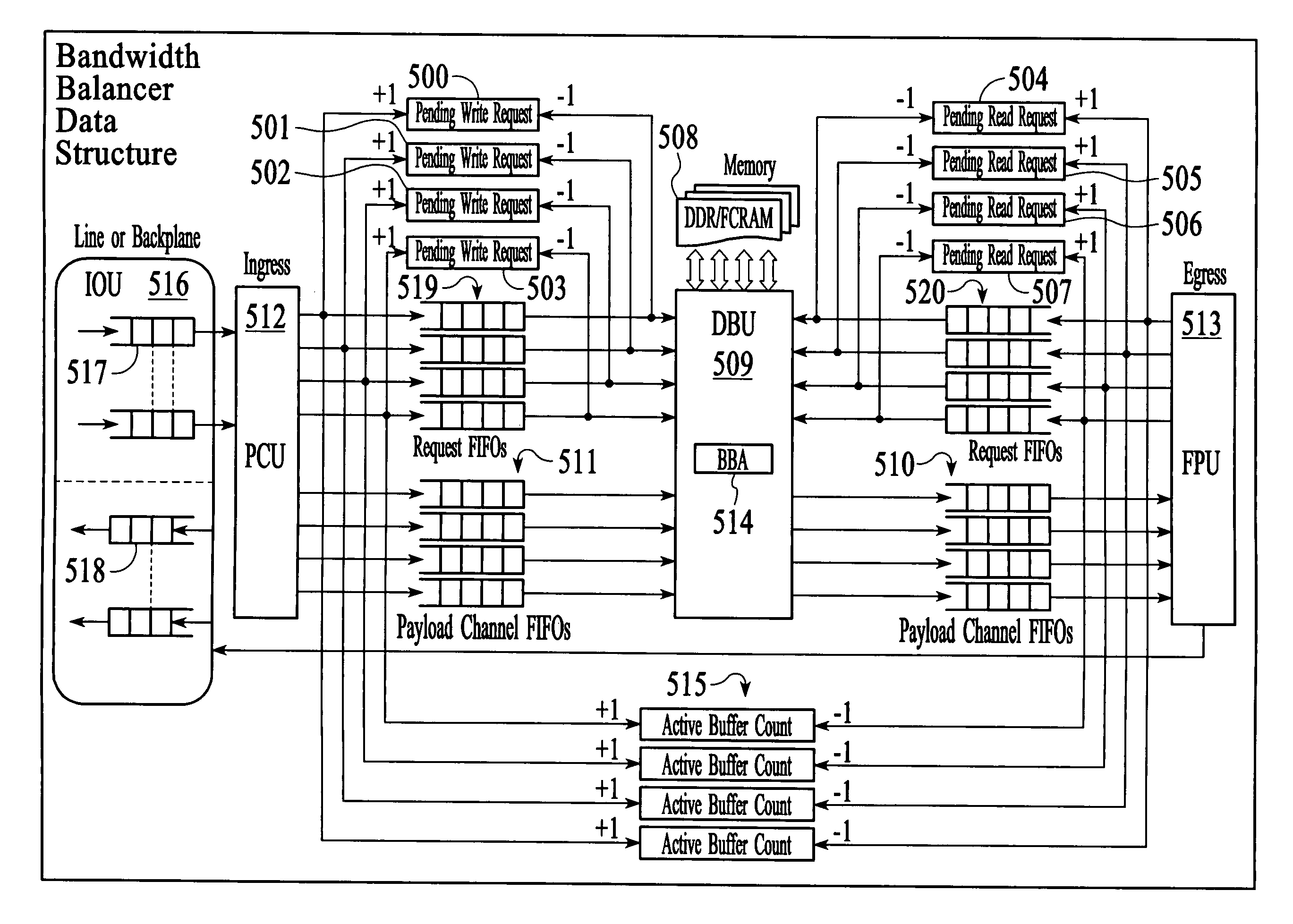
An embodiment of this invention pertains to a system and method for balancing memory accesses to a low cost memory unit in order to sustain and guarantee a desired line rate regardless of the incoming traffic pattern. The memory unit may include, for example, a group of dynamic random access memory units. The memory unit is divided into memory channels and each of the memory channels is further divided into memory lines, each of the memory lines includes one or more buffers that correspond to the memory channels. The determination as to which of one or more buffers within a memory line an incoming information element is stored is based on factors such as the number of buffers pending to be read within each of the memory channels, the number of buffers pending to be written within each of the memory channels, and the number of buffers within each of the memory channels that has data written to it and is waiting to be read.
Owner:BAY MICROSYSTEMS INC
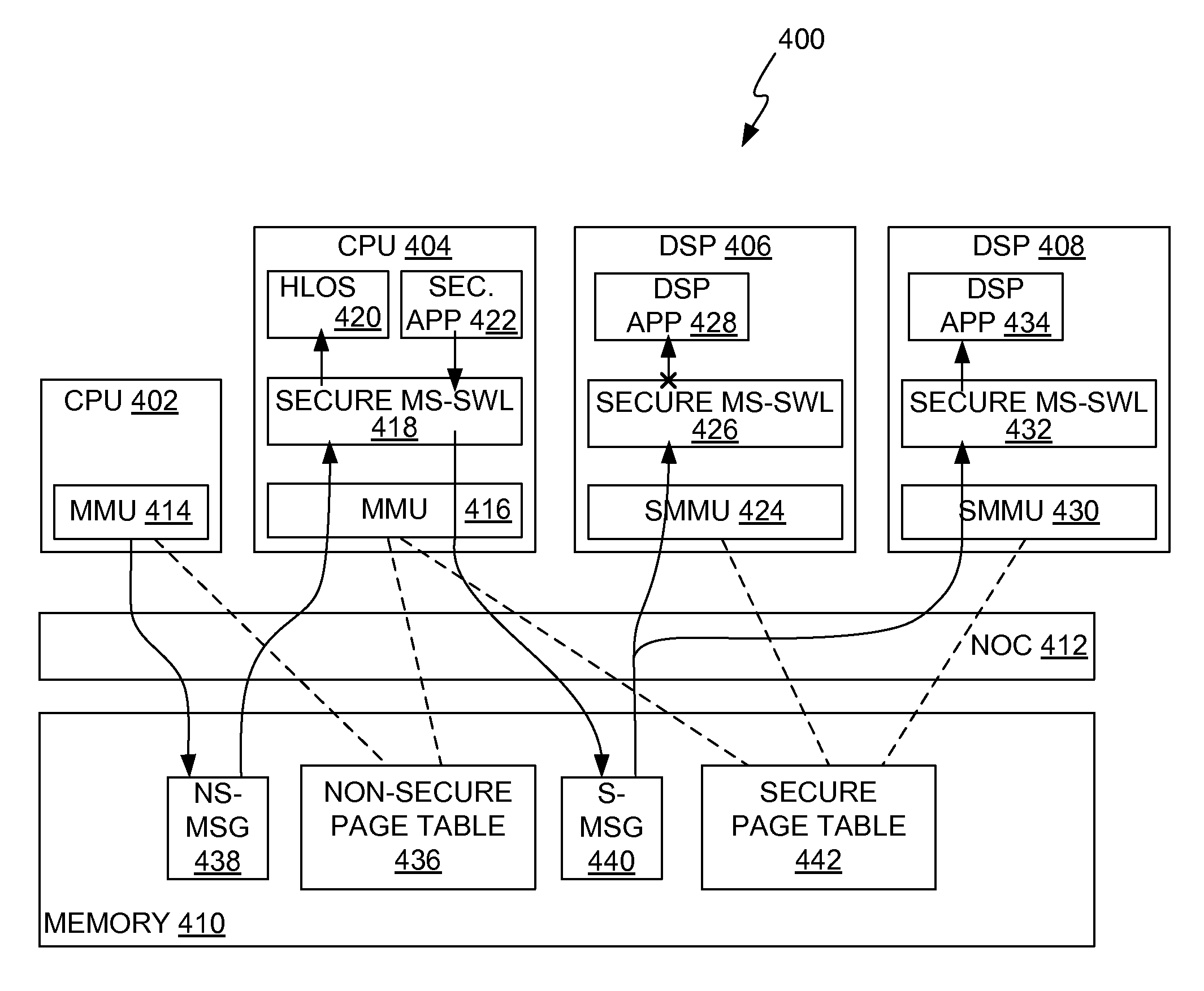
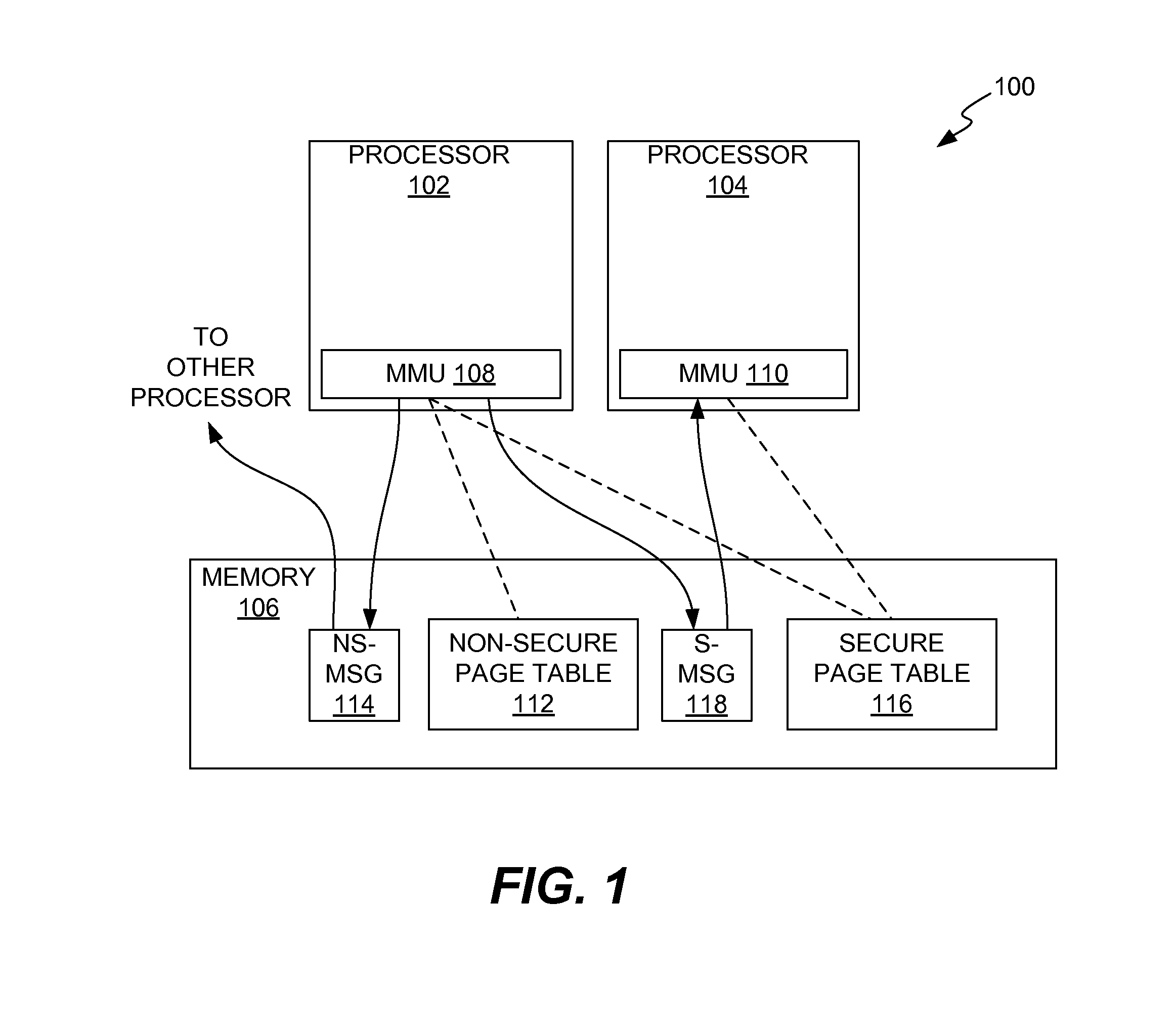
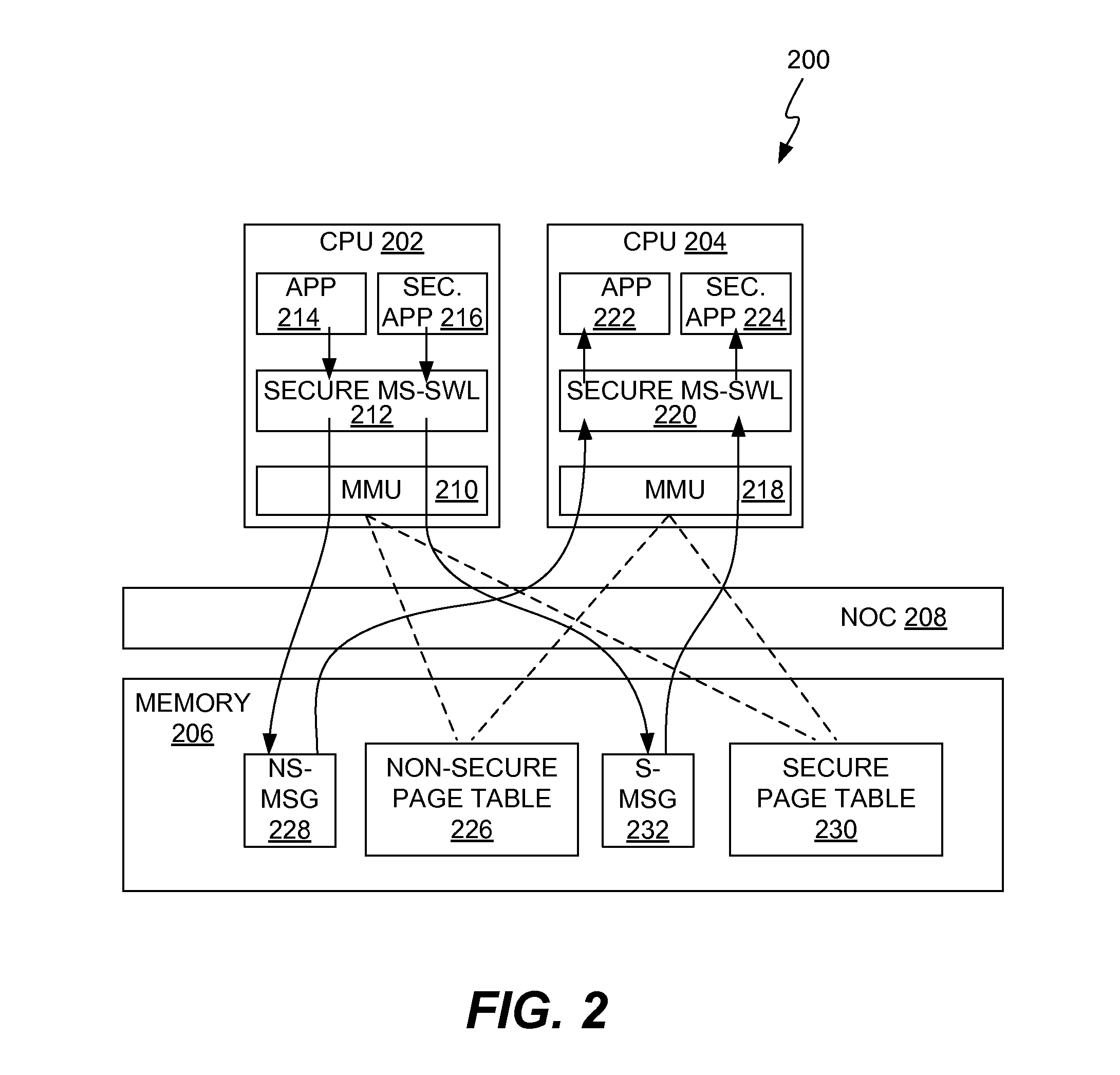
Distributed dynamic memory management unit (MMU)-based secure inter-processor communication
InactiveUS9170957B2Memory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationPage tableInterprocessor communication
A first processor and a second processor are configured to communicate secure inter-processor communications (IPCs) with each other. The first processor effects secure IPCs and non-secure IPCs using a first memory management unit (MMU) to route the secure and non-secure IPCs via a memory system. The first MMU accesses a first page table stored in the memory system to route the secure IPCs and accesses a second page table stored in the memory system to route the non-secure IPCs. The second processor effects at least secure IPCs using a second MMU to route the secure IPCs via the memory system. The second MMU accesses the second page table to route the secure IPCs.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Apparatus and method for supporting memory management in an offload of network protocol processing
ActiveUS7930422B2Firmly connectedNumber of neededMultiple digital computer combinationsMemory systemsProtocol processingZero-copy
