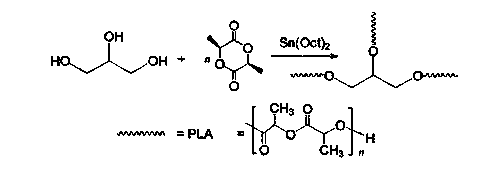
Patents
Literature
52results about How to "High drug load" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Polyethylene glycol-cactus oligopeptide bonded rapamycin derivative
ActiveCN104448295AHigh drug loadIncrease diversityOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderImmunologic disordersDisease
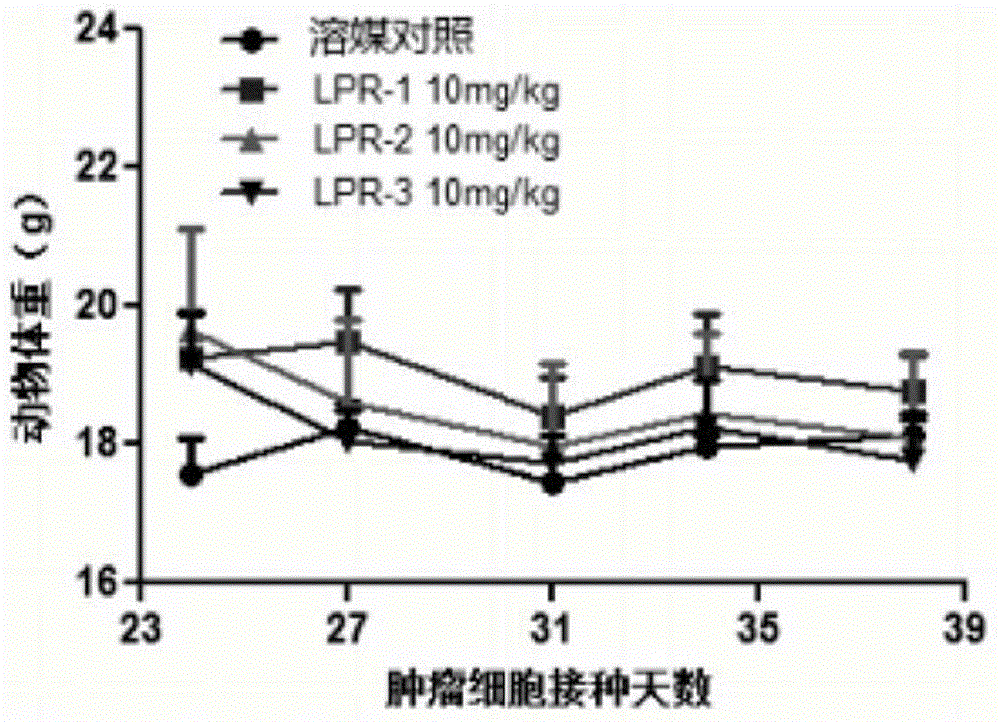
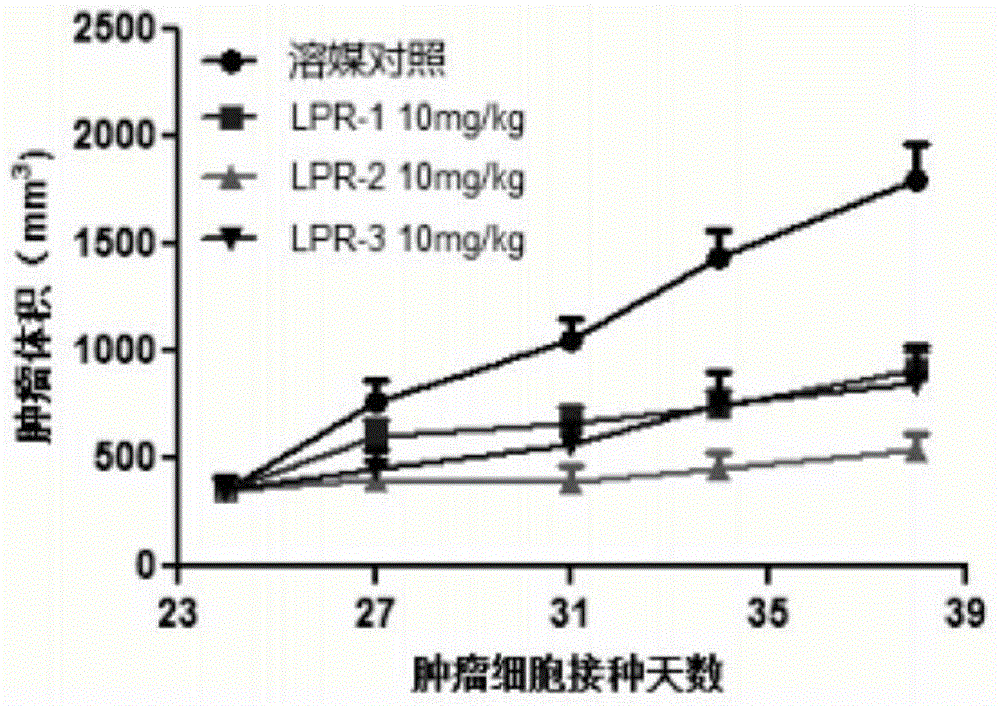
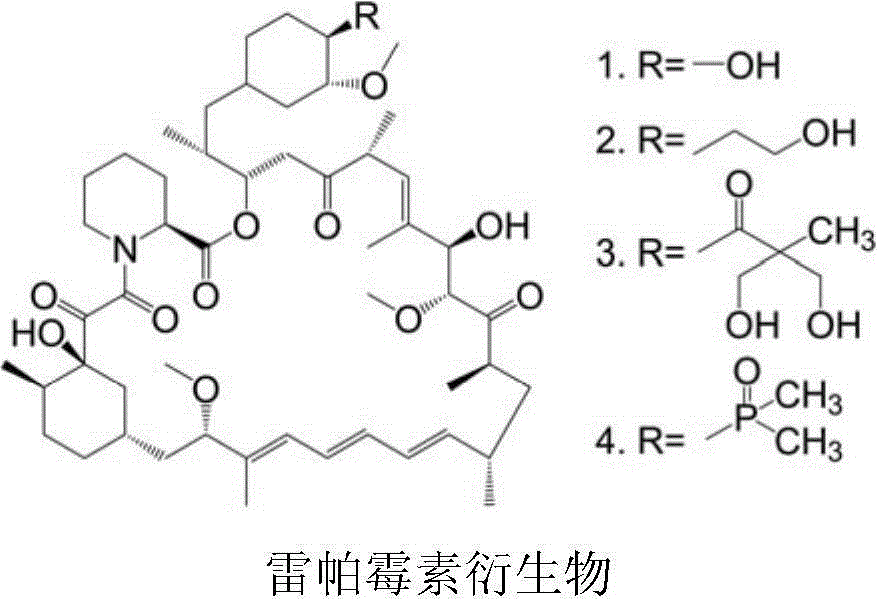
The invention provides a compound shown in the formula I in the specification and pharmaceutically acceptable salts of the compound, the preparation method of the compound and pharmaceutically acceptable salts of the compound and a medicine composition containing the compound shown in the formula I or the pharmaceutically acceptable salts of the compound. In the compound provided by the invention, each end group of the polyethylene glycol molecule is capable of bonding with a plurality of rapamycin molecules through cactus oligopeptide, and the medicine loading rate is improved. The compound can be used for inducing immunosuppression and treating transplant rejection, self-immune diseases, solid tumors, fungal infection and cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases.
Owner:JENKEM TECH
Heparin or heparin salt modified graphene oxide and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN105343890ALarge specific surface areaSynergistic therapeutic effectOrganic active ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsSolubilityRedox
The present invention discloses heparin or heparin salt modified graphene oxide and a preparation method and application thereof, the modified graphene oxide can be used as a drug, particularly an anti-cancer drug carrier material. By use of pH sensitive principle, adipic dihydrazide is used as a linker molecule, or by use of redox principle, cystamine is used as a linker molecule, heparin is used for chemically modifying graphene oxide, and the heparin has the advantages of increase of water solubility and anti-cancer drug tumor synergistic effect of graphene oxide, and solves the problems of poor water solubility and easy aggregation and the like of the graphene oxide.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Modified halloysite nanotube composite slow release pesticide and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN106212450AHigh drug loadLong release periodBiocideDead animal preservationGrowth plantHalloysite
The invention discloses modified halloysite nanotube composite slow release pesticide and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of agricultural slow release pesticide. According to the technical scheme, the method comprises the steps of 1, halloysite purification; 2, organic modification of halloysite; 3, preparation of the halloysite composite slow release pesticide. The prepared modified halloysite nanotube composite slow release pesticide is used in farmland as slow release pesticide, the utilization rate of a herbicide or insecticide or an antibacterial agent or a plant growth regulator is increased, and pollution to the environment and a water source is reduced.
