Novel medical polyethylene glycol (PEG) functional material
A technology of polyethylene glycol and functional materials, applied in the fields of polymer chemistry and polymers, to achieve the effect of reducing toxic and side effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0025] ①Preparation of star block copolymer
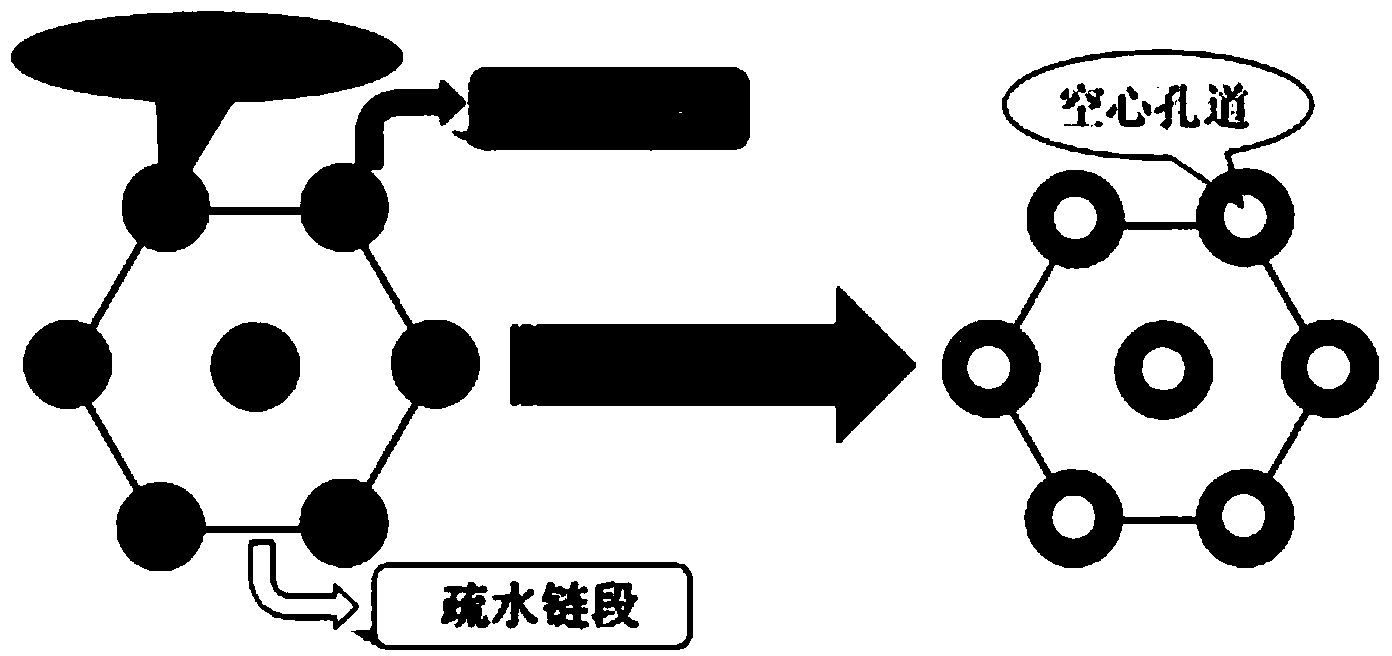
[0026] Using ethylene oxide as raw material, three-arm or multi-arm star-shaped polyethylene glycol was synthesized by classic alkali method ring-opening. Due to the existence of hydroxyl groups at the end of the polymer, glycine protected by amino Boc-groups can be used. Under the catalysis of DCC / HOBt, it reacts with SPEG to generate SPEG derivatives. In trifluoroacetic acid / dichloromethane solution, the amino group of the above product is de-Boc-protected, and the star-shaped macromolecular initiator SPEG-NH with amino-terminated functional groups is obtained. 2 . The macroinitiator and O-tert-butyl-L-threonine carboxylic acid anhydride (NCA) are subjected to ring-opening polymerization in a certain ratio to obtain poly-O-tert-butyl-L-threonine with PEG as the core star block polymers.
[0027] ②Characterization of the self-assembled structure and properties of star-shaped block copolymer materials
[0028] The chemical struc...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com