A number of improvements in network adapters that offload protocol processing from the host processor are provided. Specifically, mechanisms for handling memory management and optimization within a system utilizing an offload network adapter are provided. The memory management mechanism permits both buffered sending and receiving of data as well as zero-copy sending and receiving of data. In addition, the memory management mechanism permits grouping of DMA buffers that can be shared among specified connections based on any number of attributes. The memory management mechanism further permits partial send and receive buffer operation, delaying of DMA requests so that they may be communicated to the host system in bulk, and expedited transfer of data to the host system.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Method for managing dynamic internal memory base on discontinuous page
InactiveCN101231619AIncrease flexibilityIncrease profitMemory adressing/allocation/relocationInternal memoryPredictability
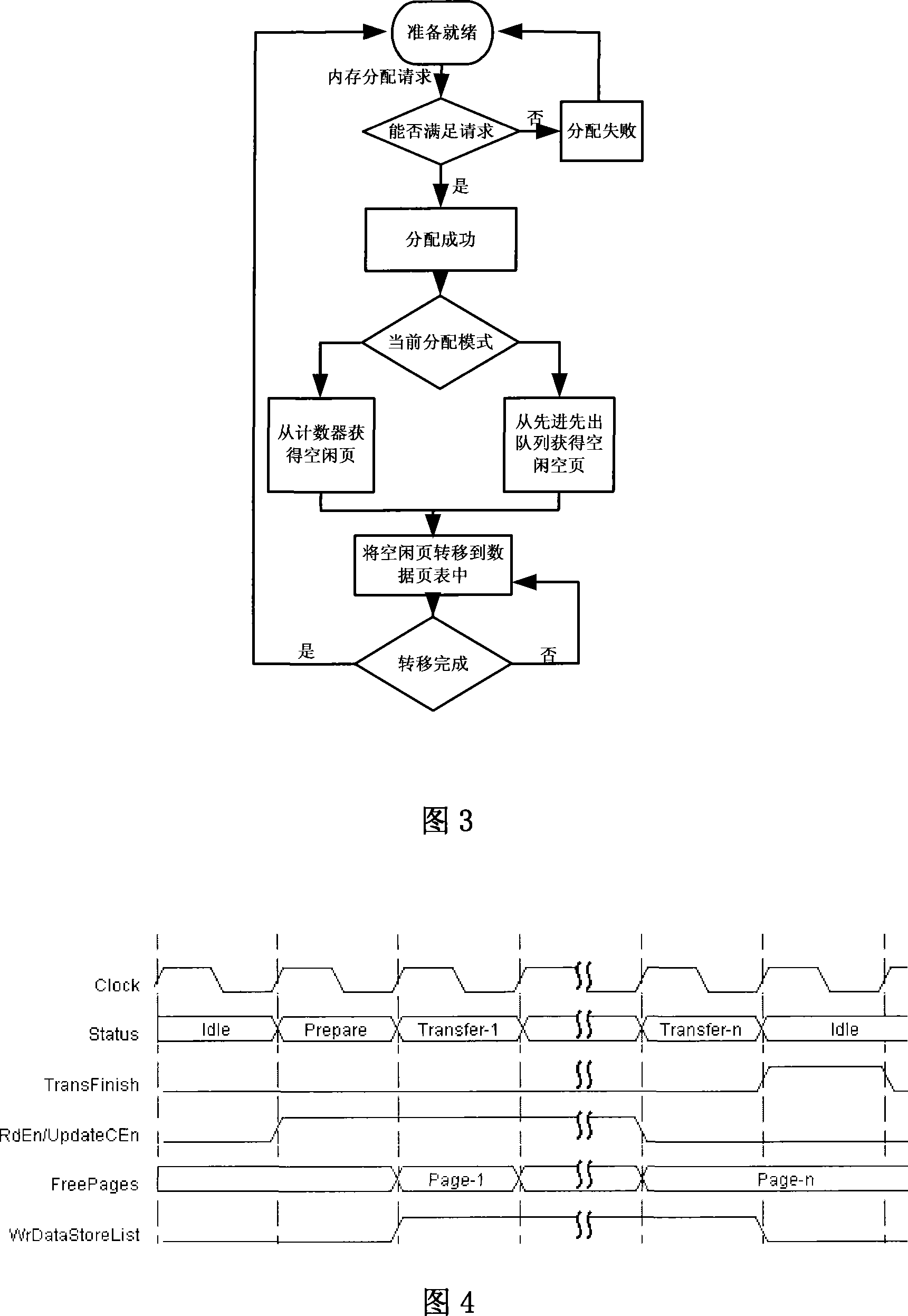
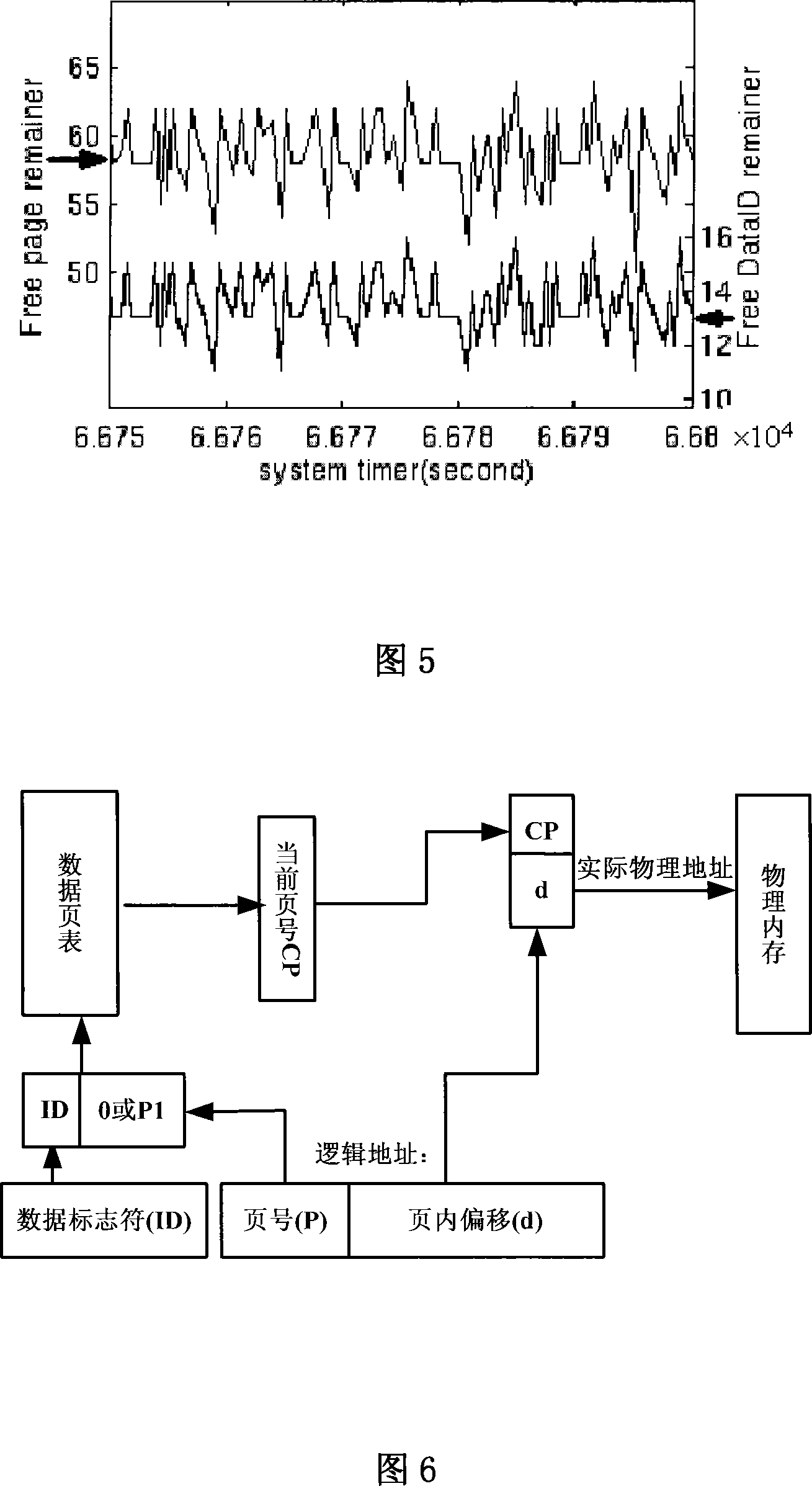
The invention relates to a dynamic memory management method. The prior memory management method influences the utilization rate and the real-time performance of the memory. The dynamic memory management method of the invention comprises the following steps of memory allocation, memory recycle and address mapping, and has the details that a memory unit is divided into memory pages with the same size, and data which are logically connected are allowed to be stored in the memory pages which are not physically connected. The invention adopts the way of combining a counter and FIFO to manage the memory pages, so as to enable the memory allocation and the memory recycle to be more flexible, and the external fragment problem during the memory allocation is eliminated, thereby the utilization rate of the memory is improved, and the allocation and the recycle of the memory have the characteristics of real-time performance and predictability.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Dynamic memory management system based on memory hot plug for virtual machine
InactiveCN102222014AMemory Pressure PredictionMemory pressure balanceMemory adressing/allocation/relocationSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationOut of memoryGNU/Linux
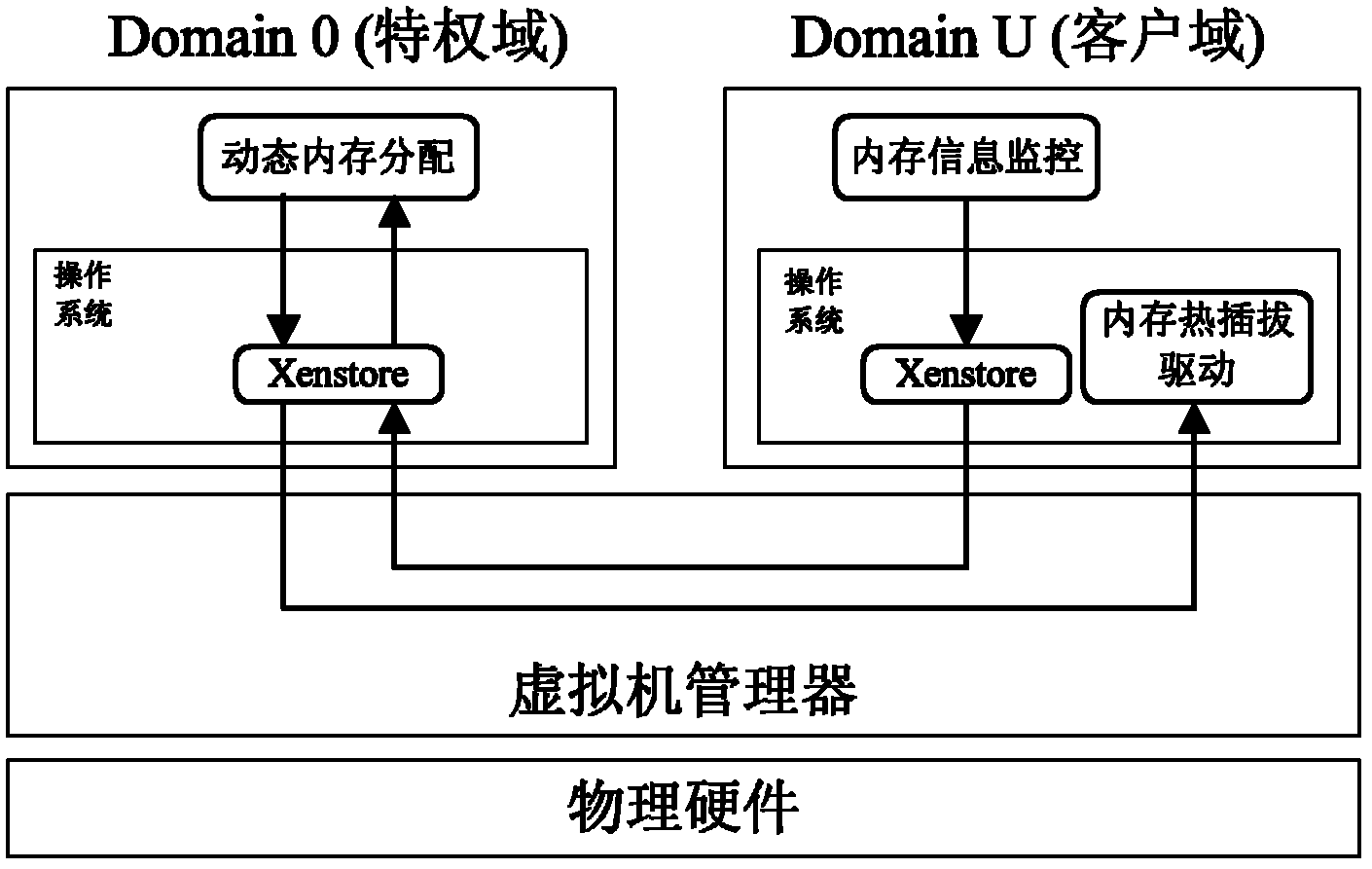
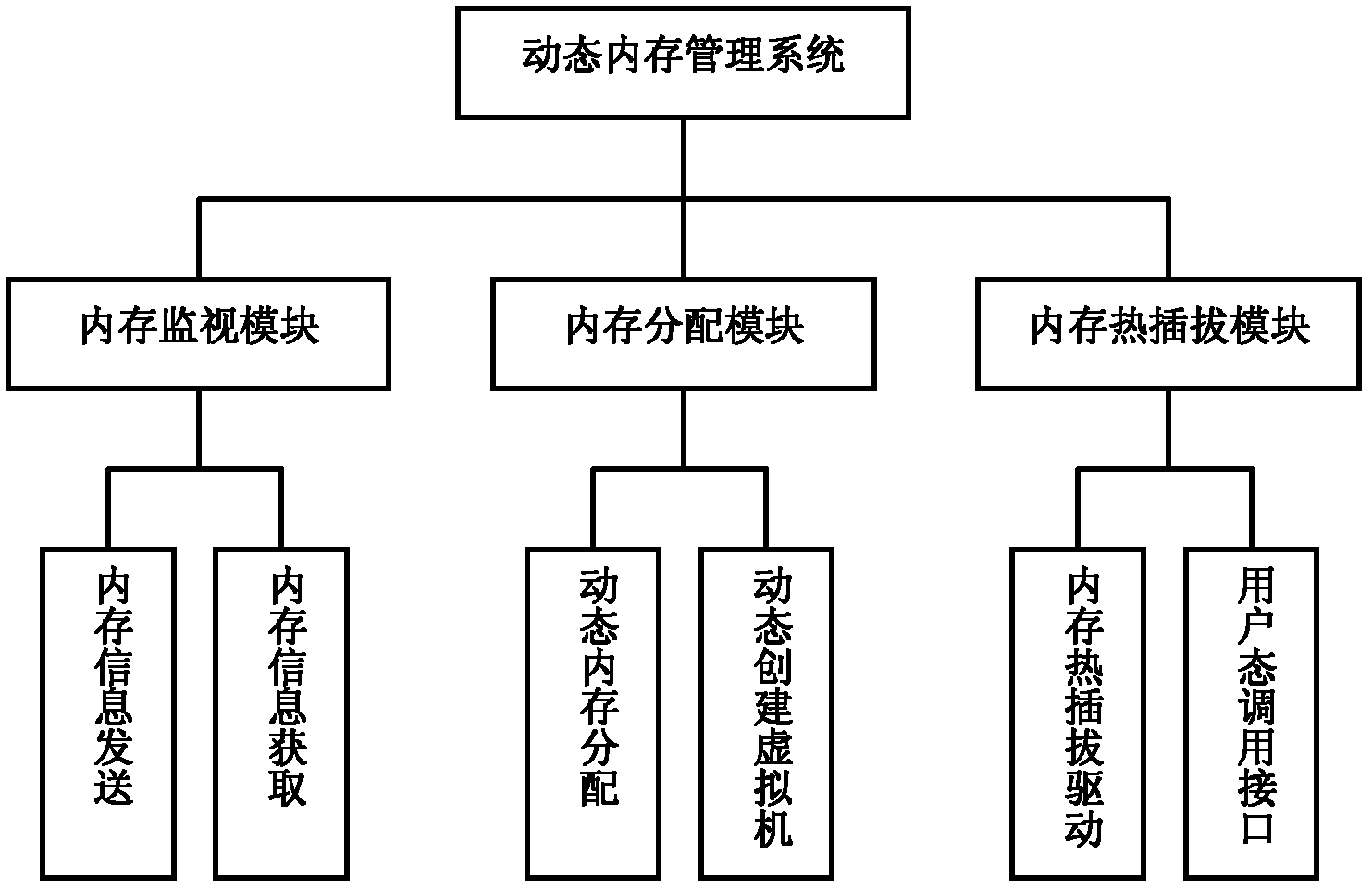
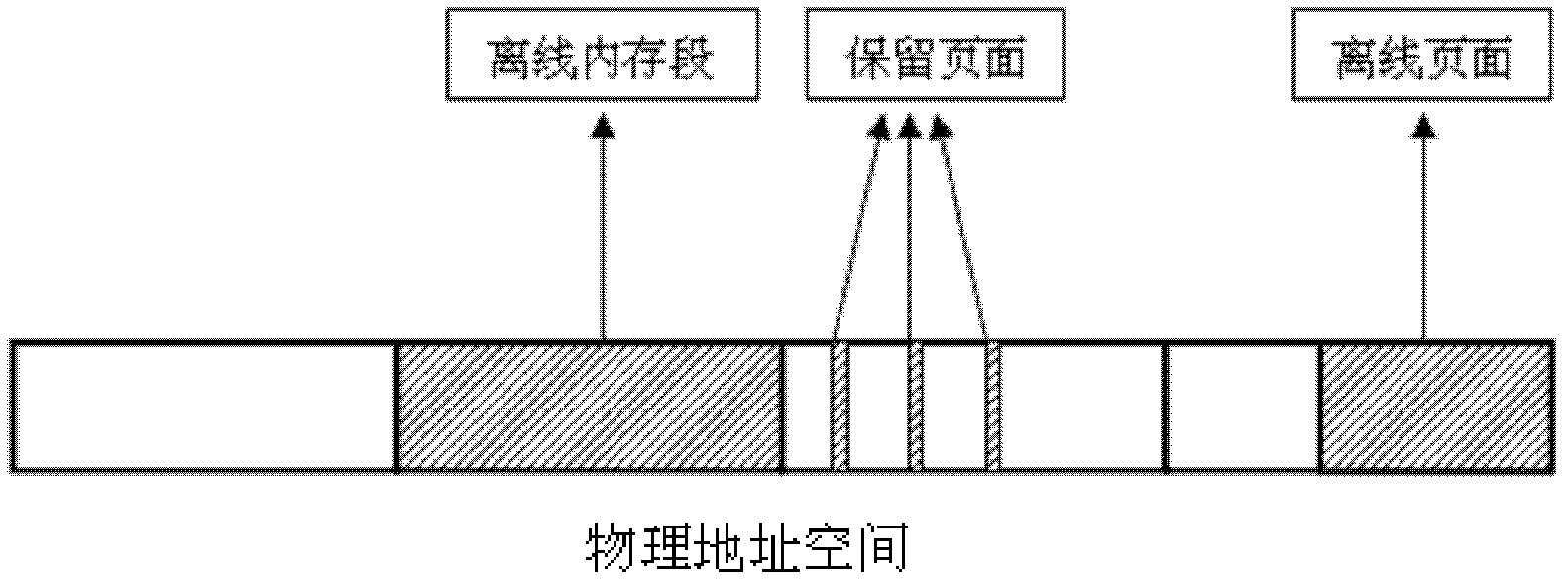