Owner:HENAN NORMAL UNIV
Preparation method and application of photothermal double stimulation response hydrogel containing alpha-cyclodextrin
ActiveCN110423307AChange water solubilityHigh drug loadDrug photocleavageAerosol deliveryWater bathsDouble stimulation
The invention belongs to the technical field of environmental functional material preparation, and relates to a preparation method and application of a photothermal double stimulation response hydrogel containing alpha-cyclodextrin. The method comprises the following steps: firstly preparing alpha-cyclodextrin ester and acrylamido azobenzene, adding the alpha-cyclodextrin ester, the acrylamido azobenzene, methylene bisacrylamide and isopropylacrylamide into a dimethyl sulfoxide solution, and performing ultrasonic shaking to obtain a mixed solution B; adding 2,2'-azobis(2,4-dimethyl)valeronitrile into a dimethyl sulfoxide solution to obtain a mixed liquid D; and finally, adding the mixed liquid D into the mixed liquid B, after mixing is completed, performing a reaction in a water bath to obtain the photothermal double stimulation response hydrogel. According to the method provided by the invention, the cyclodextrin and the photo and temperature structure response units are introduced into the hydrogel prepared by the method, so that the hydrogel can load a large amount of drug molecules, and when an external temperature and an illumination wavelength are changed, the hydrogel can have responsive change of adjusting a release speed of the drug molecules in time; and at the same time, the method is simple and convenient to operate, and the prepared hydrogel is safe and environmentally friendly and has good stability.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Preparation method and application of pH-responsive dual-drug-release metal-organic framework-upconversion nano-system
InactiveCN109172587AReduce forming sizeEasy to manufacturePowder deliveryOrganic active ingredientsSolubilityPolymer modified
The invention discloses a preparation method of a pH-responsive dual-drug-release metal-organic framework-upconversion nano-system. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: adopting apolymer modification method to improve the water solubility of the upconversion nano-crystal with a core-shell structure, and growing a metal-organic framework on the surface of the upconversion luminescent nano-crystal to obtain an upconversion nano-system coated with the metal-organic framework; and attaching Adriamycin hydrochloride containing amino group to the surface of the metal-organic framework, and adsorbing other anticancer drugs into the porous structure of the metal-organic framework to obtain the double-drug-loaded metal-organic framework-up-conversion nano-system. The nano system provided by the invention has good stability, good biocompatibility, simple and reliable preparation method and good repeatability. The nanosystems have tumor diagnostics-Therapeutic integration canbe used as an imaging agent for fluorescence imaging and magnetic resonance imaging, as well as drug delivery and pH-responsive dual drug release, and can be used as a drug carrier.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
