A Method for Determining the Stability of Dangerous Rock Mass in Environmental Slopes of Hydropower Projects
A technology for hazardous rock mass and environment, which is applied in basic structure engineering, excavation, climate change adaptation, etc. The actual problems of hydropower projects, etc., to avoid project investment, save construction period, and ensure the effect of safety
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
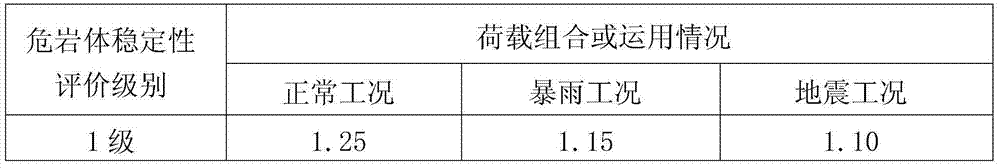
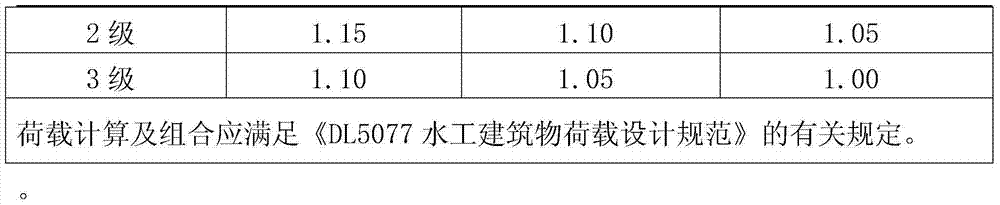
[0017] The 25# dangerous rock mass of Dadu River Shuangjiangkou Hydropower Station is located directly above the axis of the left dam abutment dam, on the steep cliff, with a distribution elevation of 2635-2731m and a cubic volume of 18900m 3 , is weakly weathered and strongly unloaded granite with a subfast structure. Under the action of weathering and unloading, the cracks open 5-10cm and are filled with debris and mud. Main cracks: ①N45°—55°W / SW∠50°—55°, along the slope; ②N70°—75°E / SE∠75°—80°, on the air surface; ③N25°—35°W / NE ∠50°—60°, reverse slope. Among them, the cracks along the slope form the bottom sliding surface, the air surface is parallel to the valley to form a nearly upright cliff, the cracks on the reverse slope form a lateral cut, the three groups of cracks cut each other, local weathering forms a cavity, and the stability is poor. It is prone to collapse under the influence of other factors. The main threat to the dam.
[0018] The 27# dangerous rock mass...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com