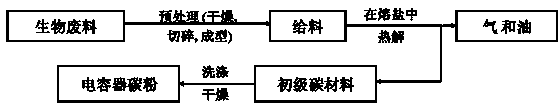
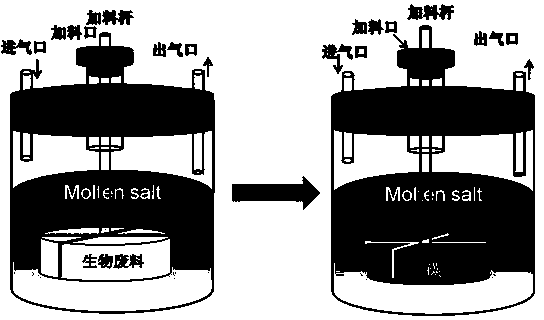
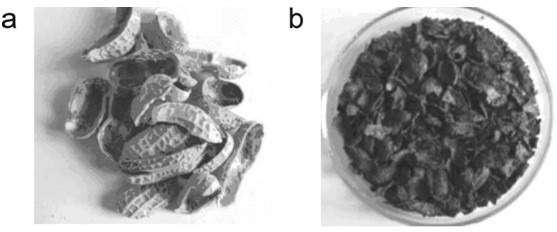
Method for preparing capacitive active carbon powder through biomaterial treated by fused salt
A biomass and capacitive technology, applied in the field of carbon materials, can solve the problems of large consumption of activators, difficult recovery of activators, difficulty in separating the product activated carbon from activators, etc., and achieve the effect of short reaction process and pollution reduction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0025] Embodiment 1: One-step treatment of peanut shells with sodium carbonate-potassium carbonate molten salt to prepare capacitive activated carbon powder
[0026] Na with a mass ratio of 1:1 2 CO 3 and K 2 CO 3 Mix molten salt as the molten salt medium for the reaction of peanut shells. Wash the peanut shells and dry them. Then chop the dried peanut shells and press them into a cake shape. Then wrap the cake-shaped peanut shells with a high-temperature-resistant material net and use a liftable The operating rod of high temperature resistant material is immersed in the molten salt for cracking, and the molten salt is heated to 850 ℃ for 1 hour by electric energy. After cracking for 1 hour, the processed product is taken out of the molten salt and placed in the reaction Cool in the inert atmosphere above the reactor, then take it out from the reactor and wash the molten salt in the product with water, and finally dry the product to obtain capacitive activated carbon powd...
Embodiment 2
[0028] Example 2: Li 2 CO 3 -Na 2 CO 3 -K 2 CO 3 Preparation of capacitive activated carbon powder by one-step processing of peanut shells with ternary mixed molten salt at different temperatures
[0029] With Li 2 CO 3 -Na 2 CO 3 -K 2 CO 3 Mix molten salt (the molar ratio is 43.5:31.5:25) as the molten salt medium for peanut shell cracking reaction, and use the same method as in Example 1 at different temperatures (450°C, 550°C, 650°C, 750°C, 850°C) Methods and steps Treat peanut shells to prepare activated carbon powder. It is found that the carbon powder obtained at the temperature of 650 ℃ and below has basically no capacitance, and the capacitance of the carbon powder prepared at the temperature of 750 ℃ and above increases significantly. Among them, the capacitance value at 750 ℃ is 82.5 F / g, and the capacitance value at 850 ℃ is 120 F / g.
[0030]
Embodiment 3
[0031] Example 3: One-step treatment of peanut shells in different carbonate molten salt systems at the same temperature to prepare capacitive carbon powder
[0032] Under the condition of cracking temperature of 850℃, Na 2 CO 3 -K 2 CO 3 , Li 2 CO 3 -Na 2 CO 3 -K 2 CO 3 Molten salt is as the molten salt medium of peanut shell cracking, handles peanut shell with the same method and step in embodiment 1 and prepares gac powder, finds that in Na 2 CO 3 -K 2 CO 3 Peanut shells prepared in molten salt have a capacitance (149 F / g) higher than that of Li 2 CO 3 -Na 2 CO 3 -K 2 CO 3 system (120 F / g).
[0033]
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com