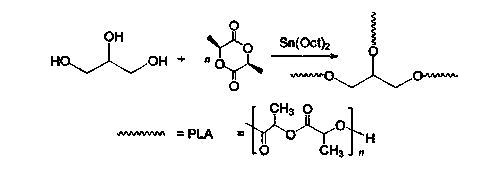
Preparation method for degradable porous polyethylene glycol
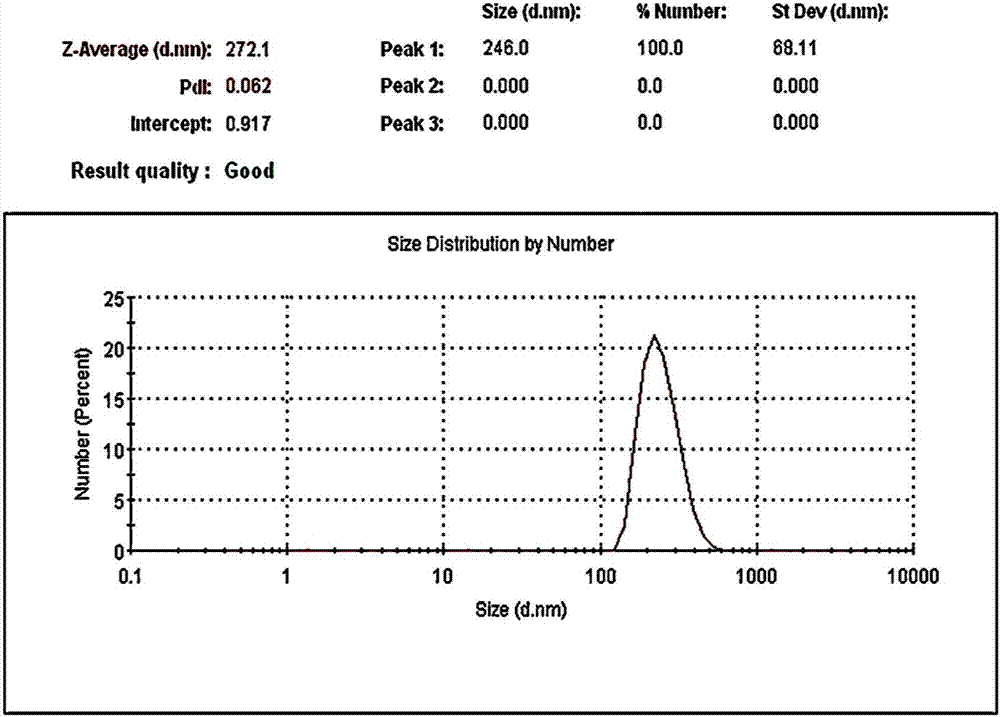
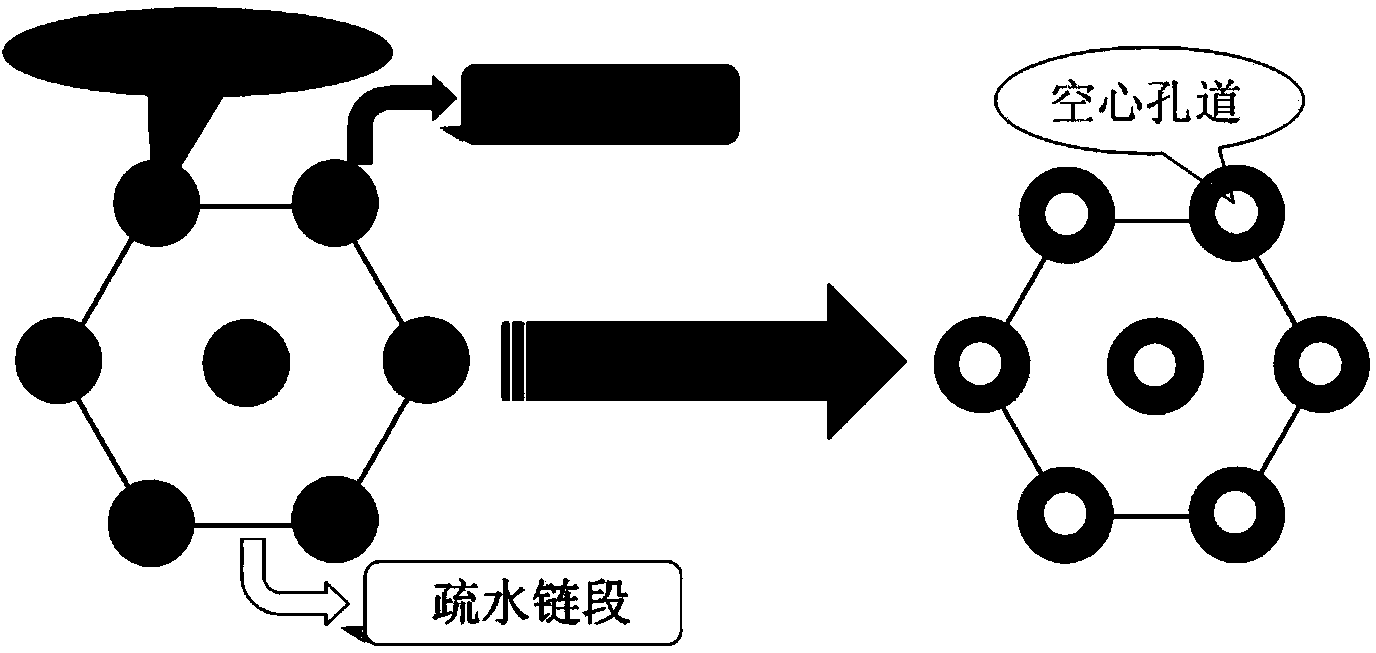
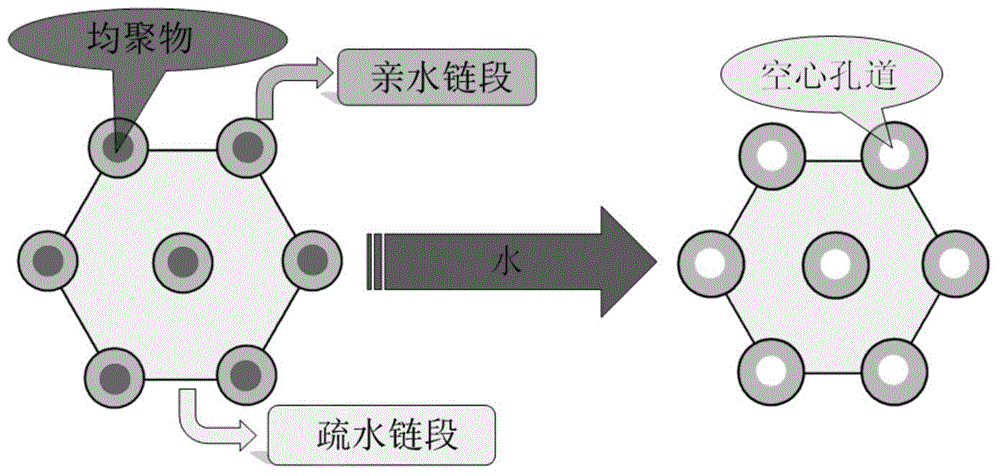
InactiveCN103980487AHas a nanoscale microporous structureHigh drug loadPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsPolymer sciencePolyethylene glycol
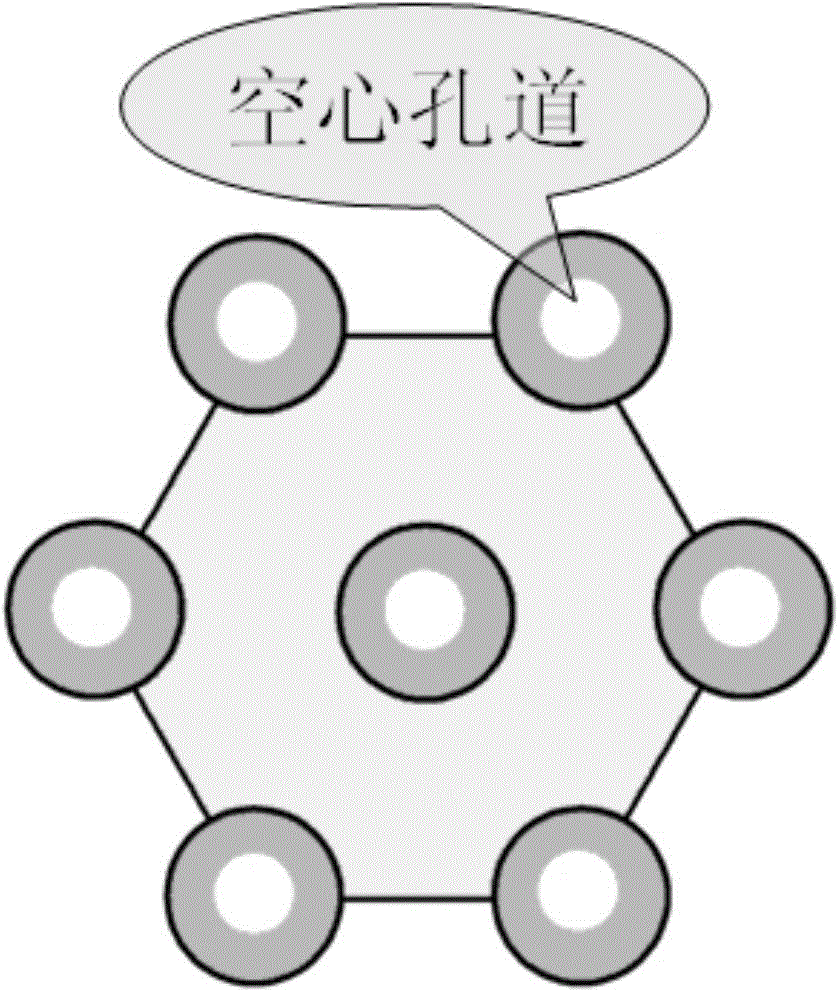
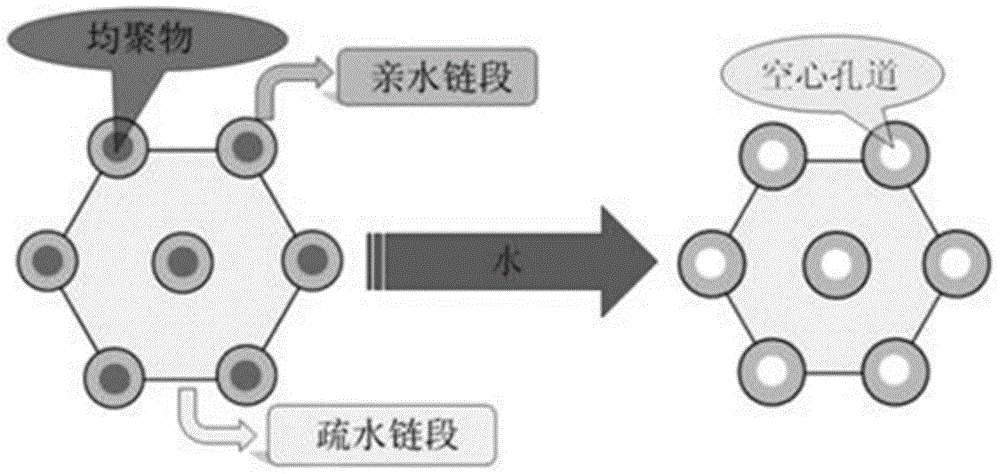
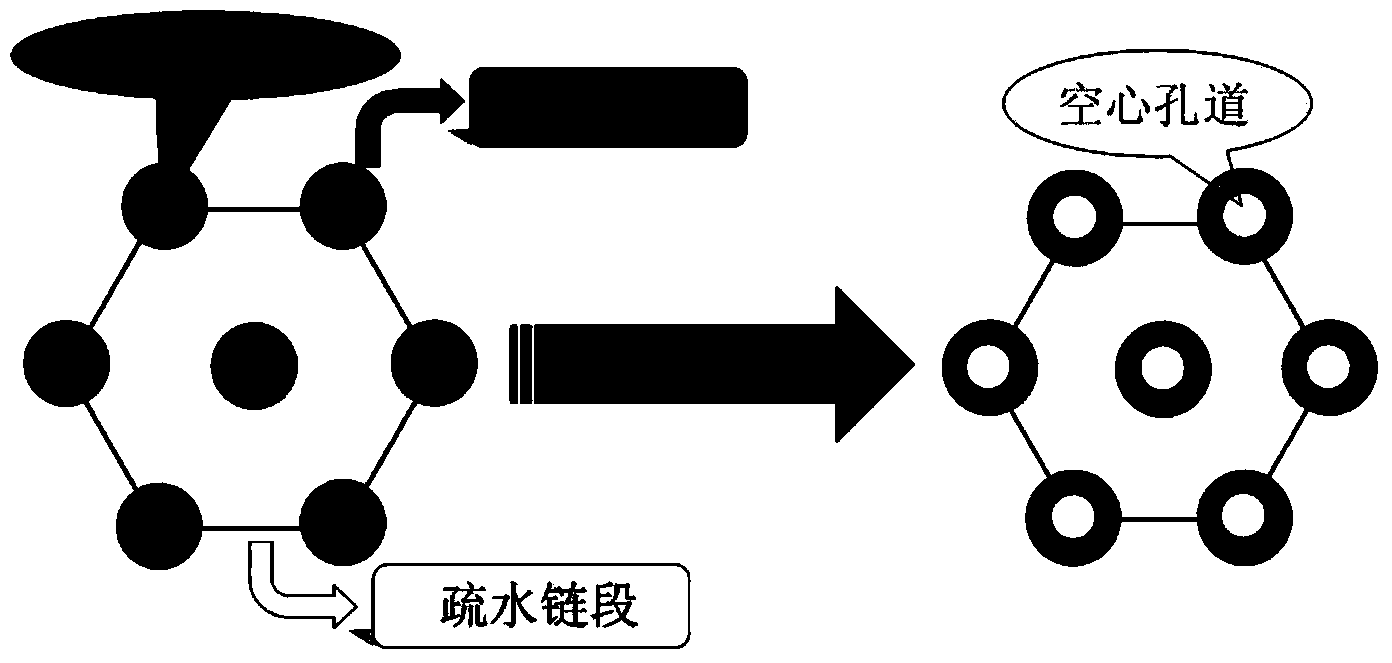
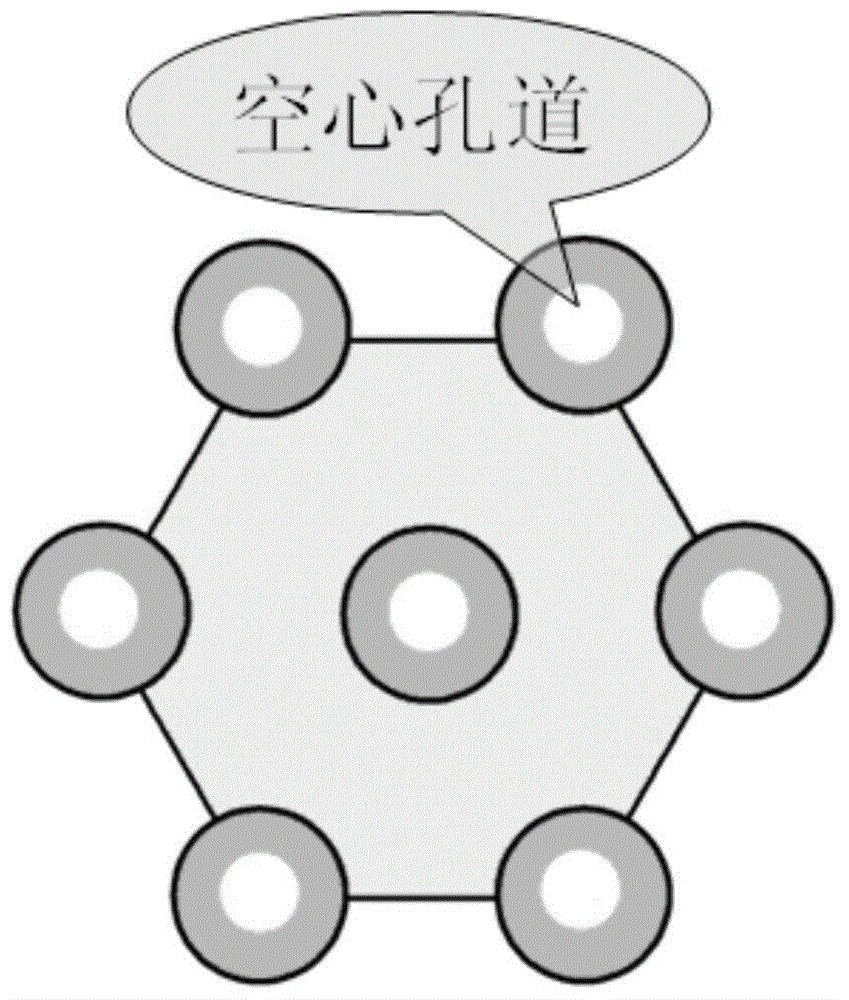
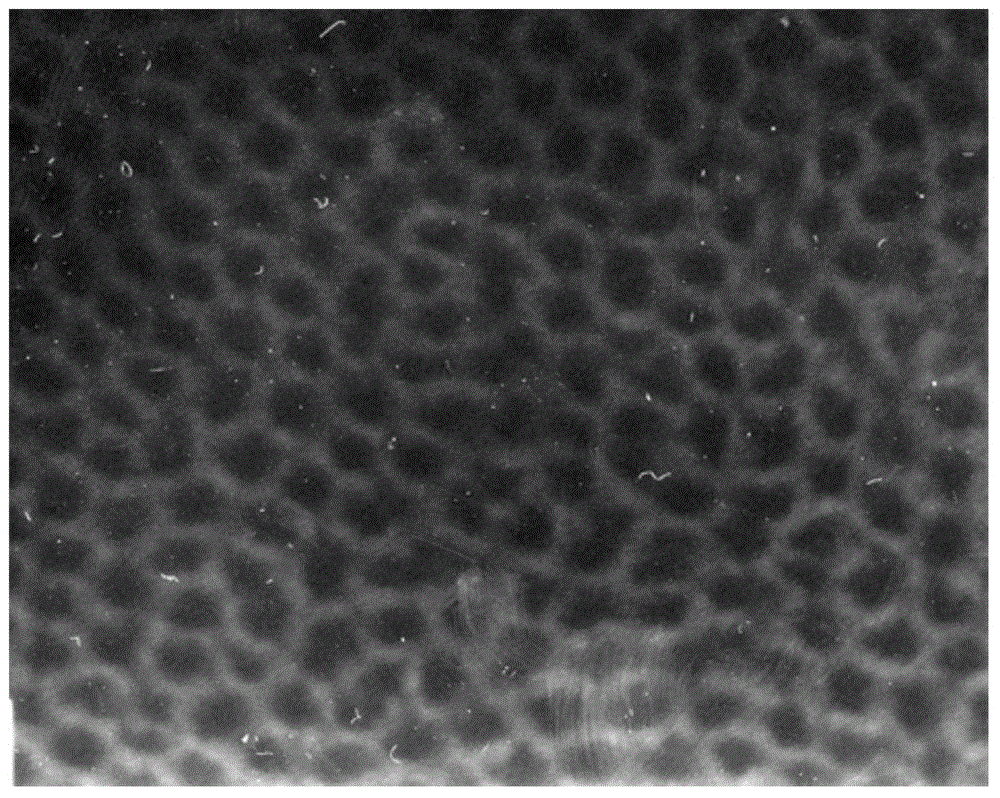
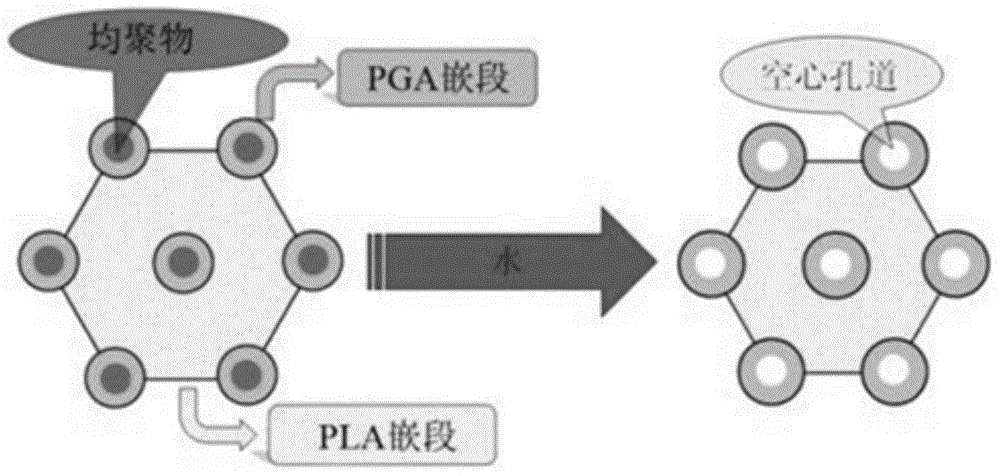
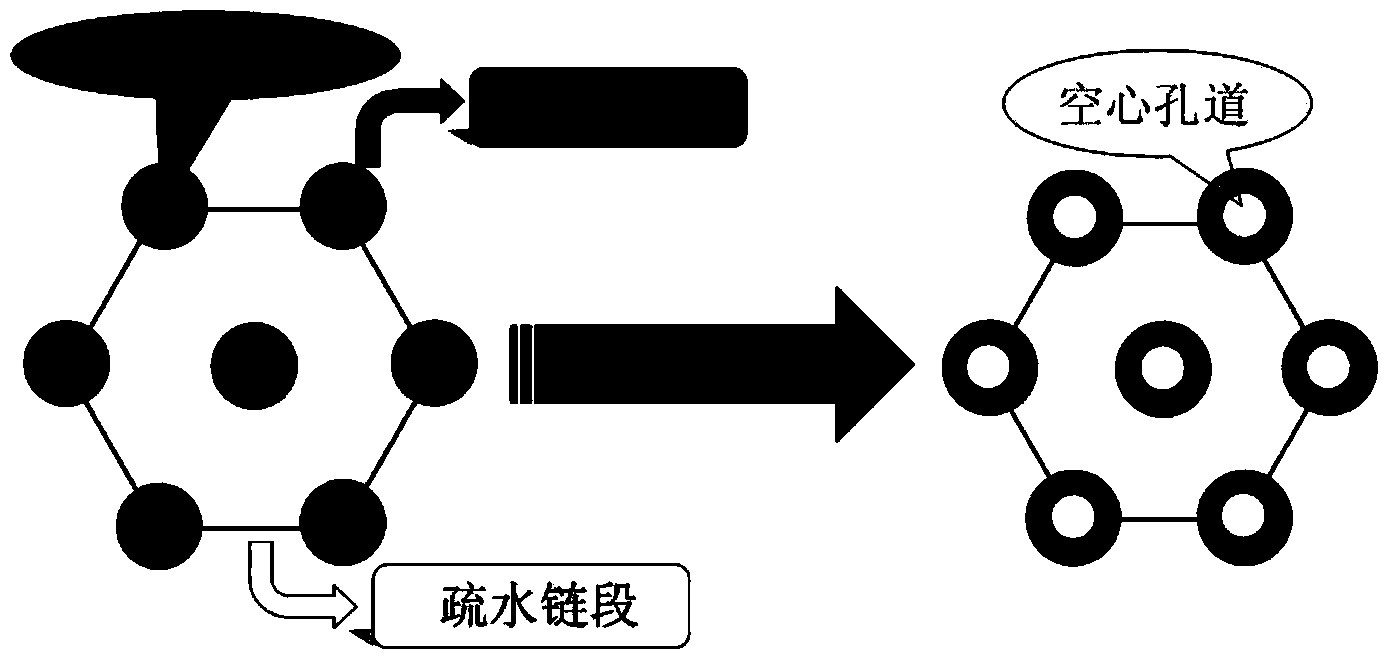
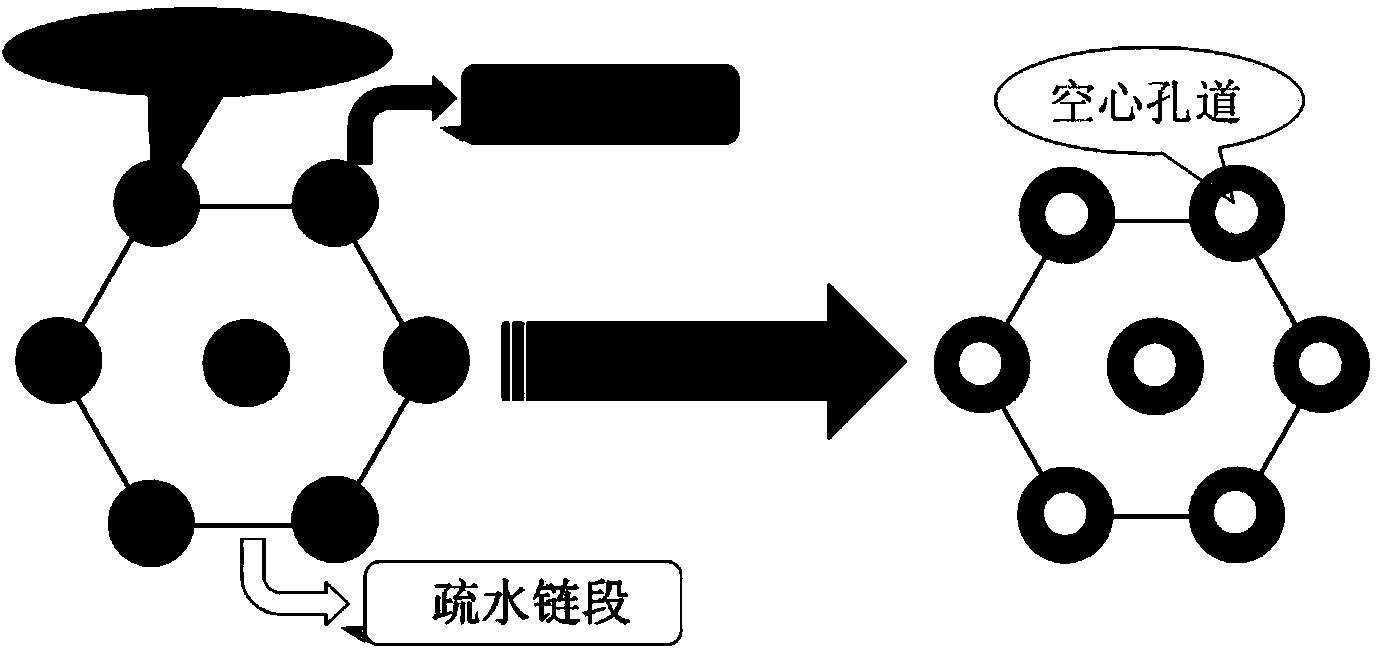
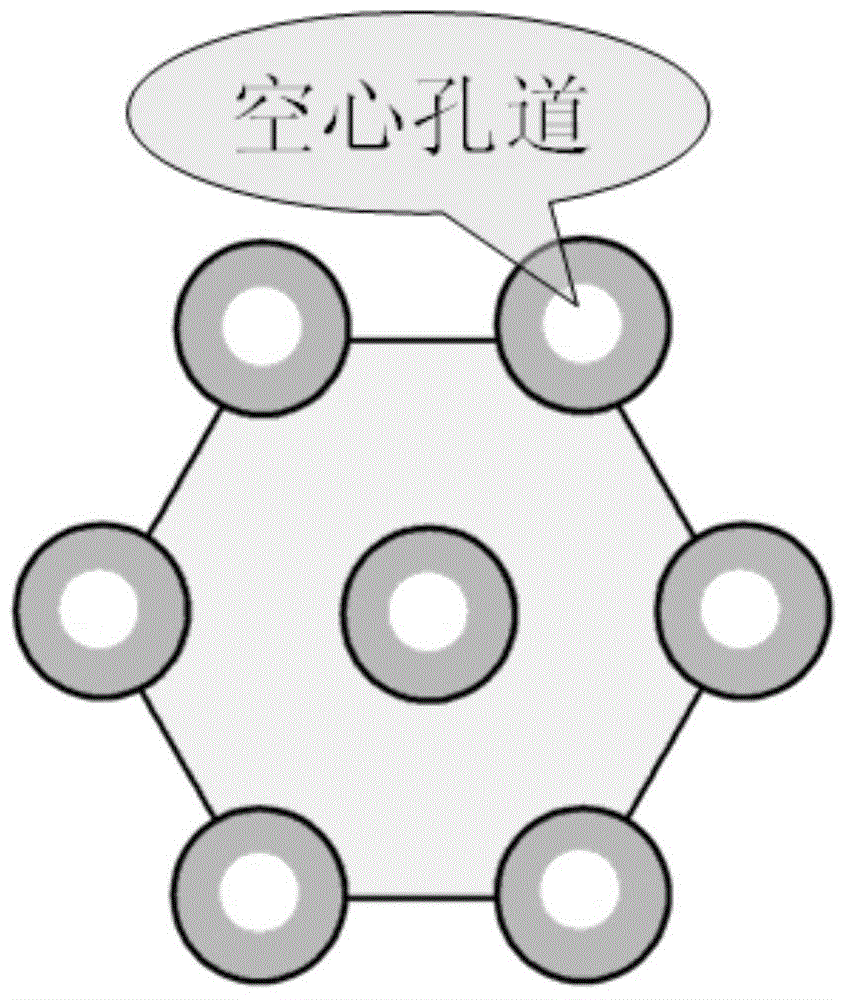
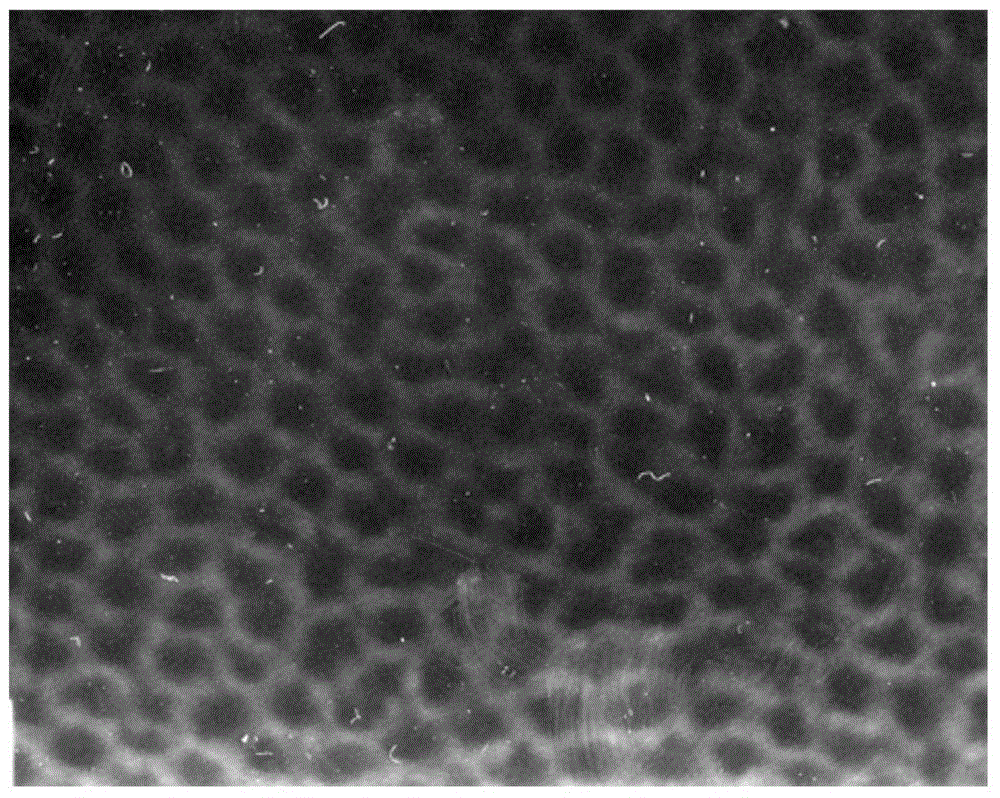
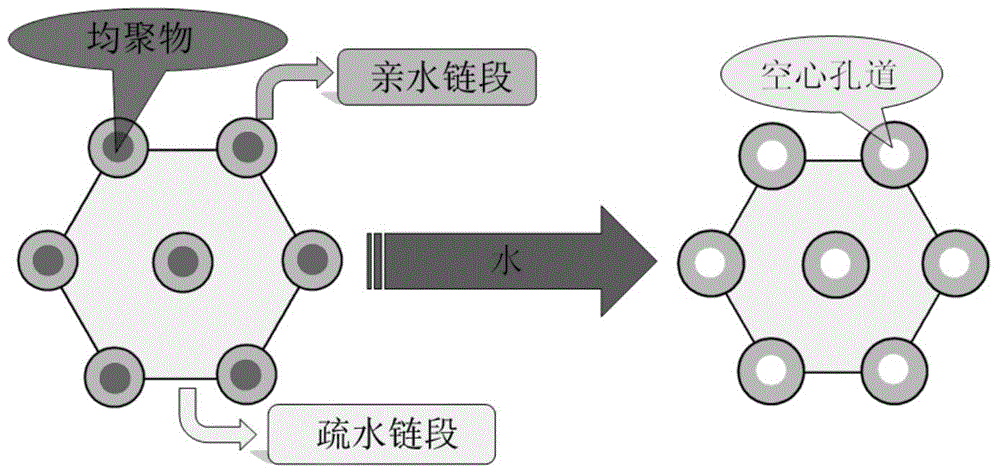
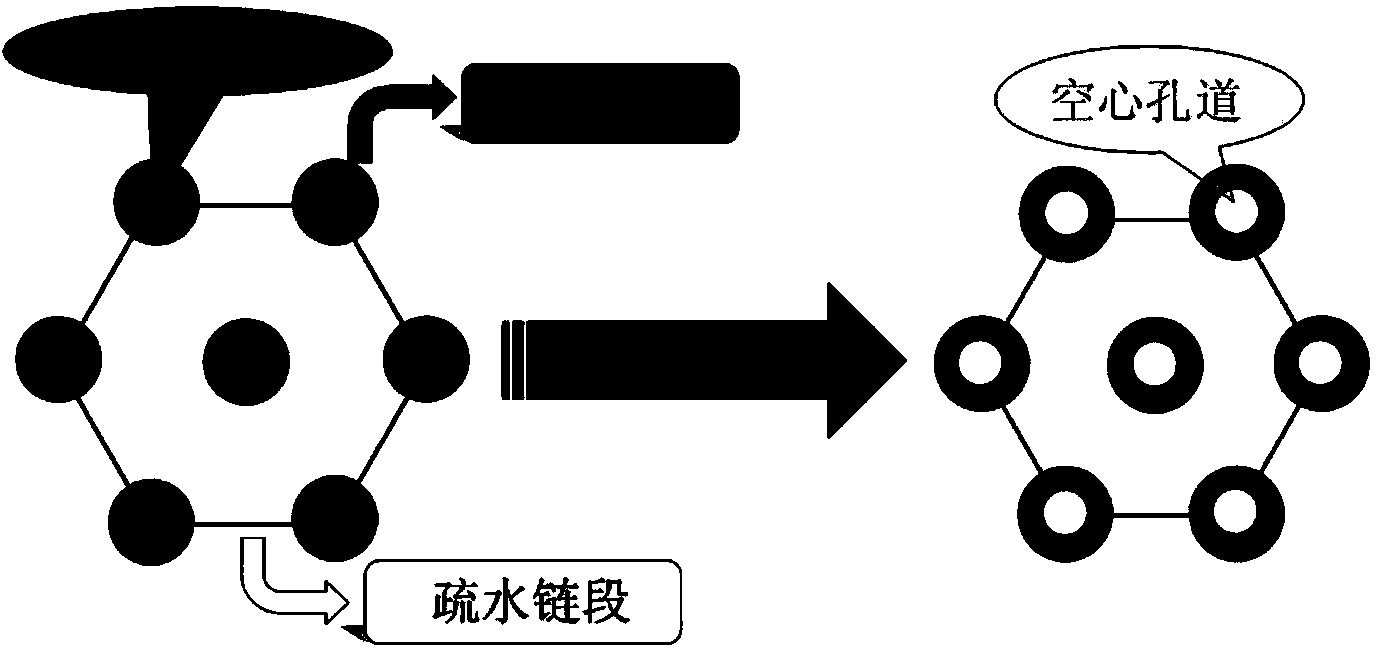
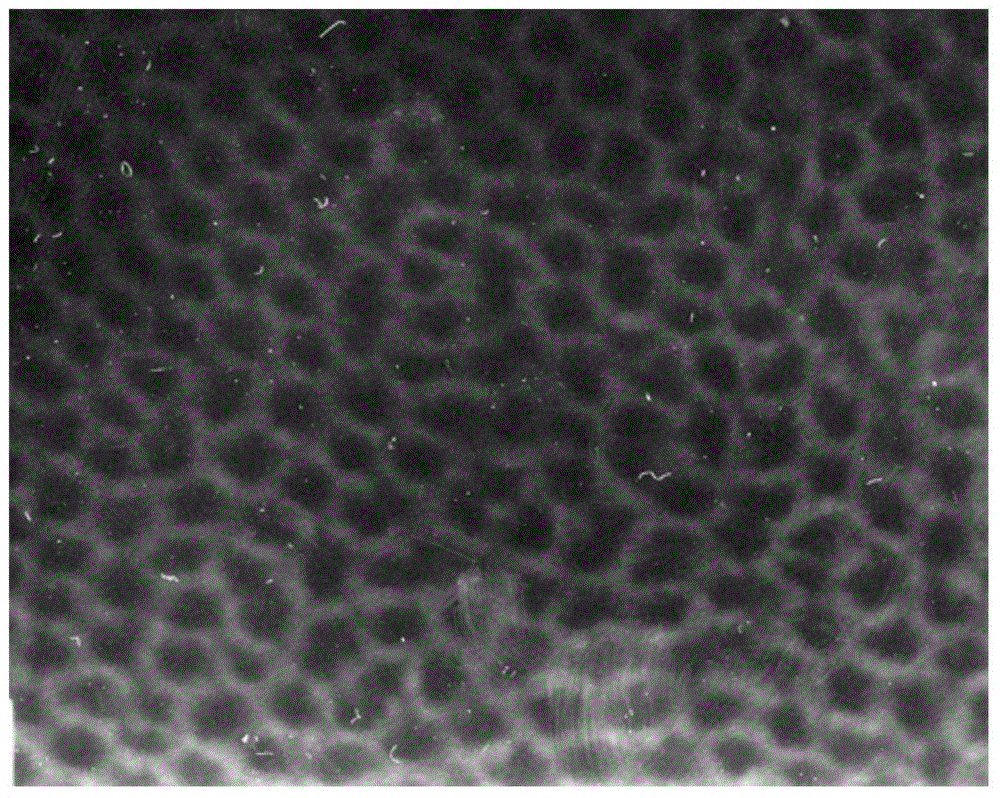
The invention discloses a preparation method for degradable porous polyethylene glycol. The preparation method comprises the following steps: with oxirane as a raw material, synthesizing three-arm polyethylene glycol by using an alkaline ring opening process; preparing a macro-molecular initiator; carrying out ring-opening polymerization with gamma-benzyl-L-glutamate-carboxylic acid anhydride (NCA) so as to obtain a star-block copolymer with PEG as a core and poly(gamma-benzyl-L-glutamate) as an arm; removing a benzyl protective group in poly(gamma-benzyl-L-glutamate) through hydrolysis so as to obtain a star polyethylene glycol / polyglutamic acid block copolymer; and adding low-molecular-weight polyglutamic acid and dissolving the block copolymer with water by using amphipathicity of the block copolymer so as to form a nanometer porous material. The block copolymer has a hexagonal prism-like structure, the continuous phase of the block copolymer is polyethylene glycol, and the material has nanometer holes. The material has nanometer holes, overcomes the disadvantage of poor processability of a traditional linear polyethylene glycol material, exerts no toxic and side effects and can be used as a drug carrier material, a medical implant material and a material for a part of an in-vivo continuous dosing apparatus.
Owner:CHENGDU LVKE HUATONG TECH
Method for preparing nano drug-carrying capsule-loaded alginate fibers
ActiveCN103436992AHigh drug loadIncrease loadAlginate artificial filamentsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsFiberSpinning
