Radar time resource joint distribution method related to residence time and re-access interval
A dwell time and joint allocation technology, applied in the direction of radio wave reflection/re-radiation, using re-radiation, measuring devices, etc., can solve the problem of limiting resource optimization effects, unsatisfied revisit time interval, revisit time interval and other resources Problems such as inability to allocate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0077] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with accompanying drawing:
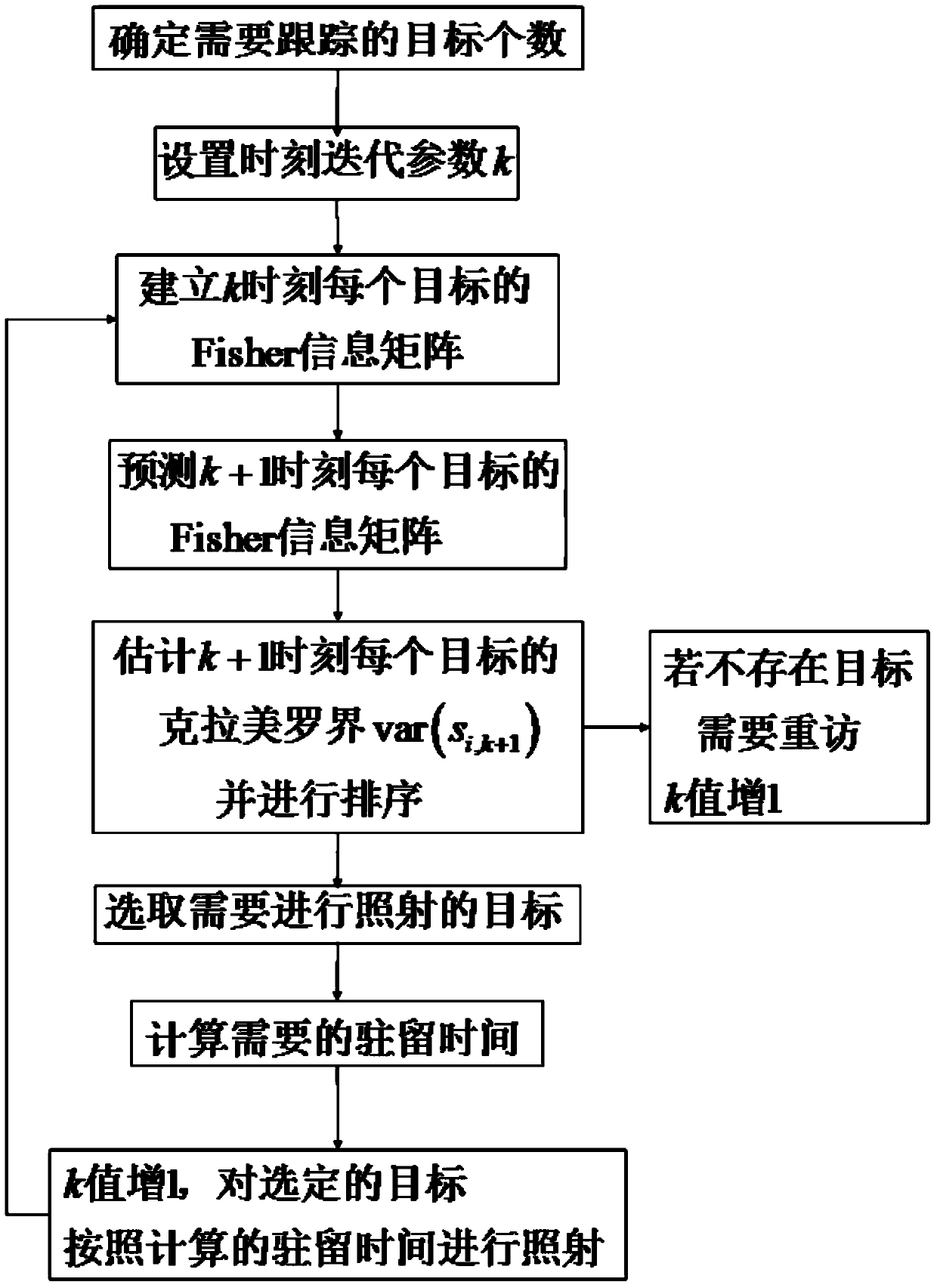
[0078] refer to figure 1 , is a flow chart of the method for jointly allocating radar time resources of dwell time and revisit interval in the present invention. The radar time resource joint allocation method about dwell time and revisit interval includes the following steps:
[0079] Step 1. At the initial moment, the number N of targets that the radar needs to track at the initial moment is determined through the radar's current detection information and previous tracking information. Set 0 time, the 0 time is the initial time, set the time iteration parameter k, k=0,1,2...; when k=0, execute step 2; in the embodiment of the present invention, the radar is phase Control array radar.
[0080] Step 2: Establish the initial Fisher information matrix of each target at time k.
[0081] Its specific sub-steps are:
[0082] (2.1) According to the radar observation data of ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com