The invention discloses a dynamic memory management system based on memory hot plug for a virtual machine, comprising a memory monitoring module, a memory distributing module and a memory hot plug module. The memory hot plug module adopts Linux memory hot plug mechanism to realize memory hot plug on a semi-virtual Linux virtual machine, thereby breaking through the initial memory toplimit of the virtual machine and efficiently improving the memory expandability of the virtual machine by increasing and reducing the memory randomly. On one hand, the memory distributing module dynamically predicts the memory requirement of the virtual machine and balances the memory pressure of each virtual machine, thereby being capable of satisfying the memory requirement of the virtual machine and also improving the memory utilization ratio of a physical machine; on the other hand, the memory distributing module can establish a new virtual machine by reasonably reducing the memory of the existing virtual machine when the memory of the physical machine is not enough, thereby realizing memory overuse and improving the memory utilization ratio of the physical machine.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
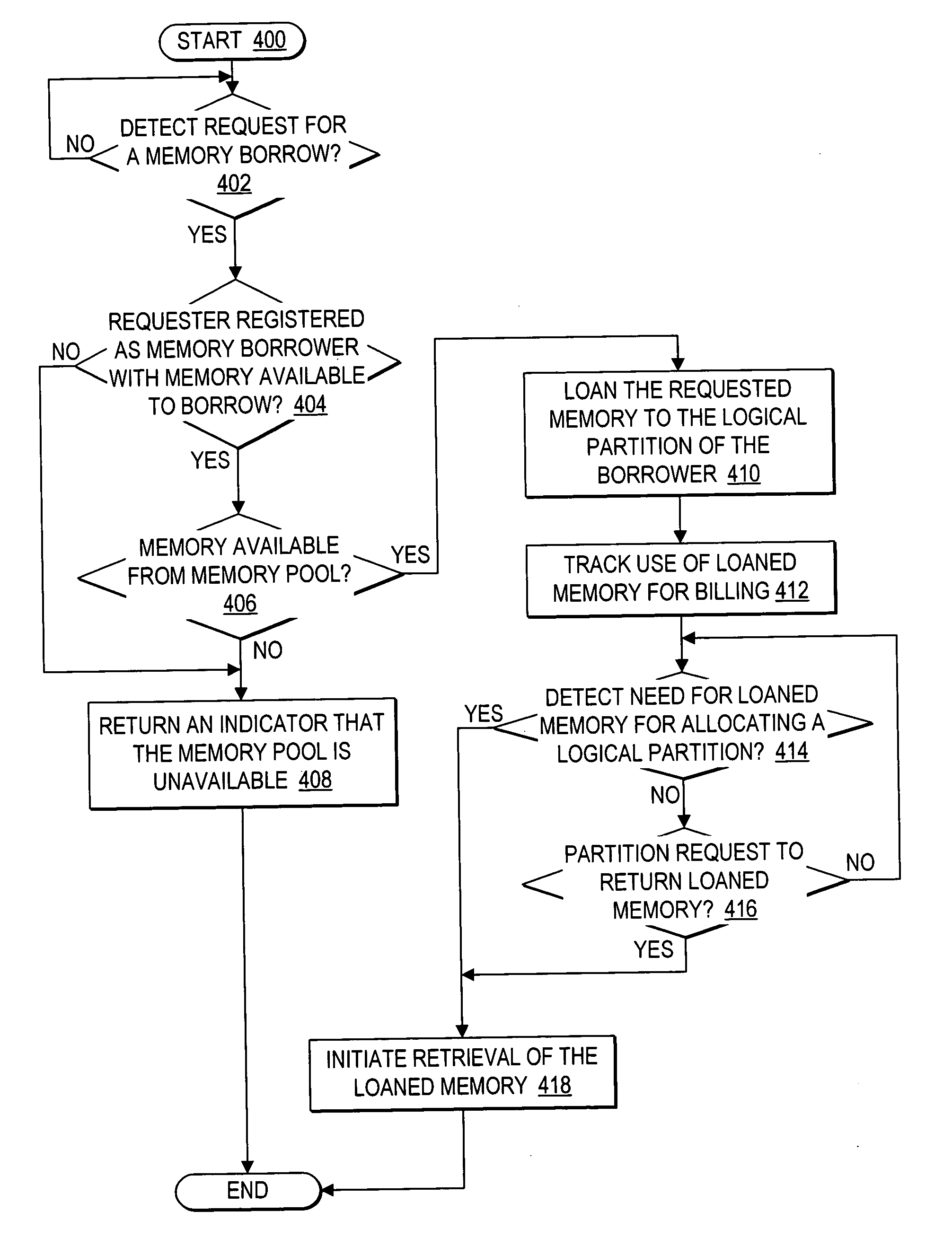
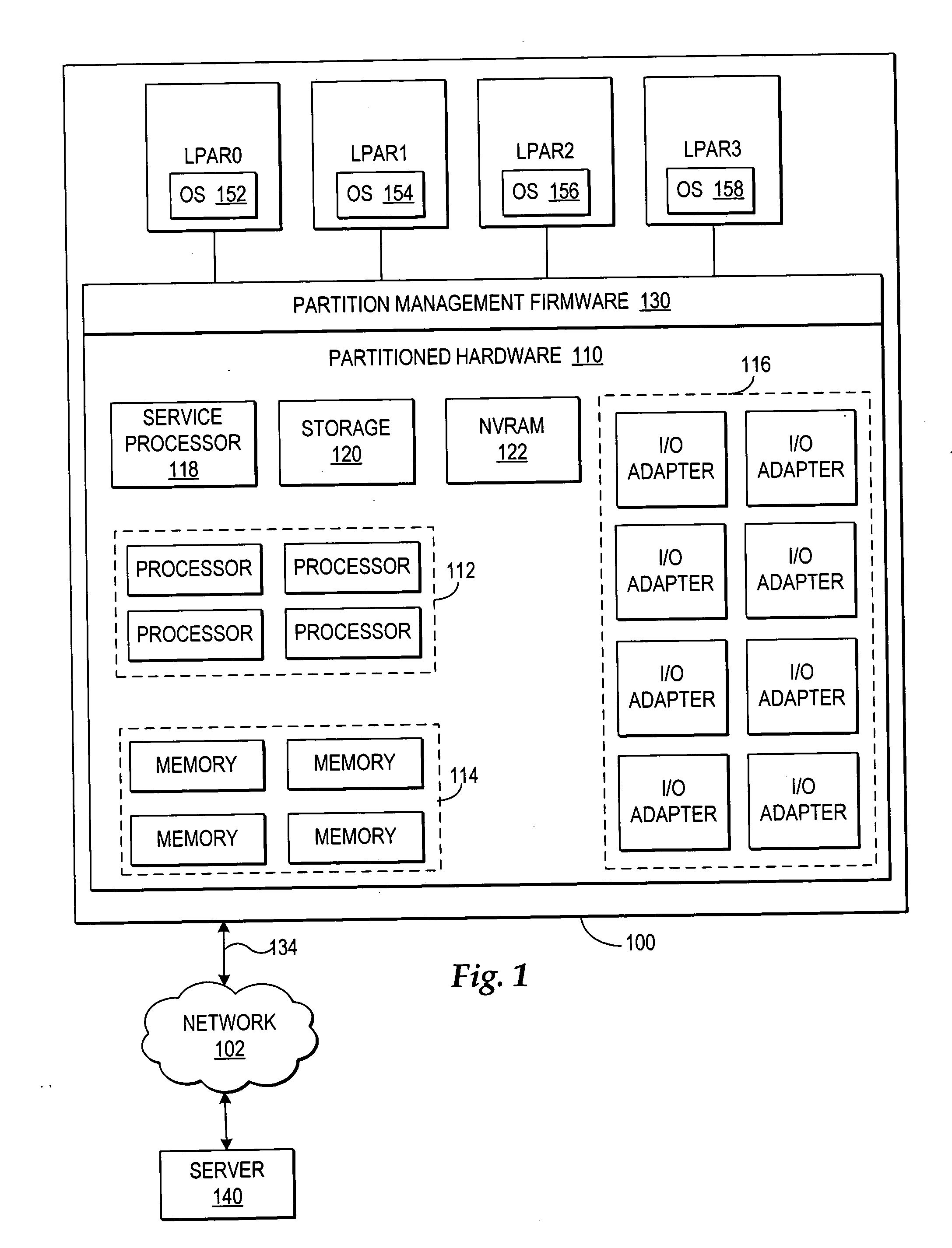
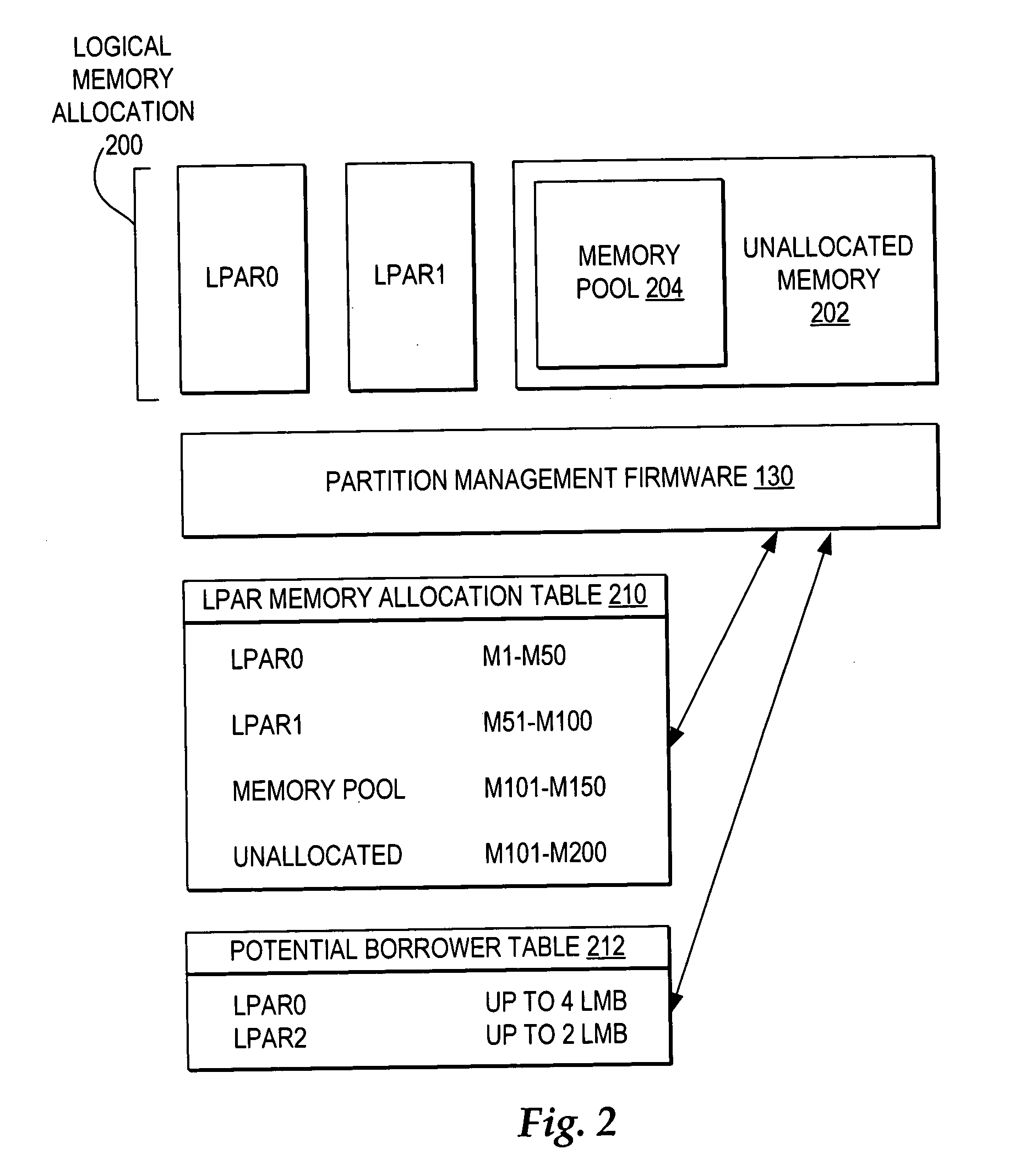
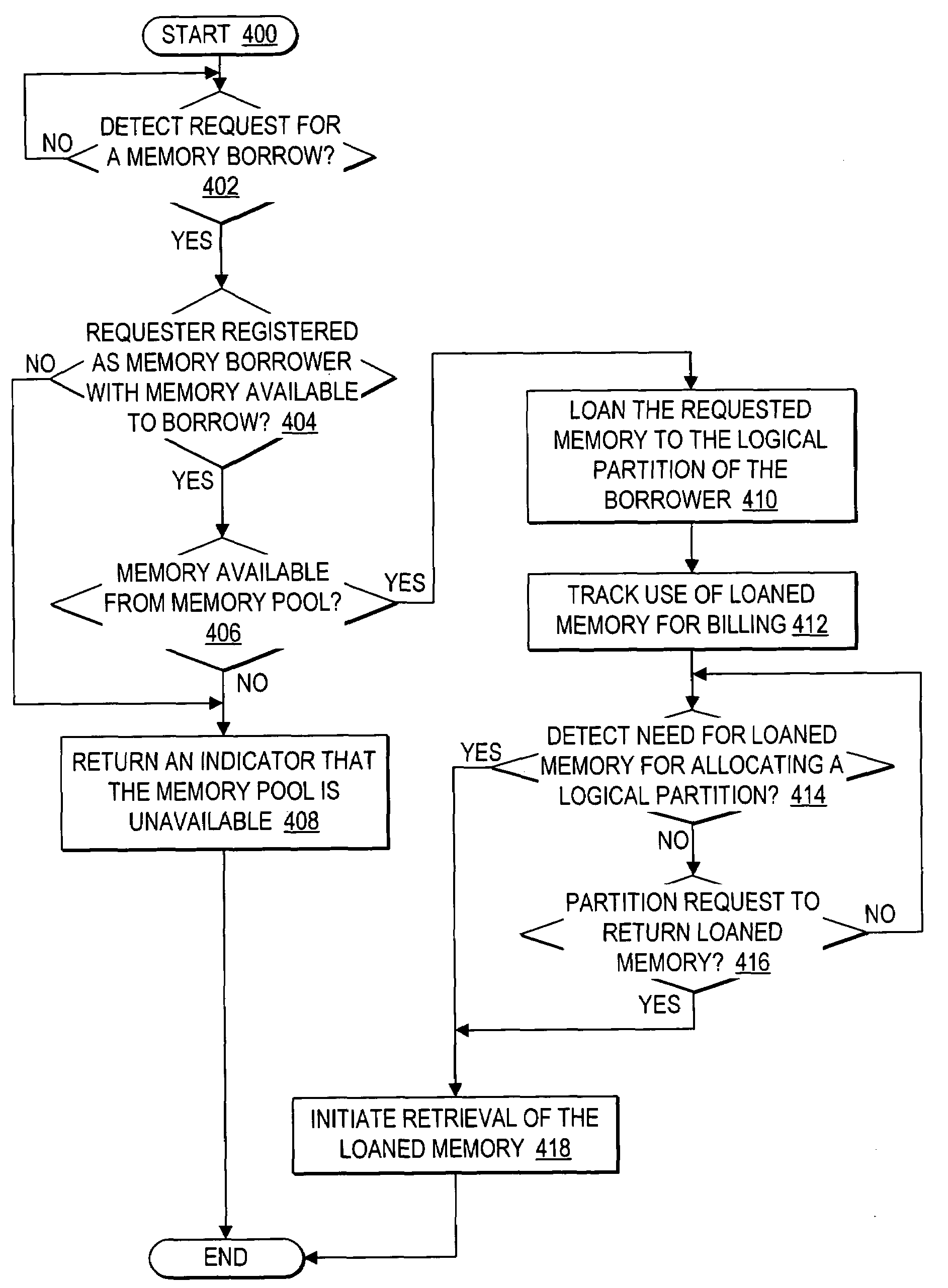
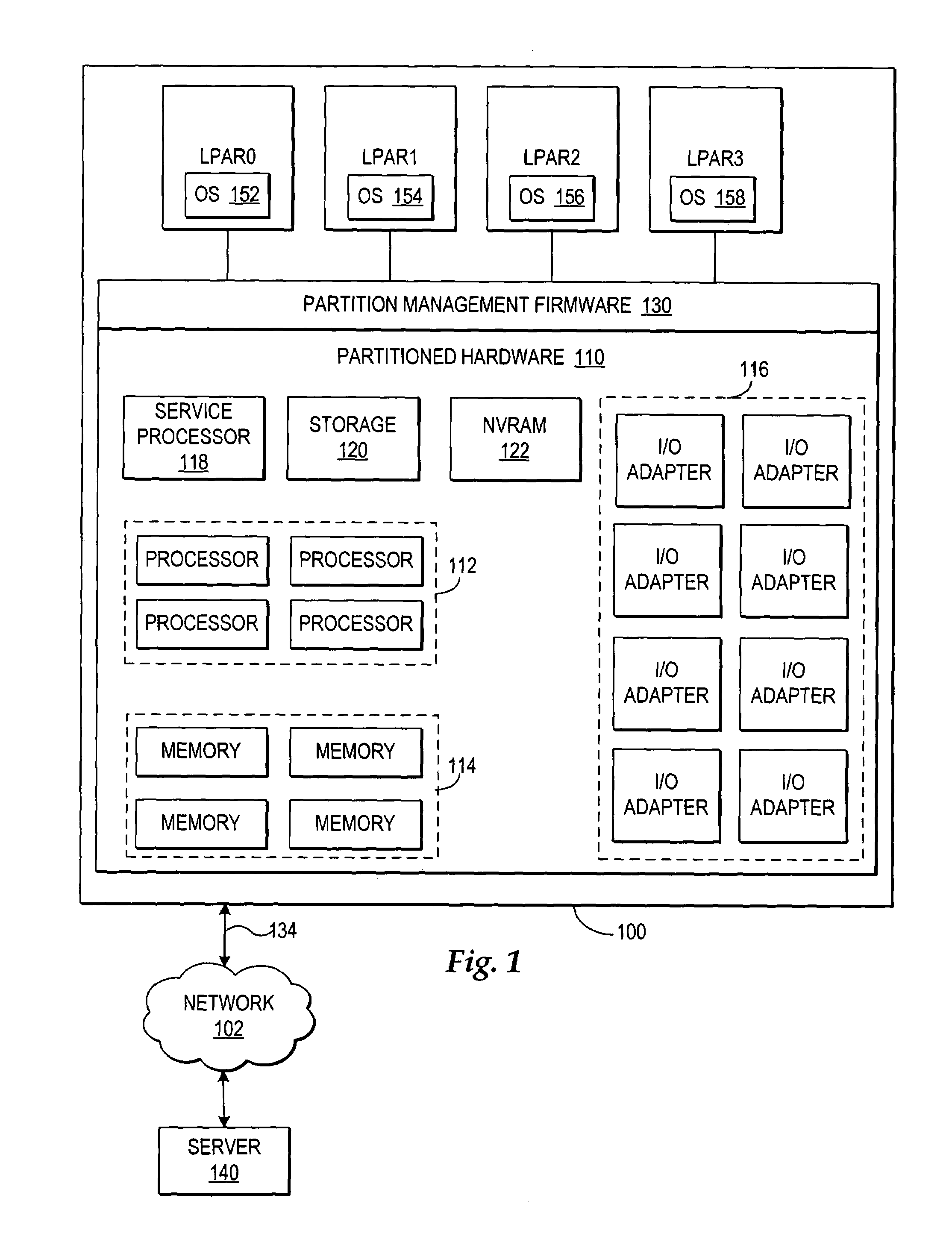
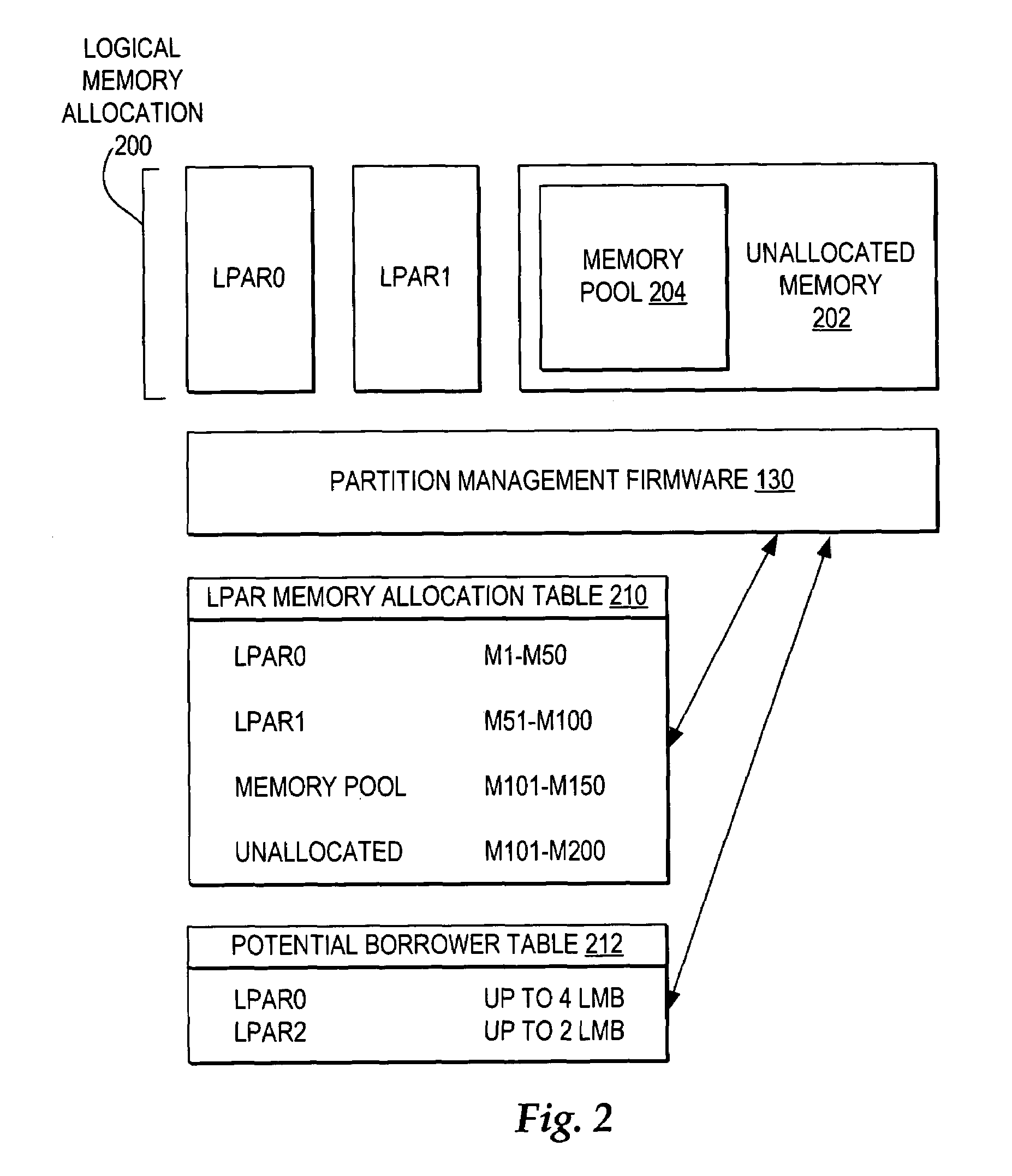
Dynamic memory management of unallocated memory in a logical partitioned data processing system
InactiveUS20050257020A1Maximizing usage of memoryMaximize useResource allocationMemory systemsData processing systemTerm memory
A method, system, and program for dynamic memory management of unallocated memory in a logical partitioned data processing system. A logical partitioned data processing system typically includes multiple memory units, processors, I / O adapters, and other resources enabled for allocation to multiple logical partitions. A partition manager operating within the data processing system manages allocation of the resources to each logical partition. In particular, the partition manager manages allocation of a first portion of the multiple memory units to at least one logical partition. In addition, the partition manager manages a memory pool of unallocated memory from among the multiple memory units. Responsive to receiving a request for a memory loan from one of the allocated logical partitions, a second selection of memory units from the memory pool is loaned to the requesting logical partition. The partition manager, however, is enabled to reclaim the loaned selection of memory units from the requesting logical partition at any time.