The invention discloses a method for preparing nano drug-carrying capsule-loaded alginate fibers. The method comprises the steps of preparing a nano drug-carrying capsule by taking sodium alginate as a matrix; adding the nano drug-carrying capsule in a sodium alginate spinning solution; and preparing nano drug-carrying capsule-loaded alginate fibers through wet spinning. According to the method, the loss of drugs in the spinning process can be reduced, and because a drug is wrapped in the capsule, so that the drug can be effectively prevented from degenerating, and different kinds of drugs can be loaded in the capsule. In addition, the capsule is prepared by taking sodium alginate as the matrix, compared with homogeneous fibers, the alginate fibers have good interface compatibility, and the drug-carrying capsule is in nanoscale, does not affect the spinnability and the final fiber performances of the sodium alginate spinning solution. The method disclosed by the invention can be applied to medical materials such as dressings, gauzes, bandages, drug patches, drug pads and the like, and achieves the effects of reducing wound infection and inflammation possibility, stimulating cell proliferation and implementing other actions so as to accelerate wound healing; the method is also applied to the local chemotherapy after tumor surgeries.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SCI-TECH UNIV
Drug sustained-release alginic acid embolism microsphere and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN111773428AEvenly distributedAchieve in situ controlled releaseSurgical adhesivesEmbolization TherapyMicrosphere
The invention discloses a drug sustained-release alginic acid embolism microsphere and a one-step electrostatic spraying preparation method thereof. Sodium alginate is compounded with a chemotherapeutic drug with positive charges, and the drug-loaded alginic acid embolic microsphere is prepared through a multi-nozzle one-step electrostatic spraying technology, so that combined treatment of embolism treatment and chemotherapy is realized. According to the multi-nozzle one-step electrostatic spraying preparation method provided by the invention, the drug sustained-release embolism microsphere can be prepared in one step, the prepared microsphere is uniform in particle size and controllable in size, the diameter is 100-1000 microns, and the microsphere has the potential of large-scale production. According to the alginic acid embolism microsphere provided by the invention, the drug loading capacity of common embolism microspheres is greatly improved, long-term slow release of chemotherapeutic drugs can be realized, nutrient source blood supply required by tumor growth can be blocked, the local drug concentration of a focus part can be improved, and meanwhile, the drug concentration inother organs is reduced, toxic and side effects are reduced, synergistic treatment of embolism treatment and chemotherapy is achieved, and the method has great development prospects.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Tumor targeted drug nanocrystal delivery system
PendingCN112426535AGood water dispersibilityGood acupunctureOrganic active ingredientsPowder deliveryPolythylene glycolSuccinic acid
