Methylacrylic acid (MAA) contained medical polylactic acid (PLA) derivative material
A technology of polylactic acid and copolymer, which is applied in the field of preparation of degradable polylactic acid materials and block polymer materials, to achieve the effects of reducing toxic and side effects, good biocompatibility, and high drug loading capacity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0023] ①Preparation of star block copolymer
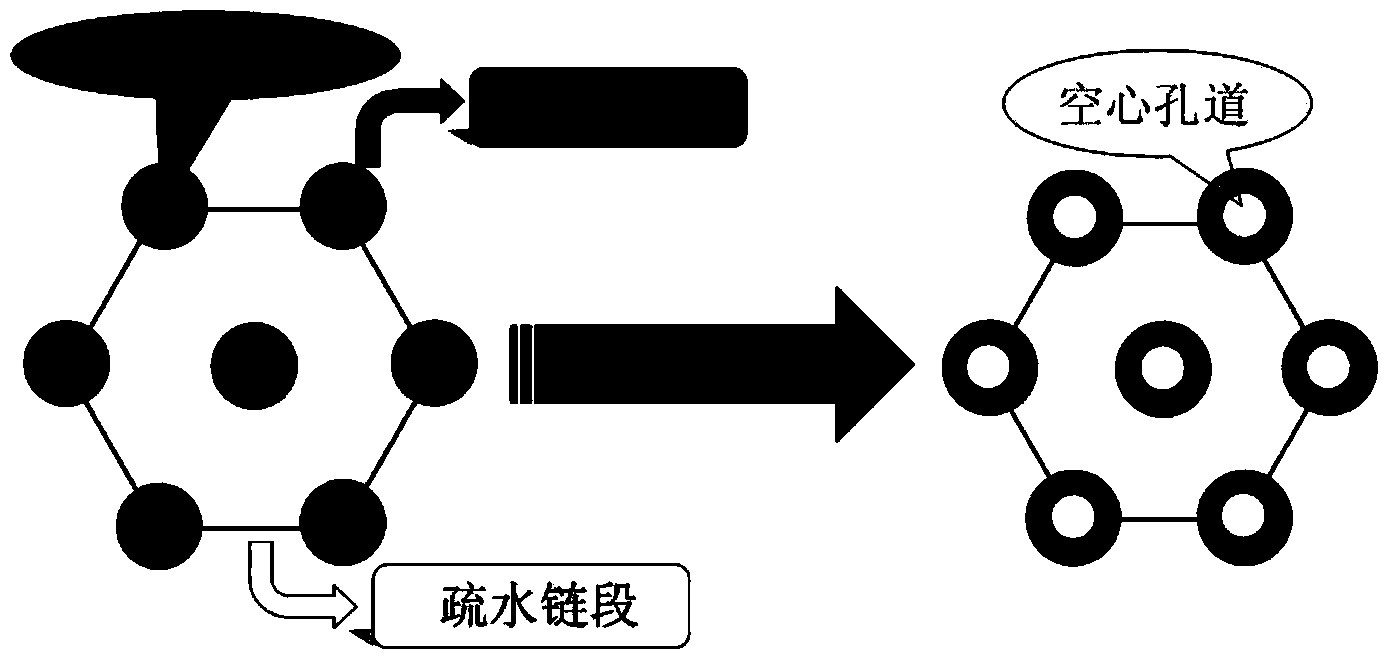
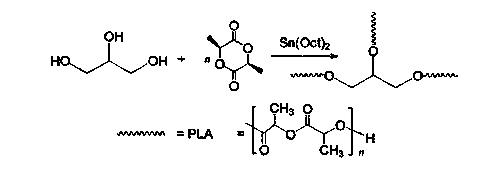
[0024] Using L-lactide as raw material, a three-armed or multi-armed star-shaped polylactic acid was synthesized by the classic stannous octoate-catalyzed ring-opening method. After the reaction, the star-shaped macromolecular initiator SPLA-Br with bromine terminal functional groups was obtained. The macroinitiator and MAA were subjected to ATRP polymerization in a certain ratio to obtain a star-shaped block polymer with PLA as the core PMAA.
[0025] ②Characterization of the self-assembled structure and properties of star-shaped block copolymer materials
[0026] The chemical structure and morphology of polymers are the basis for studying the properties of polymers. This topic intends to use gel permeation chromatography (GPC), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) and nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) methods to detect the chemical structure and degree of polymerization of polymers, and use thermogravimetric analysis (...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com