Distance measurement method for power distribution network ground fault based on zero-mode travelling wave difference
A technology of ground fault and ranging method, which is applied in the fault location and uses the pulse reflection method to detect faults, etc., can solve the problems of false fault points, ranging errors, and many branches of the distribution network, so as to improve the accuracy and reduce the cost. The effect of small random disturbances
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
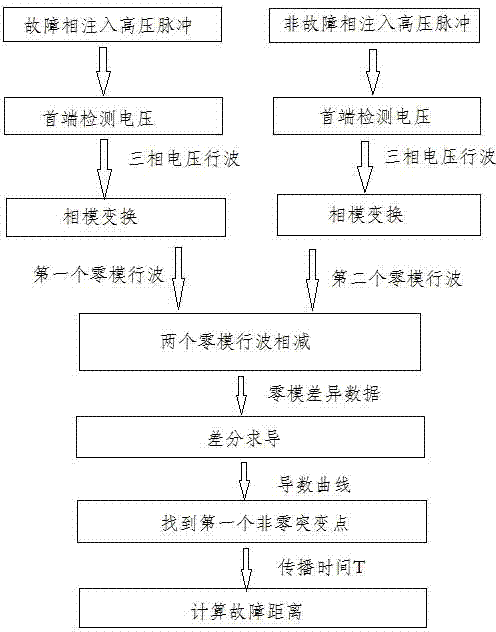
[0045] A distance measurement method for a distribution network ground fault based on zero-mode traveling wave difference, comprising the following steps:
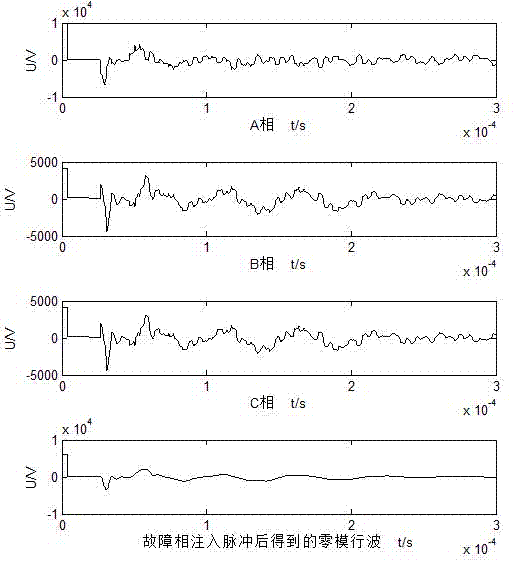
[0046] (A) Inject high-voltage pulses into the faulty phase at the first end of the distribution network, and detect the voltage traveling waves returned by the three phases. The voltage traveling waves returned by the three phases are transformed by phase mode to obtain the first zero-mode voltage traveling wave data; the injected high voltage The pulse is a high-voltage pulse with a pulse width of Xμs and an amplitude of YkV, such as image 3 , detect the voltage traveling wave returned by the three phases and obtain the corresponding zero-mode voltage traveling wave;
[0047] (B) Inject a high-voltage pulse consistent with step (A) into a non-faulty phase at the head end of the distribution network, and detect the voltage traveling waves returned by the three phases. The traveling voltage waves returned by the three pha...
Embodiment 2
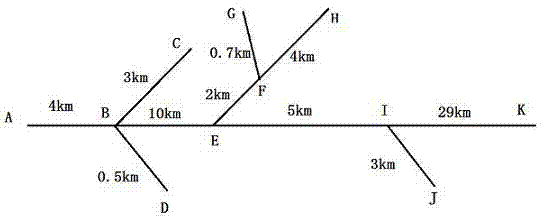
[0065] Such as figure 1 As shown, this embodiment is an experiment of single-phase ground fault distance measurement in a distribution network, using the Frequency Dependent Models in PSCAD (Power Systems Computer Aided Design); figure 2 It is the structure diagram of the experimental circuit, A is the head end of the line (that is, the detection point), and the end of each branch is connected with a 10kV / 0.4kV distribution transformer (Dyn or Yyn connection) and a three-phase unbalanced load, and the sampling frequency is 10MHz. Setup failure occurs at figure 2 For the EI section line from point E to point I, the grounding resistance is 100Ω, and the distance from the head end is 17km. The above is the element setting.
[0066] First, a high-voltage pulse with a pulse width of 4μs and an amplitude of 10kV is injected into the faulty phase at the head end of the line (at point A), and the voltage traveling wave returned by the three phases is detected, and used Get the f...
Embodiment 3
[0068] A distance measuring method for a distribution network ground fault based on zero-mode traveling wave difference, comprising the following steps: wherein phase A is a fault phase, and phase B and phase C are non-fault phases;
[0069] (A) Inject high-voltage pulses into phase A (faulty phase) at the head end of the distribution network, and detect the traveling voltage waves returned by the three phases. The traveling voltage waves returned by the three phases are transformed by phase mode to obtain the first zero-mode voltage traveling wave data ; The injected high-voltage pulse is a high-voltage pulse with a pulse width of Xμs and an amplitude of YkV, such as image 3 , detect the voltage traveling wave returned by the three phases and obtain the corresponding zero-mode voltage traveling wave;
[0070] (B) Inject a high-voltage pulse consistent with step (A) into phase B (non-fault phase) or phase C (non-fault phase) at the head end of the distribution network, and de...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com