The invention belongs to the field of pharmaceutical preparations, and relates to a tumor targeted drug nanocrystal delivery system and a preparation method and application thereof in pharmacy. The tumor targeted drug nanocrystal delivery system is composed of an anti-tumor drug nanocrystal core and a coating material; one or more biocompatible phospholipids, vitamin E polyethylene glycol 1000 succinate, folic acid-polyethylene glycol-phosphatidyl ethanolamine and methoxy polyethylene glycol-phosphatidyl ethanolamine are mixed according to a certain ratio, and insoluble anti-tumor drug nanocrystals are coated with the obtained mixture; the obtained tumor targeted drug nanocrystal drug delivery system can be stably dispersed in an aqueous environment, and experiments prove that the tumor targeted drug nanocrystal drug delivery system can effectively inhibit the growth of tumor cells and can effectively reduce the tumor volume after being subjected to peritumoral injection for an animalmodel. The invention provides a new preparation form capable of peritumoral injection for preoperative adjuvant chemotherapy of a solid tumor.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Method for preparing star-shaped block copolymer porous drug carrier
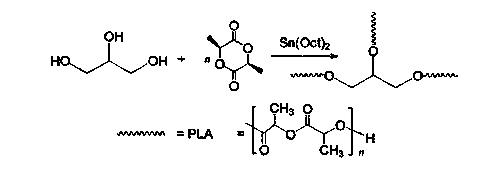
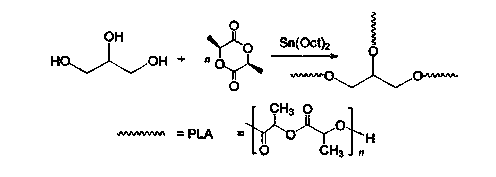
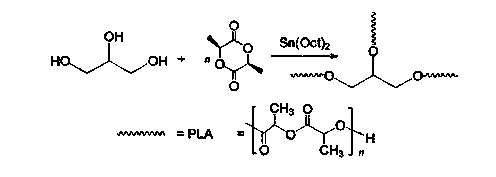
InactiveCN104072707AHas a nanoscale microporous structureHigh drug loadPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsPolymer science(Hydroxyethyl)methacrylate
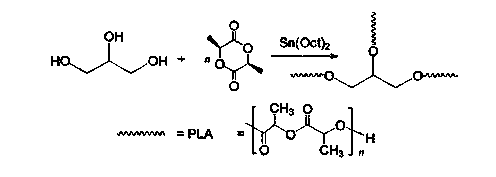
The invention discloses a method for preparing a star-shaped block copolymer porous drug carrier. The method comprises the steps: synthesizing three-arm or multi-arm star-shaped polylactic acid (SPLA) from L-lactide, which serves as a raw material, by using a classical stannous octoate catalyzed ring opening method, and enabling SPLA to react with bromo-isobutyryl bromide in an ice bath due to the existence of terminal hydroxyl of the polymer, so as to obtain a star-shaped macromolecular initiator SPLA-Br with bromine-terminated functional groups; carrying out ring opening polymerization on the macromolecular initiator and HEMA (Hydroxyethyl Methacrylate) according to a certain ratio, so as to obtain a PHEMA (Poly(Hydroxyethyl Methacrylate)) star-shaped block polymer which takes PLA (Polylactic Acid) as a core; and adding PHEMA with low molecular weight, and dissolving the block copolymer by using the amphiphilic nature of the block copolymer, thereby forming a nano-scale porous material. The block copolymer has a hexagonal columnar structure, and a continuous phase is PLA, so that the material is provided with nano-scale pores. The material has the following advantages that the material is provided with nano-scale micropores; the defect of the traditional linear PLA materials that the processability is poor is overcome; the material is free from toxic and side effects; the material can serve as a drug carrier material; the material can serve as a medical implant material; and the material can serve as a component material for in-vivo sustained medication devices.