Owner:IBM CORP
Object sampling technique for runtime observations of representative instances thereof
InactiveUS6799191B2Data processing applicationsMemory adressing/allocation/relocationObject lifetimeWaste collection
With better knowledge of the behavior of objects in a running application, it is possible to improve execution environment decisions that affect management of such objects. For example, if available, object lifetime statistics could be employed in decisions that affect how and where objects are placed, e.g., on allocation or during operation of automatic dynamic memory management facilities such as a garbage collector. Typically, instrumenting all objects to sample lifetimes or other characteristics would impose an impractical level of overhead. We present a technique for dynamic sampling of a subset of allocated objects that incurs low runtime overheads. Coupled with automatic memory management or collection facilities, this technique allows us to improve the efficiency of a collector by segregating objects, sampled and non-sampled alike, based on observed characteristics such as object lifetime. The sampling techniques facilitate tracking of many kinds of object information. For purposes of illustration, an exemplary implementation is described in which such sampling techniques are exploited to improve performance of generational garbage collectors.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
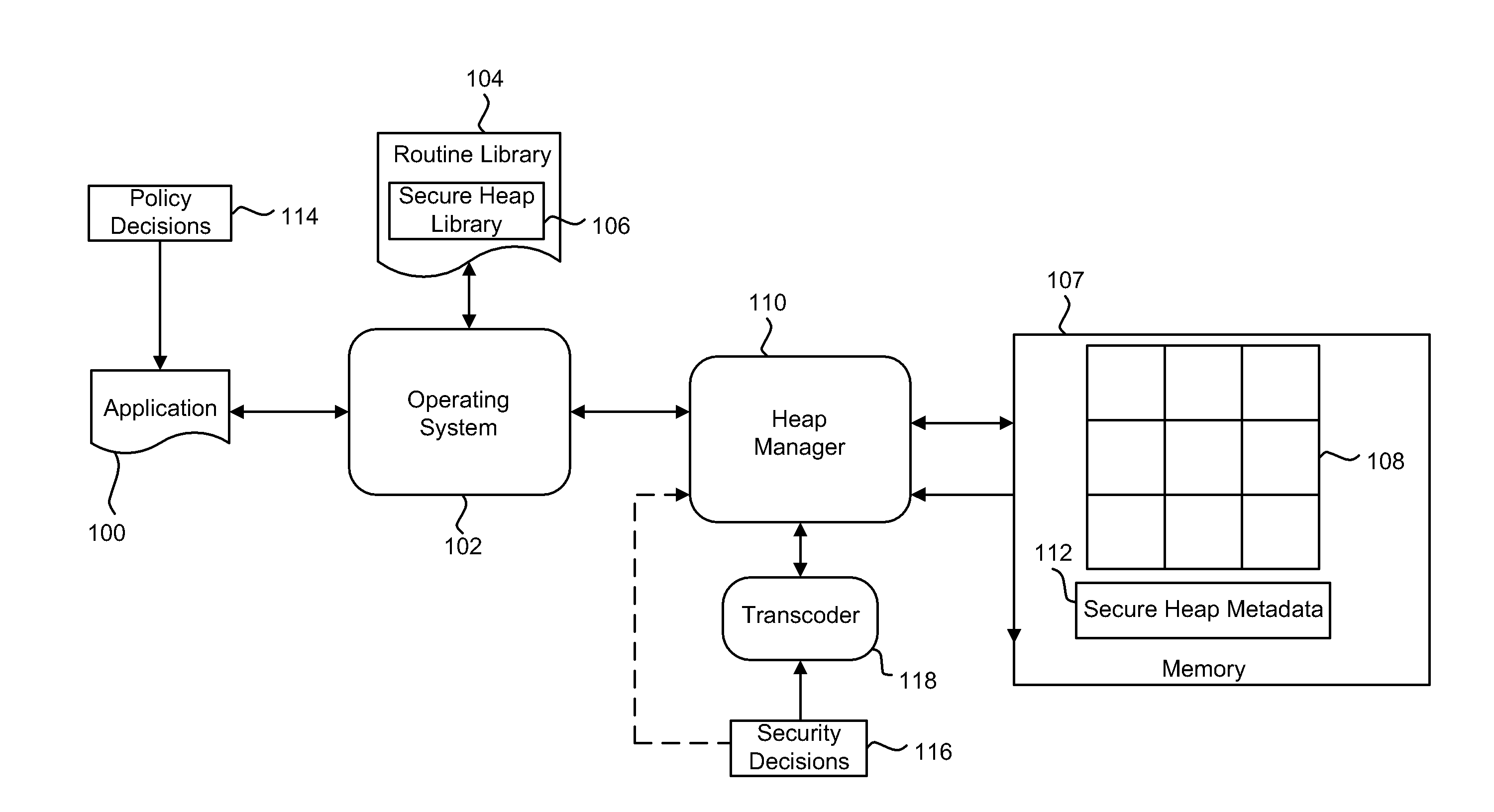
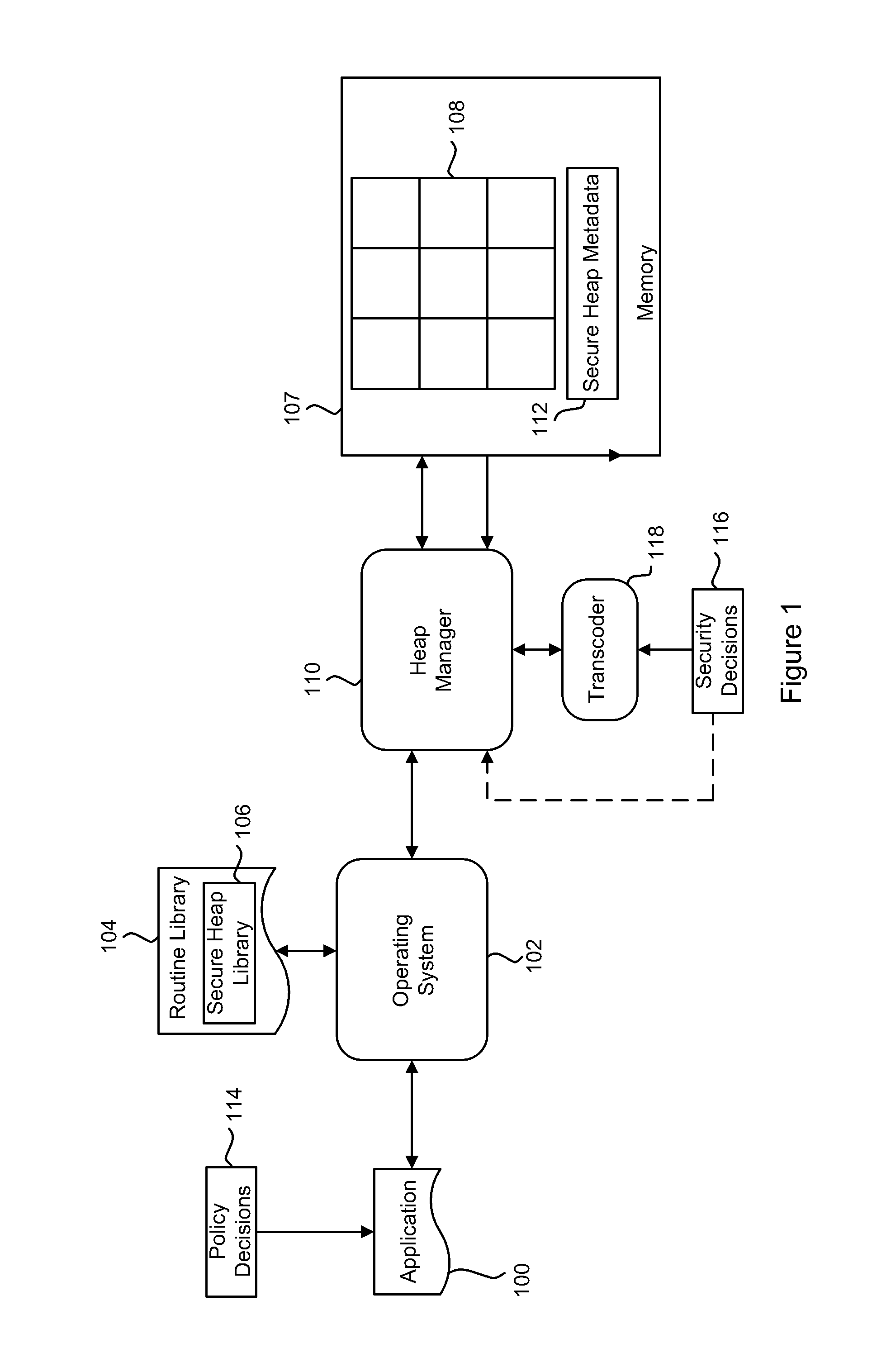
Method of Securing Memory Against Malicious Attack
InactiveUS20140020112A1Digital data processing detailsAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsRandom access memoryDynamic storage
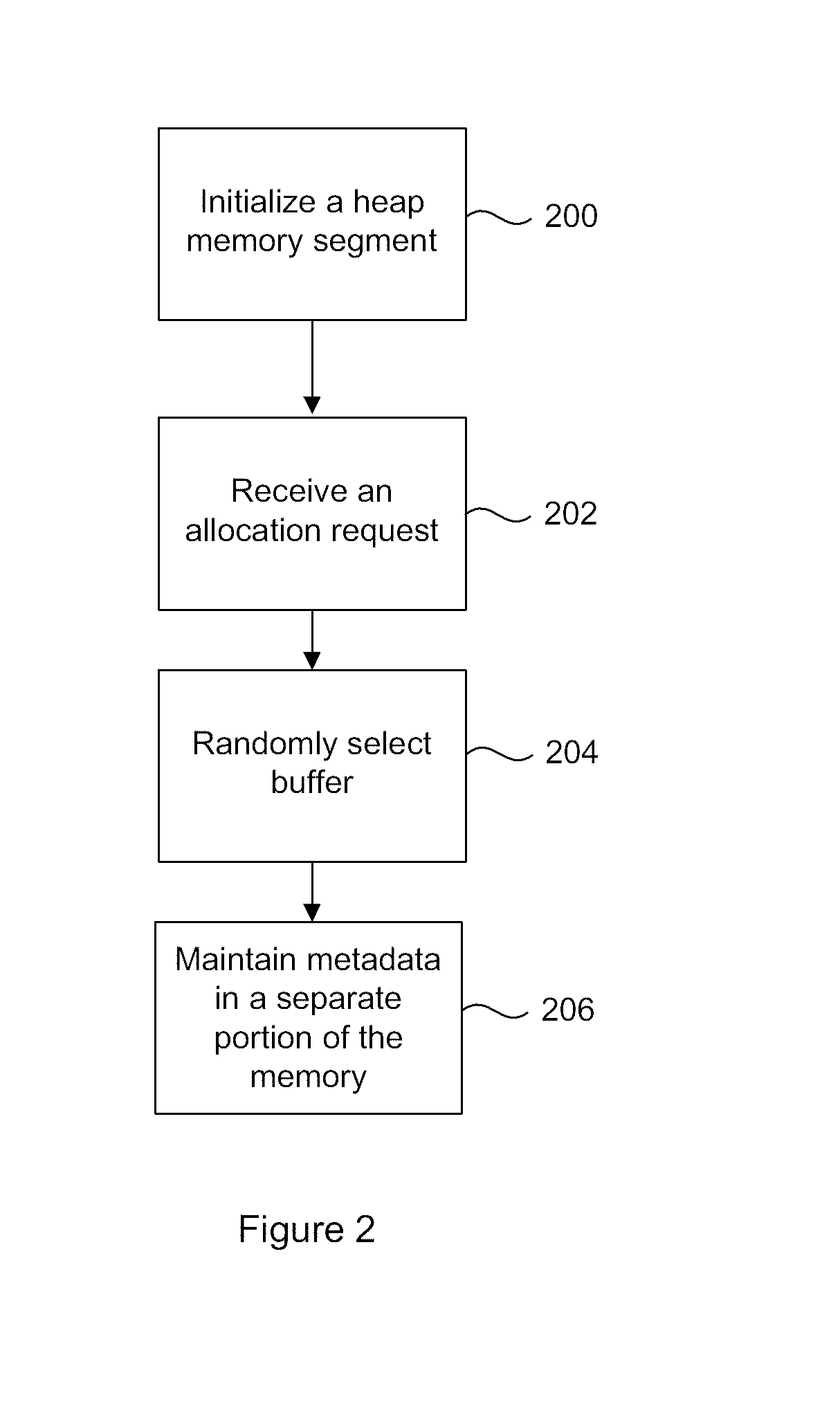
A method and system for secure dynamic memory management using heap memory, or analogous dynamic memory allocation, that includes initializing a heap memory segment, having a plurality of buffers, within a random access memory. When an allocation request to store data in the heap memory segment is received, one of the buffers is randomly selected. Metadata, containing details of allocated and unallocated buffers of the heap memory segment, is then maintained in a portion of the memory separate from the heap object. According to certain embodiments, the secure heap of the present disclosure can securely implement the functions of those portions of the C / C++ stdlib library related to dynamic memory management, specifically malloc ( ) free ( ) and their variants.
Owner:IRDETO ACCESS
Fast, high reliability dynamic memory manager
InactiveUS20050154851A1Quick searchRapid deallocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationTerm memoryDependability
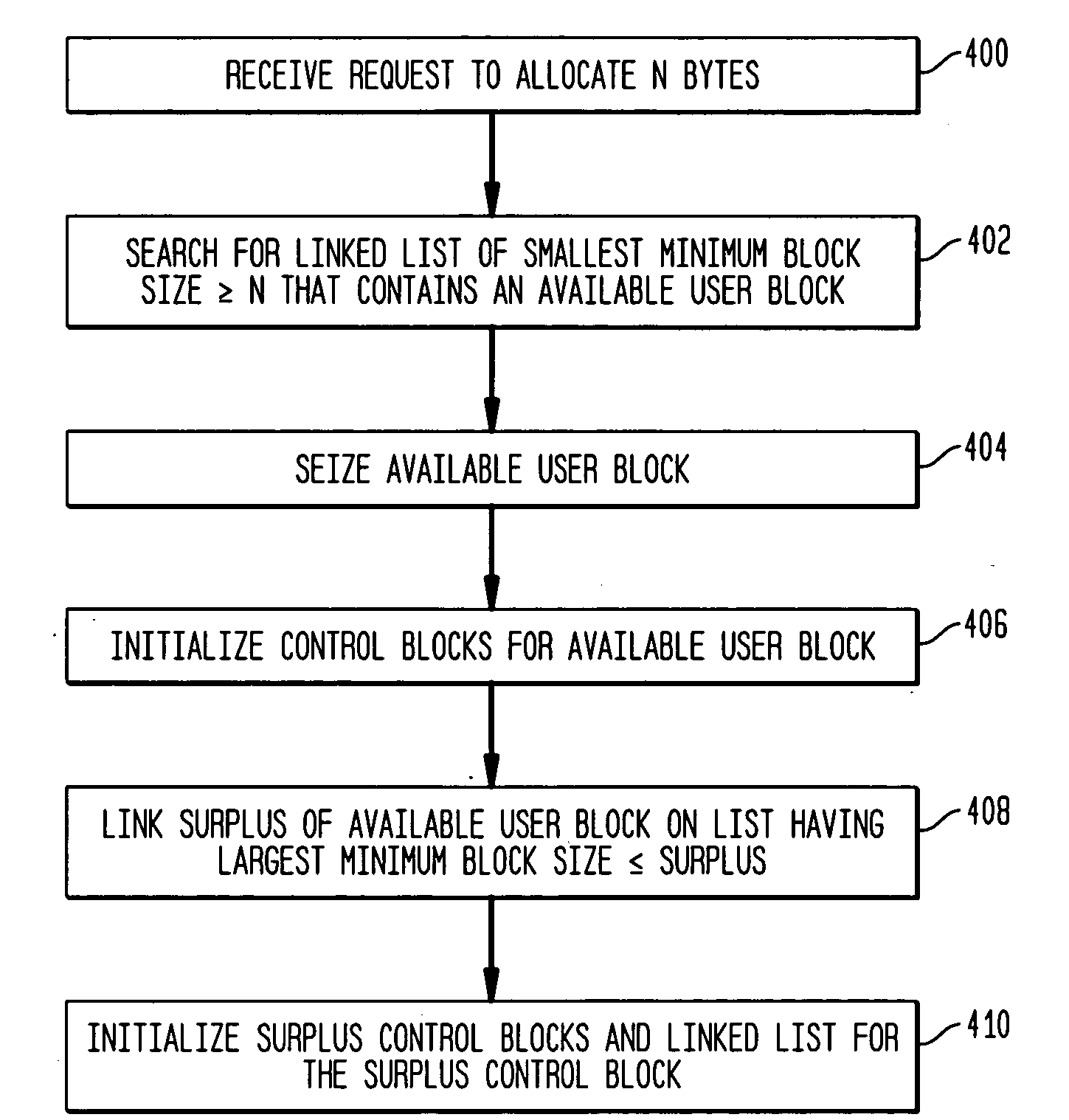
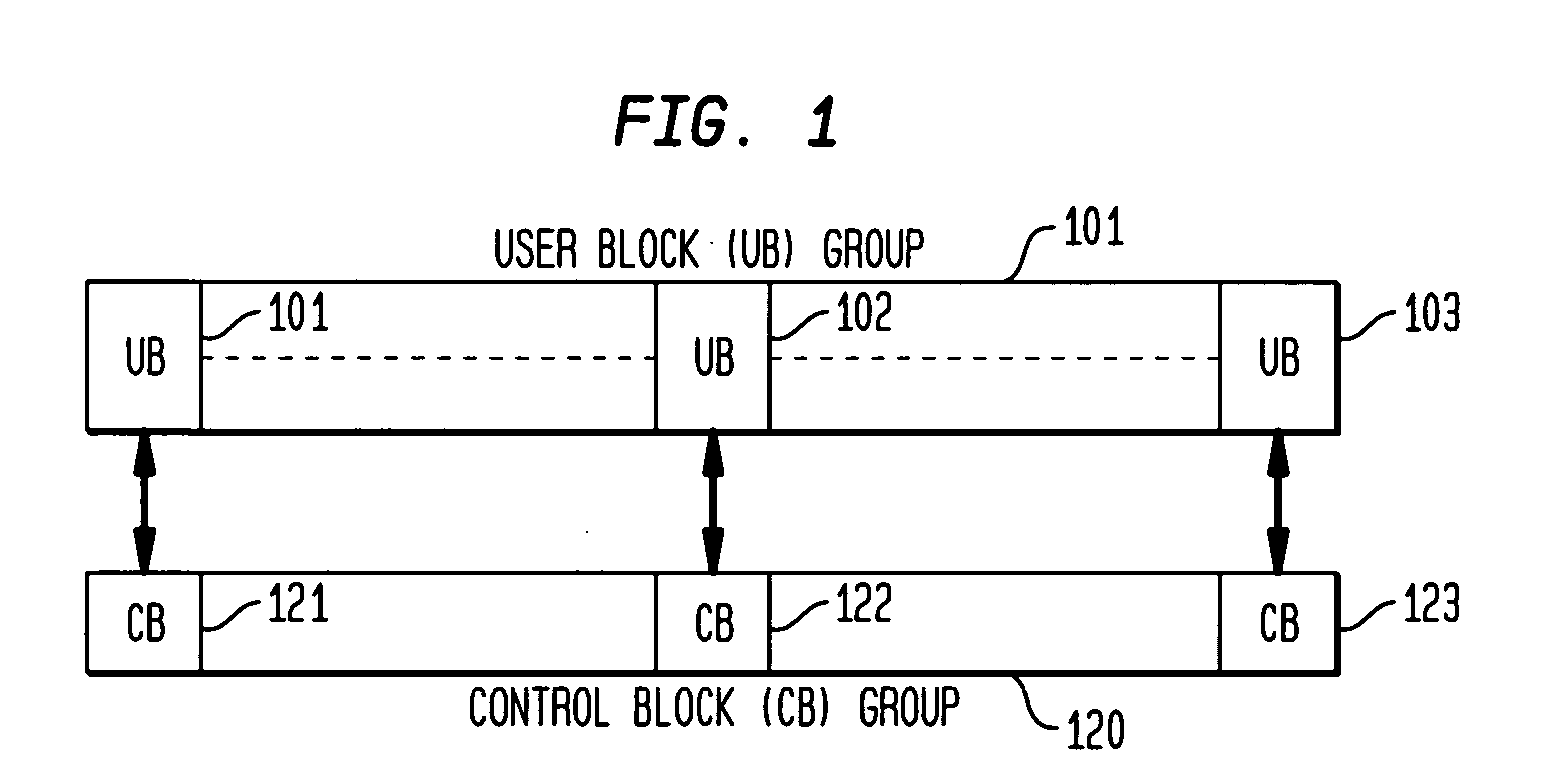
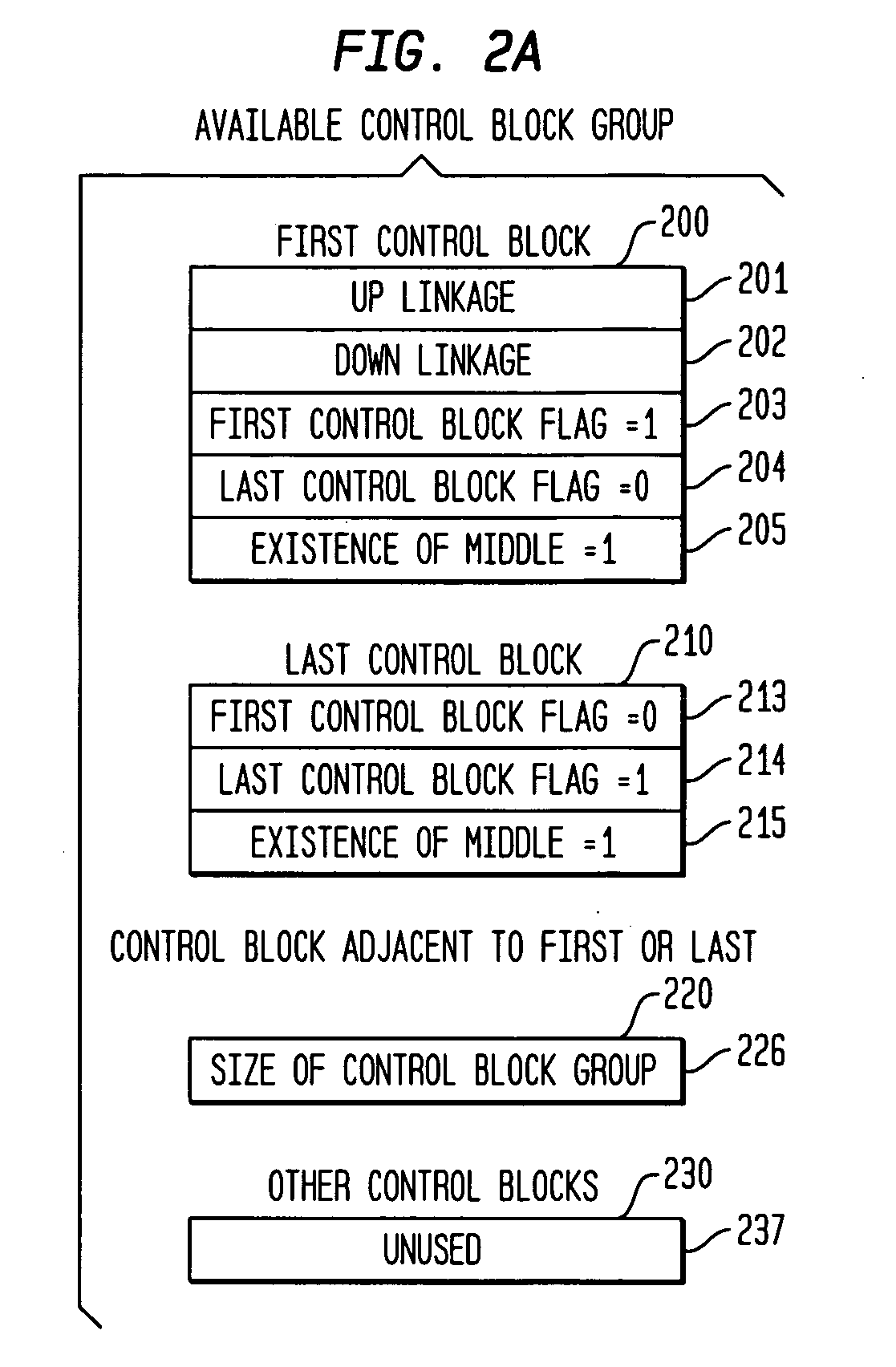
A method and apparatus for allocating and deallocating memory in a multi-processing system. Each unit of user memory has an associated control block. All units of user memory are contiguous as are all control blocks. Available user memory blocks are stored in linked lists, one linked list for each range of user memory block sizes. When a user memory block is allocated, a memory block is seized using a linked list of adequate size memory blocks; the surplus of the adequate size memory block beyond what is needed in the request for user memory is retained as available user memory and is added to another appropriate linked list of available memory. When deallocating, both the memory block being deallocated and, if available, the previous and / or next memory block are added to create a merged memory block. The merged memory block is then restored as available memory and added to the appropriate one of the linked lists of available memory blocks while the previous and / or next memory blocks, if available, are removed from the list of available memory blocks of the size of the previous or next block.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
Dynamic memory management of unallocated memory in a logical partitioned data processing system
InactiveUS7231504B2Maximize useResource allocationMemory systemsData processing systemDynamic storage
A method, system, and program for dynamic memory management of unallocated memory in a logical partitioned data processing system. A logical partitioned data processing system typically includes multiple memory units, processors, I / O adapters, and other resources enabled for allocation to multiple logical partitions. A partition manager operating within the data processing system manages allocation of the resources to each logical partition. In particular, the partition manager manages allocation of a first portion of the multiple memory units to at least one logical partition. In addition, the partition manager manages a memory pool of unallocated memory from among the multiple memory units. Responsive to receiving a request for a memory loan from one of the allocated logical partitions, a second selection of memory units from the memory pool is loaned to the requesting logical partition. The partition manager, however, is enabled to reclaim the loaned selection of memory units from the requesting logical partition at any time.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Real-time dynamic memory manager achieving method for multi-core processor
ActiveCN103164278AImprove real-time performanceImprove stabilityResource allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationNon real timeOperational system
The invention relates to a real-time dynamic memory manager for a multi-core real-time system, in particular to a real-time dynamic memory manager achieving method for multi-core processor. Cache shared by a physical memory and the multi-core processor is divided into a monopoly area, a shared area, a communication area and a non-real-time area by the page coloring technique, spare page management systems are respectively built for the monopoly area and the shared area, the communication area is packed by various synchronous mechanisms to achieve high-speed communication between tasks based on Cache, and the non-real-time area is managed by a host operation system. The real-time dynamic memory manager achieving method for the multi-core processor divides a memory and the Cache into a plurality of independent areas, prevents high priority hard real-time tasks from being interfered by other tasks through the Cache and improves system real time performance and stability. Thus, a high speed communication mechanism based on tasks of the Cache is achieved to further improve system real time performance.
