A ship celestial navigation method based on fuzzy matching of binary star vertex subdivided radian sets
A vertex segmentation and fuzzy matching technology, applied in astronomical navigation, navigation, surveying and navigation, etc., can solve the problems of inertial navigation equipment error, low positioning accuracy of positioning and navigation methods, and easy interference of satellite navigation signals. The effect of recognition and more accurate star recognition
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
[0021] Specific implementation mode one: combine figure 1 and figure 2 Describe this embodiment, the ship celestial navigation method of this embodiment based on the fuzzy matching of double-star vertex subdivision radian set includes the following steps:
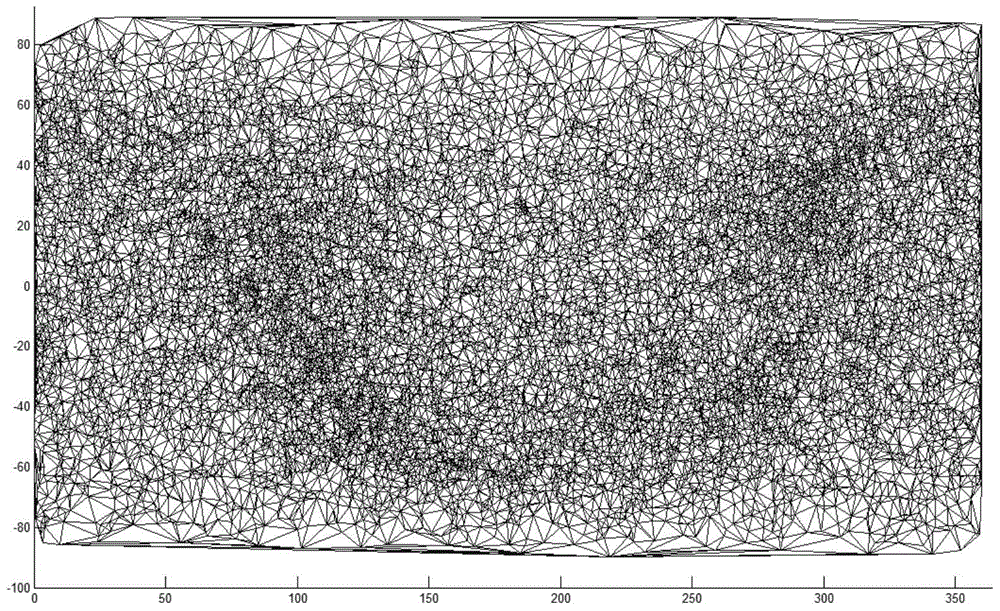
[0022] (1) Use the delaunay triangulation method to divide the Smithsonian star catalog and establish a characteristic star library;
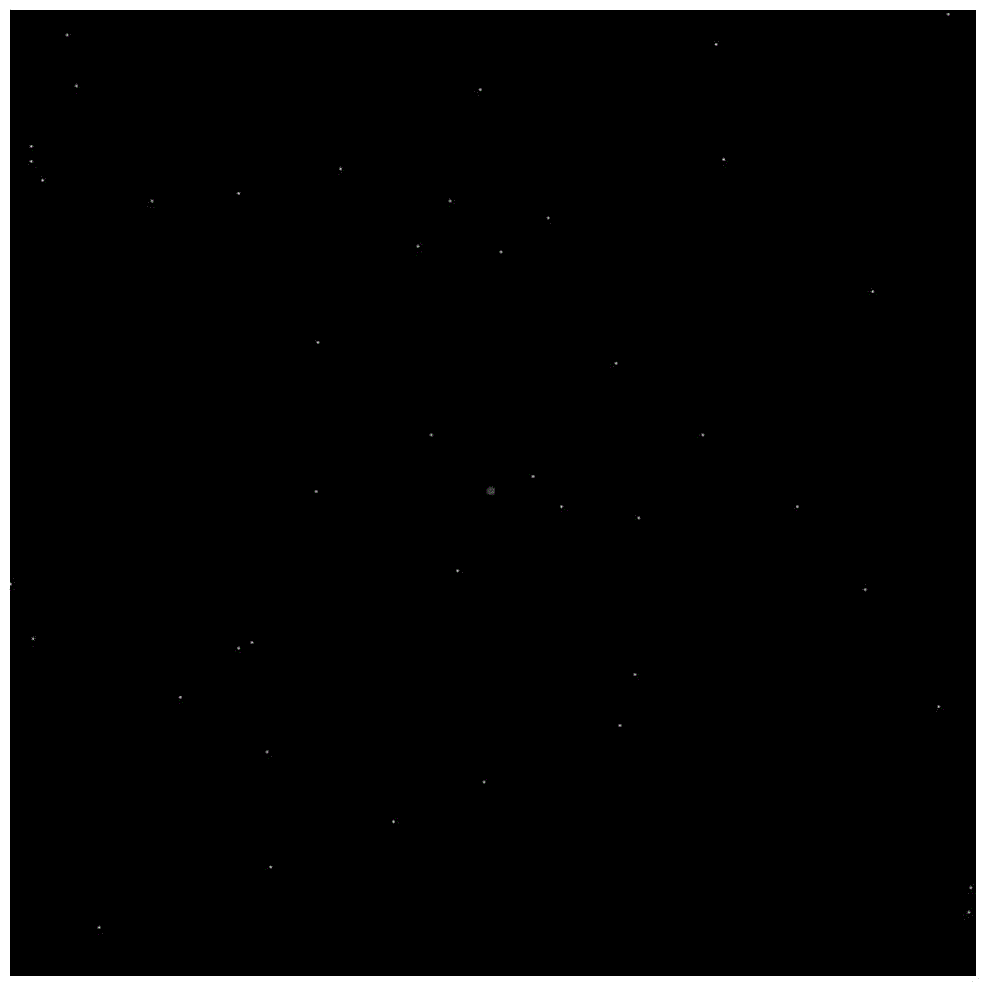
[0023] (2) Shoot the star map vertically above the plane of the ship, use the delaunay triangulation method to subdivide the star map, take out the adjacent double stars from the star map, take out the radian subdivision vectors of the double stars, and perform fuzzy matching in the feature star database to obtain two A possible star point feature vector X, Y, while reading the angle of inclination from the ship level;
[0024] (3) compare the star angular distance between the stars in two possible star point feature vectors X, Y, the star angular distance is the smallest is the desired s...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0026] Specific embodiment two: the difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment one is: the feature star library described in step (1) is to use the delaunay triangulation SAO star catalog, with each star as a feature mark, this star The different radian values divided by the 2π space around the star are stored in the database whose table structure is star name, radian value 1, radian value 2... radian value n, and become the feature star library.
[0027] Other steps and parameters are the same as those in Embodiment 1.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0028] Specific embodiment three: what this embodiment is different from specific embodiment one or two is: the radian subdivision vector of the binary star described in step (2) carries out fuzzy matching in feature star storehouse The specific steps are:
[0029] 1. Take out possible star point feature vectors X and Y in the star map;
[0030] Two, fuzzy comparison of each star point feature vector feature in the feature star library with possible star point feature vectors X and Y; wherein, the specific method of the fuzzy comparison is: by comparing the difference of each star point feature vector in the feature star library To describe the average value of the metric, the Cartesian product correspondence comparison method is used to find the closest element in the possible star point feature vector X, Y:
[0031] X×Y={(xi,yi)}{(x,y)|x∈X,y∈Y}
[0032] The above formula is represented by a matrix
[0033] x ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com