Owner:CHENGDU LVKE HUATONG TECH
Degradable porous poly lactic acid preparation method
InactiveCN104448807AHas a nanoscale microporous structureHigh drug loadPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsCrystallographyDrug carrier
The present invention discloses a degradable porous poly lactic acid preparation method, which comprises: adopting L-lactide as a raw material, adopting a stannous octoate catalyzed ring opening method to synthesize tri-arm poly lactic acid, preparing a macromolecule initiator, carrying out ring opening polymerization on the tri-arm poly lactic acid and benzyl glutamate carboxylic anhydride (NCA) to obtain a star block polymer adopting PLA as the core and adopting poly benzyl glutamate (PBLG) as the arm, carrying out hydrolysis to remove the benzyl protection group in the PBLG to obtain a star poly lactic acid / poly glutamic acid block copolymer, adding a low molecular weight poly glutamic acid, and dissolving with water by utilizing the amphiphilicity of the block copolymer to form the nano-scale porous material. According to the present invention, the block copolymer has a hexagonal columnar structure, the continuous phase is the poly lactic acid, and the material has the nano-scale hole and has the following advantages that: the material has the nano-scale micro-pores, the disadvantage that the traditional linear poly lactic acid material processability is poor is overcome, the material does not have the toxic-side effect, can be adopted as a drug carrier material, can be adopted as a medical implant material, and can be adopted as a part material of the in vivo sustained drug delivery device.
Owner:CHENGDU LVKE HUATONG TECH
Preparation method of gentamicin sulphate-loading porous hydroxyapatite/PLGA (poly(DL-lactide-co-glycolide) microspheres
ActiveCN103751116AGood pore connectivityPore connectivity is goodAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsBiocompatibility TestingFreeze dry
The invention discloses a preparation method of gentamicin sulphate-loading porous hydroxyapatite / PLGA (poly(DL-lactide-co-glycolide) microspheres. The preparation method comprises the following steps: adding PLGA microspheres in an acetone / alcohol solution, adding a diammonium hydrogen phosphate solution, pouring in a calcium nitrate solution, adjusting pH, ageing, washing, drying, calcining, and grinding to obtain porous hydroxyapatite; placing the porous hydroxyapatite powder in a water solution containing gentamicin sulphate / PEG (polyethylene glycol), and carrying out freeze drying to obtain gentamicin sulphate-loading porous hydroxyapatite; and uniformly mixing the PLGA solution and the gentamicin sulphate-loading porous hydroxyapatite, pouring in a polyvinyl alcohol solution, stirring, washing, and carrying out freeze drying to obtain the gentamicin sulphate-loading porous hydroxyapatite / PLGA (poly(DL-lactide-co-glycolide) microspheres. The gentamicin sulphate-loading porous hydroxyapatite / PLGA (poly(DL-lactide-co-glycolide) microspheres prepared by adopting the preparation method are high in medicine loading rate, small in burst release, good in biocompatibility, simple in preparation process, easily available in raw materials, and low in cost; and industrialization is easily realized.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Nanocapsule type polydopamine drug material and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN110251484AEasy to synthesizeIncrease loadPowder deliveryDrug photocleavageEngineeringNanocapsules
The invention discloses a nanocapsule type polydopamine drug material and a preparation method and application thereof and belongs to the field of nano-drugs and preparation thereof. The nanocapsule type polydopamine drug material is prepared by a one-step synthesizing method. The preparation method has the advantages that an organic metal frame is used as the template to fix drugs, and accordingly drug loading capacity is increased greatly; the prepared nanocapsule type polydopamine drug material is high in drug loading capacity and capable of promoting drug release under near infrared mediation to achieve combined treatment; the preparation method is mild in conditions, low in requirements such as equipment requirements, operation requirements and environment requirements, economical in raw material, easy in raw material obtaining, easy to implement and good in stability and reproducibility.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Acrylic acid and polyactic acid (PAA) contained functional polymer material
InactiveCN104059207AHas a nanoscale microporous structureHigh drug loadPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsSide effectAtom-transfer radical-polymerization
The invention discloses an acrylic acid and polyactic acid (PAA) contained functional polymer material which is prepared through the following steps of with L-lactide as a raw material, synthesizing three-arm or multi-arm star-shaped polylactic acid (PLA) by using a classical stannous octoate catalyzed ring-opening method, and due to the existence of hydroxyl at the terminal of a polymer, enabling three-arm or multi-arm star-shaped PLA to react with bromoisobutyryl bromide in ice bath to obtain a star-shaped macroinitiator SPLA-Br of a bromo-terminal functional group; carrying out ring opening polymerization on the macroinitiator and AA (Acrylic Acid) according to a certain ratio to obtain a star-shaped PAA block polymer with PLA as a core, then, adding N-isopropylacrylamide, and carrying out ATRP (Atom Transfer Radical Polymerization) to obtain a triblock copolymer; adding PAA with low-molecular weight, and dissolving the PAA with water by means of the amphipathicity of the block copolymer to form a nanoporous material. The block copolymer is of a hexagonal prism shaped structure, contains PLA as a continuous phase and is provided with nano-grade micropores. The material has the advantages that the material is provided with the nano-grade micropores; the defect of poor processability of the traditional linear PLA material is overcome; no toxic or side effect is generated; the material can be used as a drug carrier material, a medical implant material and an in-vivo continuous dosing device part material.
Owner:CHENGDU LVKE HUATONG TECH
Nano-drug carrier capable of near-infrared light afterglow imaging tracing and preparation thereof
ActiveCN110755626AIncrease penetration depthSmall sizeOrganic active ingredientsPowder deliveryCarboxylic acidIn vivo
The invention discloses a nano-drug carrier capable of near-infrared light afterglow imaging tracing and preparation thereof, and belongs to the technical field of nano-drug carriers. The preparationof the nano-drug carrier comprises the following steps: preparing carboxylic acid modified near-infrared luminescece long-afterglow nano-particles (PLNPs); dissolving metal salt and organic ligand into an organic solvent to obtain a mixture, then adding the mixture into dispersion liquid of the PLNPs, and completely performing hydrothermal reaction to obtain a PLNPs@MOFs core-shell material; putting the PLNPs@MOFs into a muffle furnace and carrying out calcination; selecting different calcination temperatures and time to obtain a mesoporous carbon nano-cage material which is controlled in specific surface area, is adjustable in pore sizes, can emit near-infrared afterglow light, and is higher in affinity in hydrophobic drugs. According to the nano-drug carrier has an afterglow signal tracing function disclosed by the invention, an in vivo circulation route of the drug carrier capable of in-site-free stimulated near-infrared light afterglow imaging real-time tracing, and storage and slow release of drugs are realized, and the nano-drug carrier has good application prospects.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Allisartan isoproxil pharmaceutical composition, preparation containing pharmaceutical composition and preparation method of pharmaceutical composition
InactiveCN107441048AEasy to operateStrong process controllabilityPowder deliveryOrganic active ingredientsNanoparticleAllisartan isoproxil
The invention provides an allisartan isoproxil pharmaceutical composition. Through the stabilizing and protecting effects of a prescription, allisartan isoproxil can be conveniently prepared into nano-scale particles through a milling process, the nano-scale particles are stably dispersed in a pharmaceutical composition, and allisartan isoproxil exists in the form of the stable nanoparticles in the follow-up process. The invention further provides an allisartan isoproxil preparation which has the characteristics of high loading capacity, high stability and the like.
Owner:SHENZHEN SALUBRIS PHARMA CO LTD
Methylacrylic acid (MAA) contained medical polylactic acid (PLA) derivative material
InactiveCN104059205AHas a nanoscale microporous structureHigh drug loadPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsSide effectAtom-transfer radical-polymerization
The invention discloses a methylacrylic acid (MAA) contained medical polylactic acid (PLA) derivative material which is prepared through the following steps: with L-lactide as a raw material, synthesizing three-arm or multi-arm star-shaped PLA by using a classical stannous octoate catalyzed ring-opening method, and due to the existence of hydroxyl at the terminal of a polymer, enabling three-arm or multi-arm star-shaped PLA to react with bromoisobutyryl bromide in ice bath to obtain a star-shaped macroinitiator SPLA-Br of a bromo-terminal functional group; carrying out ATRP (Atom Transfer Radical Polymerization) on the macroinitiator and MAA according to a certain ratio to obtain a star-shaped PMAA block polymer with PLA as a core, then, adding N-isopropylacrylamide, and carrying out ATRP again to obtain a triblock copolymer; adding PMAA with low-molecular weight, and dissolving PMAA with water by means of the amphipathicity of the block copolymer to form a nanoporous material. The block copolymer is of a hexagonal prism shaped structure, contains PLA as a continuous phase and is provided with nano-grade micropores. The material has the following advantages that the material is provided with the nano-grade micropores; the defect of poor processability of the traditional linear PLA material is overcome; no toxic or side effect is generated; the material can be used as a drug carrier material, a medical implant material and an in-vivo continuous dosing device part material.
Owner:CHENGDU LVKE HUATONG TECH
Method for synthesizing ABC multiblock copolymer drug polymer
InactiveCN104072701AHas a nanoscale microporous structureHigh drug loadPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsSide effectAtom-transfer radical-polymerization
The invention discloses a method for synthesizing an ABC multiblock copolymer drug polymer. The method comprises the steps: synthesizing three-arm or multi-arm star-shaped polylactic acid (SPLA) from L-lactide, which serves as a raw material, by using a classical stannous octoate catalyzed ring opening method, and enabling SPLA to react with bromo-isobutyryl bromide in an ice bath due to the existence of terminal hydroxyl of the polymer, so as to obtain a star-shaped macromolecular initiator SPLA-Br with bromine-terminated functional groups; carrying out ring opening polymerization on the macromolecular initiator and VP (Vinyl Pyrrolidone) according to a certain ratio, so as to obtain a PVA (Poly Vinyl Pyrrolidone) star-shaped block polymer which takes PLA as a core, then, adding N-isopropylacrylamide, and carrying out ATRP (Atom Transfer Radical Polymerization) once again, so as to obtain a triblock copolymer; and adding PVA with low molecular weight, and dissolving the block copolymer by using the amphiphilic nature of the block copolymer, thereby forming a nano-scale porous material. The block copolymer has a hexagonal columnar structure, and a continuous phase is PLA, so that the material is provided with nano-scale pores. The material has the following advantages that the material is provided with nano-scale micropores; the defect of the traditional linear PLA materials that the processability is poor is overcome; the material is free from toxic and side effects; the material can serve as a drug carrier material; the material can serve as a medical implant material; and the material can serve as a component material for in-vivo sustained medication devices.