Owner:SHENYANG GOLDING NC & INTELLIGENCE TECH CO LTD
Highly-concurrent real-time memory resource management and scheduling method
ActiveCN102567107AOvercome limitationsSolve the speed problemProgram initiation/switchingConcurrent instruction executionSoftware systemDynamic management
The invention discloses a highly-concurrent real-time memory resource management and scheduling method, which includes the steps: initializing by allocating memory with designated quantity as a management heap, dividing the memory into a plurality of memory blocks and setting up a mapping module through a memory management module; performing memory management by creating a local heap for a current thread and maintaining the corresponding relationship between the local heap and the current thread through the mapping module after a thread needing dynamic memory management is added to the memory management module; and allocating dynamic memory by returning the memory to the current thread and completing the current thread after service logic of the current thread is processed. The method solves the problem of bottleneck in concurrent memory resource scheduling on modern multi-core high-end commerce servers, so that hardware resource potential of modern computers is sufficiently explored without changing any codes of a traditional application system, and real-time running efficiency of a software system is greatly improved.
Owner:ELECTRIC POWER RES INST OF GUANGDONG POWER GRID +1
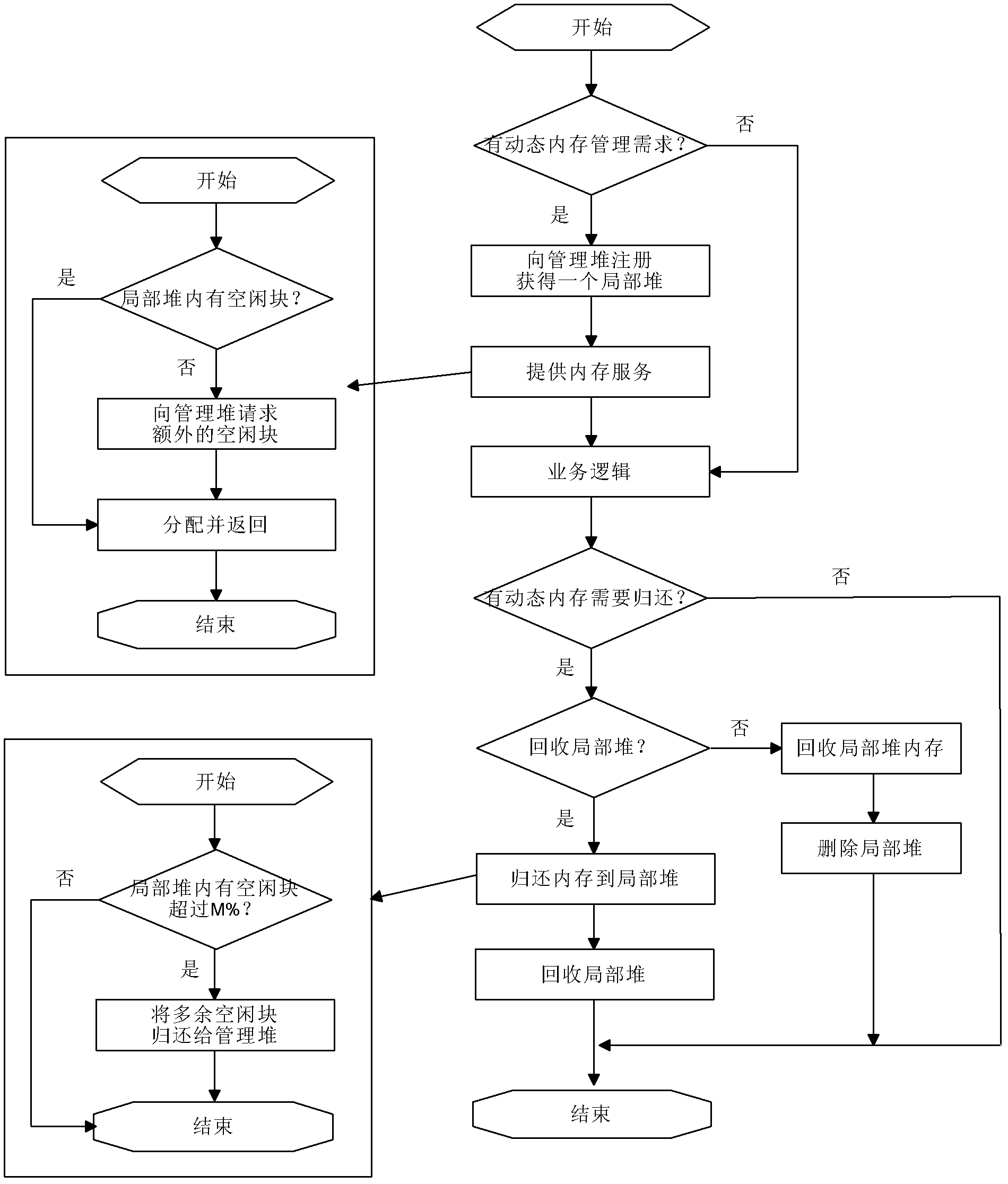
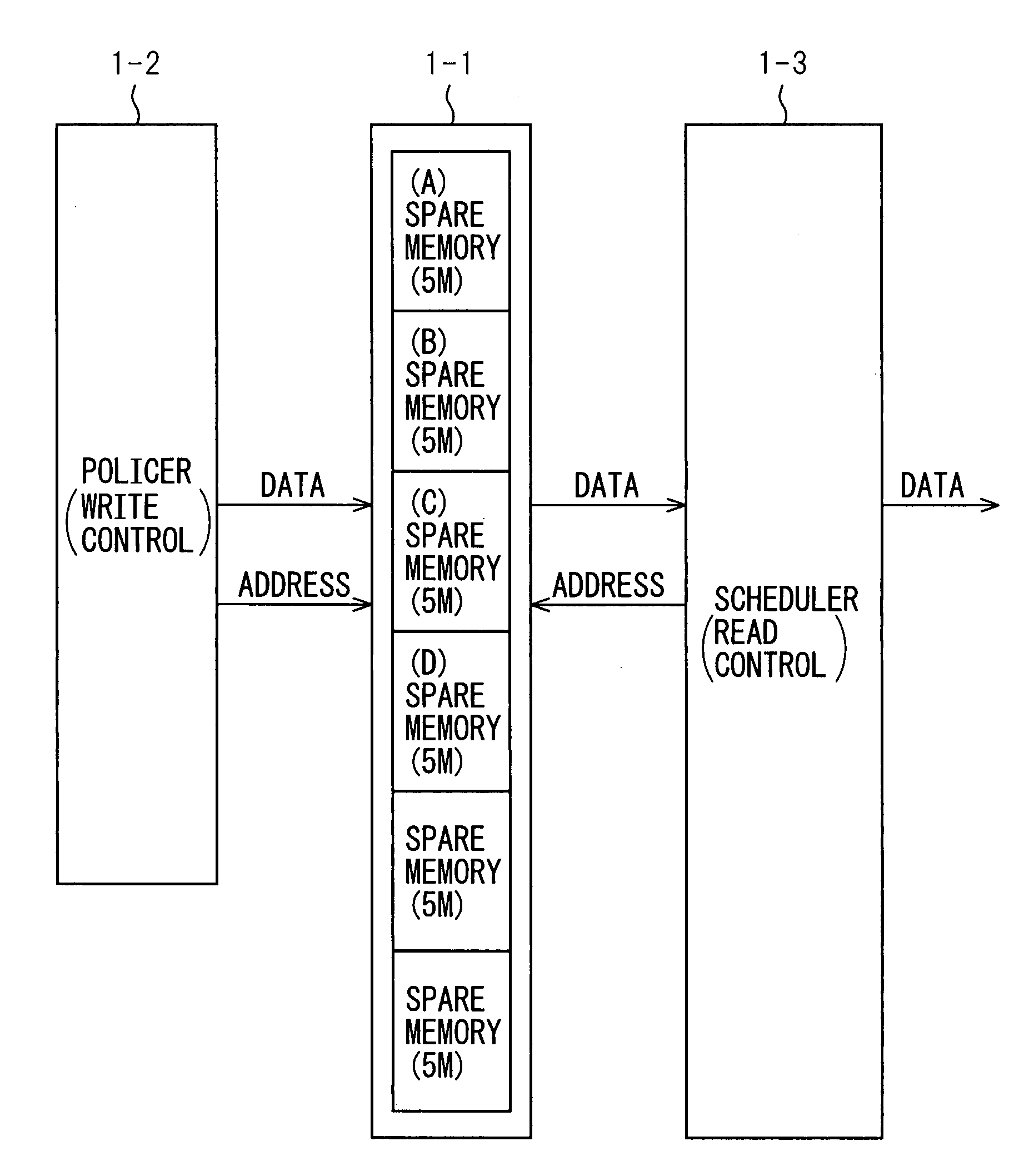
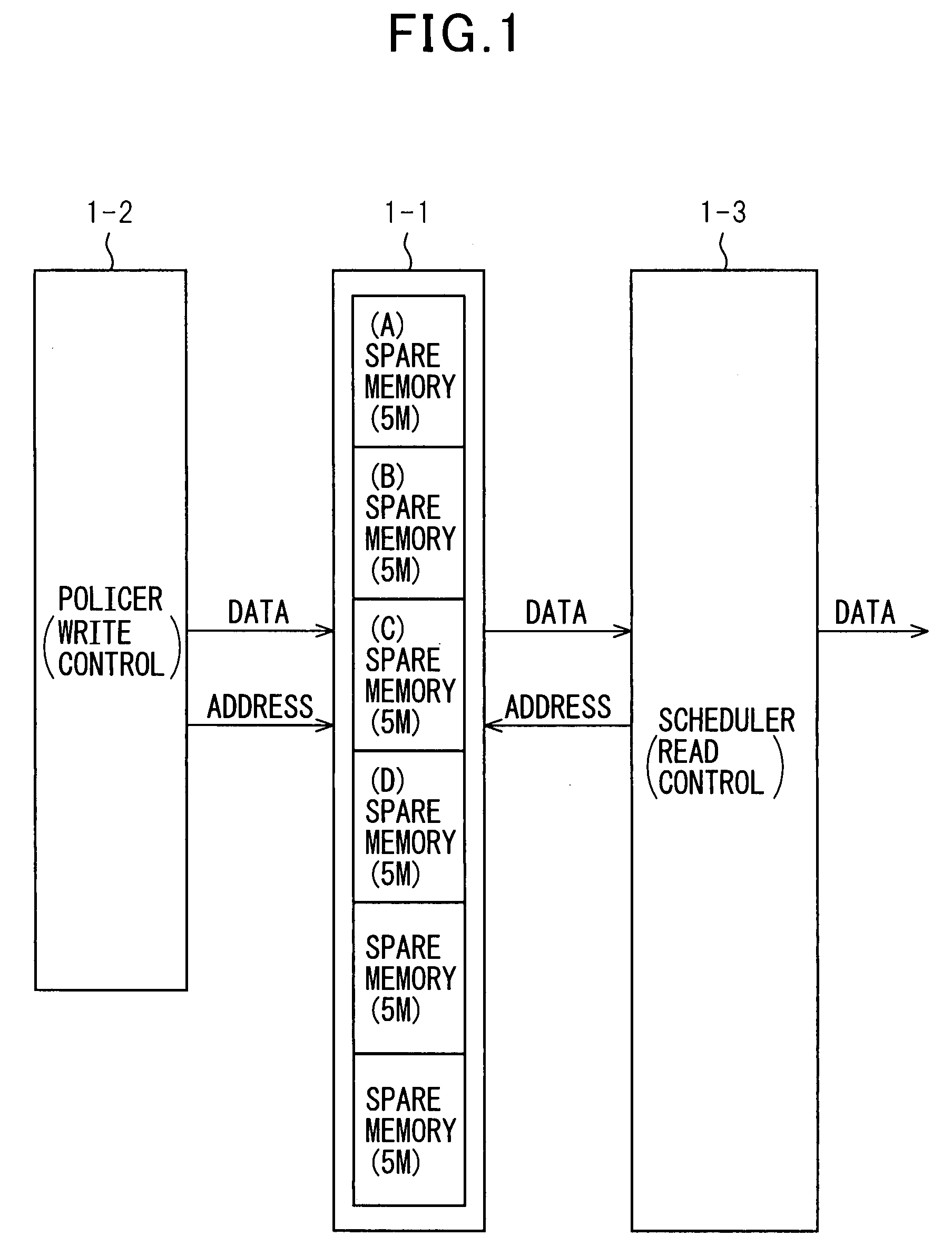
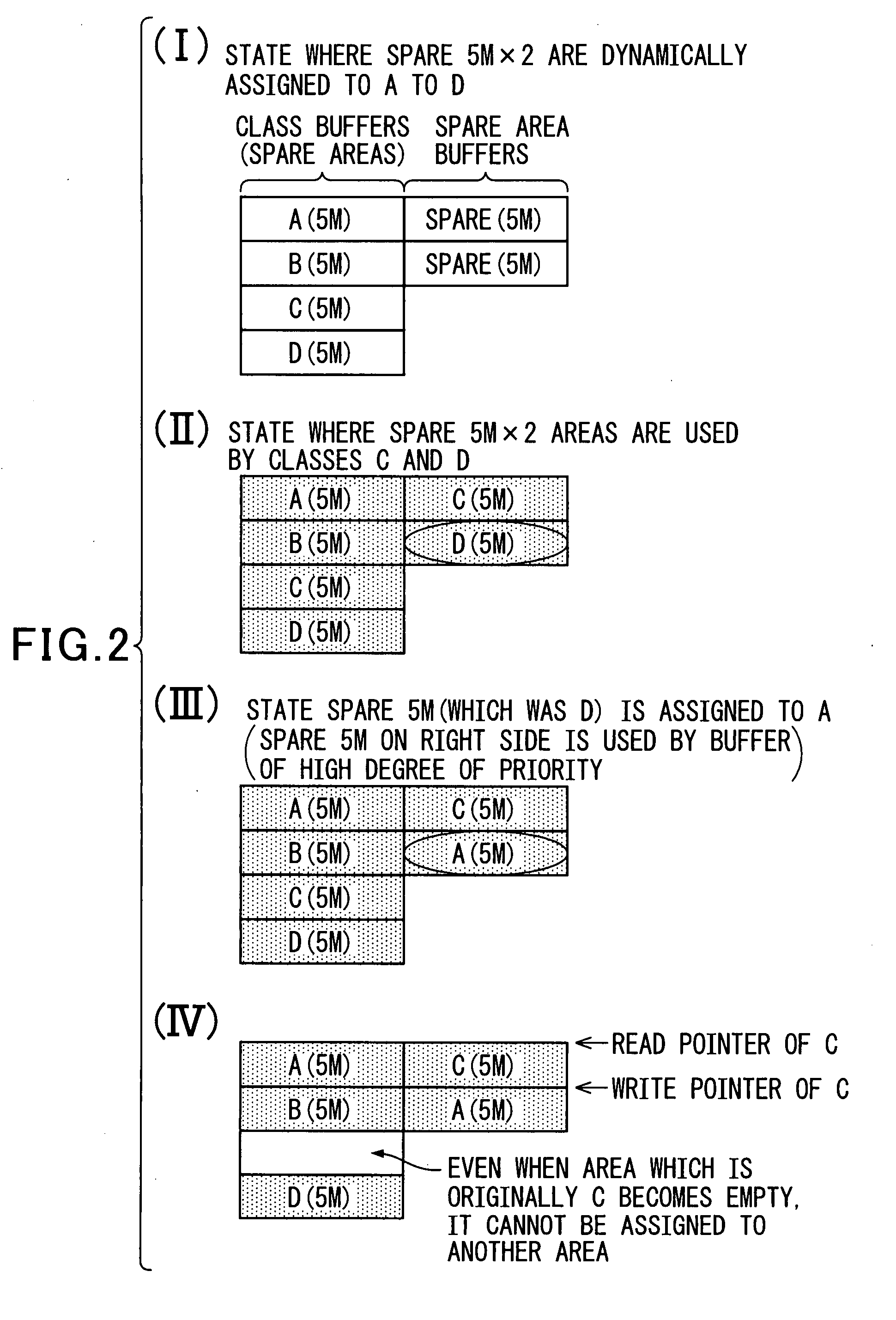
Method and apparatus for dynamically managing memory in accordance with priority class
InactiveUS20080077741A1Improving inefficient use of memoryEasy to controlMemory systemsMemory bankDynamic management
A dynamic memory management method and apparatus wherein an area of a memory is partitioned into a plurality of areas to form memory banks. The different priority classes share the memory banks. A policer (write controller) dynamically assigns input frame data of a plurality of classes having different degrees of priority to memory banks in accordance with the degrees of priority and stores the data there for each priority class. A scheduler (read controller) sequentially reads out the data from the frame data stored in the memory bank assigned to the class having the highest degree of priority and transmits the same. For storage of frame data of a priority of class input in a burst like manner, a plurality of memory banks are assigned to that priority class so as to raise the burst tolerance. By controlling writing and reading of data in units of memory banks, the control can be simplified. Due to this, the efficiency of usage of memory is improved and the write / read control is simplified.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