Owner:CHENGDU LVKE HUATONG TECH
Novel medical functional polyethylene glycol material
InactiveCN104086769AHigh drug loadGood biocompatibilityPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsSide effectPolyglutamate
The invention discloses a novel medical functional polyethylene glycol material. A preparation method for the novel medical functional polyethylene glycol material comprises the steps of by taking ethylene oxide as material, synthesizing three-arm polyethylene glycol by utilizing alkaline-process ring opening; preparing a macro-initiator; carrying out ring-opening polymerization with octodecane esterbenzyl ester carboxylic acid anhydride glutamate (NCA) to obtain star block polymers taking octodecane ester benzyl ester polyglutamate with PEG (polyethylene glycol) as core as arms to obtain star polyethylene glycol / octodecane ester polyglutamate block polymers; adding low molecular weight octodecane ester polyglutamate, dissolving the low molecular weight octodecane ester polyglutamate in water by utilizing amphipathicity of the block polymers to form a nano-scale porous material. The block copolymers have hexagonal columnar structures, continuous phase is polyethylene glycol, and the material has nano-scale holes. The material has the following advantages that the material has nano-scale micro holes, overcomes the defect that the conventional linear polyethylene glycol material is poor in processing performance, is free of toxic and side effect, can be used as a drug carrier material, can be used as a medical implanting material, and can be used as a part material of an in-vivo lasting dosing device.
Owner:CHENGDU LVKE HUATONG TECH
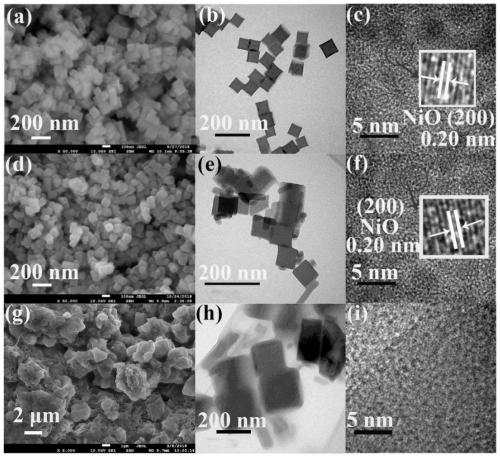
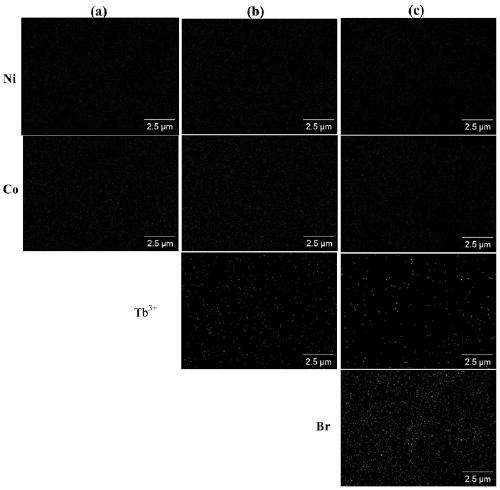
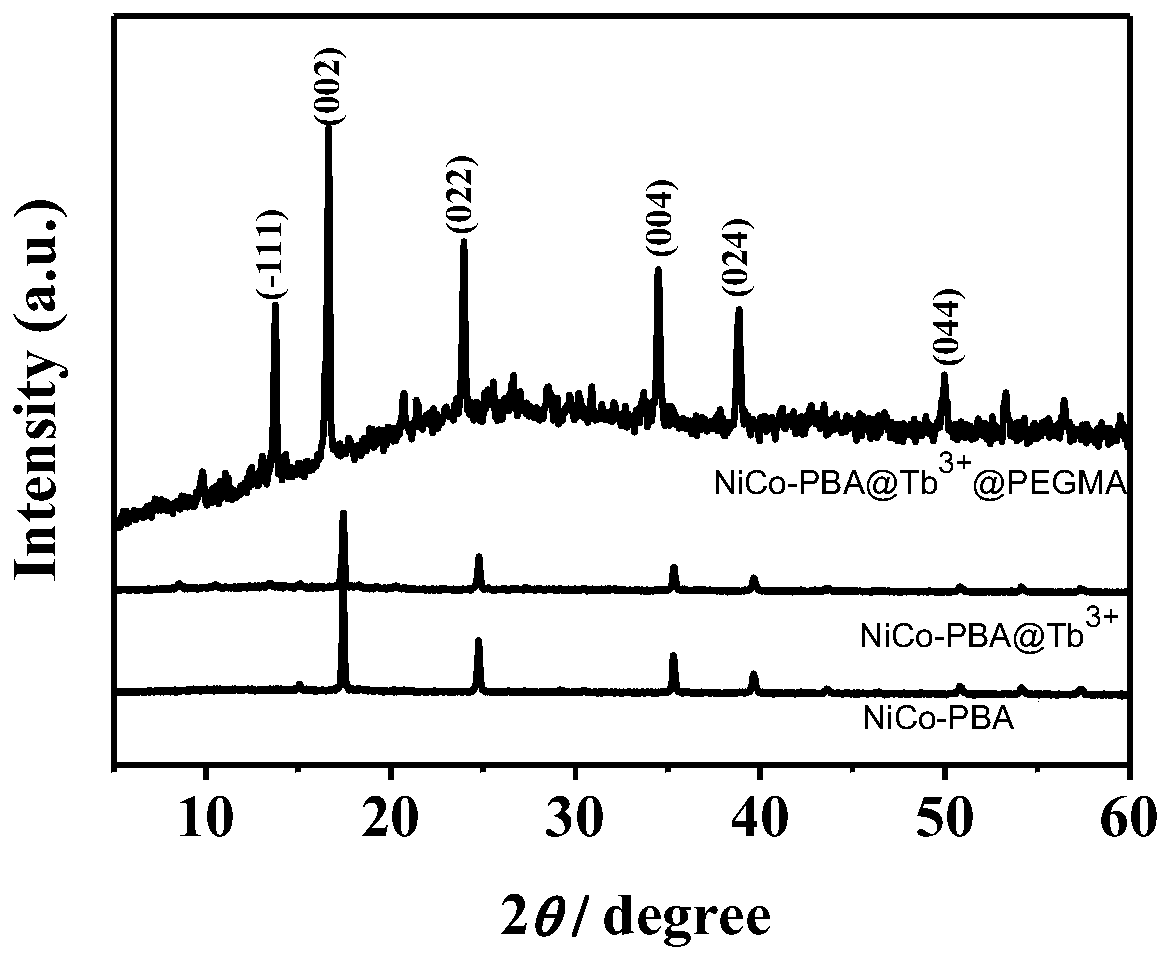
Modified nickel-cobalt Prussian blue analogue nano material and application thereof, and targeted drug
ActiveCN111514114AGood biocompatibilityHigh drug loadInorganic non-active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsPolymer chemistryPolyethylene glycol
The invention belongs to the technical field of biomedical materials, particularly relates to a modified nickel-cobalt Prussian blue analogue nano material and an application thereof, and further relates to a targeted drug. The modified nickel-cobalt Prussian blue analogue nano material comprises a nickel-cobalt Prussian blue analogue nano cube and a polymer which is coated on the surface of the nickel-cobalt Prussian blue analogue nano cube and has pH responsiveness, wherein the polymer is formed by polymerizing polyethylene glycol methacrylate. The modification is realized by modifying THE polymer with pH responsiveness on the surface of THE nickel-cobalt Prussian blue analogue nano cube. When the modified nickel-cobalt Prussian blue analogue nano material is used as a drug carrier, themodified nickel-cobalt Prussian blue analogue nano material has relatively high drug loading efficiency and has pH response capability, so that controlled release of a drug can be realized.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIVERSITY OF LIGHT INDUSTRY
Preparation method for carboxymethyl chitosan-loaded porous poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) (PLGA) nanoparticle, as well as product and application thereof
InactiveCN109432058AGood biocompatibilityControl degradation ratePowder deliveryOrganic active ingredientsUltrasonic emulsificationFreeze-drying
The invention relates to a preparation method for a carboxymethyl chitosan-loaded porous poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) (PLGA) nanoparticle, a product and application thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: dissolving carboxymethyl chitosan in deionized water and taking the mixture as an inner water phase; dissolving PLGA in dichloromethane and taking the mixture as a copolymer phase; mixing the inner water phase with the copolymer phase, and performing ice-bath ultrasonic emulsification by a cell disruption instrument to form a primary emulsion; adding ammonium bicarbonate aqueous solution or isopyknic deionized water into the primary emulsion and performing ultrasonic emulsification; forming a compound emulsion under a stirring condition of a homogenizer, and removing dichloromethane; and centrifuging for freeze-drying to obtain a dry carboxymethyl chitosan PLGA nanoparticle. The porous PLGA nanoparticle is adopted by the invention and has a larger drug capacityand a better effect.
Owner:SHANGHAI NAT ENG RES CENT FORNANOTECH
Multifunctional polylactic acid (PLA) derivative drug carrier material
InactiveCN104072706AHas a nanoscale microporous structureHigh drug loadPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsPolymer scienceSide effect
The invention discloses a multifunctional polylactic acid (PLA) derivative drug carrier material. A preparation method of the material comprises the steps: synthesizing three-arm or multi-arm star-shaped polylactic acid (SPLA) from L-lactide, which serves as a raw material, by using a classical stannous octoate catalyzed ring opening method, and enabling SPLA to react with bromo-isobutyryl bromide in an ice bath due to the existence of terminal hydroxyl of the polymer, so as to obtain a star-shaped macromolecular initiator SPLA-Br with bromine-terminated functional groups; carrying out ring opening polymerization on the macromolecular initiator and N-isopropylacrylamide (NIPAM) according to a certain ratio, so as to obtain a PAA (Polyacrylic acid) star-shaped block polymer which takes PNIPAM (Poly N-isopropylacrylamide) as a core, then, adding AA (Acrylic Acid), and carrying out ATRP (Atom Transfer Radical Polymerization) once again, so as to obtain a triblock copolymer; and adding PAA with low molecular weight, and dissolving the block copolymer by using the amphiphilic nature of the block copolymer, thereby forming a nano-scale porous material. The block copolymer has a hexagonal columnar structure, and a continuous phase is PLA, so that the material is provided with nano-scale pores. The material has the following advantages that the material is provided with nano-scale micropores; the defect of the traditional linear PLA materials that the processability is poor is overcome; the material is free from toxic and side effects; the material can serve as a drug carrier material; the material can serve as a medical implant material; and the material can serve as a component material for in-vivo sustained medication devices.
Owner:CHENGDU LVKE HUATONG TECH
Drug-loaded nano-composite, preparation method thereof and application of nano-composite
InactiveCN110123762AIncrease loadImprove stabilityOrganic active ingredientsPowder deliverySide effectTumor targeting
The invention provides a drug-loaded nano-composite, a preparation method thereof and an application of the nano-composite. The drug-loaded nano-composite comprises a core-shell structure and anti-tumor drugs, the core-shell structure takes metal-containing fullerol as a core and takes an amphiphilic polymer as a shell, and the anti-tumor drugs are loaded on the surface of the metal-containing fullerol core. The core-shell structure of the drug-loaded nano-composite can achieve massive steady load and slow release functions for the drugs, the metal-containing fullerol has anti-tumor activity and the function of relieving toxic and side effects of chemotherapeutic drugs on bodies, so that a drug carrier and the anti-tumor drugs are cooperatively matched with each other, immunological therapy and chemotherapy for tumors can be combined, and tumor therapy effects are greatly improved. The drug-loaded nano-composite has good long cycle effects and tumor targeting properties, and the preparation method is simple and good in stability.