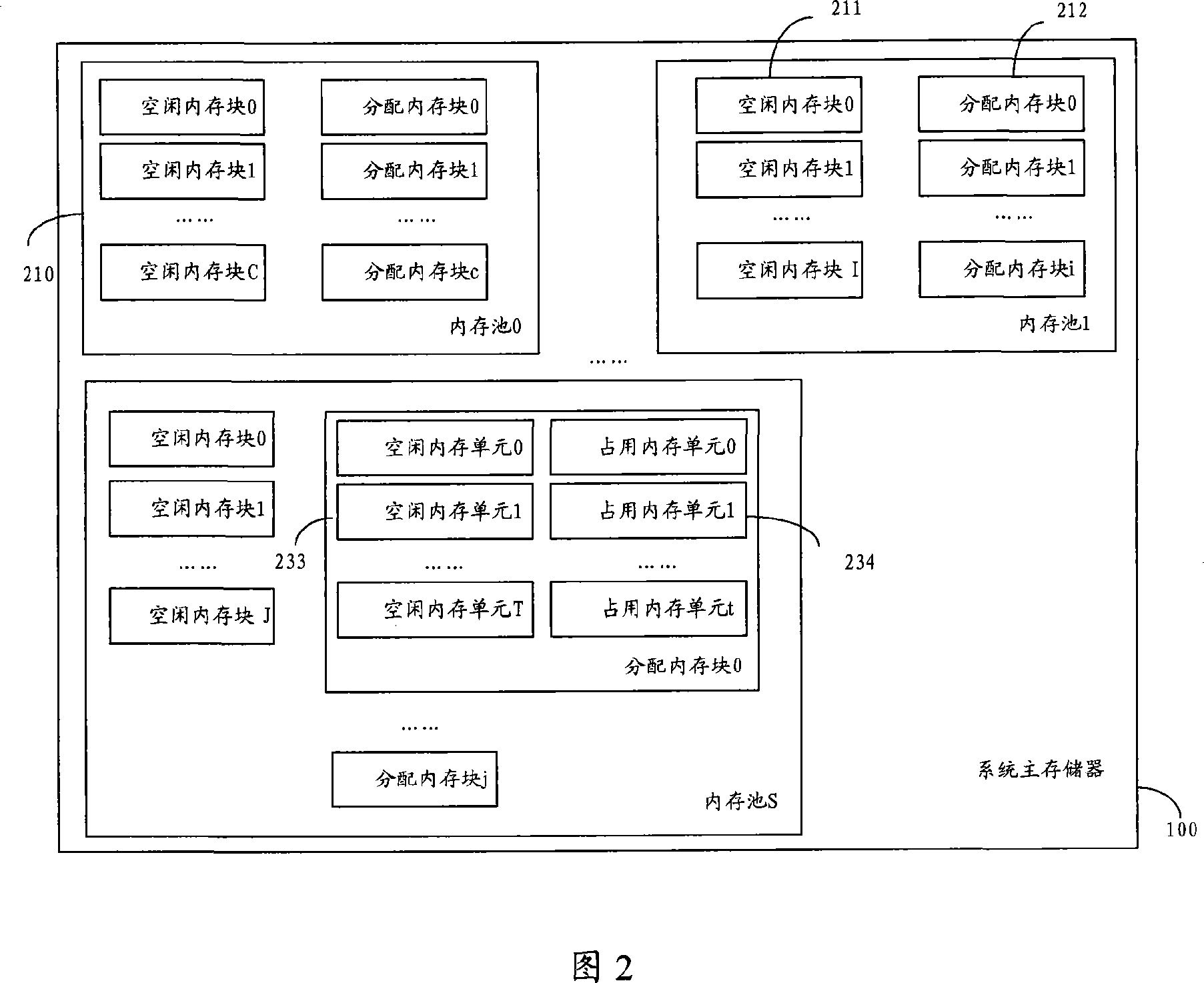
Memory allocation method
ActiveCN102012870AAvoid it happening againRealize distributionMemory adressing/allocation/relocationMemory addressDistribution method
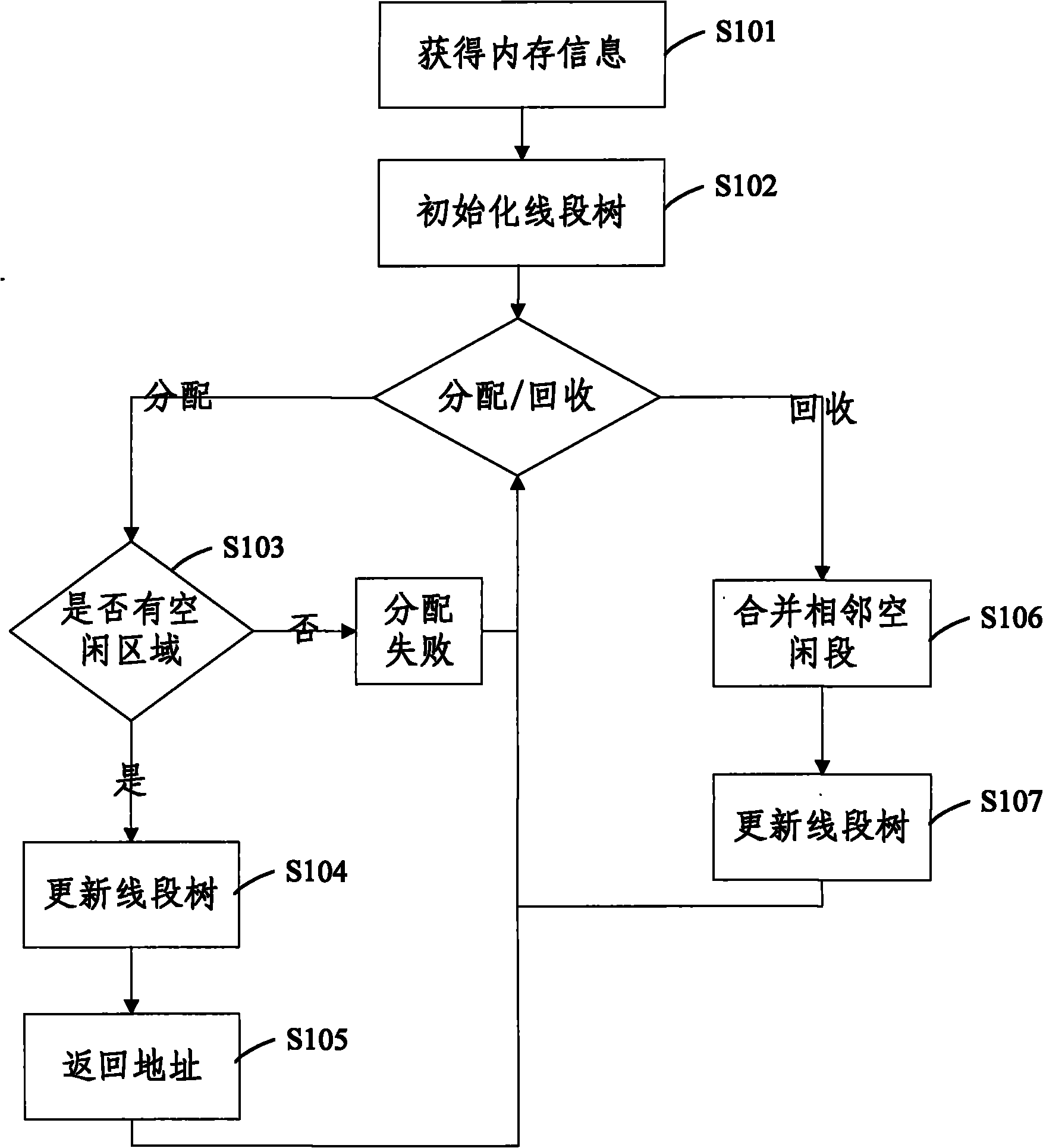
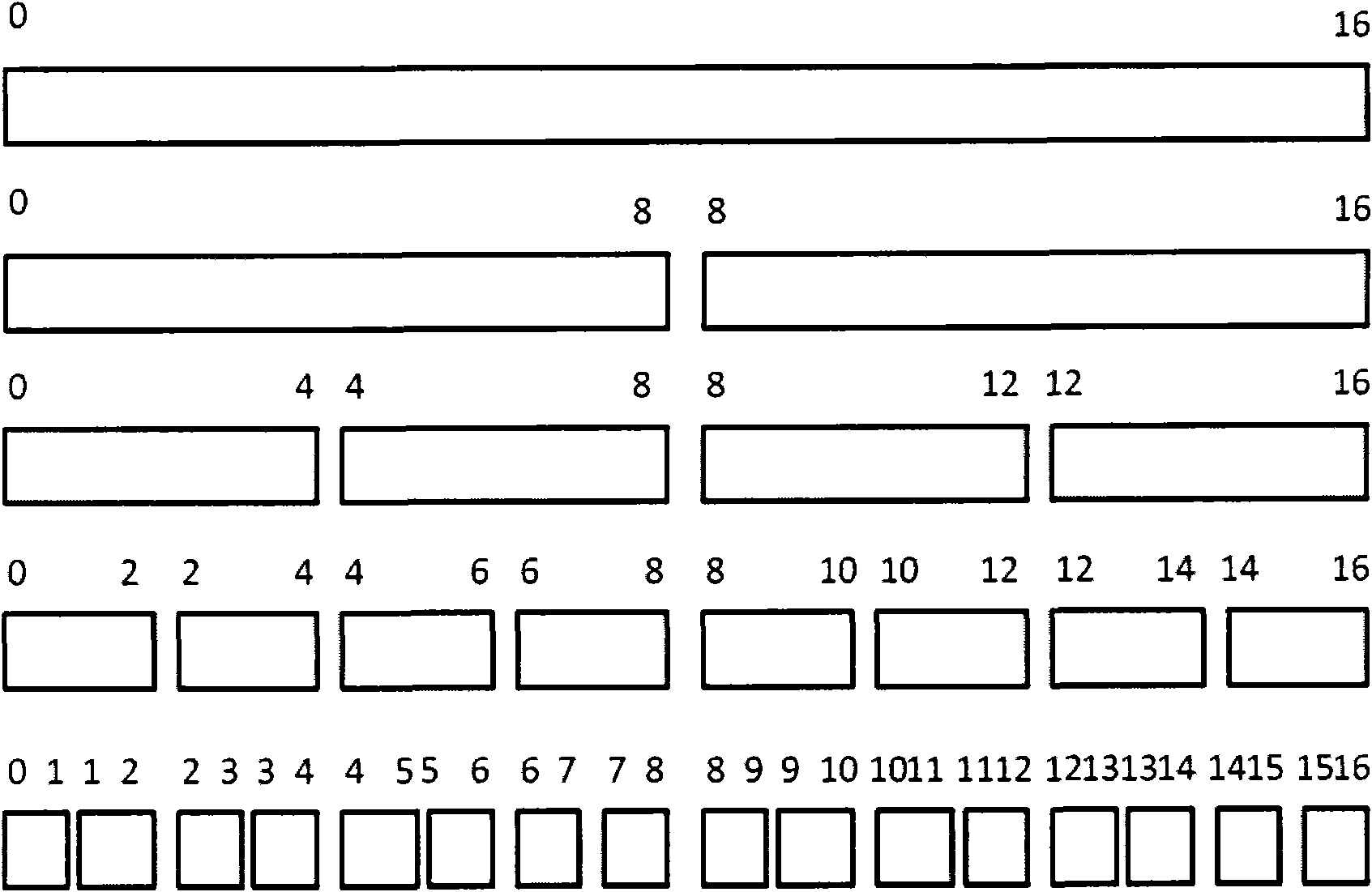
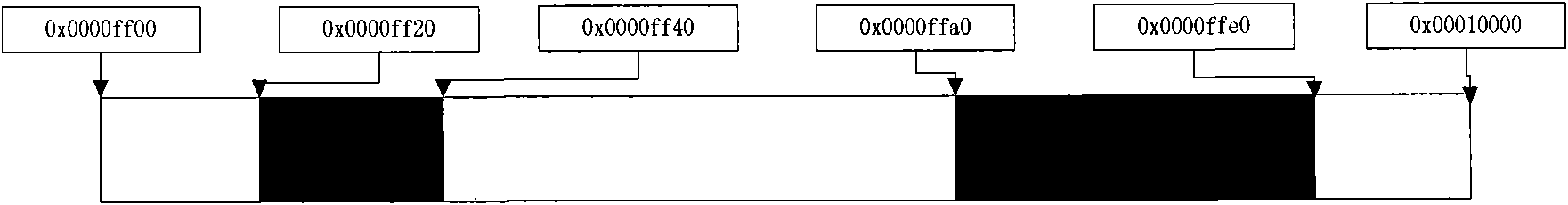
The invention discloses a memory allocation method, comprising the following steps: S1, establishing and initializing a segment tree structure for a memory to be managed; S2, applying for the memory by a kernel or an application program; and S3, recovering the memory released by the kernel or the application program by a segment tree. Physical memory management is performed by adopting the segment tree mode, thereby ensuring that the provided memory address is in physical continuity, efficiently applying for the memory with the specific physical address without influencing the overall performance, and overcoming the defects that the common memory management is easy to generate memory fragments, the efficiency is low, the continuity of the physical address can not be ensured and the like.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
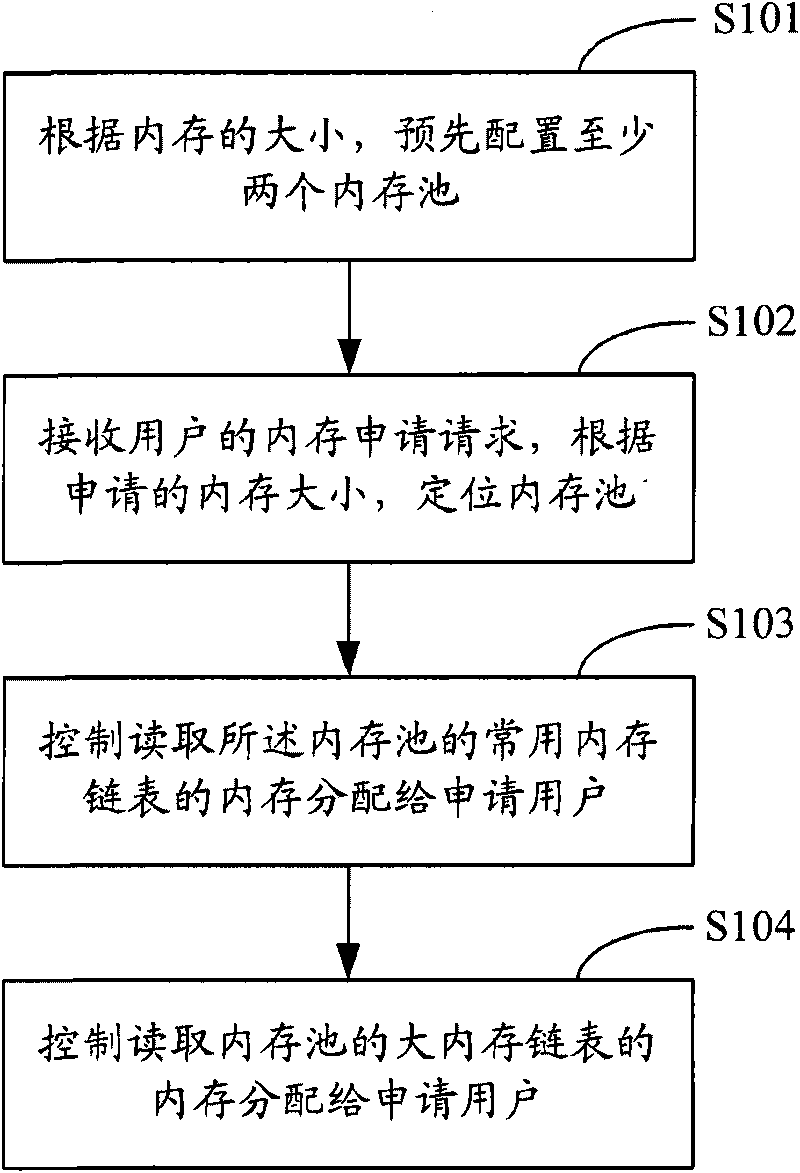
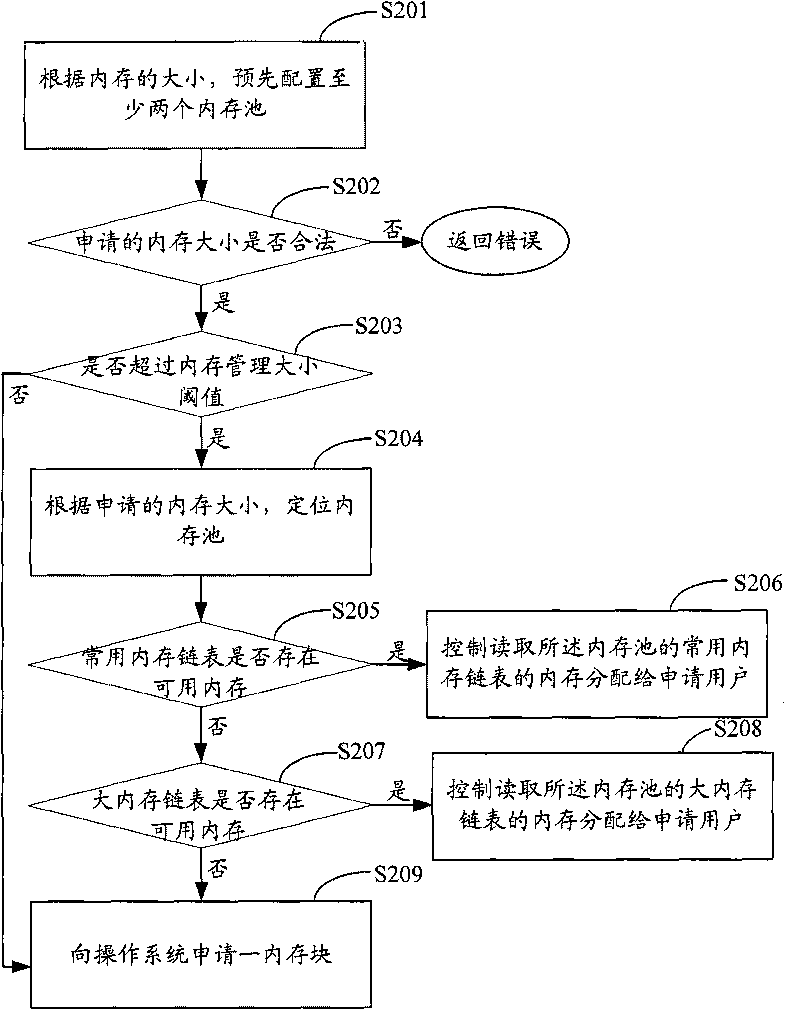
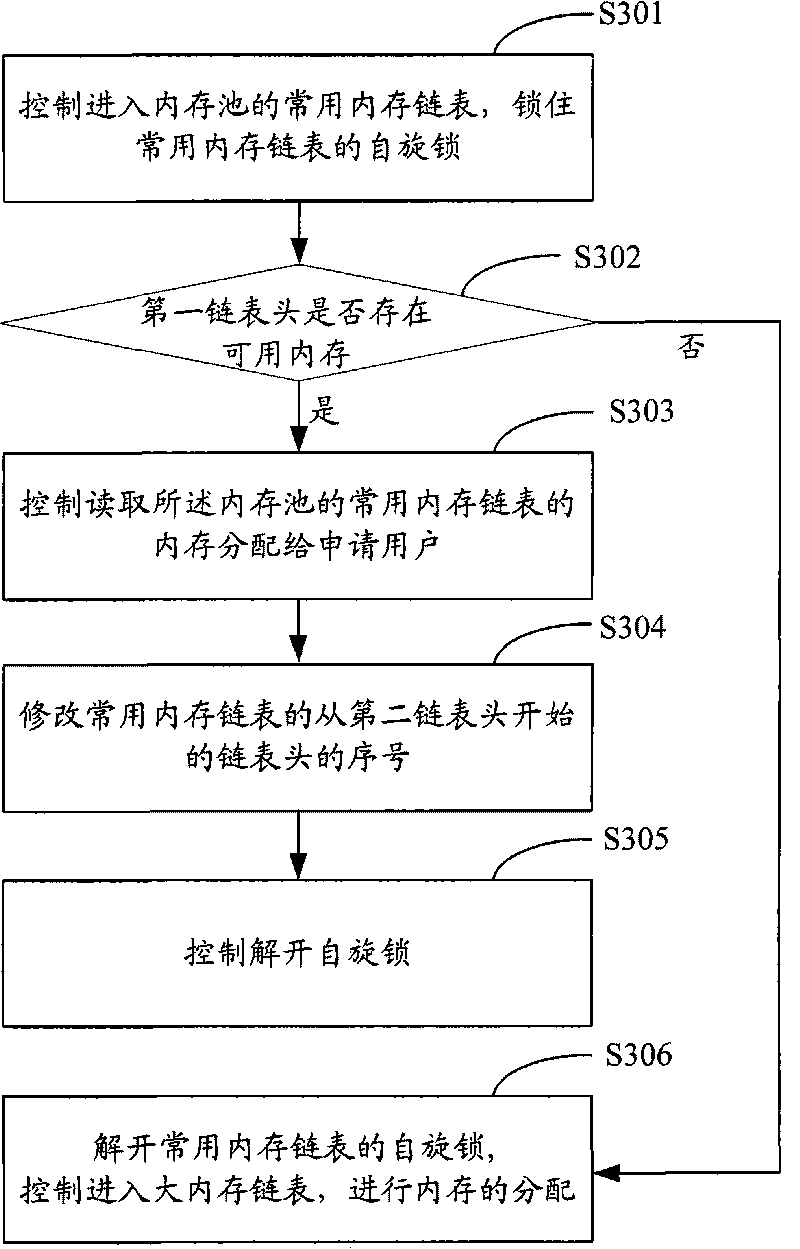
Memory management method, memory management system and server
InactiveCN101702138AHigh allocation concurrencyImprove distribution efficiencyResource allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationHigh memoryMemory management unit
The invention provides a memory management method, a memory management system and a server, belonging to the technical field of the server. The memory management method comprises the following steps: presetting at least two memory pools which comprise frequently-used memory chain tables and big memory chain tables according to the size of the memory; receiving the user's request for applying for the memory and positioning the memory pool according to the size of the memory applied by the user; controlling and allotting the memory of the frequently-used memory chain table reading the memory pool to the user applying for the memory when there is available memory in the frequently-used memory chain table of the positioned memory pool; controlling and allotting the memory of the big memory chain table reading the memory pool to the user applying for the memory when there is no available memory in the frequently-used memory chain table of the positioned memory pool. The invention has high memory allotting efficiency and high memory allotting concurrency and realizes that the plurality of memory pools correspond to a plurality of parallel threads.