Owner:THE NAT CENT FOR NANOSCI & TECH NCNST OF CHINA
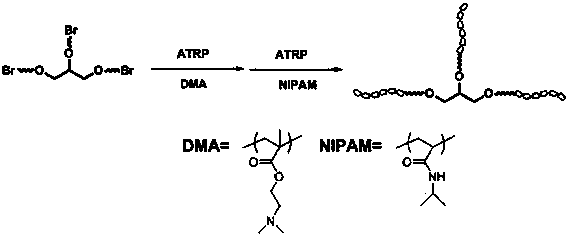
Drug-carrying block macromolecular material with star-shaped and porous structure
InactiveCN104072698AHas a nanoscale microporous structureHigh drug loadPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsMethacrylatePolymer science
The invention discloses a drug-carrying block macromolecular material with a star-shaped and porous structure. A preparation method of the material comprises the steps: synthesizing three-arm or multi-arm star-shaped polylactic acid (SPLA) from L-lactide, which serves as a raw material, by using a classical stannous octoate catalyzed ring opening method, and enabling SPLA to react with bromo-isobutyryl bromide in an ice bath due to the existence of terminal hydroxyl of the polymer, so as to obtain a star-shaped macromolecular initiator SPLA-Br with bromine-terminated functional groups; carrying out ring opening polymerization on the macromolecular initiator and DMA (Dimethylaminoethyl Methacrylate) according to a certain ratio, so as to obtain a PDMA (Poly Dimethylaminoethyl Methacrylate) star-shaped block polymer which takes PLA (Polylactic Acid) as a core; and adding PDMA with low molecular weight, and dissolving the block copolymer by using the amphiphilic nature of the block copolymer, thereby forming a nano-scale porous material. The block copolymer has a hexagonal columnar structure, and a continuous phase is PLA, so that the material is provided with nano-scale pores. The material has the following advantages that the material is provided with nano-scale micropores; the defect of the traditional linear PLA materials that the processability is poor is overcome; the material is free from toxic and side effects; the material can serve as a drug carrier material; the material can serve as a medical implant material; and the material can serve as a component material for in-vivo sustained medication devices.
Owner:CHENGDU LVKE HUATONG TECH
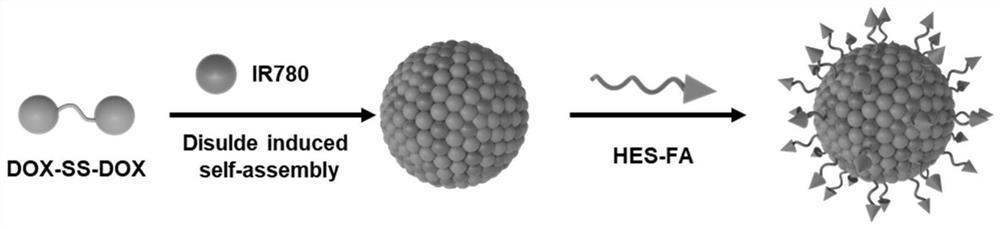
Nanometer drug-loading system of folic acid-hydroxyalkyl starch macromolecule stable co-loading photosensitizer and micromolecule prodrug, and preparation and application of nanometer drug-loading system
PendingCN114470231AImprove stabilitySolve photoacousticPowder deliveryOrganic active ingredientsPharmaceutical medicineTumor targeted
The invention belongs to the technical field of multidisciplinary crossing of chemistry, pharmacy, medicine and the like, and particularly relates to a nanometer drug loading system for stably co-loading a photosensitizer and a micromolecule prodrug through folic acid-hydroxyalkyl starch macromolecules, and preparation and application of the nanometer drug loading system. The nano drug delivery system comprises a photosensitizer and self-assembled nanoparticles of a hydrophobic small-molecule prodrug with reduction responsiveness, and further comprises a folic acid-hydroxyalkyl starch macromolecular compound, and experiments show that due to introduction of the folic acid-hydroxyalkyl starch macromolecular compound, the activity of the folic acid-hydroxyalkyl starch macromolecular compound is improved, and the activity of the folic acid-hydroxyalkyl starch macromolecular compound is improved. The stability of the self-assembled nanoparticles of the photosensitizer and the hydrophobic small-molecule prodrug can be remarkably improved, the nano drug-loading system has high drug loading capacity, can maintain long-time stability in a blood environment, remarkably improves tumor targeting, realizes photoacoustic and fluorescence imaging of tumor parts, and has wide application prospects. Meanwhile, the tumor part can be rapidly heated through laser irradiation, the chemotherapy effect of the adriamycin medicine is improved through thermal therapy, and collaborative therapy is achieved.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Novel medical polyethylene glycol (PEG) functional material
InactiveCN104109255AHas a nanoscale microporous structureHigh drug loadPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsSide effectEthylene oxide
The invention discloses a novel medical polyethylene glycol (PEG) functional material. A preparation method of the material comprises the following steps: with ethylene oxide as a raw material, synthesizing three-arm PEG by utilizing alkaline ring opening; preparing a macroinitiator; carrying out ring opening polymerization with O-tert-butyl-L-threonine carboxyl anhydride (NCA) to obtain a star-shaped block polymer with PEG as a kernel and poly(O-tert-butyl-L-threonine) as an arm; adding low molecular weight poly-threonine and dissolving low molecular weight poly-threonine with water by utilizing amphipathicity of a block copolymer to form the nanoscale porous material, wherein the block copolymer has a hexagonal prism shaped structure; the continuous phase is PEG; the material has nanoscale pores. The material has the advantages that the material has nanoscale micropores, overcomes the defect that traditional linear PEG materials have poor processability, does not have toxic or side effects and can serve as a medicine carrier material, a medical implant material and a part material of in vivo continuous administration devices.
Owner:CHENGDU LVKE HUATONG TECH
Preparation method of multifunctional medicinal polylactic acid (PLA) derivative ABC triblock polymer
InactiveCN104059206AHigh drug loadGood biocompatibilityPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsImplant materialSide effect
The invention discloses a preparation method of a multifunctional medicinal polylactic acid (PLA) derivative ABC triblock polymer. The preparation method comprises the following steps of with L-lactide as a raw material, synthesizing three-arm or multi-arm star-shaped PLA by using a classical stannous octoate catalyzed ring-opening method, and due to the existence of hydroxyl at the terminal of a polymer, enabling three-arm or multi-arm star-shaped PLA to react with bromoisobutyryl bromide in ice bath to obtain a star-shaped macroinitiator SPLA-Br of a bromo-terminal functional group; carrying out ring opening polymerization on the macroinitiator and DMA (Dimethyl Adipate) according to a certain ratio to obtain a star-shaped PDMA (Poly(dimethyl acrylamide)) block polymer with PLA as a core, then, adding N-isopropylacrylamide, and carrying out ATRP (Atom Transfer Radical Polymerization) to obtain a triblock copolymer; adding PDMA with low-molecular weight, and dissolving the PDMA with water by means of the amphipathicity of the block copolymer to form a nanoporous material. The block copolymer is of a hexagonal prism shaped structure, contains PLA as a continuous phase and is provided with nano-grade micropores. The material has the following advantages that the material is provided with the nano-grade micropores; the defect of poor processability of the traditional linear PLA material is overcome; no toxic or side effect is generated; the material can be used as a drug carrier material, a medical implant material and an in-vivo continuous dosing device part material.
Owner:CHENGDU LVKE HUATONG TECH
Polylactic acid (PLA) medicinal polymer with hexagonal columnar porous structure
InactiveCN104072697AHigh drug loadGood biocompatibilityPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsBrominePoly(N-isopropylacrylamide)
The invention discloses a polylactic acid (PLA) medicinal polymer with a hexagonal columnar porous structure. A preparation method of the polymer comprises the steps: synthesizing three-arm or multi-arm star-shaped polylactic acid (SPLA) from L-lactide, which serves as a raw material, by using a classical stannous octoate catalyzed ring opening method, and enabling SPLA to react with bromo-isobutyryl bromide in an ice bath due to the existence of terminal hydroxyl of the polymer, so as to obtain a star-shaped macromolecular initiator SPLA-Br with bromine-terminated functional groups; carrying out ring opening polymerization on the macromolecular initiator and NIPAM (N-isopropylacrylamide) according to a certain ratio, so as to obtain a PNIPAM (Poly N-isopropylacrylamide) star-shaped block polymer which takes PLA as a core; and adding PNIPAM with low molecular weight, and dissolving the block copolymer by using the amphiphilic nature of the block copolymer, thereby forming a nano-scale porous material. The block copolymer has a hexagonal columnar structure, and a continuous phase is PLA, so that the material is provided with nano-scale pores. The material has the following advantages that the material is provided with nano-scale micropores; the defect of the traditional linear PLA materials that the processability is poor is overcome; the material is free from toxic and side effects; the material can serve as a drug carrier material; the material can serve as a medical implant material; and the material can serve as a component material for in-vivo sustained medication devices.
Owner:CHENGDU LVKE HUATONG TECH
Polylactic acid (PLA) star-shaped diblock-copolymer medicinal functional material
InactiveCN104086726AHas a nanoscale microporous structureHigh drug loadPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsSide effectPolymer science
The invention discloses a polylactic acid (PLA) star-shaped diblock-copolymer medicinal functional material. A preparation method of the material comprises the steps: synthesizing three-arm or multi-arm star-shaped polylactic acid (SPLA) from L-lactide, which serves as a raw material, by using a classical stannous octoate catalyzed ring opening method, and enabling the SPLA to react with bromo-isobutyryl bromide in an ice bath due to the existence of hydroxyl at the terminal of the polymer, so as to obtain a star-shaped macromolecular initiator SPLA-Br with bromine-terminated functional groups; carrying out ring opening polymerization on the macromolecular initiator and VP (Vinyl Pyrrolidone) according to a certain ratio, so as to obtain a PVP (Poly Vinyl Pyrrolidone) star-shaped block polymer which takes PLA as a core; and adding PVP with low molecular weight, and dissolving the block copolymer by using the amphiphilic nature of the block copolymer, thereby forming a nano-scale porous material. The block copolymer has a hexagonal columnar structure, and a continuous phase is PLA, so that the material has nano-scale pores. The material has the following advantages that the material has nano-scale micropores; the defect of the traditional linear PLA materials that the processability is poor is overcome; the material is free from toxic and side effects; the material can serve as a drug carrier material; the material can serve as a medical implant material; the material can serve as a component material for in-vivo sustained medication devices.
Owner:CHENGDU LVKE HUATONG TECH
A preparation method of porous hydroxyapatite/plga microspheres loaded with gentamicin sulfate
ActiveCN103751116BEffective regulation of particle sizeGood pore connectivityAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsApatiteFreeze-drying
The invention discloses a preparation method of gentamicin sulphate-loading porous hydroxyapatite / PLGA (poly(DL-lactide-co-glycolide) microspheres. The preparation method comprises the following steps: adding PLGA microspheres in an acetone / alcohol solution, adding a diammonium hydrogen phosphate solution, pouring in a calcium nitrate solution, adjusting pH, ageing, washing, drying, calcining, and grinding to obtain porous hydroxyapatite; placing the porous hydroxyapatite powder in a water solution containing gentamicin sulphate / PEG (polyethylene glycol), and carrying out freeze drying to obtain gentamicin sulphate-loading porous hydroxyapatite; and uniformly mixing the PLGA solution and the gentamicin sulphate-loading porous hydroxyapatite, pouring in a polyvinyl alcohol solution, stirring, washing, and carrying out freeze drying to obtain the gentamicin sulphate-loading porous hydroxyapatite / PLGA (poly(DL-lactide-co-glycolide) microspheres. The gentamicin sulphate-loading porous hydroxyapatite / PLGA (poly(DL-lactide-co-glycolide) microspheres prepared by adopting the preparation method are high in medicine loading rate, small in burst release, good in biocompatibility, simple in preparation process, easily available in raw materials, and low in cost; and industrialization is easily realized.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com