Owner:关志航
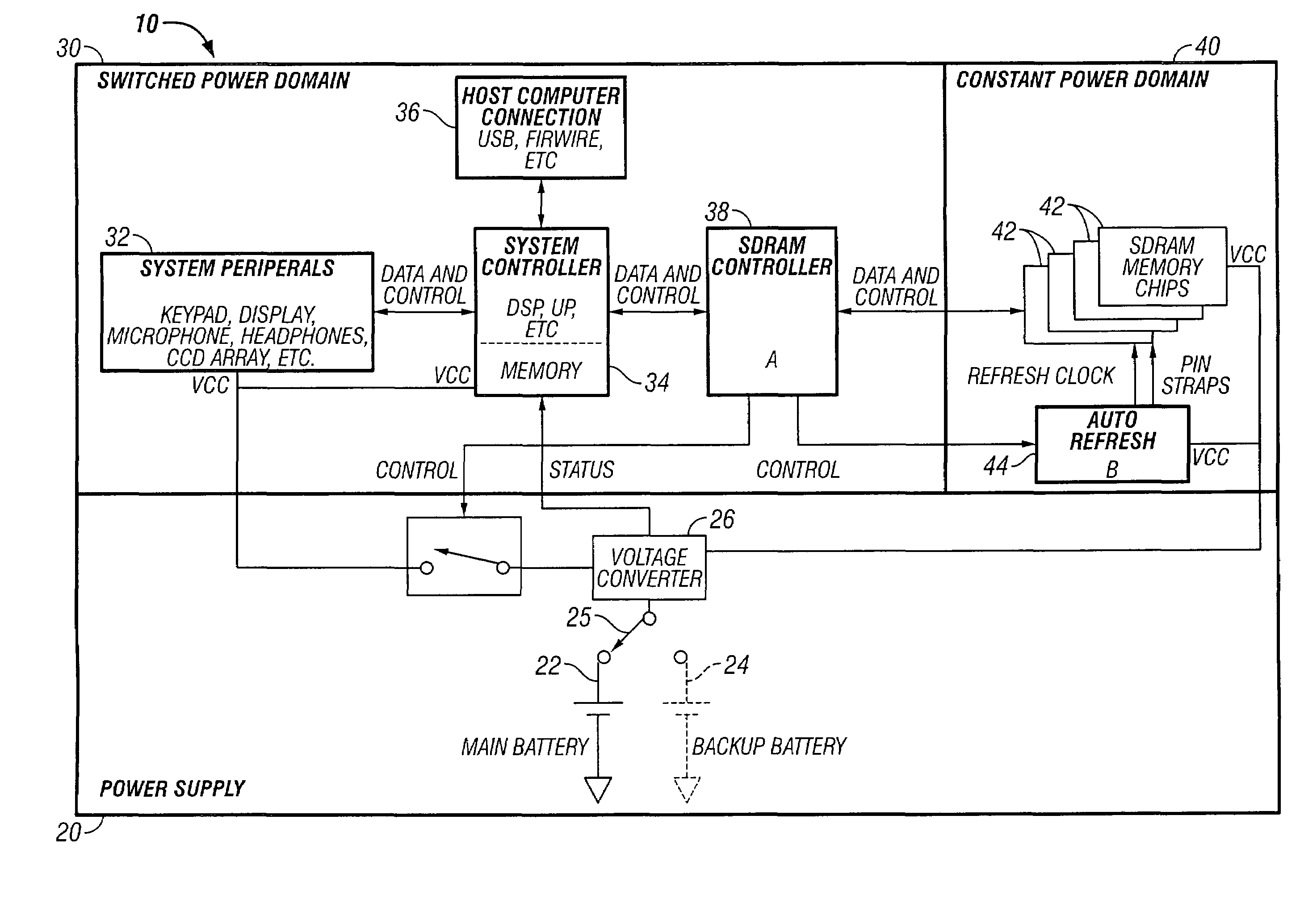
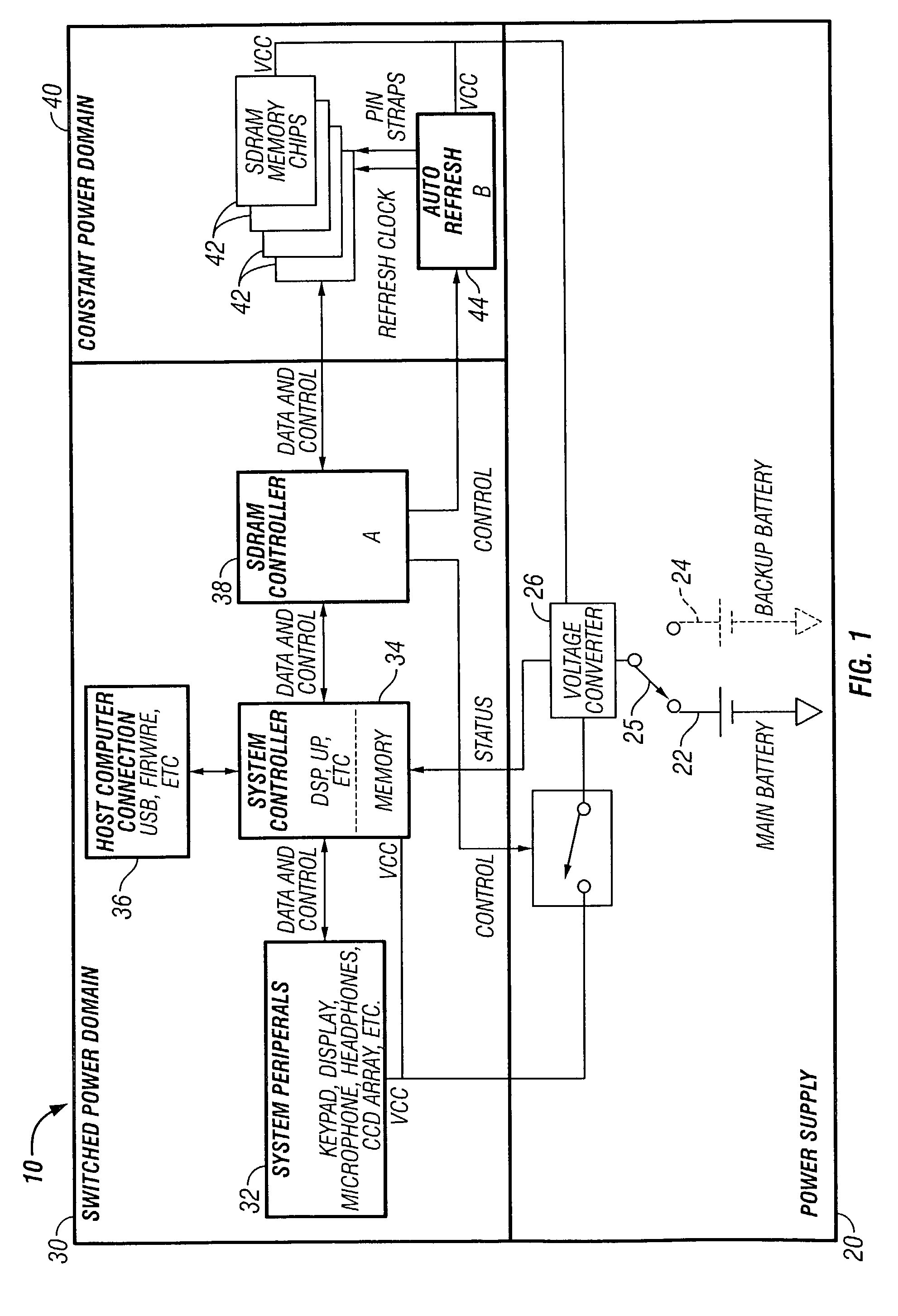
Dynamic memory management
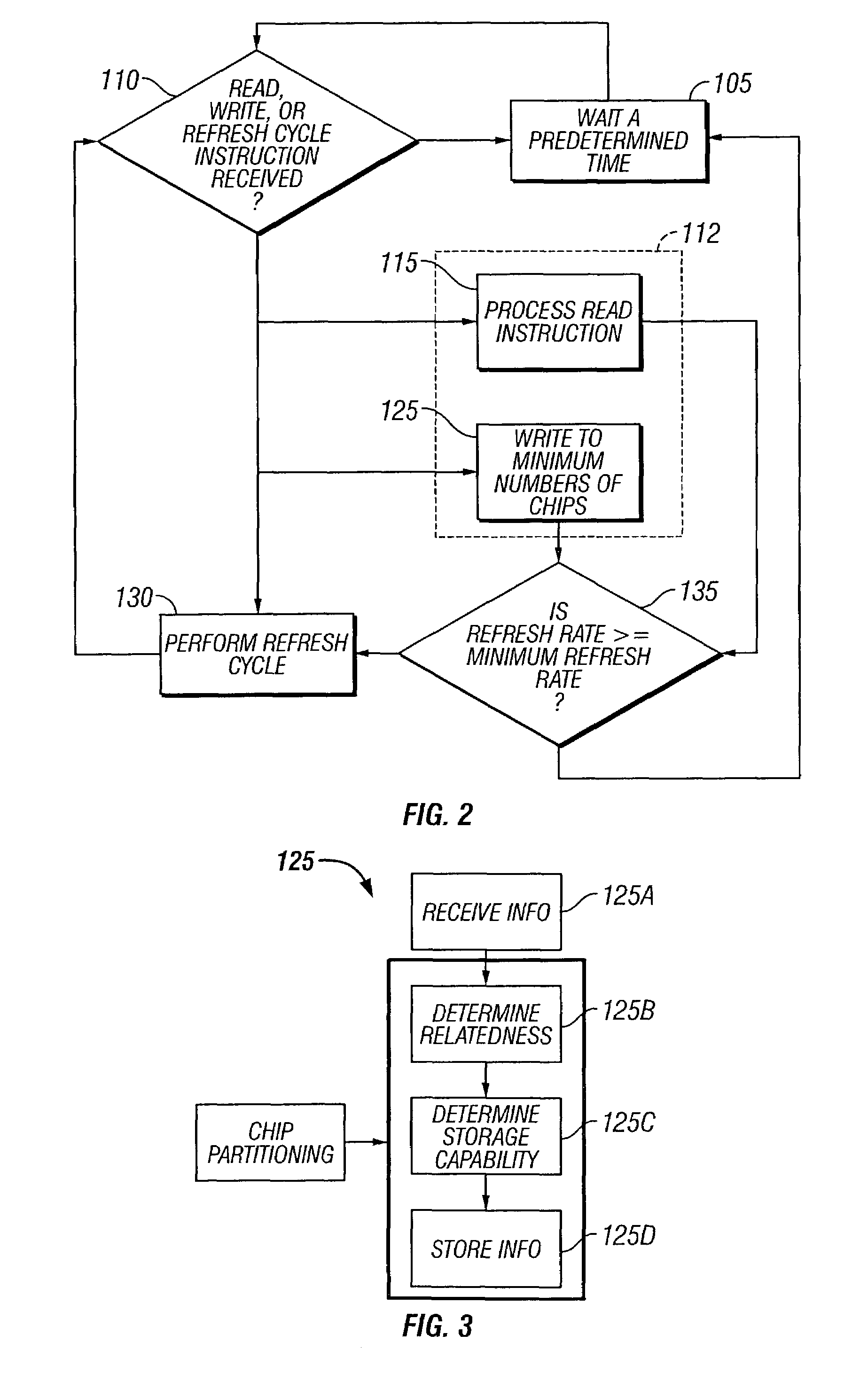
InactiveUS7035155B2Avoid lostAvoid it happening againEnergy efficient ICTDigital storageElectrical batteryDynamic storage
In a method, system and apparatus for management of dynamic memory in battery-powered devices, information is stored in dynamic memory, such as SDRAM chips. Chip partitioning minimizes the number of chips requiring power, minimum refresh rates reduce the power needed to maintain information, and a threshold for determining when to power down a battery powered device are used to maximize battery life.
Owner:XWARE
Method and apparatus for executing dynamic memory management with object-oriented program
ActiveUS20050071597A1Improve performanceShort operating timeData processing applicationsMemory adressing/allocation/relocationParallel computingUnit memory
The disclosure is a method and apparatus for operating dynamic memory management with an object-oriented program, by which objects with frequent creation and short life spans are allocated to a unit memory block in sequence. After released from the unit memory block, the objects are added on a free re-use list so as to be reused when there is an invocation of allocation for the same object size. It is advantageous to enhancing system performance.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
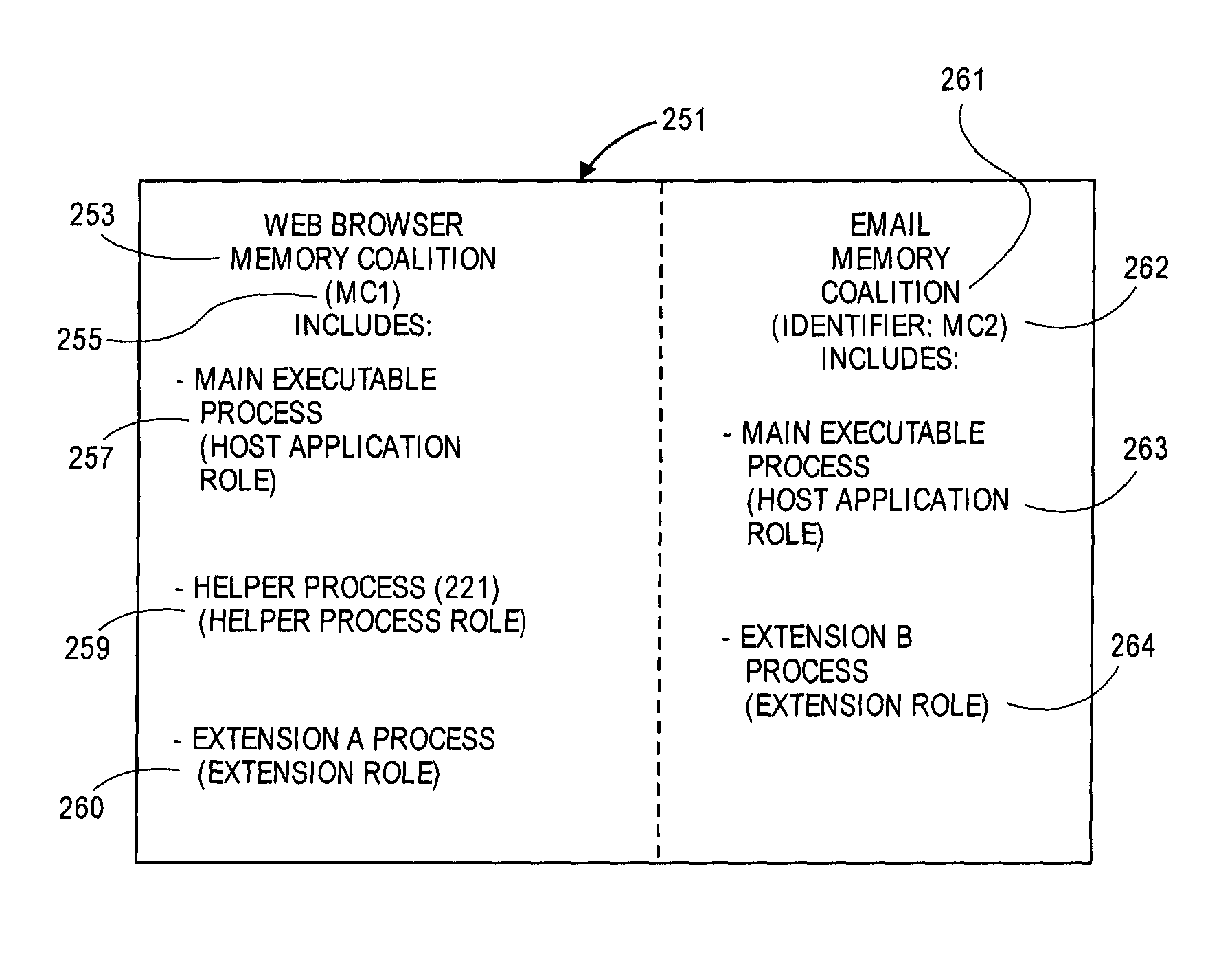
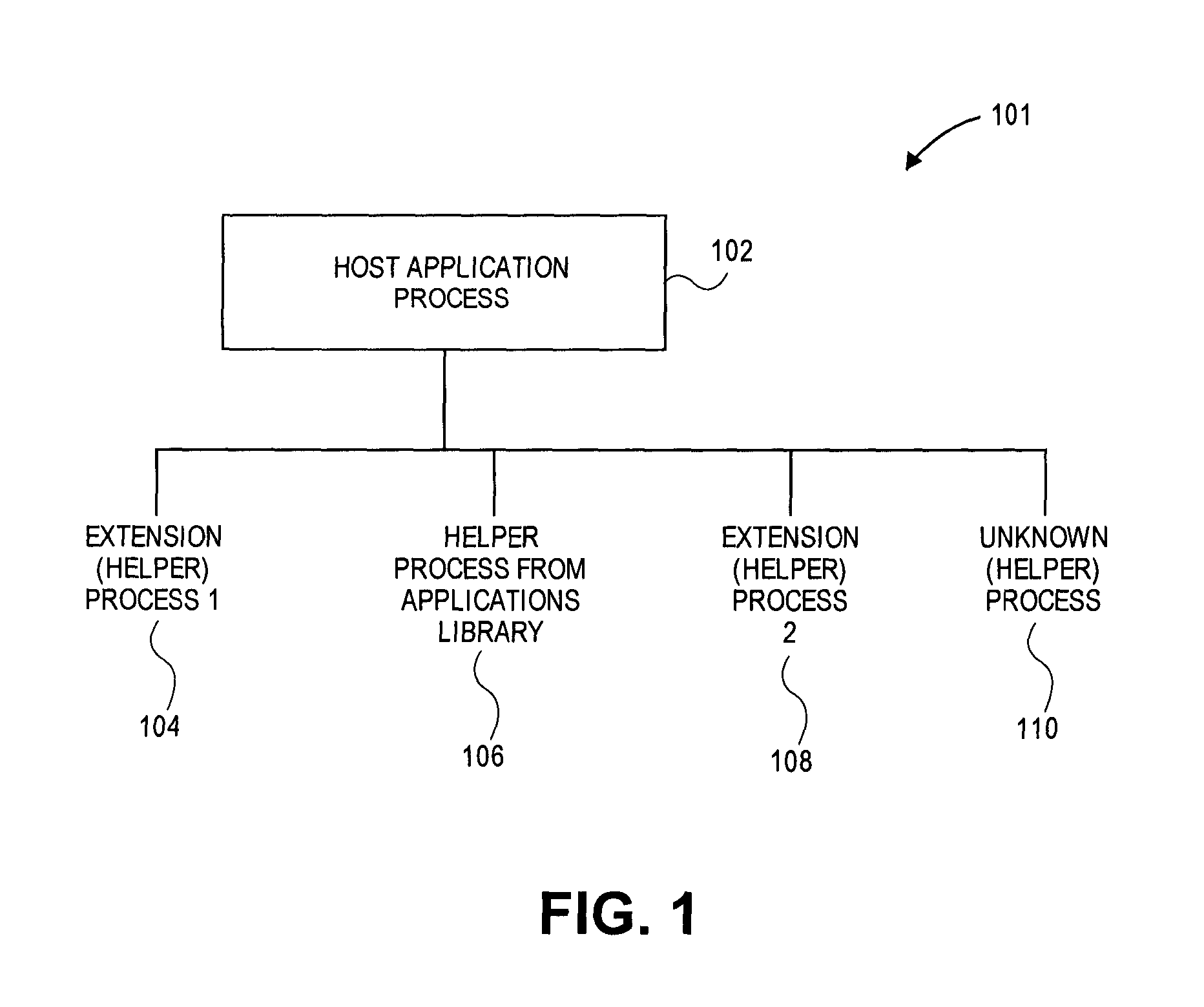
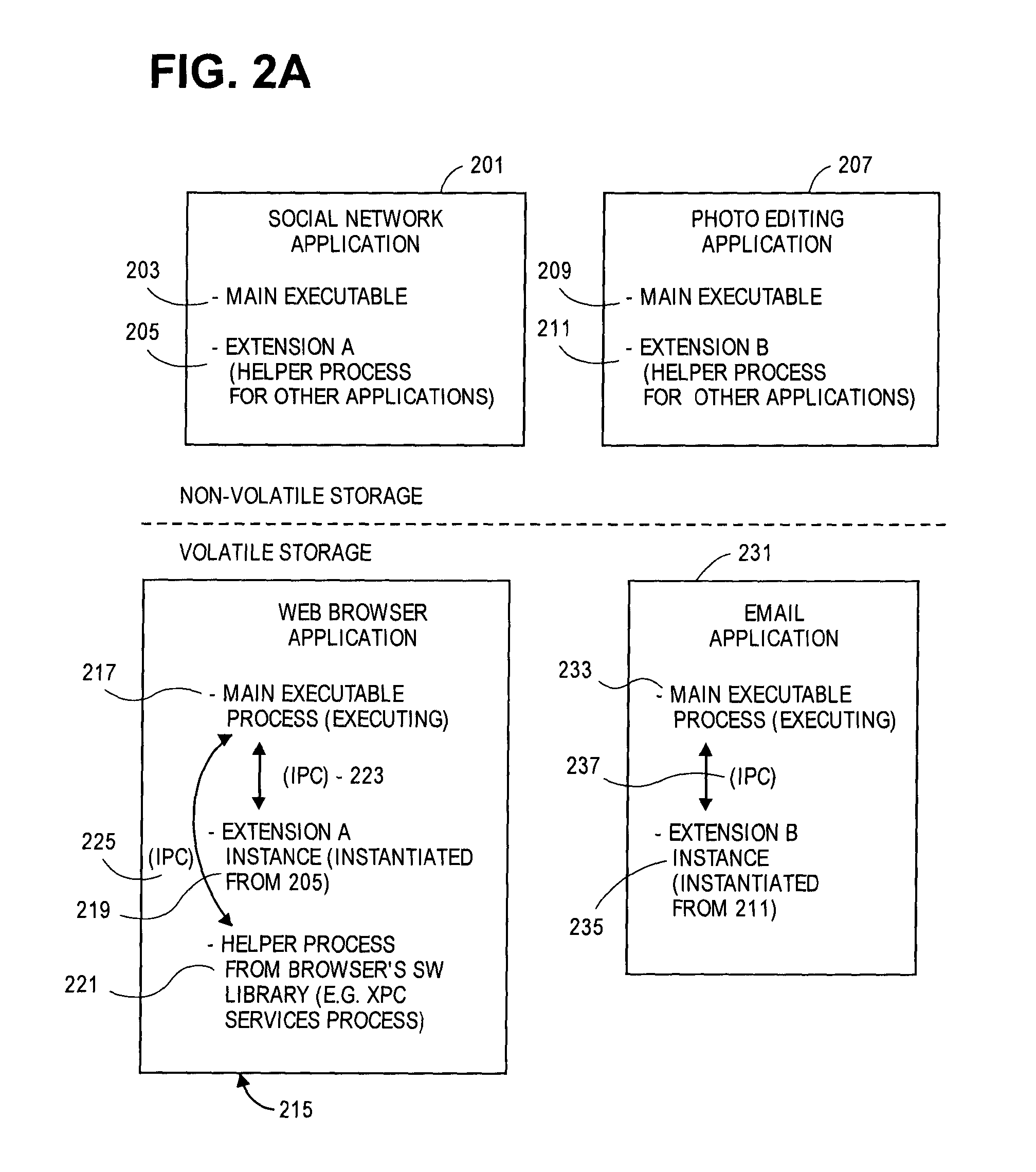
Coalition based memory management
ActiveUS9465734B1Reduce memory usageMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationData processing systemParallel computing
One or more memory coalitions of software processes are created and used to decide whether to perform memory reduction operations on a data processing system. One method in one embodiment includes adding a newly launched second process to an existing memory coalition in response to determining that the second process should be part of a memory coalition that includes a first process. In response to determining that available system memory (e.g. DRAM) is low, the system determines which memory coalition of foreground applications uses the most amount of system memory and then performs one or more memory reduction operations on that memory coalition in order to make more system memory available to other processes.
Owner:APPLE INC
Memory leak positioning method and electronic equipment
The embodiments of the invention provide a memory leak positioning method and electronic equipment, and relate to the technical field of memory management. Unified application and release interface functions of a memory unit are monitored by using a Hook technology without modifying a system memory management module, so that a block memory and a page memory with memory leak are accurately positioned. The method comprises the steps of: when the memory unit is applied via an application interface function, saving a mapping relation between the memory unit and an identifier of a function call stack, wherein the function call stack saves a function call relation of the memory unit applied via the application interface function, and the memory unit comprises block memories or page memories; when the memory unit is released via a release interface function, clearing the mapping relation between the memory unit and the identifier of the function call stack corresponding to the memory unit; and according to the multiple statistical memory sizes of the memory unit having the mapping relation with the identifier of each function call stack, determining the function call stack and the function with memory leak. The method is used for positioning memory leak.
Owner:CHENGDU HUAWEI TECH
Embedded software memory management system
ActiveCN108132842AImprove management efficiencyGeneration of restrictionsResource allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationDynamic memory managementMemory allocator
The invention relates to an embedded software memory management system, and relates to the technical field of embedded software memory management. According to the system, a static allocation method is adopted, the number of partitions in a system memory area and the number and size of memory blocks in each partition are preset, a dynamic memory allocation method is adopted on the memory area of auser based on a pool type memory management mechanism, memory requests and release requests are processed by creating a memory allocator, and traditional dynamic memory allocation and a release algorithm are improved. According to the system, flexibility of the system is enhanced by adopting a combined method of statically allocating the system memory area and dynamically allocating the system memory area, meanwhile generation of a large number of fragments is limited to prevent the occurrence of memory leaks, and the method can effectively reduce time consumption of requesting and memory releasing, so that management efficiency of dynamic memory is improved.
Owner:TIANJIN JINHANG COMP TECH RES INST
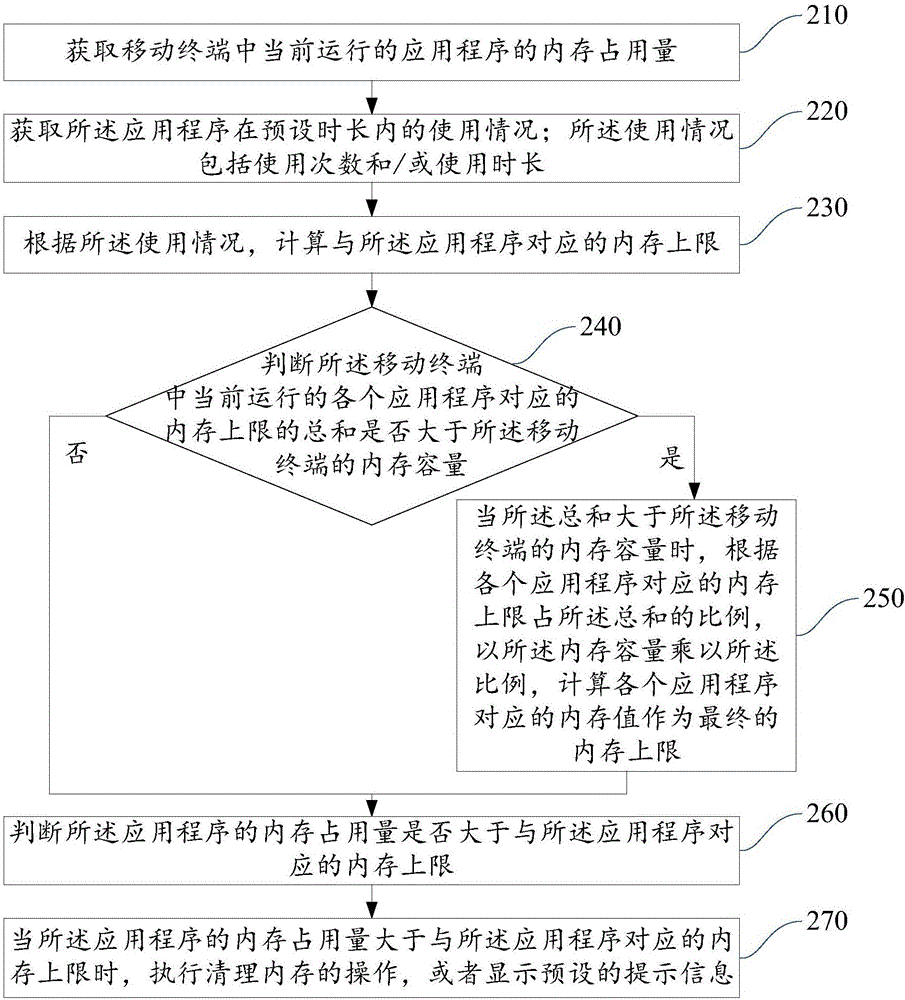
Dynamic memory management method and mobile terminal
InactiveCN106776030AIncreased memory limitReduce CatonResource allocationOut of memoryMemory footprint
The embodiment of the invention provides a dynamic memory management method and a mobile terminal and relates to the technical field of mobile terminals. The dynamic memory management method comprises obtaining the memory usage of a currently-running application in the mobile terminal; determining whether the memory usage of the currently-running application is higher than the corresponding memory upper limit of the application, which is correlated with the use condition of the application within a preset time period; if so, executing a memory cleaning operation or displaying a preset prompt message. According to the dynamic memory management method and the mobile terminal, the memory upper limit of the application is dynamically determined according to the use condition of the application within the preset time period, so that the memory upper limit of the application can be increased without updating hardware, the problem of jam of the application due to insufficient memory can be solved, and the user experience can be improved.
Owner:VIVO MOBILE COMM CO LTD
Method and computer system for memory management on virtual machine system
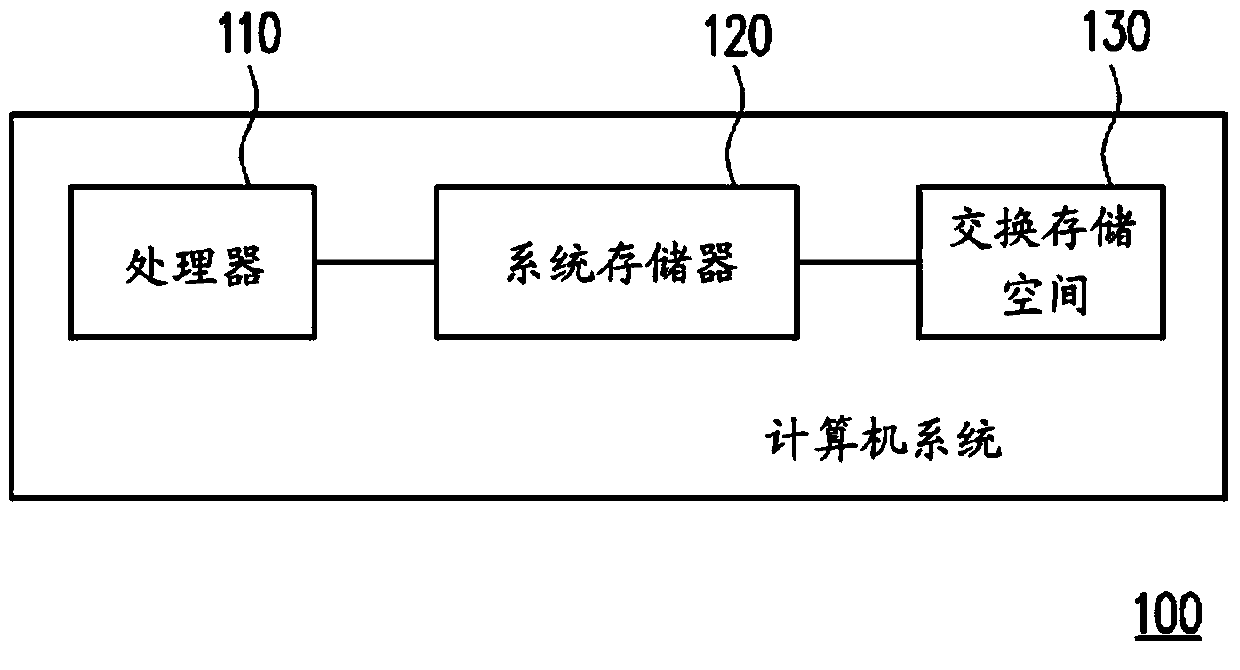
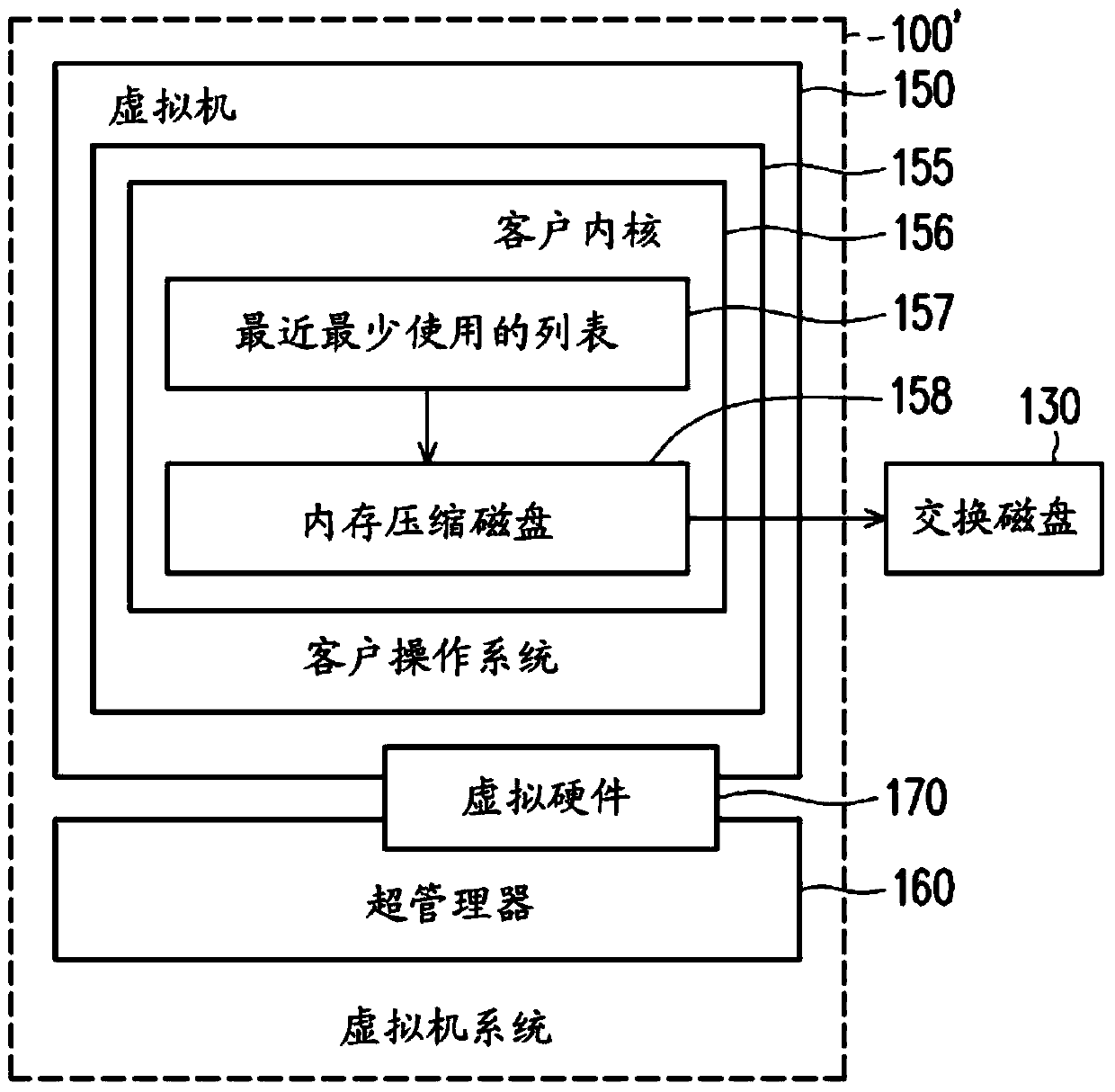
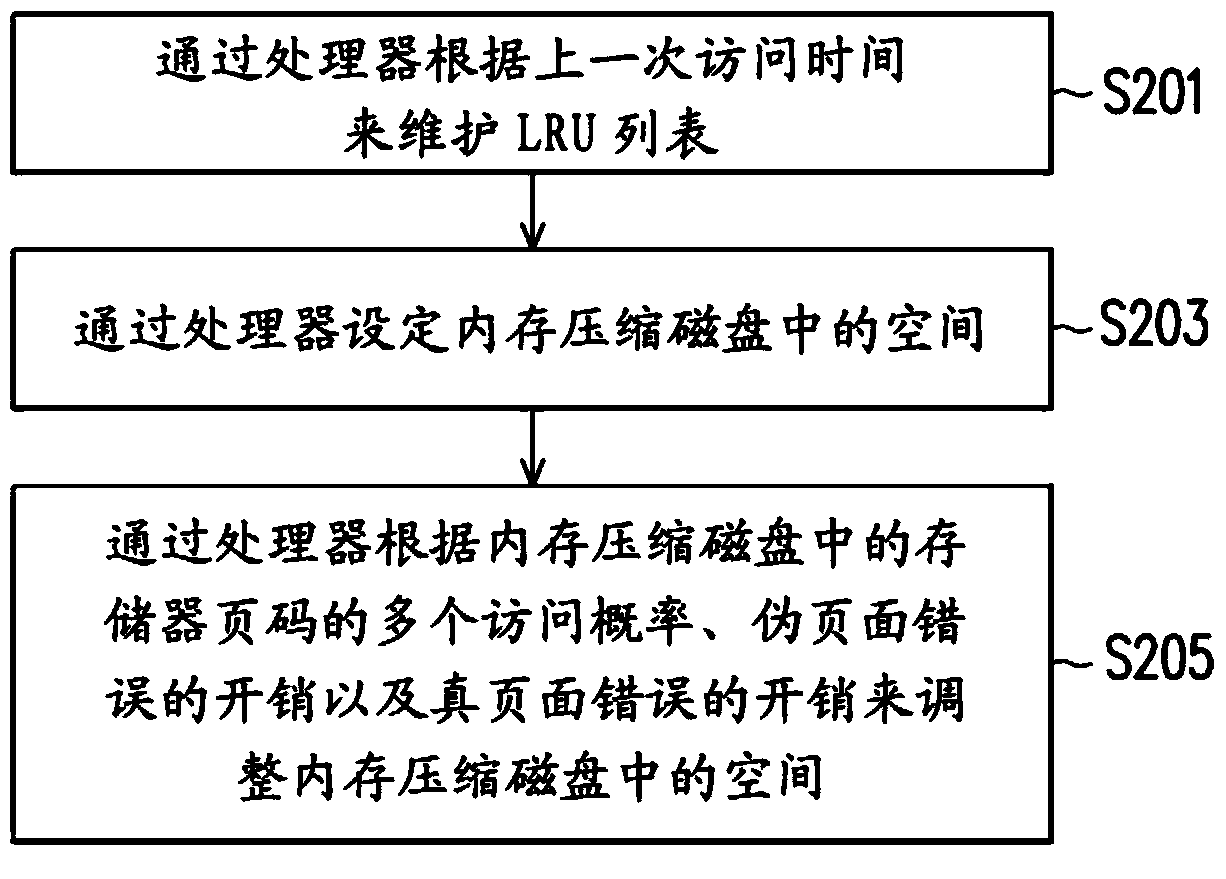
ActiveCN103729305AMemory adressing/allocation/relocationSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationAccess timeComputerized system
A method and a computer system for memory management on a virtual machine system are provided. The memory management method includes the following steps. A least recently used (LRU) list is maintained by at least one processor according to a last access time, wherein the LRU list includes a plurality of memory pages. A first portion of the memory pages are stored in a virtual memory, a second portion of the memory pages are stored in a zram driver, and a third portion of the memory pages are stored in at least one swap disk. A space in the zram driver is set by the at least one processor. The space in the zram driver is adjusted by the processor according to a plurality of access probabilities of the memory pages in the zram driver, an overhead of a pseudo page fault, and an overhead of a true page fault.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
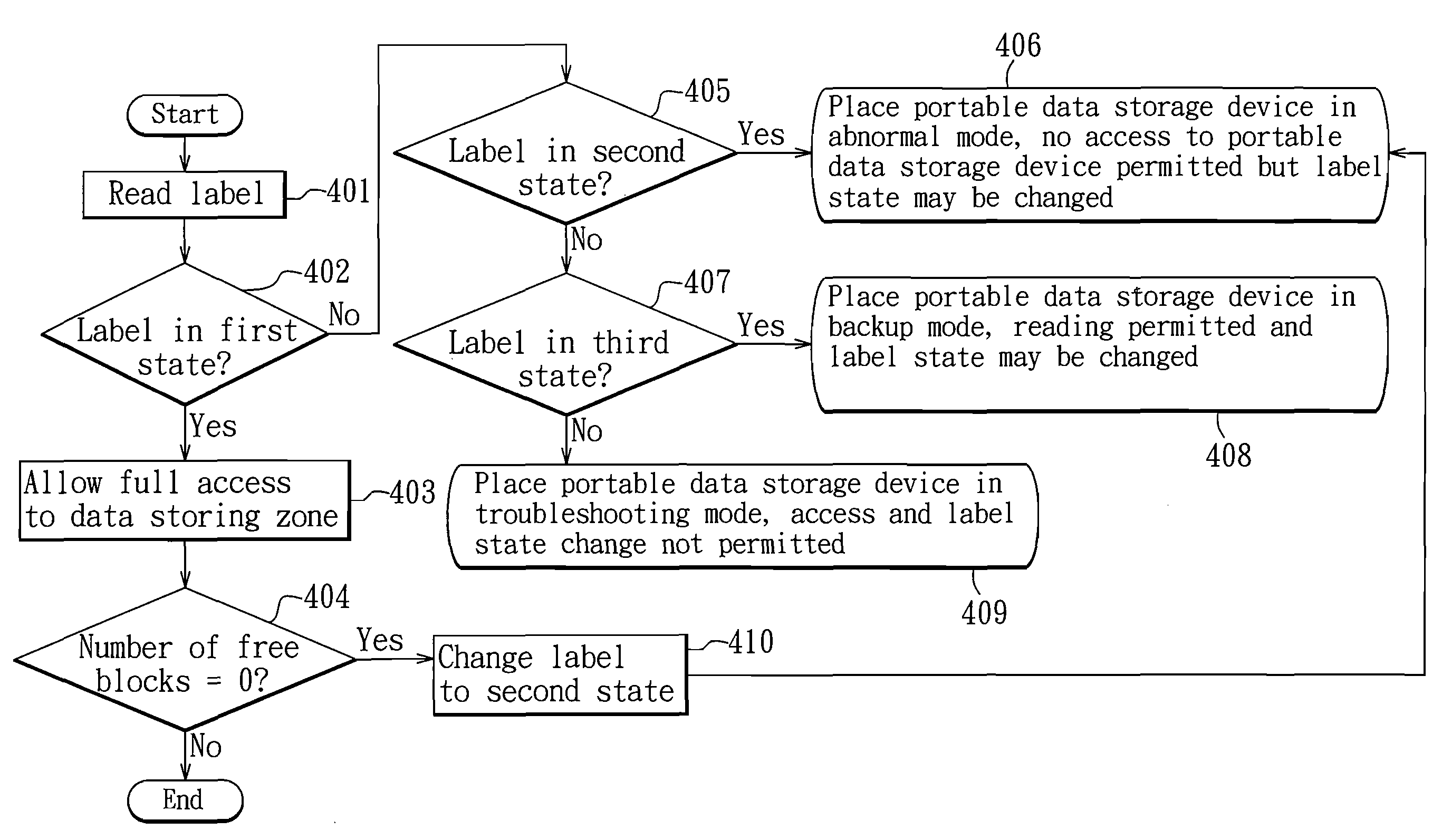
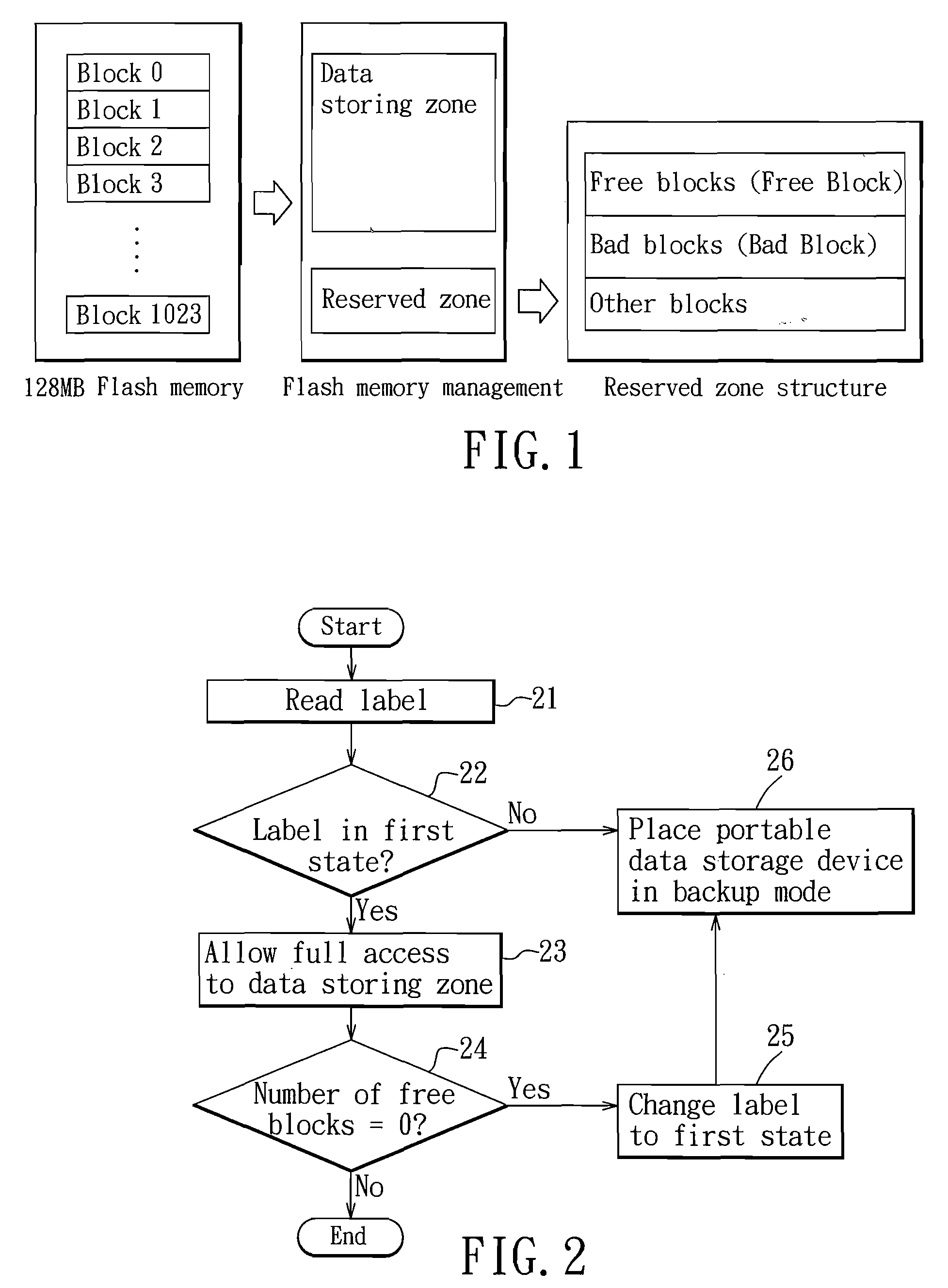
Method of dynamic memory management for a portable data storage device
InactiveUS20070260837A1Enabling changeMemory architecture accessing/allocationUnauthorized memory use protectionDynamic storageData storing
A method of dynamic memory management for a portable data storage device having a semiconductor memory includes: a) providing a state-changeable label used for setting an access state of a data storing zone of the semiconductor memory, the label being in one of a first state indicating access to data in the data storing zone is allowed, and a second state indicating access to the data in the data storing zone is restricted; b) allowing access to the data storing zone when the label is in the first state; and c) restricting access to the data storing zone when the label is in the second state.
Owner:APACER
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com